Oxybutynin chloride
- I. Introduction to Oxybutynin Chloride
- II. Composition and Properties of Oxybutynin Chloride
- III. Mechanism of Action: How Oxybutynin Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Oxybutynin Chloride
- V. Off-Label Uses of Oxybutynin
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Administration in Special Populations
- VIII. Side Effects of Oxybutynin Chloride
- IX. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- X. Important Precautions and Warnings
- XI. Overdose Management
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XIII. Careful Administration Practices
I. Introduction to Oxybutynin Chloride
Overview of Oxybutynin Chloride
Oxybutynin chloride, a man-made medication, is commonly prescribed for effectively reducing symptoms of an overactive bladder. This substance works by influencing muscle relaxation through its actions on muscarinic receptors.
Historical context and development
In the middle of the century, oxybutynin emerged as a crucial advancement in the field of urology. Its arrival signified a transition from surgical interventions, to using medication to address bladder issues.
Importance in medical treatment
Oxybutynin is considered essential in urology due to its impact on enhancing the well-being of patients with bladder issues. It helps reduce both the discomfort and emotional challenges linked to urinary incontinence.
II. Composition and Properties of Oxybutynin Chloride
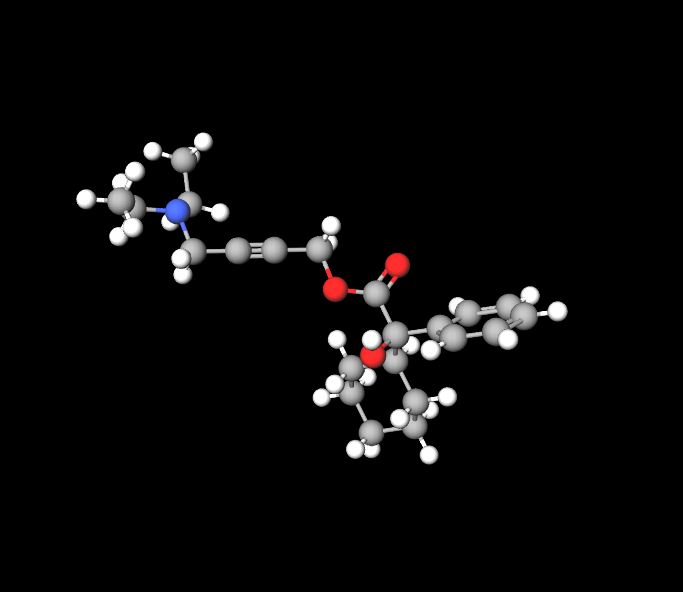
Chemical structure and characteristics
Oxybutynin structure features an amine group that plays a key role in its anticholinergic effects. The hydrochloride version improves its solubility and absorption in the body.
Formulations available
Medication delivery methods include immediate-release tablets, extended-release tablets, transdermal patches, and topical gels.
III. Mechanism of Action: How Oxybutynin Works
Pharmacodynamics: Interaction with the body
The main way it works is by blocking the acetylcholine receptors in the bladder's detrusor muscle, which helps decrease sudden contractions and improve the bladder's storage ability.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
Following administration, oxybutynin is quickly taken in and primarily processed by the liver, and its byproducts are mainly eliminated through the system.
IV. Approved Uses of Oxybutynin Chloride
Treatment of overactive bladder
Oxybutynin is used to treat symptoms of overactive bladder, such as frequent or urgent urination, incontinence (urine leakage), and increased night-time urination. It reduces muscle spasms of the bladder and urinary tract. Additionally, it is used in children (at least 5 years old) with overactive bladder related to a neurologic condition like spina bifida. Oxybutynin extended-release tablets are also used in children (at least 6 years old) with overactive bladder related to a neurologic condition1.
V. Off-Label Uses of Oxybutynin
-
Primary Pediatric Hyperhidrosis:
- Hyperhidrosis is a condition characterized by excessive sweating beyond what is physiologically necessary for thermoregulation. Primary hyperhidrosis is localized and can affect areas such as the axillae (armpits), palms, soles, and face. It is idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown.
- The prevalence of hyperhidrosis in the United States is estimated to be 2.8% of the population, with about 1.4% having the axillary form (affecting the armpits).
- Early detection and management are crucial for improving a patient’s quality of life, yet hyperhidrosis remains underdiagnosed and undertreated, especially among pediatric patients1.
-
Oxybutynin for Hyperhidrosis:
- Effectiveness: Oxybutynin has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the severity of primary hyperhidrosis. Real-life studies indicate that it is safe and provides significant improvement in the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS), both in children and adults2.
Other emerging applications
- Oxybutynin has been shown to relieve menopausal hot flushes and sweats in almost 40% of women. While its primary use is for overactive bladder, it offers a potential solution for menopausal symptoms2.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended dosages for different conditions
The right amount of needed depends on the type and specific condition being treated taking into account how the patient responds to it and their tolerance levels.
Methods of administration: Oral, topical, etc.
Various formulations help create customized treatment plans that cater to preferences and individual medical needs.
Adjustments for specific populations
It is important to make changes to the dosage for individuals with kidney or liver issues and other at-risk populations to avoid negative reactions.
VII. Administration in Special Populations
Elderly: Adjustments and cautions
Elderly individuals should be prescribed doses because they are more sensitive to anticholinergics and are more likely to experience side effects in the central nervous system.
Pregnant women and nursing mothers: Safety and recommendations
There is no data available, but oxybutynin should only be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding if the advantages outweigh any potential risks to the baby.
Pediatric use: Guidelines and limitations
Safety and effectiveness standards, for children are carefully established to make sure that the advantages of therapy outweigh the risks.
VIII. Side Effects of Oxybutynin Chloride
Common side effects: Dry mouth, constipation, dizziness
Common side effects of medications include dry mouth, which about 70% of patients experience, constipation that often requires dietary changes, and dizziness, particularly noticeable in older individuals.
Serious side effects: Arrhythmia, severe allergic reactions
Rare but serious adverse reactions could involve heartbeats and severe allergic reactions, which require prompt medical intervention.
Long-term side effect considerations
Regularly checking for cognitive deterioration and heart problems is important, especially among older adults who use it for a long time.
IX. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Common interactions: Impact on efficacy and toxicity
The effectiveness of chloride might decrease, or its harmful effects could worsen when taken with certain medications. Specifically, combining it with anticholinergic drugs can enhance overall anticholinergic effects, while certain antidepressants may impact how it is processed in the body.
Contraindications: Absolute and relative contraindications
This medicine should not be used by individuals with glaucoma, urinary retention, or those who have displayed hypersensitivity to any ingredient in the medication. It is important to be cautious when administering this drug to patients with bladder outflow blockages or gastrointestinal obstructive conditions.
Special considerations and risk factors
Special considerations may be needed for people with liver or kidney issues, and the potential for side effects emphasizes the need for careful use among older adults.
X. Important Precautions and Warnings
Known health conditions that warrant caution
Patients who have illnesses such as myasthenia gravis, severe colitis, and tachyarrhythmia need to be extra careful when using oxybutynin, as it could make these conditions worse.
Signs of potential overdose and what to do
Signs of taking much of a medication may involve extreme mouth dryness, unclear vision, and rapid heartbeat. In these situations, getting medical help is essential for proper care.
Precautions during surgery or other medical procedures
It is advisable to be cautious when using Oxybutynin during operations, particularly those that involve bowel resection, as it can impact gastrointestinal motility.
XI. Overdose Management
Symptoms of oxybutynin overdose
Symptoms of an overdose usually worsen the side effects of the medication, leading to dryness in the mouth, feelings of dizziness, and a risk of instability in the cardiovascular system.
Immediate actions and antidotes
Prompt medical attention is required. The treatment could include washing the stomach providing fluids through a vein and giving antidotes such, as physostigmine.
Long-term management and monitoring
After an overdose, it is crucial to monitor the heart rhythm and observe for any signs of recovery in the central nervous system.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal storage conditions to maintain efficacy
Keep Oxybutynin in a dry place, at room temperature, to maintain its effectiveness.

Safety measures for handling and disposal
We should be careful in how we deal with things to limit risks, and when getting rid of them, we need to follow the rules in our area to keep the environment safe from harm.
Stability and shelf life
The expiration date for oxybutynin is generally years as long as it's stored properly, and you can find the specific expiry dates on the packaging.
XIII. Careful Administration Practices
Monitoring requirements for long-term use
It is advised to check the functioning of organ systems, especially the kidneys and liver, to avoid negative reactions when undergoing long-term treatment.
Educational strategies for patients and caregivers
It's important to offer information on the advantages, possible side effects, and correct usage of medication to ensure the best results from treatment.
Regular assessment and adjustment of therapy
It's important to evaluate how well the treatment is working for the patient and how well they are tolerating it. This helps adjust the treatment plan as needed to provide the possible care.