Bethanechol Chloride
- Introduction to Bethanechol Chloride
- Composition of Bethanechol Chloride
- Mechanism of Action: How Bethanechol Chloride Works
- Indications and Uses of Bethanechol Chloride
- Off-Label Uses of Bethanechol Chloride
- Dosage and Administration
- Administration in Specific Populations
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Side Effects of Bethanechol Chloride
- Warnings and Important Precautions
- Handling and Storage of Bethanechol Chloride
- Management of Overdosage
Introduction to Bethanechol Chloride
Bethanechol chloride plays a role in medical treatment, particularly in addressing issues like urinary retention. This medication works by activating receptors in the bladder muscles, helping to promote urination and relieve discomfort associated with urinary hesitancy. Developed in the 1900s, Bethanechol chloride has been extensively studied to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Originally designed as a muscle stimulant, it has since been tailored for precise urological treatments, becoming an essential component of urological pharmacotherapy.
Composition of Bethanechol Chloride
Bethanechol chloride's chemical structure and properties are intricately designed to engage with the receptors in the nervous system. Its chemical composition allows for solubility and quick absorption, resulting in a rapid therapeutic effect. Different forms of Bethanechol chloride are available for administration, including tablets and injections.
- Oral tablets come in handy to cater to individual treatment needs, offering flexibility in dosing schedules. Injectable solutions are utilized in emergency situations to elicit an immediate response.
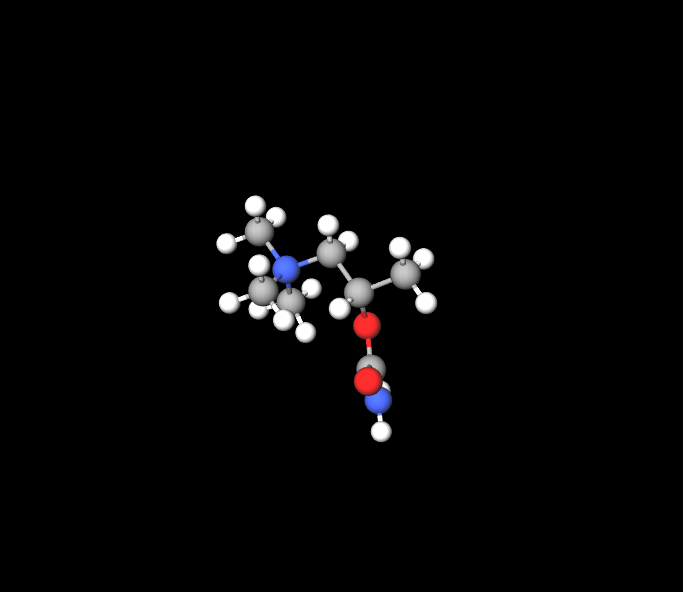
Mechanism of Action: How Bethanechol Chloride Works
Pharmacodynamics: Bethanechol chloride works by targeting muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to trigger reactions that boost muscle tone and natural movements in the stomach and bladder. It notably boosts movement and helps relieve non-obstructive urinary issues, ultimately enhancing patients' well-being.
Indications and Uses of Bethanechol Chloride
Off-Label Uses of Bethanechol Chloride
- This medication has been used in the treatment of postoperative urinary retention, postpartum urinary retention, and overflow incontinence caused by neurogenic atony of the bladder1.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage Instructions for AdultsThe dose of Bethanechol chloride for adults depends on the seriousness and type of the condition being addressed, with specific dosing adjusted to meet individual treatment requirements.
Changes in Dosing for Certain Conditions It is essential to make dosage modifications for individuals with existing conditions or those particularly sensitive to the drug's impact.
Administration in Specific Populations
- When caring for individuals it's important to be mindful of potentially needing lower medication doses due to their heightened sensitivity and slower metabolism. Monitoring them closely is crucial.
- For women and nursing mothers, using Bethanechol chloride should be approached cautiously. It should only be considered if the benefits outweigh any risks to the baby.
- When it comes to children administering Bethanechol chloride should be done under medical supervision since there is limited information on its use in pediatric patients. The focus should always be, on ensuring that the treatment benefits outweigh any risks involved.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Common Interactions with Other Medications
Bethanechol chloride, because of its properties, might interact in a cooperative or opposing manner with different medications.
- For example, using it with anticholinergic drugs could reduce its effectiveness, while combining it with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may enhance its effects, potentially causing medication-related issues.
- Additional significant interactions to consider are; Increased risk of bradycardia when taken alongside beta blockers, pharmacodynamic interactions with other cholinergic agonists
- Heightened effects of opioid pain relievers, which could require dosage adjustments
Absolute Contraindications for Use
Bethanechol chloride should not be used in patients with health conditions as it can cause serious side effects. These conditions include:
- Allergies to bethanechol or any of its ingredients cause ulcer disease as it can worsen due to increased stomach acid
- Bladder blockage or a weak bladder wall, which could result in bladder rupture
- Recent intestinal surgery, which may lead to increased pressure and potential rupture
- Patients with asthma as bethanechol might trigger bronchoconstriction.
Side Effects of Bethanechol Chloride
Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal and Systemic
When Bethanechol chloride is administered, it can cause side effects, with the gastrointestinal tract being the most commonly affected.
- Patients might encounter symptoms such as discomfort, cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea resulting from increased gastrointestinal movement.
- On a scale, bethanechol can trigger systemic effects like increased salivation and sweating.
- Higher doses may even lead to lacrimation due to its impact on the entire system.

Serious Adverse Reactions and Emergency Responses
In instances, Bethanechol chloride may cause significant cardiovascular reactions like low blood pressure and slow heart rate, which could require urgent medical attention. There have been reports of outcomes such as seizures or temporary loss of consciousness as well. Healthcare professionals must stay alert and ready to handle these emergencies by focusing on monitoring and quick response tactics.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Precautions in Patients with Asthma and Other Respiratory Issues
Extreme care must be taken when using bethanechol chloride in patients with issues. Due to its ability to worsen bronchoconstriction, close monitoring, and quick intervention are crucial.
Impact on Patients with Cardiac Conditions
Patients who have existing heart conditions, such as those related to the heart's conduction system or muscle weakness, need to undergo a thorough evaluation before starting treatment with Bethanechol chloride. The drug's cholinergic properties can impact heart rate and blood pressure, requiring careful monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Handling and Storage of Bethanechol Chloride
Recommended Storage Conditions to Ensure Stability
To preserve the chemical stability and effectiveness of bethanechol chloride, it is important to store it under the following conditions:
- Store it at room temperature in a dry and dark place.
- Always keep the container tightly sealed when not in use.
- Avoid exposing the medication to freezing temperatures, as this could potentially change its chemical composition.
Safe Handling Practices for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to follow protocols to avoid unintended contact with Bethanechol chloride. They should wear gloves and protective gear when handling the medication, administer it in a controlled setting, and dispose of any leftover medication as per safety rules.
Management of Overdosage
Symptoms and Immediate Actions to Take
Taking too much Bethanechol chloride can result in a cholinergic crisis, showing signs like drooling, sweating, breathing difficulties, and weak muscles. Quick steps to take are:
- Giving atropine, the antidote to balance out muscarinic symptoms
- Offering supportive help like aiding with breathing and managing fluids
- Keeping a close eye on vital signs and symptoms constantly.
Long-term Management Strategies for Overdosage
After treating an overdose, the next steps involve preventing it from happening again and checking for any possible issues that may result from the overdose. This includes keeping a watch on the patients' breathing and heart function as well as reviewing their medication plan to avoid similar incidents in the future.