Gatifloxacin
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Gatifloxacin
- III. How Gatifloxacin Works
- IV. Uses of Gatifloxacin
- V. Off-label Use of Gatifloxacin
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Gatifloxacin
- VII. Specific Administration Guidelines
- VIII. Gatifloxacin Interactions
- IX. Side Effects of Gatifloxacin
- X. Warnings, Contraindications, and Precautions
- XI. Overdose: Signs, Risks, and Actions
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Gatifloxacin
- XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
1.1 What is Gatifloxacin?
Gatifloxacin is an antibiotic that falls under the category of fluoroquinolones. Its primary purpose is to treat infections, especially those affecting the eyes.
1.2 Historical Context and Development of Gatifloxacin
Throughout history, Gatifloxacin has played a role in the family of fluoroquinolones. These antibiotics emerged from the discovery of quinolone compounds in the 1960s. Developed as a response to the growing challenge of antibiotic bacteria, Gatifloxacin has undergone extensive testing and scientific investigation reaffirming its effectiveness as a potent medical treatment.
1.3 Primary Medical Function and Classification
Gatifloxacin primarily functions, as an agent explicitly targeting gram-positive bacteria. It belongs to the generation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics, which are widely recognized for their ability to combat a broad range of bacterial infections.
II. Composition of Gatifloxacin
2.1 Core Ingredients and Compounds
Gatifloxacin, the active component in this medication, is a synthetic compound with antibacterial properties. It belongs to the fluoroquinolone class. Consists of a central quinolone core, accompanied by different functional groups that enhance its effectiveness against bacteria.
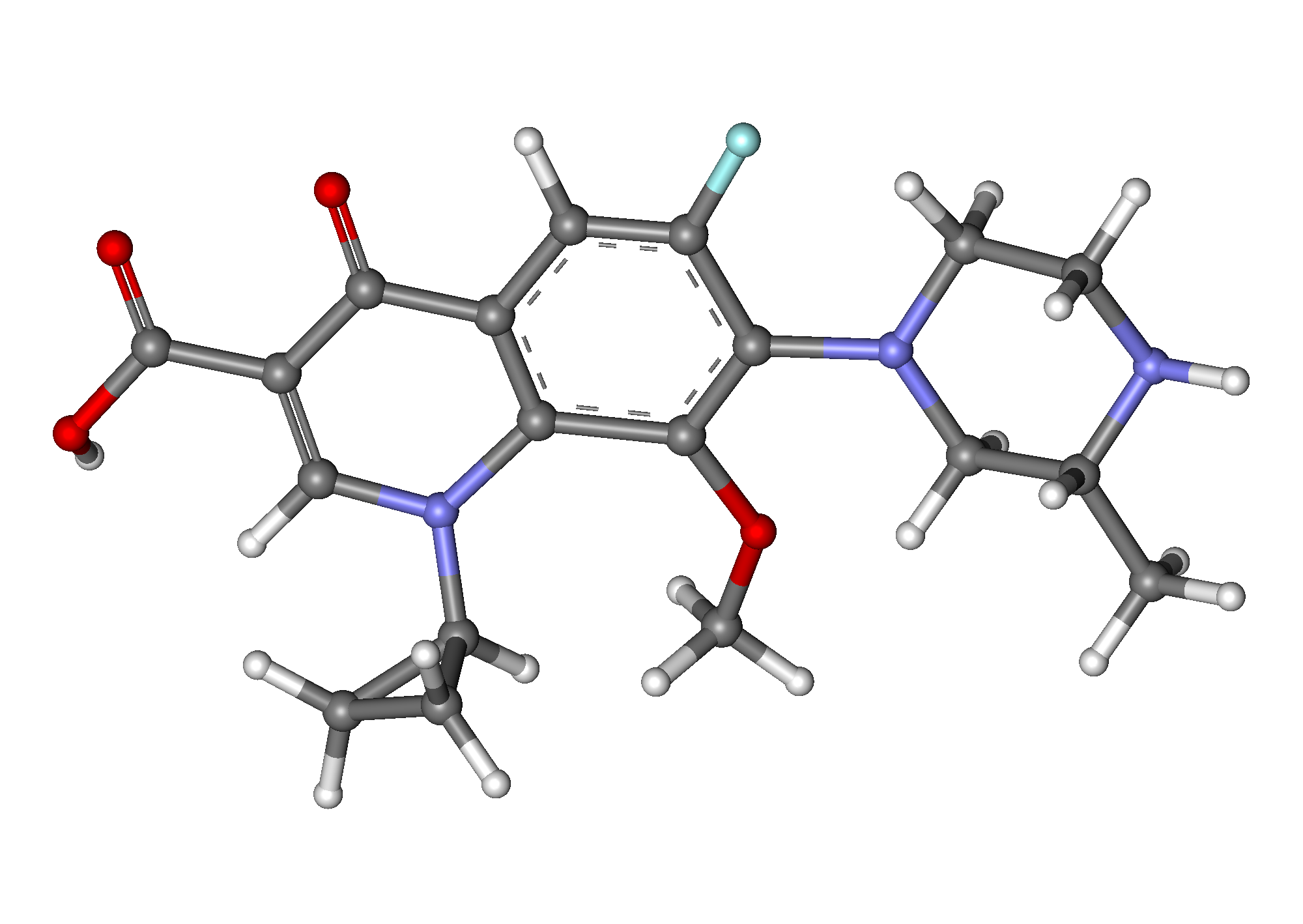
2.2 Unique Molecular Structure and Attributes
The robust antibacterial activity of gatifloxacin is attributed to its molecular structure. Unlike generations of fluoroquinolones, it contains a fused pyridobenzoxazine ring and its core quinolone structure. This fusion, combined with the presence of fluorine and cyclopropyl groups not enhances the bactericidal activity but also expands its effectiveness, against a broader range of bacterial pathogens.
III. How Gatifloxacin Works
3.1 Mechanism of Action
Gatifloxacin works by blocking enzymes in bacteria that are crucial for DNA replication. It targets explicitly two enzymes, namely DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. By hindering the activity of these enzymes, Gatifloxacin interferes with the process of DNA replication and transcription in cells resulting in their eventual demise and the resolution of the infection.
3.2 Impact on the Human Body at the Micro and Macro Level
On a scale, Gatifloxacin works by directly targeting and destroying bacterial cells. This action disrupts the synthesis of DNA, causing a decrease in the number of bacteria present. This, in turn helps the system effectively eliminate the infection. Looking at things from a perspective, this reduces symptoms typically associated with bacterial infections, like inflammation and discomfort. As a result, Gatifloxacin enhances the patient's well-being and speeds up recovery from bacterial infections.
IV. Uses of Gatifloxacin
4.1 Officially Approved Uses
Gatifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to combat bacterial infections in various body parts, such as lung, sinus, skin, and urinary tract infections. It is also effective in managing sexually transmitted diseases1. Fluoroquinolones are a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics that are used to treat a variety of infections2.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about Gatifloxacin and fluoroquinolones:
- Merck Manuals Professional Edition
- Merck Manuals Consumer Version
- The Role of 3 Newer Fluoroquinolones
4.2 Conditions and Diseases Commonly Treated with Gatifloxacin
Lung infections caused by bacteria Sinus infections caused by bacteria Skin infections are caused by bacteria Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria-transmitted diseases like gonorrhea.
- Lung Infections: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment - Verywell Health
- Symptoms of Lung Infection - Healthline
- Bacterial Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention - Cleveland Clinic
V. Off-label Use of Gatifloxacin
5.1 Understanding Off-label Use: Definition and Legal Aspects
Off-label use is a term used to describe when doctors prescribe a drug for purposes other than the ones regulatory agencies have officially approved for it. It is a widely accepted practice among medical professionals to prescribe drugs off-label1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about off-label drug use:
- Off-Label Drugs: What You Need to Know - AHRQ
- What to know about off-label drug use - Medical News Today
- Off-Label Drug Use: Why Do Doctors Prescribe Them? - Drugwatch
5.2 Documented Off-label Uses for Gatifloxacin
Gatifloxacin belongs to a group of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones. Its purpose is to combat infections within the body specifically targeting the lungs sinuses, skin and urinary tract. Additionally it has been utilized in the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases1.
GoodRx reports that Gatifloxacin is frequently prescribed off-label for an expanding range of conditions such as disorder, diabetic nerve pain, complex regional pain syndrome (a form of chronic arm or leg pain after injury or surgery), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), restless leg syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia (a type of persistent facial pain) migraines and withdrawal seizures related to drug and alcohol dependency.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about Gatifloxacin and fluoroquinolones:
- Fluoroquinolones - Infectious Diseases - Merck Manuals Professional Edition
- Fluoroquinolones - Infections - Merck Manuals Consumer Version
- The Role of 3 Newer Fluoroquinolones
5.3 Research and Studies Supporting Off-label Use
Gatifloxacin belongs to a group of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones. Its purpose is to combat infections within the body, specifically targeting the lungs, sinuses, skin, and urinary tract. Additionally, it has been utilized in the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases1.
DrugBank Online reports that gatifloxacin has demonstrated its effectiveness against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Besides its approved applications, researchers have also investigated gatifloxacin for its potential in treating keratitis and other conditions1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about Gatifloxacin and fluoroquinolones:
- Gatifloxacin: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online
- Fluoroquinolones - Infections - Merck Manuals Consumer Version
- Fluoroquinolones - Infectious Diseases - Merck Manuals Professional Edition
VI. Dosage and Administration of Gatifloxacin
6.1 General Guidelines for Dosage
The recommended amount of Gatifloxacin differs based on the condition being addressed. In general, for eye infections, a typical amount is one drop in the affected eye(s) every two hours during waking hours up to 8 times per day for the initial two days. Afterward, it is usually reduced to one drop in the affected eye(s) two to four times for the rest of the treatment duration.
6.2 Factors Affecting Dosage: Age, Weight, and Disease Severity
The dosage of gatifloxacin can vary based on aspects such as the patient's age. It's important to note that adult dosages might not be appropriate for children. Additionally, body weight can also impact how the drug is metabolized and distributed within the body. Moreover, severe infections might require higher doses or longer treatment duration. Healthcare professionals need to take these factors into account in order to determine the suitable therapeutic approach for each individual patient.
6.3 Specific Instructions for Safe and Effective Administration
To ensure the administration of Gatifloxacin, please adhere to the following instructions; Refrain from touching the dropper tip against any surface, including your eye in order to prevent contamination. Additionally, it is advised not to wear contact lenses if you are experiencing symptoms of conjunctivitis or are undergoing treatment with Gatifloxacin.
VII. Specific Administration Guidelines
7.1 Administration to Elderly Patients
As people grow older, their organs may not work efficiently as before, impacting how medications are processed and eliminated from the body. Although Gatifloxacin has been used safely in individuals, it is essential to exercise caution and regularly monitor its effects.
7.2 Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Gatifloxacin may be considered for use, during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks to the developing baby. It is essential to exercise caution when giving Gatifloxacin to a breastfeeding mother as many medications can pass into breast milk.
7.3 Administration to Children
The use of Gatifloxacin in infants under the age of one has not been proven to be safe and effective. In the case of children, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage to avoid any possible adverse effects.
7.4 Careful Administration: Who Needs Special Attention?
It is essential to monitor patients with kidney problems as their dosage may need to be adjusted. Patients who have a history of QT prolongation or imbalances or are taking other medications that can prolong QT intervals should also be closely monitored due to an elevated risk of developing heart rhythm irregularities.
VIII. Gatifloxacin Interactions
8.1 Common Drug-Drug Interactions
Certain medications like antacids that contain aluminum or magnesium products containing iron or zinc or multivitamins with minerals can interact with gatifloxacin. This interaction can hinder the absorption of gatifloxacin.
8.2 Interaction with Food and Lifestyle Factors
The intake of food does not have an impact on how the body absorbs Gatifloxacin. However, it is recommended that you avoid consuming amounts of caffeine while undergoing treatment as it may potentially lead to heightened stimulation of the nervous system.
8.3 How to Avoid Harmful Interactions
To prevent interactions, you must inform your healthcare providers about all the medications you are taking. It is also advisable to avoid taking over-the-counter medicines without consulting a professional. Additionally, limiting your caffeine intake while undergoing treatment would be beneficial.
IX. Side Effects of Gatifloxacin
9.1 Common Side Effects and Their Management
Similar to medications, Gatifloxacin can potentially result in specific side effects. Some reported ones may include; Redness or swelling of the eyes, Blurred vision, Sensitivity to light, Discomfort or pain in the eyes Excessive tearing Typically, these side effects are temporary and tend to diminish as your body becomes accustomed to the medication. However, if they persist or become more severe, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
9.2 Serious Side Effects: Signs and When to Seek Medical Attention
Serious adverse effects from taking Gatifloxacin are not very common. They might include the following; Allergic reactions like rashes, itching, swelling, intense dizziness, or difficulty breathing—unusual discharge from the eyes, changes in vision, and eye pain. If you encounter any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention.
9.3 Long-term Effects and Monitoring
The long-term impacts of Gatifloxacin are not very common. They may involve experiencing prolonged eye discomfort or noticing changes in your vision. Eye examinations are crucial to keep track of your condition and promptly identify and address any potential long-term effects.
X. Warnings, Contraindications, and Precautions
10.1 General Warnings Associated with Gatifloxacin Use
Patients with hypersensitivity to quinolones must be careful when using gatifloxacin. Moreover, patients must stop using the medication and contact their doctor immediately if they encounter any reactions or notice their symptoms worsening.
10.2 Contraindications: Who Shouldn’t Use Gatifloxacin?
Gatifloxacin should not be used by patients known to have a hypersensitivity to Gatifloxacin or other quinolones. It is also advisable to avoid its use in patients with eye infections as there is limited research on its effectiveness in such cases.
10.3 Important Precautions to Ensure Safe Use
It is essential to take precautions when using gatifloxacin eye drops. Remember to wash your hands before applying the drops and avoid touching the tip of the bottle to your eyes or any other surfaces. If your eyes are red, it is advisable not to wear contact lenses while using gatifloxacin. Additionally, make sure to follow the prescribed duration of use and avoid using it for a more extended period than recommended by your healthcare provider.
XI. Overdose: Signs, Risks, and Actions
11.1 Identifying Overdose Symptoms
Symptoms of an overdose may include experiencing long-lasting discomfort in the eyes, excessive watering or changes in vision. However, it is highly improbable to experience an overdose that affects the body due to the localized administration of this medication.

11.2 Risks and Complications from Overdose
Taking much Gatifloxacin can cause long-lasting irritation and potential damage to the eye. However the chances of experiencing any problems, throughout the body are low because Gatifloxacin is not highly absorbed systemically.
11.3 Actions to Take in Case of Overdose
If someone experiences an overdose, it's essential to rinse their eyes with water for a cleansing. If they still feel discomfort it is advised to seek immediate medical assistance.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Gatifloxacin
12.1 Optimal Storage Conditions
Store gatifloxacin at room temperature, away from light and moisture. Make sure to keep this medication out of reach of children and pets. Also, avoid storing it in the bathroom, as humidity can affect its effectiveness. Remember to close the bottle when not using it tightly.
12.2 Guidelines for Proper Handling and Disposal
When dealing with Gatifloxacin, it's crucial to be extremely careful. Ensure you don't touch or let the dropper tip contact any surface, including your eyes or hands, to avoid contamination. To properly dispose of Gatifloxacin, refrain from flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into a drain. Instead, consult guidelines or ask your pharmacist for guidance on safely disposing of it and protecting the environment.
XIII. Conclusion
13.1 Recap of Gatifloxacin's Uses, Benefits, and Risks
Gatifloxacin is an antibiotic commonly used to treat bacterial eye infections. It offers the advantage of providing rapid and effective relief from the symptoms associated with these infections. However, like all medications, there are risks involved. These risks include the possibility of eye irritation and potential interactions with drugs. It is crucial to manage these risks by ensuring accurate dosage and administration, conducting thorough monitoring, and paying close attention to any signs of adverse reactions.
13.2 Importance of Patient-Educator Communication for Safe Use
Patients and healthcare providers must have communication to ensure the safe usage of Gatifloxacin. Patients should be adequately educated about the risks and side effects associated with this medication, and they should also be advised to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any severe adverse reactions. Regular follow-up appointments can also help monitor the treatment's effectiveness and make any needed adjustments. Always remember when patients are well-informed, they become patients.
Gatifloxacin FAQ
- What are Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution?
- What are Gatifloxacin side effects?
- What are Gatifloxacin Dexamethasone eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin?
- What is the brand name of Gatifloxacin?
- What are the uses of Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- What is the price of Gatifloxacin?
- What is the cost of Gatifloxacin?
- What is Gatifloxacin used for?
- What is the dosage for Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- What is the price of Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- How does Gatifloxacin compare to Moxifloxacin?
- What is the brand name of Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- Why was Gatifloxacin eye drops banned?
- What is Prednisolone Gatifloxacin Bromfenac used for?
- What is the generic name of Gatifloxacin?
- What is Gatifloxacin 0.5?
- What are Gatifloxacin 0.5 eye drops?
- What are the uses of Gatifloxacin?
- What are the side effects of Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- Are Gatifloxacin eye drops safe?
- Why is Gatifloxacin banned?
- What is Gatifloxacin used to treat?
- What is Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution used for?
- What are the contraindications for Gatifloxacin?
- How does Gatifloxacin compare to Ciprofloxacin?
- Are Gatifloxacin eye drops used for cataract surgery?
- What are the alternatives to Gatifloxacin?
- What are the warnings associated with Gatifloxacin?
- How does Gatifloxacin compare to Ofloxacin?
- Is there a generic version of Gatifloxacin?
- Can Gatifloxacin be used for dogs?
- How does Gatifloxacin compare to Moxifloxacin eye drops?
- Can Gatifloxacin and Moxifloxacin be used together?
- What are Gatifloxacin and Dexamethasone eye drops?
- What are Gatifloxacin and Dexamethasone ophthalmic solution?
- Can Gatifloxacin and Prednisolone be used together?
- What are the uses of Gatifloxacin and Dexamethasone eye drops?
- What are the uses of Gatifloxacin and Dexamethasone ophthalmic solution?
- What are Gatifloxacin and Loteprednol eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin and Difluprednate ophthalmic emulsion?
- What are Gatifloxacin and Ketorolac eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin oral?
- What is the dosage for Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5?
- What are the uses for Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin ointment?
- What are Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution eye drops?
- What is the price of Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5?
- What are Gatifloxacin ophthalmic eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin GoodRx?
- What are Gatifloxacin with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin Zymar?
- What is Zymar Gatifloxacin eye ointment?
- What is Zymaxid Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.5?
- What is Zymar Gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.3?
- What are Zymar Gatifloxacin eye drops?
- What is the mechanism of action for Gatifloxacin?
- What is Gatifloxacin MSDS?
- What are Gatifloxacin Prednisolone eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin Prednisolone Acetate Ophthalmic Suspension?
- What is Gatifloxacin plus Ketorolac ophthalmic solution?
- What is Gatifloxacin Prednisolone Acetate Ophthalmic Suspension in Hindi?
- What are Gatifloxacin Prednisolone Acetate eye drops?
- What are Gatifloxacin Prednisolone eye drop brands?
- What is the dosage for Gatifloxacin?
- Are Gatifloxacin eye drops safe for dogs?
- What class does Gatifloxacin belong to?
- What is the classification of Gatifloxacin?
- What is Gatifloxacin Sesquihydrate?
- What is Gatifloxacin Sol 0.5?
- What is the structure of Gatifloxacin?
- What is Gatifloxacin synthesis?
- What is a Gatifloxacin tablet?
- What is a Gatifloxacin tablet 400 mg?
- What is Gatifloxacin Tetes Mata?
- What is the brand name for Gatifloxacin tablets?
- What is Tymer Gatifloxacin?
- What is Tequin Gatifloxacin?
- What are Gatifloxacin drops?
- What are the uses of Gatifloxacin tablets?
- What are Prednisolone-Gatifloxacin-Nepafenac eye drops used for?
- What is Gatifloxacin FDA status?
- What are Gatifloxacin Ketorolac Tromethamine eye drops?
- What is Gatifloxacin Loteprednol ophthalmic suspension?
- What is Gatifloxacin Lasik?
- What are the interactions of Gatifloxacin?
- What are the indications for Gatifloxacin?

















