Ciprofloxacin
- I. Introduction to Ciprofloxacin
- II. Composition of Ciprofloxacin
- III. How Ciprofloxacin Works
- IV. Common Uses of Ciprofloxacin
- V. Common Uses of Ciprofloxacin
- V. Off-Label Uses of Ciprofloxacin
- V. Off-Label Uses of Ciprofloxacin
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Ciprofloxacin
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Ciprofloxacin
- VII. Interaction of Ciprofloxacin with Other Medicines
- VIII. Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration of Ciprofloxacin
- XI. Handling an Overdose of Ciprofloxacin
- XII. Storage of Ciprofloxacin
- XIII. Handling Precautions for Ciprofloxacin
I. Introduction to Ciprofloxacin
A. Background and History of Ciprofloxacin
When introduced by Bayer AG in 1987, Ciprofloxacin revolutionized critical care for patients suffering from severe bacterial infections- previously untreatable with other antibiotics- through its chemotherapeutic abilities as a fluoroquinolone drug. Its innovative product design opened up new avenues from which better health care could be delivered and fought against otherwise life-threatening ailments while respecting patients' lifestyles and needs.
B. Classification and Category of Ciprofloxacin
As part of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic family lies Ciprofloxacin, a member of this group's second-generation drugs. What distinguishes it is its ability to combat both types of bacteria - Gram-positive and negative - through its potent broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. Its usage potential spreads far beyond respiratory infections alone, encompassing other areas including but not limited to urinary tract infections or diseases affecting the digestive system and skin too!
II. Composition of Ciprofloxacin
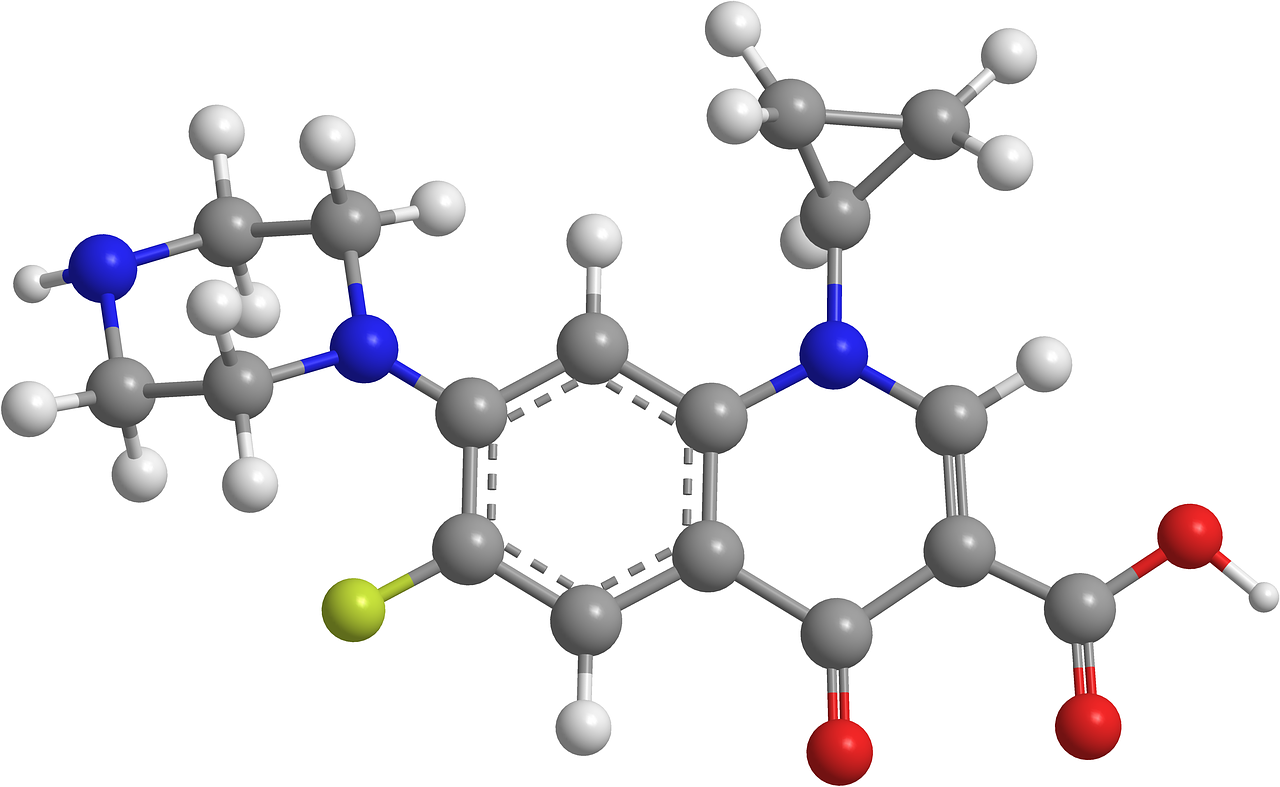
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Ciprofloxacin bears the chemical nomenclature of 1 cyclopropyl 6-fluoro 1 4 dihydro 4-oxo 7-(1 piperazinyl)-3 quinoline carboxylic acid with a molecular mass of 331.4 and exists as white to slightly yellowish powder which readily dissolves in water while demonstrating only partial solubility in ethanol, as a compound possessing good pharmacokinetic properties such as high bioavailability and extensive distribution within body tissues. Ciprofloxacin is highly effective against infections affecting various bodily systems - urinary tract infections are one example where this antibiotic has been successful. Ultimately, Ciprofloxacin's primary mode of excretion involves filtration primarily through the kidneys.
B. Active and Inactive Ingredients
Essential to Ciprofloxacin's efficacy is its active ingredient: Ciprofloxacin. The composition likewise incorporates different idle additives to enhance stability and absorption properties. As an example thereof are such compounds as cornstarch or silicon dioxide; similarly included might be microcrystalline cellulose as well as crospovidone plus magnesium stearate, among others mentioned earlier.
III. How Ciprofloxacin Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of two essential topoisomerase enzymes - DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV- are one-way Ciprofloxacin neutralizes harmful bacteria. These enzymes perform vital roles like facilitating bacterial DNA replication, transcriptional regulation, and complex genomic repair tasks that enable adaptation to various environmental shifts. By disrupting their functions by blocking them directly at the active sites within these proteins with the administration of Ciprofloxacin's chemical structure, which inhibits specific enzymatic activity, essentially throwing a kink into their genomic supercoiling machinery, resulting in interruption from progressing proliferation processes, ultimately leading towards an accelerated rate of cell death.1
References:
B. Effect on Bacterial Cells
An extraordinary attribute of Ciprofloxacin is its capability to render irreversible damage to bacterial cell-DNA which augments its efficacy as an antibiotic. The destruction caused by this drug impairs critical cellular processes like supercoiling, leading to disturbed transcription and replication mechanisms. Consequently, this hinders bacterial growth and division, leading to cell death which indeed controls bacterial infections.1
References:
IV. Common Uses of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin's wide-reaching antibacterial potential makes it an effective treatment option for various bacterial infections. Below are some common uses:
- Addressing urinary tract conditions such as pyelonephritis or cystitis1
- Treating respiratory tract issues like bacterial pneumonia or chronic bronchitis' acute exacerbations2
- Managing gastrointestinal problems like Travelers' diarrhea or E. coli related infections such as Campylobacter jejuni3
- Combating skin and soft tissue ailments including burns and cellulitis resulting from animal bites4
- Treatment of bone and joint conditions such as osteomyelitis & septic arthritis5
However, it should be noted that the drug should only be prescribed by licensed healthcare professionals who reserve its use for severe cases with few treatment options available.
References:
- Urinary Tract Infection, Female - NCBI
- Antimicrobial resistance in community-acquired pneumonia - NCBI
- Traveler's Diarrhea - CDC
- Animal Bites - NCBI
- Current concepts in the management of septic arthritis - NCBI
V. Common Uses of Ciprofloxacin
A. Approved Indications
With ciprofloxacin's broad spectrum of activity against bacteria strains comes several applications for treating bacterial-based ailments. Its approval by the FDA positions it in efficacy for managing varied medical conditions such as Urinary tract infection, including acute or chronic pyelonephritis1, infectious diarrhea caused by E.coli, Campylobacter jejuni or shigella species2, skin/soft tissue, bone/joint3, intrabdominal4, LRT lower respiratory,(pneumonia/acute exacerbations)5 Typhoid fever6, ear/nose/throat related conditions7.
References:
- Urinary Tract Infection, Female - NCBI
- Traveler's Diarrhea - CDC
- Current concepts in the management of septic arthritis - NCBI
- Intraabdominal Infections - NCBI
- Antimicrobial resistance in community-acquired pneumonia - NCBI
- Typhoid Fever - CDC
- Otitis Externa - NCBI
B. Bacterial Infections Treated by Ciprofloxacin
V. Off-Label Uses of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, an effective antibacterial agent, has demonstrated an exceptional ability to target Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial strands. This drug effectively treats various types of infection caused by these strands, such as Urinary Tract Infections or Infectious Diarrhea1. Klebsiella pneumoniae causes serious health issues like bacterial-induced pneumonia2 along with wound/surgical site infections, bloodstream infections, and in some cases, even meningitis/encephalitis3. Staphylococcus aureus commonly known for causing respiratory illnesses and skin related ailments4 food poisoning could also be cured through this medication. Pseudomonas aeruginosa--generally acquired via hospital infections5 can result in life-threatening conditions like septicemia/pneumonia and urinary tract-related problems. Enterobacter cloacae can generate several health complications, including lower respiratory tract infections, sepsis, and skin-related complications6, but it also causes UTIs, bacteremia, and intra-abdominal disorders7.
A word of caution, however, is that susceptibility tests ought to be conducted before using Ciprofloxacin since bacterial resistance cannot be overlooked8.
References:
- Traveler's Diarrhea - CDC
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: going on the offense with a strong defense - NCBI
- Invasive Infections with Multidrug-Resistant Yeast Candida auris, South Africa, 2012–2016 - NCBI
- Staphylococcus aureus Infections - NCBI
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections - NCBI
- Enterobacter Infections - NCBI
- Intra-Abdominal Infections: Considerations for the Use of the Carbapenems Including Ertapenem - NCBI
- Predicting Antibiotic Resistance - NCBI
V. Off-Label Uses of Ciprofloxacin
A. Unconventional Uses
While primarily intended for fighting bacterial infections, Ciprofloxacin has demonstrated benefits beyond its intended use. When appropriate circumstances arise, healthcare practitioners may choose to leverage Ciprofloxacin to address:
- Tuberculosis (TB) instances resistant to initial anti-tubercular drugs1
- Particular kinds of malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum2
- Prevention against meningococcal meningitis in close associates of infected people3
- Treatment of gonorrhea when first-line antibiotics prove inadequate4
It's crucial to emphasize that these choices are at the healthcare providers' discretion and consider several components, such as the person's overall health condition, disorder severity, and availability of other therapies.
References:
- Fluoroquinolones for the treatment of tuberculosis - NCBI
- Malaria FAQs - CDC
- Prevention and Control of Meningococcal Disease - CDC
- 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines - Gonorrhea - CDC
B. Evidence Supporting Off-Label Uses
Studies and clinical trials indicate promising results for using Ciprofloxacin in off-label cases:
- Tuberculosis: Research highlights that using Ciprofloxacin may prove efficacious as a second-line agent in combating multidrug-resistant tuberculosis cases1.
- Malaria: Multiple studies demonstrate potent in-vitro activity by using Ciprofloxacin against Plasmodium falciparum, one species responsible for causing malaria2.
- Meningococcal meningitis: Researchers suggest that prophylactic doses of ciprofloxacin may help prevent meningococcal meningitis in individuals who come into close contact with patients3.
- Gonorrhea: Despite increasing resistance, certain regions report continued effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin against gonorrhea when other options are unavailable or unsuitable4.
However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new treatment regimen instead of taking self-medication.
References:
- Fluoroquinolones for the treatment of tuberculosis - NCBI
- In Vitro Activities of the Fluoroquinolones Gatifloxacin and Trovafloxacin against Plasmodium falciparum - NCBI
- Single-dose ciprofloxacin for the chemoprophylaxis of meningococcal disease - NCBI
- Emerging resistance to empirically selected antimicrobials for the treatment of gonorrhea in Alberta's sexually transmitted infection clinic population - NCBI
VI. Dosage and Administration of Ciprofloxacin
Due to Ciprofloxacin belonging to a class of potent antibiotics, it requires careful administration and dosing under strict medical supervision for optimal results. Several factors are considered during its usage; age, underlying health issues, kidney function, and severity/type of infection - all play an essential role in guiding this process. Most patients take Ciprofloxacin orally twice daily, either with or without food, accompanied by a full glass of water. Doctors prescribe between 250 mg and 750mg every twelve hours based on individuals' symptoms and severity of infection when treating adult patients for children's treatment plans. Physicians calculate dosages based on body weight while adjusting them if diagnosed with renal impairment. The risk of drug resistance due to misuse renders it crucial that all doses prescribed be completed despite any visible improvement in symptoms each time someone undergoes antibiotic therapy using Ciprofloxacin.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Ciprofloxacin
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
For optimal effectiveness in treating infections with Ciprofloxacin proper dosage determination and administration is crucial. This medication must be administered correctly depending on various aspects, such as the nature of a condition for any given patient's age and overarching health status. A doctor would typically have this consideration before prescribing. This being said, even though these prescriptions ate tailored to each case to maintain efficacy, some standard recommendations do apply. Usually, Ciprofloxacin requires being taken orally twice per day. On an average daily adult, the dosage ranges between 250mg to 750mg, a decision informed by the level of the infection’s severity and type. Children, however, typically receive dosages calculated from their body weight. Patients should always complete their prescribed course of treatment, not stopping halfway through or altering the timing. This approach is fundamental in preventing antibiotic resistance development and guarantees positive results.
B. Special Dosage Considerations
There are specific instances where it is critical to thoroughly adjust dosages according to individual needs. Patients suffering from renal impairment typically require modified doses as Ciprofloxacin mainly gets eliminated via the kidneys. Furthermore, alterations might become essential for older individuals experiencing declining kidney function due to aging processes. Additionally important is assessing if treating severe life-threatening infections or dealing with highly-resistant bacteria that are categorized as non-standard treatment necessitates appropriately administering medication at higher-end dosages within prescribed limits.
VII. Interaction of Ciprofloxacin with Other Medicines
A. Common Drug Interactions
Compounded effects encountered while taking Ciprofloxacin could result from interactions with other medications. Pay attention since this factor could make it less effective and bring about severe side effects. The following are recognized problematic scenarios:
- Antacids, multivitamins, and dietary supplements containing calcium, iron, or zinc should be avoided when taking this medication since they reduce the absorption, which thereby decreases its efficacy.
- Using Theophylline simultaneously could have dire results, such as amplified risks related to this drug due to elevated blood levels caused by both drugs acting on each other.
- Concurrent use of Coumadin and Ciprofloxacin may increase the bleeding probability by heightening the anticoagulant effect.
- The shallow blood pressure produced by the simultaneous use of Tizanidine requires close monitoring.
B. Potential Side Effects from Interactions
Patients must appreciate that drug interactions could have significant implications. It leads to reduced therapeutic efficacy or severe side effects that might necessitate prompt medical attention. Take, for instance, when antacids, and calcium supplements, among others, are used alongside Ciprofloxacin; its ability to treat typical bacterial infections significantly reduces. Additionally, mixing Theophylline with Ciprofloxacin increases the risk of seizures, palpitations, and tremors, escalating the severity of such adverse reactions. Coumadin usage with Ciprofloxacin also heightens its anticoagulant effect causing more bleeding risks. Combining tizanidine may cause extreme lethargy or annoyingly low blood pressure levels when mixed alongside ciprofloxacin - as a general rule, always seek medical consultation before using any new medication.
VIII. Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
A. Common Side Effects
Ciprofloxacin is typically well tolerated. However, it can sometimes result in some common side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, lightheadedness, and headache. While these effects are generally low in severity and fade away as the body adjusts to the medicine it's important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional if these symptoms persist or worsen.
B. Less Common but Severe Side Effects
In sporadic cases where Ciprofloxacin usage is administered, side effects capable of causing disastrous consequences necessitating expedited medical attention have been identified.
- The most common such manifestations have presented themselves as an allergic reaction exemplified through identifiable instances of rashes developing or associated symptoms such as itching/swelling being experienced; concurrent onset symptoms towards life-threatening conditions, including difficulty breathing coupled with extreme vertigo, have also presented themselves before certain patients.
- Further evidence has implicated the presence of unusual behavior patterns, including inexplicable feelings ranging from confusion up to experiences corresponding to hallucinations aside from consequential representations of depression, including suicidal thoughts occupying the minds of specific users.
- Finally, a liver condition known as cirrhosis is marked by revealing indications like persistent nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, or sudden decline thereof with severe stomach / abdominal pain phenomenon alongside yellowing tint in eyes or skin that also results in the dark coloring of urine has been found to emerge in some circumstances possibly.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
It is critical to exercise caution when contemplating using ciprofloxacin because various circumstances may prohibit its utilization.
- Individuals who are prone to hypersensitivity or allergic reactions related to ciprofloxacin and entirely to quinolones are discouraged from getting treated with this substance altogether,
- Alongside those who experience concurrent tizanidine use or protecting pregnant or breastfeeding mothers.
- Moreover, children under 18 require absolute scrutiny before receiving dosage for potential benefits that might outweigh the risks. When using ciprofloxacin.
Careful consideration should be given to its possible side effects.
- The drug warns of tendon damage with higher chances of occurrence in older adults and individuals taking corticosteroids simultaneously. Therefore any signs related to tendon ruptures, such as sudden pain, swelling, bruising, stiffness, or movement disorders, require immediate discontinuation of its consumption and seek medical advice.
- Another warning entails specific heart conditions such as QT prolongation that are rare but may occur following prolonged ciprofloxacin usage and may turn fatal if not discovered early through prompt intervention.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. When to Avoid Ciprofloxacin
There are some instances when Ciprofloxacin may not be suitable for use despite being a potent antibiotic medicine. People with known allergies or hypersensitivity to the Quinolones class of antibiotics, including Ciprofloxacin, should refrain from taking it. Moreover, if someone is already taking tizanidine (muscle relaxant medicine), they should avoid taking Ciprofloxacin simultaneously as it could lead to severe adverse outcomes on health. Further, while considering the usage of this medicine among children, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers, the potential benefits must outweigh the possible risks since its safety & efficacy profile is yet unclear in these groups.
B. Special Warnings and Precautions
Using Ciprofloxacin requires circumspection due to several informational alerts linked with its usage that merit attention before selection as medication for patients receiving treatment for infections. The possibility for harm or injury involving tendons, principally common among elderly individuals or those with previous corticosteroid use, must be underscored. Swift medical assistance must be sought at the first signs of inflammation/pain around tendons to avoid complications. Another warning worth noting is the greater probability of QT prolongation associated with Ciprofloxacin which can cause concerning cardiac arrhythmias necessitating urgent attention by healthcare practitioners.
X. Careful Administration of Ciprofloxacin
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Given the potential for adverse reactions in older patients taking Ciprofloxacin, particularly regarding QT prolongation and tendon rupture, its imperative to approach treatment with great care. To minimize these risks effectively and ensure patient safety, Clinical monitoring tailored for geriatric populations should be implemented alongside dose adjustments based on individualized assessment.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Careful consideration must be given before using Ciprofloxacin during pregnancy or while breastfeeding to ensure safety for both mother and child. The decision to administer this medication should weigh potential benefits against risks. And if necessary, steps are taken to prevent any adverse reactions that may occur in an infant who is nursing.
C. Administration to Children
The administration of Ciprofloxacin to minors should be approached with care. However, the drugs' usage has been authorized for some pediatric infections. There are inadequate studies exploring its safety and efficacy as a remedy for other ailments.
XI. Handling an Overdose of Ciprofloxacin
A. Symptoms of Overdose
When you take too much Ciprofloxacin medicine than what is recommended, your health might deteriorate rapidly: This is something that cannot be taken lightly since the consequences could be dire, including seizures accompanied by severe headaches and tremors also showing symptoms similar to fatigue, muscle weakness or paleness in the skin area especially seen around lips and fingertips may occur which indicate an emergency that needs managing quickly through professional care at a medical facility. Other issues, such as exhibiting signs of allergies toward medication, including itching along with rampant rashes, have been known consequences too, so it is imperative to rush for assistance right away should safety become a concern.
B. Immediate Actions and Treatment Options
In case of a suspected drug overdose, swift action must be taken by immediately bringing the affected person to a medical facility. The primary approach generally involves offering essential support - this may include ensuring that their breathing is unobstructed and monitoring vital signs like heart rate or blood pressure while keeping them hydrated through fluid administration.
XII. Storage of Ciprofloxacin
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
Storing Ciprofloxacin appropriately can help maximize its therapeutic potential. To achieve the desired outcome always consider storing this medication away from heat, moisture and direct light under room temperature conditions. Be mindful to also keep this medication securely so that children cannot access it.
B. Impact of Incorrect Storage
Improper storage conditions like extreme temperatures, moisture, and sunlight could harm the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin. Therefore it's crucial not to use any drugs stored inappropriately.
XIII. Handling Precautions for Ciprofloxacin
A. Safety Measures During Use
To prevent adverse reactions from occurring due to increased sensitivity of skin caused by Ciprofloxacin use: minimize unnecessary outdoor activities during peak midday hours between ten in the morning till four in the evening; use UVA/UVB broad-spectrum sunscreen products generously on all exposed areas before going outside; incorporate protective hats or clothing such as long sleeve shirts when feasible while outdoors, especially for extended periods.
B. Disposal Guidelines
We urge you to handle unused or expired Ciprofloxacin with care and dispose of it properly. It's imperative not to flush it down the toilet or pour it into a drain. Where possible kindly seek advice from your pharmacist or local waste disposal company on how best to manage its safe disposal.