Azithromycin Oral Suspension
- Introduction
- Uses of Azithromycin Oral Suspension
- Off-Label Uses
- How Azithromycin Oral Suspension Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition of Azithromycin Oral Suspension
- Storage Guidelines for Azithromycin Oral Suspension
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- Special Administration Guidelines
- Overdosage and Its Management
- Handling Precautions
Introduction
The pharmaceutical world is filled with various medications created to treat different health conditions. However, one medication that stands out for its versatility is Azithromycin Oral Suspension. This powerful formulation contains an antimicrobial agent and has proven helpful in addressing many bacterial infections. It plays a role in modern healthcare, and this article aims to explore the diverse applications of Azithromycin Oral Suspension, highlighting its importance in treating diseases and preventive measures.
Uses of Azithromycin Oral Suspension
Treating Bacterial Infections
Azithromycin Oral Suspension is highly effective in treating infections. This medication works by inhibiting their protein synthesis by preventing the growth of bacteria. It is a component in the arsenal of antibacterial treatments for medical professionals, mainly due to its excellent absorption into the body and long-lasting effects. Depending on the concentration used, it can. Stop or kill bacteria. Additionally, it has adverse side effects and can penetrate cells effectively.
Respiratory Tract Infections
When taking care of our health, Azithromycin Oral Suspension is incredibly important. It is commonly used to treat acute bronchitis, pneumonia, and obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations. This medication helps protect our system from getting worse. What is excellent about it is that it can easily reach the lung tissue and effectively treat these illnesses. It also has lasting effects, so we don't have to take it as often.
Skin Infections
Azithromycin Oral Suspension is also used to treat skin infections such as cellulitis, impetigo, and folliculitis. Targeting the area the medication concentrates its antibacterial effects where they are needed most. It is particularly effective against Gram bacteria and tends to accumulate in the skin.

Ear Infections
Regarding ear conditions that impact the middle ear, Azithromycin Oral Suspension proves to be extremely helpful. It is a resource for treating otitis media, a common ailment among children. This medication has shown results by effectively alleviating urgent symptoms quickly. It is also known for its effectiveness against pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.

Preventive Measures
Another critical aspect of Azithromycin Oral Suspension is its ability to act as a measure against surgical site infections. It is sometimes recommended before procedures for patients with certain heart conditions to prevent bacterial endocarditis. Additionally, it can help reduce the risk of infection before surgery in cases related to cardiac diseases.
Traveler's Diarrhea
Traveling can bring about challenges, including encountering different bacterial pathogens. When dealing with the issue of travelers' diarrhea, having Azithromycin Oral Suspension in your medical kit can provide fast relief and be highly beneficial. It acts quickly and effectively against bacteria, helping to alleviate gastrointestinal disturbances.
Secondary Infections
Finally, Azithromycin Oral Suspension has demonstrated potential in treating bacterial infections that arise as complications of viral illnesses such as influenza. It explicitly targets bacteria that take advantage of a weakened system, providing extra assistance in managing diseases with multiple factors. This helps combat superimposed infections and enhances outcomes in complex clinical situations.
Off-Label Uses
Lyme Disease
Although Azithromycin Oral Suspension is not officially approved as a treatment for Lyme disease, it has been used off-label to address this tick-borne illness. Its ability to inhibit growth makes it a viable option, particularly for patients who cannot tolerate doxycycline. This use of the medication demonstrates its adaptability in treating bacterial infections and offers an alternative for individuals who cannot take doxycycline due to intolerance. It has proven effective against Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria responsible for causing Lyme disease.
Gastroparesis
Azithromycin Oral Suspension also has uses in treating gastroparesis, a condition where the stomach takes longer to empty. Although this antibiotic isn't primarily intended for this purpose, it has been found to improve gastrointestinal motility, resulting in better gastric emptying. The medication exhibits properties that contribute to its positive effects on gastric function.
Antimalarial Applications
It's fascinating to note that Azithromycin Oral Suspension has been studied for its potential in treating malaria. Researchers have found that this drug can inhibit the growth of Plasmodium falciparum, which is responsible for the most severe type of malaria. This suggests that Azithromycin may have medical applications beyond its antibacterial properties, providing a new and promising approach to managing malaria.
How Azithromycin Oral Suspension Works
Mechanism of Action
Azithromycin Oral Suspension1 essentially works by preventing the growth of bacteria. It does this by interfering with the production of proteins in cells, specifically by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit. This binding action inhibits steps involved in bacterial replication, ultimately stopping them from multiplying. By inhibiting the 50S subunit, Azithromycin Oral Suspension effectively prevents bacterial replication.
The Role of Antibiotics in Infection Management
Antibiotics like Azithromycin play a role in controlling bacterial infections. They can. Kill bacteria directly or slow down their growth, enabling the immune system to limit pathogens effectively. This can be achieved by eliminating the bacteria or preventing their further multiplication and spread, allowing the immune system to act.
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
Azithromycin demonstrates a killing effect dependent on its concentration in the body. It also has a pharmacokinetic profile with a high volume of distribution and a longer half-life. These properties enable frequent dosing schedules to be adopted. The high volume of distribution indicates that the medication is distributed widely throughout the body. At the same time, the extended half-life means it remains active for some time before being eliminated.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines
Dosage instructions typically follow an approach, including an initial dose to kickstart the treatment and a regular maintenance dose. The specific dosage3 for adults may vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. The loading and maintenance doses are adjusted accordingly.
Methods of Administration
You can take Azithromycin Oral Suspension with or without food. It is recommended to take it at the time every day for a steady and effective treatment. You have the flexibility to eat it with types of food, and it's essential to maintain consistent timing.
Oral Use
The suspension provides a way for individuals who may find tablets challenging to take orally. This is particularly beneficial for patients who struggle with swallowing. Advantages of the rest: It is suitable for individuals with eating difficulties. It offers a method of administration.
Pediatric Use
In pediatrics, using the suspension form of medication provides a precise way to administer the correct dosage. Weight-based dosing is commonly employed for children to ensure adequate treatment while maintaining accuracy in administration.
Duration of Treatment
The length of treatment varies depending on the infection being treated and how the patient responds to therapy. Generally, a shorter treatment duration is preferred to minimize the chances of antimicrobial resistance developing. The time will be determined based on the infection and how well the patient's body reacts to the treatment. The aim is to use a course whenever possible to reduce the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
Composition of Azithromycin Oral Suspension
Active Ingredients
The main ingredient in Azithromycin Oral Suspension is azithromycin dihydrate. This type of antibiotic belongs to the class and is known for its strong antibacterial properties, effectively disrupting bacterial protein synthesis. Azithromycin dihydrate acts as a component of the medication.
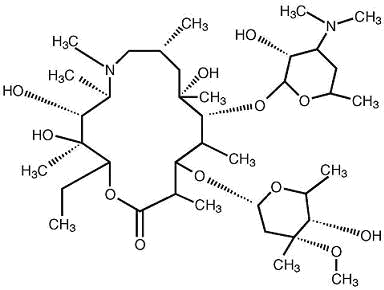
Inactive Ingredients
In addition to the ingredients, Azithromycin Oral Suspension contains several inactive ingredients. These include sucrose, sodium phosphate, and various flavoring agents. These components are used to improve the taste and stability of the product by adding sweetness (through sucrose) and enhancing stability (sodium phosphate).
Formulation Information
The Azithromycin Oral Suspension is created by combining the inactive ingredients into a well-mixed powder that needs to be reconstituted. After reconstitution, it becomes a tasting liquid suspension, which is easy to administer. Reconstitution is necessary to obtain the liquid form after mixing.
Storage Guidelines for Azithromycin Oral Suspension
Ideal Storage Conditions
The best way to store Azithromycin Oral Suspension is to keep it in a controlled environment. Holding it in a dark place with temperatures between 15 and 30°C (59 86°F) is recommended. This will help prevent any degradation of the ingredient. Also, make sure to avoid exposing it to sunlight.
Shelf Life
The duration for which Azithromycin Oral Suspension remains usable depends on how it's stored and the condition of its packaging. Generally, if the bottle is unopened and stored correctly, it can last anywhere from 18 to 24 months. However, its effectiveness diminishes significantly once you mix it with water or reconstitute it. It usually remains viable for only about ten days.
Signs of Deterioration
The product can deteriorate in ways, such as changing color, forming solids, or emitting a bad smell. These signs are indications that the medication is no longer suitable for therapeutic purposes and should be disposed of promptly—changes in color as a warning sign and the presence of an odor indicating spoilage.
Interactions with Other Medications
Potential Drug Interactions
Azithromycin Oral Suspension can potentially interact with other medications. These interactions may. Enhance or reduce the drug's effectiveness or even lead to unwanted side effects. The drug's therapeutic effects can be either. Diminished, and there is also a possibility of experiencing adverse effects.
Blood Thinners
One vital interaction to consider is with anticoagulants or blood thinners such as warfarin. When these medications are taken together, they can significantly increase the effect. As a result, it is crucial to monitor coagulation parameters to ensure optimal treatment. This enhanced anticoagulant effect requires monitoring of various coagulation metrics.
Antacids
When you take Azithromycin at the time as an antacid that contains aluminum or magnesium, it can affect how well your body absorbs the medication. This can make Azithromycin less effective in treating your condition. To avoid this problem, it is often suggested to take antacids and Azithromycin at times, allowing for a temporal separation between the doses. This helps ensure that your body can adequately absorb Azithromycin and get the therapeutic benefit from it.
Food Interactions
While Azithromycin Oral Suspension can be taken with or without food, high-fat meals may slightly delay absorption. However, this delay does not significantly affect the effectiveness of the medication. Nevertheless, it is recommended to maintain a timing for the best therapeutic results.
Warnings and Contraindications
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to Azithromycin Oral Suspension may present as anaphylaxis, skin rashes, or difficulty breathing. It is crucial to stop taking the medication and seek medical help when faced with these situations. Anaphylactic shock can occur as an allergic response, while dermatological symptoms such as hives or a rash may also be observed.
Pre-existing Conditions
Patients with conditions like liver dysfunction, renal impairment, and cardiac arrhythmias should undergo careful assessment before starting treatment with Azithromycin Oral Suspension. It may be necessary to adjust the medication dosage to prevent the worsening of these conditions. Specifically, liver dysfunction requires dose adjustment, while renal impairment necessitates monitoring.
Contraindication with Alcohol and Recreational Drugs
The simultaneous consumption of Azithromycin Oral Suspension with alcohol or recreational drugs may lead to a combination. Such combinations can result in liver damage. Worsen potential heart-related side effects. Increased risk of liver damage and intensified heart-related side effects should be considered when using Azithromycin Oral Suspension alongside alcohol or recreational drugs.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Liver Functions
It is essential to monitor liver functions while undergoing treatment with Azithromycin Oral Suspension. If there is an increase in liver enzymes, it could be a sign of liver damage, which may require adjusting the dosage or stopping the medication altogether. Regular tests to check liver function are crucial. The treatment plan should be modified accordingly if there is any elevation in enzyme levels.
Symptoms to Watch For
Patients and caregivers need to stay alert for signs such as yellowing of the skin, pain in the abdomen, and irregular heartbeat. If any of these symptoms appear, they could indicate medication reactions and should not be ignored. Yellowing of the skin is often a sign of liver problems, while abdominal pain can point toward issues with the system.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience side effects, allergic reactions, or symptoms that suggest organ dysfunction, it is crucial to seek medical consultation promptly. Taking action can help prevent irreversible harm and improve the outcome for the patient. When dealing with severe side effects, consulting a healthcare professional as soon as possible is necessary. Acting in a manner can make a significant difference in preventing permanent damage.
Special Administration Guidelines
Administration to Elderly Patients
When dealing with individuals, exercise caution when administering Azithromycin Oral Suspension. This is because it is not uncommon for this demographic to have reduced kidney function and take medications simultaneously. These factors contribute to a risk of experiencing adverse interactions and side effects resulting from the medication usage. Furthermore, the potential for interactions due to taking medications concurrently adds another concern in the elderly population.

Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The use of Azithromycin Oral Suspension in women and nursing mothers presents a dilemma that requires careful evaluation of the risks and benefits involved. While there is no evidence of harmful effects on the fetus, exercise caution, especially during the initial three months of pregnancy. Similarly, breastfeeding mothers should also use their judgment as azithromycin may be passed into breast milk. A rigorous evaluation is needed to weigh the risks and benefits of transfer into breast milk.

Administration to Children
When caring for children, it's essential to take an approach. Azithromycin Oral Suspension is generally considered safe for children six months or older. However, paying attention to the dosage based on their body weight is crucial to prevent potential adverse effects. It's always better to err on caution and ensure the dosage is appropriate for their weight.

Overdosage and Its Management
Symptoms of Overdose
If someone experiences an overdose, they may have hearing loss, intense nausea, and diarrhea. The seriousness of these symptoms usually depends on the extent of the overdose. Temporary hearing loss can indicate an overdose; its severity is linked to how much was taken.

Immediate Actions
The first step is to remove the contents from the stomach through vomiting or gastric lavage. This is usually followed by giving activated charcoal to reduce the drug absorption into the body. It is essential to seek advice without any hesitation. Removing stomach contents Administering activated charcoal
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term effects of taking much medication are poorly understood, but they could potentially lead to liver damage and hearing problems. Monitoring and following up with patients is essential to prevent any permanent harm. It is necessary to conduct ongoing monitoring over an extended period.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling of Medicine
Healthcare providers and patients must handle Azithromycin Oral Suspension safely. To ensure dosing, always use a measuring device that has been calibrated. Store the medication according to the recommended conditions to maintain its effectiveness. Using a measuring device and adhering to the recommended storage conditions are vital aspects of handling Azithromycin Oral Suspension safely.
Disposal Guidelines
To prevent contamination, it is essential to use proper disposal methods for Azithromycin Oral Suspension. Please do not dispose of this medication in wastewater or household waste. It is recommended to consult guidelines or healthcare providers for appropriate disposal methods. Additionally, it is advised to avoid disposing of the medication via wastewater. Don't forget to check with disposal guidelines for the right way to dispose of it properly.














































































