Alendronic Acid
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Composition and Properties
- 3. How It Works
- 4. Uses of Alendronic Acid
- 5. Off-Label Use and Investigational Therapies
- 6. Dosage and Administration
- 7. Side Effects and Management
- 8. Important Precautions
- 9. Drug Interactions
- 10. Contraindications
- 11. Careful Administration
- 12. Overdosage
- 13. Storage and Handling Precautions
1. Introduction
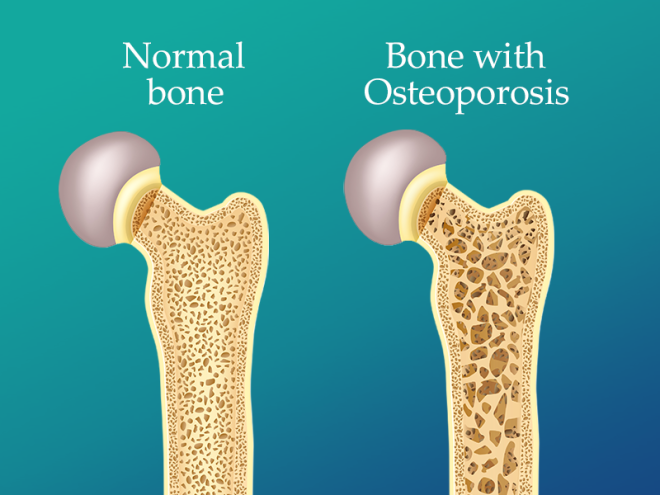
Alendronic Acid, a remedy for osteoporosis, has transformed the way bone loss and fragility fractures are handled. This medication, derived from a group of bisphosphonates, was designed to strengthen bones by preventing driven bone breakdown. The introduction of Alendronic Acid represented an advancement in the treatment of osteoporosis, bringing optimism to individuals at risk of fractures.
Overview of Alendronic Acid
Alendronic Acid plays a role as a key member of the bisphosphonate group aimed at halting bone deterioration. Its arrival has brought advantages in managing and thwarting osteoporosis, notably decreasing the likelihood of fractures in at-risk individuals.
Historical Context and Development
Alendronic Acid was created through research on bone health and treatments for osteoporosis. After studying various compounds to prevent bone loss safely and efficiently, its invention marked a milestone.
Importance in Osteoporosis Management
Alendronic Acid plays a role in managing osteoporosis by providing a preventive method for maintaining bone health, reducing the risk of fractures in people with this condition.
2. Composition and Properties
Alendronic Acid stands out due to its makeup and medicinal properties, which are key to its success in treating osteoporosis.
Chemical Structure and Classification
- It falls under the category of bisphosphonates.
- Is designed to imitate pyrophosphate a natural regulator of bone growth.
Pharmacological Properties
Its ability to work effectively is based on its binding to hydroxyapatite in the bone, which helps in preventing osteoclasts the cells that break down bone tissue, from functioning.
3. How It Works
The way Alendronic Acid strengthens bone structure and density is complex and captivating.
Mechanism of Action
Alendronic Acid works by attaching to the surfaces of bone minerals in areas where resorption is happening. This action slows down the activity of osteoclasts, leading to a reduction in bone loss.
Impact on Bone Metabolism
This treatment leads to an improvement in bone strength and a decrease in bone turnover, ultimately lowering the risk of fractures.
Comparative Efficacy with Other Osteoporosis Treatments
In comparison, Alendronic Acid has shown results in building bone density and lowering the chances of fractures, outperforming other forms of treatment in terms of effectiveness and impact.
4. Uses of Alendronic Acid
-
Treatment and Prevention of Osteoporosis:
- Alendronic acid is indicated for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women. It helps maintain bone strength and reduces the risk of fractures, including those of the spine and hip12.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis:
-
Paget’s Disease of Bone:
5. Off-Label Use and Investigational Therapies
- Alendronic acid is approved for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It increases bone mass and reduces the incidence of fractures, including those of the hip and spine (vertebral compression fractures)2.
Potential in Osteogenesis Imperfecta
There is research into its application in osteogenesis imperfecta, a hereditary bone condition with certain studies indicating a positive influence, on bone density and fracture occurrence.
Use in Certain Cancers with Bone Metastasis
- Alendronic Acid, a type of bisphosphonate, has shown promise in treating bone metastasis:
- Breast Cancer: It can manage bone weakness or pain caused by breast cancer spread to the bones.
- Hypercalcemia: Alendronic Acid helps normalize calcium levels.
- Research: Recent studies explore its efficacy in bone metastasis treatment23.
Exploratory Studies in Dental and Periodontal Applications
Researchers are currently investigating the effectiveness of Alendronic Acid in treating periodontal conditions, with a particular emphasis on its ability to combat bone loss in such situations.
6. Dosage and Administration
The effectiveness of Alendronic Acid treatment depends on following the dosage and administration instructions, which are customized to suit each patient's unique requirements and health conditions.
Recommended Dosage for Various Conditions
- Postmenopausal women with osteoporosis are typically prescribed a weekly dose to promote adherence and efficacy.
- For individuals, with induced osteoporosis the dosage is tailored according to the glucocorticoid amount and how patients respond.
- In cases of Paget's disease of bone, a higher dosage is often recommended to address the severity of the condition and meet the therapeutic response.
Administration Guidelines for Optimal Absorption
Make sure to take Alendronic Acid with a glass of water about half an hour before having your first meal, drink, or medicine for the day to ensure better absorption and effectiveness.
Adjustments for Renal Impairment
Patients with kidney problems might need changes in their medication dosage. They may not be ideal candidates for Alendronic Acid treatment. It's important to assess their kidney function before starting the therapy.
7. Side Effects and Management
Alendronic Acid plays a role in treating osteoporosis, but it comes with possible side effects that require careful management.
Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal Distress, Musculoskeletal Pain
- Digestive problems like esophagitis, feelings of nausea, and discomfort in the abdomen are frequently mentioned as side effects.
- Additionally, individuals may experience discomfort in their muscles, joints, or bones, though these issues generally improve with time.
Serious Adverse Reactions: Osteonecrosis of the Jaw, Atypical Femoral Fractures
Serious side effects such as jaw bone death and unusual thigh fractures, though uncommon, have been linked to use requiring close observation and precautionary actions.
Management Strategies for Side Effects
To be a manager it's important to educate patients about how to prevent side effects report any negative reactions quickly and adjust or stop the dose if needed.
8. Important Precautions
To ensure the safety of patients and maximize the effectiveness of treatment, it is important to follow steps when prescribing Alendronic Acid.
Identifying High-Risk Patients
It's essential to pinpoint patients who are at high risk of experiencing negative effects, like those with existing gastrointestinal issues or severe kidney problems, in order to reduce the chances of complications.
Monitoring Bone Density and Renal Function
Monitoring bone density and kidney function on a basis is important to evaluate how well the medication is working and make any necessary treatment adjustments, for better patient results.
Guidelines for Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation
To maximize the effectiveness of Alendronic Acid it may be beneficial to take vitamin D and calcium supplements. This highlights the significance of taking an approach to managing osteoporosis.
9. Drug Interactions
The effectiveness and safety of Alendronic Acid may be affected by how it interacts with substances. It's crucial to grasp these interactions to improve treatment results and reduce any impacts.
Interactions with Calcium Supplements and Antacids
Taking calcium supplements or antacids at the time, as Alendronic Acid, can reduce its absorption. It is recommended that patients wait at least 30 minutes after taking Alendronic Acid before consuming these substances.
Effects of NSAIDs and Aspirin on Alendronic Acid Efficacy
When taking NSAIDs and aspirin at the time, as Alendronic Acid there could be an increased chance of experiencing stomach irritation. It's important to be careful and weigh the advantages against the drawbacks.
Potential Interactions with Other Osteoporosis Medications
When Alendronic Acid is combined with treatments for osteoporosis, it is important to closely monitor the impact on bone metabolism to prevent excessive suppression of bone turnover.
10. Contraindications
Detecting situations where Alendronic Acid should be avoided can protect patients from risks guaranteeing that the medication is administered in a way that prioritizes safety.
Absolute and Relative Contraindications
- Absolute contraindications consist of having a known sensitivity to Alendronic Acid or its components.
- On the hand, relative contraindications involve conditions such as ongoing gastrointestinal problems that could worsen with the use of Alendronic Acid.
Precautions in Patients with Esophageal Disorders
Patients who have issues with their esophagus should be careful when using Alendronic Acid as it could worsen these problems and may require treatment options.
Risk Assessment in Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients with kidney problems should be carefully evaluated and monitored for possible side effects due to the way Alendronic Acid is excreted through the kidneys.
11. Careful Administration
Administering Alendronic Acid to groups of people requires careful attention to both safety and effectiveness, to maximize the treatment's benefits while reducing potential risks.
Administration to the Elderly: Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Older patients might need changes in dosage or careful observation due to their higher vulnerability to side effects like kidney problems.
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Known Risks and Guidelines
Alendronic Acid should not be used during pregnancy. While breastfeeding because may have negative effects on the development of the baby's bones. It is advisable to explore options, for women in these situations.
Pediatric Use: Safety Profile and Dosing Guidelines
The safety and effectiveness of Alendronic Acid in children have not been confirmed, It is essential to carefully assess and consider its use, in this group.
12. Overdosage
In cases of taking too much Alendronic Acid, it is important to act quickly and appropriately to avoid serious problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Symptoms might consist of calcium levels, low phosphorus levels, and negative gastrointestinal reactions that need immediate medical care.
Immediate Management and Treatment Options
Supportive management actions involve using substances like milk or antacids to bind Alendronic Acid and decrease its absorption while also closely watching serum electrolytes and renal function.
Long-term Monitoring and Support
Continuous observation might be required to evaluate and address any delayed consequences of taking too much medication, prioritizing the safety and well-being of the patient.
13. Storage and Handling Precautions
Ensuring that Alendronic Acid is stored and handled correctly is crucial to maintaining its effectiveness and avoiding contact or consumption.
Recommended Storage Conditions
Alendronic Acid needs to be kept in a dry place, at room temperature shielded from moisture and sunlight to ensure it stays effective and potent.
Handling and Disposal Guidelines
Be sure to avoid touching your skin or eyes directly when dealing with this substance and make sure to dispose of it properly in accordance with local rules to reduce its impact on the environment.
Stability and Shelf Life
The durability of Alendronic Acid, when stored as directed, guarantees a shelf life for optimal utilization as long as proper handling and disposal instructions are diligently adhered to.