Nitrofurantoin
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses
- III. Off-label Use
- IV. How It Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interaction
- X. Warning
- XI. Contraindication
- XII. Careful Administration
- XIII. Important Precautions
- XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
- XV. Over Dosage
- XVI. Storage
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Nitrofurantoin origins can be traced back to the 1950s, when it emerged as a breakthrough in the field of antimicrobial therapy—unlike antibiotics discovered during that time, Nitrofurantoin, a nitrofuran derivative, displayed distinct chemical and pharmacological properties. Its introduction marked a shift in addressing the growing need for effective urinary antiseptics. While many antimicrobial agents have become less effective in medicine due to resistance, Nitrofurantoin has remained resilient. It continues to hold a place in medical practice, particularly for treating lower urinary tract infections. Its specific mechanism of action and limited spectrum of activity help prevent resistance, ensuring its ongoing relevance. From a standpoint, Nitrofurantoin belongs to the class of nitrofurans. It is an antimicrobial agent primarily effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive uropathogens. Although its limited systemic efficacy, its concentrated excretion through the system makes it ideal for treating urinary tract infections.
II. Uses
Nitrofurantoin is commonly used to treat tract infections (UTIs), one of the most common infections worldwide. It is effective against bacteria like Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus saprophyticus, that's often responsible for UTIs. Regarding bladder infections in women Nitrofurantoin is considered a top-choice treatment option due to its effectiveness and safety compared to other antibiotics. In treating UTIs Nitrofurantoin can also be used as a measure for patients who frequently experience recurrent UTIs. Taking a low-dose regimen can significantly reduce the chances of recurring infections.
References:
- Nitrofurantoin: antibiotic to treat bacterial infections - NHS1
- Nitrofurantoin: 7 things you should know - Drugs.com2
- Nitrofurantoin - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf3
III. Off-label Use
Other than its approved uses, Nitrofurantoin may have benefits in other areas. While there is documentation, some studies suggest that it could effectively treat certain nonurinary infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. However, it is essential to approach these off-label uses and seek guidance from experts. The available literature on this topic is still developing; There are indications that Nitrofurantoin could be used for staphylococcal skin infections due to its activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Nevertheless, given the lack of clinical trials, it is advisable to exercise caution when considering such applications.
References:
- Nitrofurantoin - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf1
- Nitrofurantoin - Infectious Diseases - MSD Manual Professional Edition2
- Role of Old Antibiotics in the Era of Antibiotic Resistance3
IV. How It Works
The way Nitrofurantoin works against bacteria is quite complex. It undergoes a process where bacterial flavoproteins help reduce it enzymatically, creating reactive substances. These substances disrupt bacterial functions such as DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis, ultimately leading to the death of bacterial cells. Nitrofurantoin primarily targets both Gram Gram positive uropathogens. Some common examples include Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. However, certain organisms like Pseudomonas aeruginosa have resistance to this drug. Despite being used for a long time, Nitrofurantoin has meager resistance rates. This can be attributed to its mechanism of action and its rapid excretion through urine. Nonetheless, it is essential to remain vigilant by monitoring resistance patterns to achieve the best possible treatment outcomes.
V. Dosage and Administration
The usual recommended dosage for urinary tract infections (UTIs) for adults is between 50 to 100 mg taken four times a day. The treatment duration depends on the infection's severity, typically lasting for five to seven days. Several factors need to be considered when determining the dosage; 1. Age; Dosage adjustments are necessary for geriatric populations taking into account their metabolic rates and renal function. 2. Renal function; Since nitrofurantoin is eliminated through the kidneys, impaired renal function may require dose adjustment. Even contraindicate its use in severe cases. 3. Severity of infection: higher doses or longer treatment durations may be necessary for severe or persistent infections. Nitrofurantoin is commonly administered orally. Comes in different formulations, such as macro crystals and monohydrate/microcrystals. These formulations cater to varying absorption rates and individual patient needs.
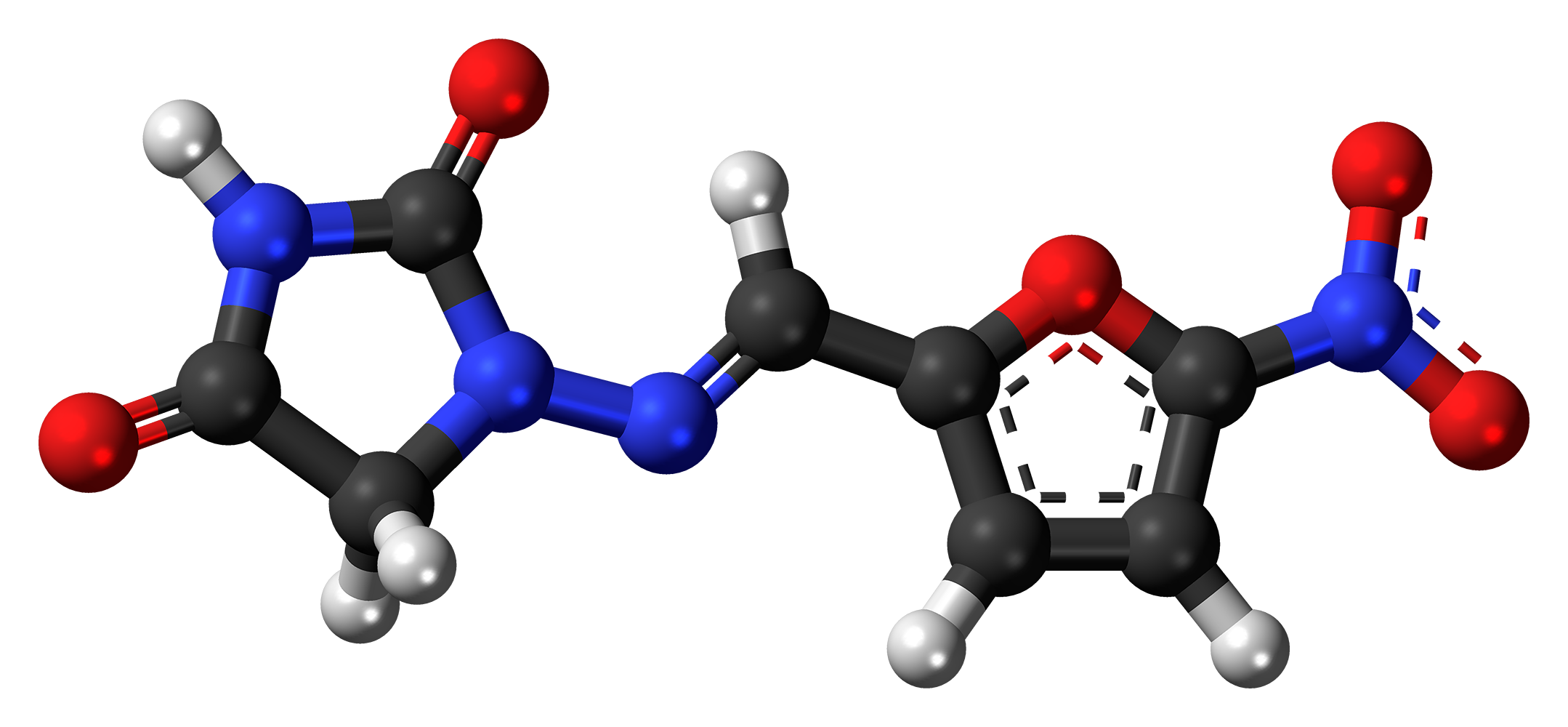
VI. Composition
The main component of Nitrofurantoin, a nitrofuran derivative, has a unique chemical structure that helps it fight against bacteria. Its molecular formula, C8H6N4O5, comprises carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms. In addition to the ingredient, Nitrofurantoin formulations also contain various other substances called excipients. These excipients serve purposes such as binding the ingredients together and making sure the medication remains stable and acceptable for patients. Nitrofurantoin comes in forms depending on the needs and preferences of patients, including capsules that release the drug immediately or gradually over time and suspensions.

VII. Side Effects
An overview of the safety profile Nitrofurantoin despite being known for its effectiveness in treating tract infections, does have some potential side effects. Like medications, it can cause various adverse reactions. However, overall, it is considered safe when used under the supervision of medical professionals. Distinguishing between common and rare side effects Side effects can occur with frequencies and levels of severity. Some are commonly experienced and are considered "common," while others are less common. It is essential for both doctors and patients to understand this distinction so that they can monitor any issues closely and take appropriate action when needed.
VIII. Common Side Effects
Issues; It's not unusual for patients to experience various gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. These issues are usually temporary. Tend to improve as the body gets used to the medication. Headaches; Patients may experience throbbing in their temples or a dull ache, which are common side effects of Nitrofurantoin. Skin rash and reactions; Some patients may develop skin-related symptoms like rashes, itching, or in rare cases, exfoliative dermatitis. In some instances, stopping or adjusting the treatment plan might be necessary. Pulmonary reactions; Although uncommon, there have been reported cases of chronic pulmonary reactions associated with Nitrofurantoin. These can range from acute pneumonitis to lung disease and require immediate medical attention.
IX. Interaction
Drugs that could affect the effectiveness of Nitrofurantoin When it comes to using Nitrofurantoin for treatment, drug interactions are always a concern. Certain medications, like magnesium trisilicate, commonly used as an antacid, can interfere with the absorption of Nitrofurantoin. This can lead to medication concentrations in the urine resulting in decreased efficacy. Nitrofurantoin's ability to impact medications On the other hand, it can influence how other drugs work. It can affect the enzymes in the liver that are responsible for metabolizing certain medications taken alongside it. Therefore it's essential to monitor therapy when using Nitrofurantoin and other medicines.
X. Warning
There are situations where it is essential to be cautious when using Nitrofurantoin to treat urinary tract infections. For example, patients with kidney function may have a higher risk of experiencing adverse effects due to reduced drug excretion. It is also essential to consider the risks of long-term treatment, such as pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity, and peripheral neuropathy. Regular health assessments should be conducted in these cases to monitor any issues.
XI. Contraindication
There are conditions or situations where Nitrofurantoin should not be used. Despite its therapeutic effects, it is not suitable for everyone. If someone has kidney problems, a history of chronic lung reactions to the drug, or is in the later stages of pregnancy, they should avoid using it. Whenever the potential risks outweigh the benefits, it is necessary to reconsider the use of the drug in pharmacotherapy.
XII. Careful Administration
Tips for patients with conditions Certain groups, such as the elderly or individuals with other medical conditions, require personalized care. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage, closely monitor their health or even consider treatments. Importance of monitoring during treatment When it comes to using Nitrofurantoin, it's not just passively taking the medication. In long-term cases, regular tests to assess kidney function, liver health, and even lung function are aspects that need to be monitored closely.
XIII. Important Precautions
To avoid any complications, it is essential to use medications wisely. Follow the doses refrain from consuming alcohol, and promptly report any side effects to minimize the risks. Additionally, patients must be cautious about self-medicating, especially when using medications that may interact with each other. During your treatment, some signs should raise concerns and require medical attention. While mild side effects may be expected, if you experience shortness of breath, persistent vomiting, yellowing of the eyes or skin, or a sudden and severe rash, it is crucial to seek immediate medical consultation as these could indicate serious issues.
XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
a. Elderly
When considering how to administer Nitrofurantoin to the population, viewing their unique physiological characteristics is vital. As people age, their renal function tends to decline, so adjusting the dosage may become necessary. It's worth noting that older individuals, due to their frailty, are more vulnerable to side effects such as peripheral neuropathy or pulmonary reactions. Therefore it's crucial to remain vigilant and regularly monitor them, especially when they're in therapy.
b. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
When using medication during pregnancy, it's essential to be cautious. While Nitrofurantoin is generally considered safe in the stages of pregnancy, there are potential risks if used in the later stages, such as causing anemia in the newborn. The use of Nitrofurantoin while breastfeeding also presents a dilemma. Although only small amounts of the medication pass into breast milk, we can't ignore the possibility of it causing hemolysis in infants with glucose six phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
c. Children
Dosage guidelines for children; Since children's physiological systems are still developing, their dosages need to be tailored for them. Typically the pediatric dosage is determined based on body weight. It is usually around 5 to 7 mg per kilogram per day divided into four doses. Safety in children; Nitrofurantoin can prevent urinary tract infections in children when used appropriately. However, it's important to administer it closely and monitor for potential rare side effects such as hemolytic anemia or pulmonary reactions.
XV. Over Dosage
Signs of taking much Nitrofurantoin; Consuming excessive Nitrofurantoin can lead to various symptoms. These symptoms can range from digestive issues to more severe conditions like hemolytic anemia or acute lung reactions. Some specific symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, peripheral nerve problems, and signs of hemolysis in susceptible individuals. Recommended management and treatment; In the event of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical advice. Although no antidotes are available, the primary approach involves providing symptomatic and supportive care while closely monitoring the patient's condition.
XVI. Storage
The effectiveness of Nitrofurantoin depends significantly on how it's stored. It is best to keep it dry away from sunlight and at temperatures between 15 to 30°C. Following these storage guidelines and paying attention to its expiry dates will help maintain its potency and ensure its effectiveness.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Here are some guidelines on how to handle and dispose of Nitrofurantoin. When driving this medication, it's essential to be cautious and knowledgeable. Wear gloves, avoid contact with your skin or eyes, and prevent the drug from becoming airborne. These basic precautions will help minimize any risks. To avoid contamination and to maintain the medication's effectiveness, storing it in its packaging is crucial. Avoid transferring it to containers and keep the environment clean. Additionally, it is recommended that you promptly dispose of any unused medication, preferably by utilizing community take-back programs available in your area.