Fipronil
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Fipronil
- III. How Fipronil Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Fipronil
- V. Off-Label Uses of Fipronil
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Administration to Specific Populations
- VIII. Side Effects and Common Side Effects
- IX. Interaction with Other Substances
- X. Warnings and Contraindications
- XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XII. Handling Precautions and Storage
- XIII. Overdosage and Its Management
- XIV. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Brief Overview of Fipronil
Fipronil is an insecticide used by the phenylpyrazole chemical group. It is widely utilized in medical and agricultural settings.
Importance in Modern Medicine and Pest Control
In today's world of medicine and agriculture, Fipronil is a solution for combating various external parasites and pests. It plays a role, in pest control methods and animal healthcare.
II. Composition of Fipronil
Chemical Structure
The composition of Fipronil includes a component that is crucial, for its effectiveness and durability.
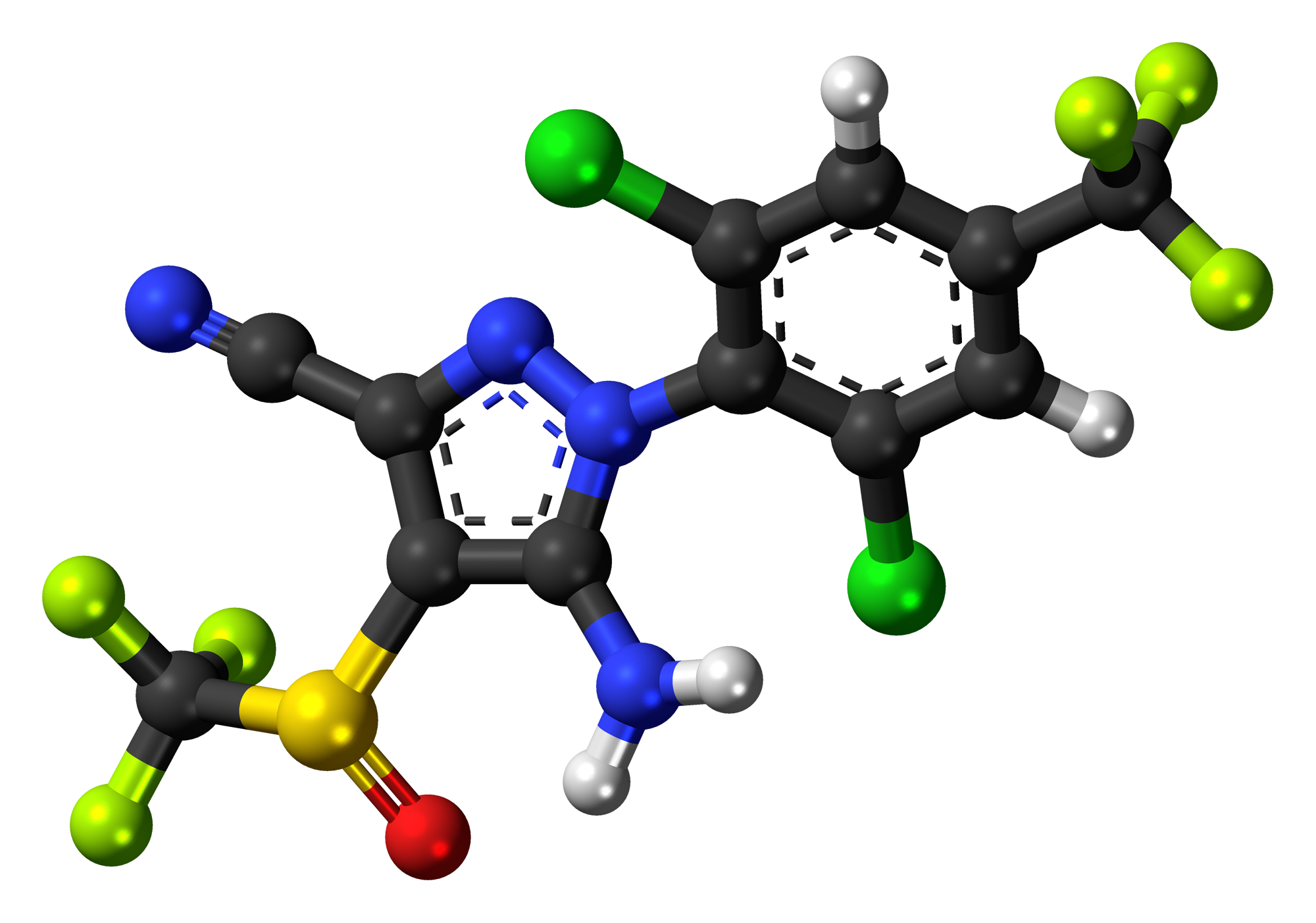
Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main component is Fipronil, while other ingredients like ethanol and propylene glycol are also present, in proportions depending on the formulation of Fipronil.
Different Formulations
Fipronil can be found in forms, for sale including:
- Sprays
- Gels
- Tablets
bifenthrin vs fipronil
Bifenthrin is very effective at controlling mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks. It also does a job against termites, although fipronil products like Taurus SC are considered more effective for this purpose. Bifenthrin is well suited for dealing with a variety of insects.
hydramethylnon vs fipronil
Fipronil bait is known to be more efficient and acts quicker than hydramethylnon bait. In contrast to Hydramethylnon bait, the mortality rates resulting from transmission are elevated with Fipronil bait. Additionally, Fipronil falls under the category of a "Group C. Human carcinogen" and has been linked to tumor development in rats, specifically thyroid tumors.
indoxacarb vs fipronil
Fipronil caused termites to die faster and in numbers compared to indoxacarb at the same concentrations. The amount of fipronil used and how it was applied also had an impact, on termite mortality. Different termite colonies showed susceptibility to both insecticides.
III. How Fipronil Works
Mechanism of Action
Fipronil blocks the chloride channels regulated by GABA in insects' nervous systems, causing stimulation and eventual elimination.
Target Pests and Parasites
- Fleas
- Ticks
- Cockroaches
- Ants
Speed and Duration of Effectiveness
IV. Approved Uses of Fipronil
Pest Control in Agriculture
Treatment of Fleas and Ticks in Pets
Commonly given to dogs and cats for treatment reasons.
Other Veterinary Applications
- Livestock safeguarding
- Bird utilization, in limited situations
V. Off-Label Uses of Fipronil
Fish Farming
Used in situations within the aquaculture industry to address parasitic infestations.
Garden Pest Control
Successful in getting rid of pests commonly found in gardens, such, as aphids and beetles.
fipronil for termites
fipronil ant killer
Injecting directly into the nest is commonly employed to address fire mounds that require swift eradication due to potential threats, to public or animal well being. Fipronil, being odorless swiftly impacts ants leading to the demise of ants within a few days.
Precautions for Off-Label Use
Make sure to seek advice from experts regarding the dosages and safety precautions.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages for Different Uses
- Pets: 10-20 milligrams per kilogram
- Agricultura: 100-200 grams per acre
Methods of Administration
- Topical use
- Taking orally
- Injecting in veterinary situations
Dosage Adjustments and Special Conditions
Adjust the dosage for patients with kidney or liver issues. Seek guidance from a healthcare provider for individual needs.
VII. Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly
Fipronil is not meant for use, so it is not relevant.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Likewise, it is not intended for human consumption.
Administration to Children
When it comes to pets, it's best to seek advice from a vet regarding the doses and precautions based on their age.
VIII. Side Effects and Common Side Effects
Classification of Side Effects
- Acute
- Chronic
Commonly Reported Side Effects
- Skin irritation in animals
- Decreased harvest output from overuse, in farming
How to Manage Side Effects
- If your skin comes into contact with Fipronil wash the area using plenty of water and mild soap without scrubbing too vigorously.
- When someone ingests Fipronil they may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness and stomach pain. It is crucial to seek medical attention and refrain from inducing vomiting unless instructed by a healthcare professional.
- In the event of inhaling Fipronil, move to an area with air and seek medical assistance promptly if breathing difficulties arise.
- For eye exposure to Fipronil, rinse the eyes with water for at least 15 minutes and consult a healthcare provider if irritation persists.
IX. Interaction with Other Substances
Drug Interactions
It is well documented that it can have interactions with certain insecticides, like organophosphates.
Food and Alcohol Interactions
What to Avoid When Taking Fipronil
X. Warnings and Contraindications
Situations Where Fipronil Should Not Be Used
There are situations where it is not recommended to use Fipronil, including:
- Animals that have shown a reaction to phenylpyrazole compounds
- Areas where endangered insects live
- Food producing animals as it can leave a lasting impact

Potential Risks and Complications
- Neurological impacts on species
- Environmental pollution if not appropriately controlled
- Potential risks to fetal development, in regions visited by pregnant animals
fipronil toxicity
Animals that have been poisoned display symptoms of neurotoxicity such as convulsions, twitching, tremors, difficulty in coordination in limbs, increased or decreased activity levels, vocalization, aggression, and abnormal neurological responses. In a study over a period of time young buffalo exposed to fipronil at a rate of 0.5 mg/kg/day exhibited harmful effects, like excessive salivation, teary eyes, feelings of sadness or low spirits reduced weight gain, muscle weakness, hair loss and sunken eyes.
XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring and Follow-up
It's important to keep an eye on pets after giving them medication. Its recommended to schedule a check up within a week of administering the medication.
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
If you experience any of the following signs of reactions, such as redness, itching, or difficulty breathing, it's important to seek advice from healthcare experts promptly.
Safe Use Guidelines
Remember to wear gloves when applying the product, wash your hands afterward, and try to avoid getting it on your skin or in your eyes.
XII. Handling Precautions and Storage
Proper Storage Conditions
Remember to store the item in a dry area Make sure to close the cap tightly Keep it away, from children and pets
Disposal Instructions
Please make sure to discard any empty or partially used containers following the guidelines set by your local environmental regulations.
Safety Measures When Handling Fipronil
- Do not consume
- Stay from breathing in vapors
- \Utilize in spaces, with good ventilation
XIII. Overdosage and Its Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Symptoms in pets can manifest as tremors, seizures, and a loss of coordination.
Immediate Steps to Take
- Stop the treatment away
- Get medical help for your pet as soon, as possible.
Long-Term Management and Care
Watch out for any lasting overall health impacts and make sure to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider when adjusting future doses.
XIV. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Fipronil, an insecticide, has various uses ranging from agricultural purposes to animal treatment. Nonetheless its application requires compliance, with safety guidelines.
Recommendations for Safe and Effective Use
Remember to follow the suggested doses at all times. Seek advice from experts for uses not specified on the label. Be careful when storing and handling to reduce the chances of any risks or issues arising.
Fipronil FAQ
What is fipronil?
Fipronil, a type of insecticide from the phenylpyrazole chemical group is widely employed to manage pests such, as ants, beetles, cockroaches, fleas, ticks, termites and others. Its mechanism involves interfering with the nervous system of insects leading to overstimulation of their nerves and muscles.
How does fipronil work?
Fipronil is harmful to bugs when they touch or eat it. It works by blocking GABAA gated chloride channels in the insects nervous system. This interference, with GABAA receptors stops the absorption of chloride ions leading to overstimulation of neurons and ultimately causing the insect to die.
How long does fipronil last for termites?
Due to its efficacy even at extremely low concentrations it continues to be potent in the soil for a minimum of five years post application. This guarantees prolonged safeguarding of the infrastructure, from termite infestations.
What does fipronil kill?
Fipronil, an used insecticide is classified under the phenylpyrazole chemical group. It is employed for managing pests such as ants, beetles, cockroaches, fleas, ticks, termites, mole crickets, thrips, rootworms, weevils and other insects. Fipronil appears as a powder, with a musty smell.