Combutol, Ethambutol
- Introduction
- How Combutol (Ethambutol) Works
- Composition of Combutol (Ethambutol)
- Ethambutol Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Ethambutol Side Effects
- Rare Side Effects
- Interaction of Combutol (Ethambutol) with Other Drugs
- Ethambutol Adverse Effects
- Ethambutol Contraindications
- Precautions for Use
- Overdosage
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Important Precautions
Introduction
Combutol is a drug used in treating infections, like tuberculosis (TB). Its effectiveness when used alongside drugs has greatly improved TB treatment since its introduction in clinical settings. Combutol holds a position as a medication in the global management and control efforts, against TB.
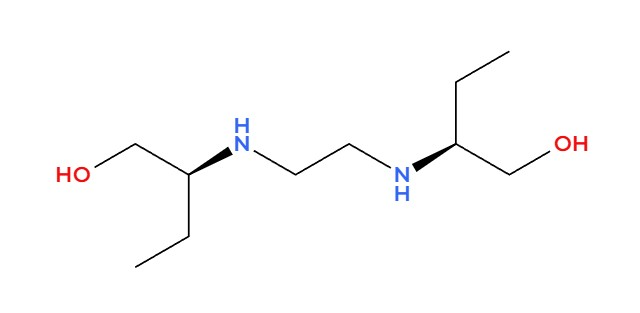
Overview of Combutol (Ethambutol)
The identification of Ethambutol, in the mid 20th-Century was a significant breakthrough in the field of antimicrobial treatment. Based on its characteristics as a substance that can impede the growth of mycobacteria without directly exterminating them. This attribute proves beneficial in averting inflammation caused by breakdown.
Combutol is currently authorized for purposes in nations across the globe. From the United States to regions in Asia and Africa. Authoritative bodies like the FDA and WHO have given their approval, for its use. Highlighted its significance, Accessibility levels differ depending on the formulations adjusted to cater to the healthcare system's requirements.
How Combutol (Ethambutol) Works
Ethambutol Mechanism of Action
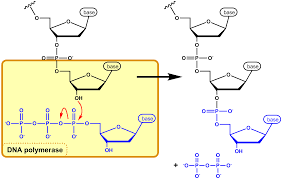
Ethambutol works by focusing on the creation process of the cell wall by hindering arabinosyl transferases. Enzymes are crucial for the formation of arabinogalactan and bacterial cell wall structures. This interference leads to a weakening of the cell wall making the bacterium more vulnerable, to antibiotics.
Effect on Mycobacteria Cell Wall Synthesis
The structure of the cell wall is intricate, it Contains a variety of lipids and sugars that provide protection, against numerous typical antibiotics Ethambutol disrupts the production of arabinogalactan causing the cell wall to become more permeable This weakness improves the effectiveness of other medications when used together in treatment.
Role in Preventing Drug Resistance When Used in Combination Therapy
Drug-resistant tuberculosis poses an increasing challenge, on a scale. Duolins ability to inhibit growth makes it a valuable addition to combination therapies for drug-resistant strains of TB. It helps reduce the development of resistance by targeting the bacteria in a way that differs from popular first-line treatments such, as isoniazid and rifampin. Some key advantages are;
The combined use of this medication, with agents can produce enhanced effects, on the treatment outcome. Preserving the availability of treatment options, for use.
Composition of Combutol (Ethambutol)
Active Ingredient: Ethambutol Hydrochloride
Combutols main ingredient is Ethambutol Hydrochloride—a crystalline powder, in water that undergoes careful synthesis for its utmost effectiveness, against mycobacteria.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Combutol formulations are also enhanced with ingredients specifically chosen to improve the stability and effectiveness, in delivering the drug into the body These can include;
- Using lactose monohydrate, in tablet production improves the bonding, between the tablet components.
- Microcrystalline cellulose is used to add volume and enhance the strength of tablets.
- Magnesium stearate serves as a lubricant, in the production process.
Every part undergoes testing to meet the standards set by pharmacopeias to guarantee safety and effectiveness.
Available Dosage Forms (Tablets, Capsules)
Combutol comes in forms to meet medical requirements with the most popular options being;
- Tablets are usually found in strengths of 100 mg and 400 mg. Are suitable, for both adults and children.
- Capsules are designed to be enclosed for ingestion and gradual release into the body.
These specific formulations enable dosages to be administered for the management of tuberculosis while reducing potential side effects.
Ethambutol Uses
Primary Use: Treatment of Tuberculosis (TB)
Ethambutol plays a role, in treating tuberculosis (TB) an infectious illness caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. The medication is well regarded for its ability to stop growth effectively without causing inflammation reactions—a key factor in its success, in treating both active and dormant TB infections.
By targeting the cell wall Ethambutol works to reduce the burden making it easier for the immune system to respond effectively. Decades worth of clinical studies support the use and effectiveness of the safety profile of Ethambutol in TB therapy.
Role in Multi-Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
The rising challenge posed by drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) has highlighted the importance and increasing significance attached to Ethambutols role, in the treatment landscape. In situations where standard medications like isoniazid and rifampin prove ineffective due to resistance mechanisms in MDR TB cases, the Ethambutols distinct mechanism disrupts a pathway within the bacterium making it a crucial element in alternative treatment approaches for strains.
Some key advantages associated with Ethambutolss utilization, in MDR TB therapy include;
- A decrease, in resilience is observed when paired with medications.
- Sustaining the effectiveness of treatment, in the face of resistance, to medications.
- Preserving drug choices, by enhancing their modes of action.
Use in Combination Therapy for TB
Ethambutol is seldom employed alone because it hinders growth than killing bacteria outright like other drugs do. It is primarily valued in combination therapies that involve using medications to address stages, in the life cycle of mycobacteria.This strategy enhances treatment effectiveness, Reduces the chances of developing drug resistance. Common components, in combination therapy regimens are;
- Isoniazid works by attacking the synthesis of DNA.
- Pyrazinamide works by blocking the energy production of bacteria.
Ethambutol works together with these medications by weakening the shell structure surrounding the bacteria cells to help other treatments penetrate efficiently and effectively within the body system.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The usual amount for adults to take Ethambutol typically falls within the range from 15 to 25 mg, per kilogram every day based on the seriousness and the overall health condition when it is prescribed by healthcare professionals. In some situations close medical monitoring is needed to manage initial doses effectively and minimize side effects.
Dosage for Children and Weight-Based Adjustments
In instances involving childrens health considerations, in medicine practice areas like pediatrics determining the dosage for Ethambutol is crucial to steer from any harmful effects on the childs health and wellbeing.The standard prescribed amount stands at 15 mg/kg per day; however modifications based on the childs weight and age are typically made.
For those children, with liver or kidney conditions that could impact how their body processes medication it may be imperative to make alterations to the dosage to avert any risks linked to accumulation and potential adverse reactions.
Duration of Treatment for Tuberculosis
Ethambutol is typically included in a combination therapy, for treating tuberculosis over a period lasting six months; although the specific duration may differ based on cases and responses, to treatment.
- Let's start with a combination therapy, for a duration of two months.
- Continuation stage involves management for a period ranging from four to seven months based on the individual's response to treatment.
Ensuring that the treatment is continued for an extended period will help in getting rid of the bacteria and lowering the chances of it coming again.
Special Instructions for Missed Doses
It is recommended for patients to take any missed doses promptly when they recall them unless its, near the time, for their scheduled dose; doubling up should be avoided to prevent complications and ensure the treatments effectiveness while minimizing the risk of drug resistance development.
Methods of Administration (Oral Route)
Ethambutol should be taken by mouth with water, for absorption purposes and can be consumed with or, without food; however, having it during meals could lessen any stomach discomforts that may arise from it. Remember to swallow the tablets without crushing them unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional.

Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Regimen
It is crucial to stick to the recommended treatment plan for tuberculosis to ensure recovery. The risk of treatment failure and the development of drug strains rises with incomplete dosing. It's important for patients to carefully follow their healthcare provider's guidance and promptly communicate any side effects they experience.
Ethambutol Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, Vomiting, and Abdominal Discomfort
Patients might encounter issues such, as queasiness and stomach discomfort when taking the medication; however, these symptoms are usually temporary and can be eased by consuming the medication, with food or following the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Visual Disturbances: Blurred Vision, Red-Green Color Blindness
Blurred eyesight trouble telling apart red and green colors is commonly known as side effects of the medication, which usually gets better once you stop taking it but should be reported away to avoid any lasting issues.
Neurological Symptoms: Dizziness and Headache
During the start of the treatment a few people may experience spells of dizziness or headaches. These effects are typically mild and tend to diminish over time with regular use.

Serious Side Effects
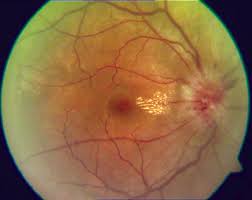
Optic Neuritis: Symptoms and Risk Factors
Optic neuritis is a yet significant reaction linked to Ethambutol usage. Its signs may involve reduced sharpness and difficulty distinguishing colors. Higher dosages,long term use and existing eye conditions are factors that may increase the risk. It is advisable to stop taking the medication once optic neuritis is detected.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Rash, Itching, and Anaphylaxis
Rarely seen but possible are reactions, like skin rashes that cause intense itching and anaphylaxis which can happen to individuals, in certain cases; it's important to promptly seek medical help if there are breathing difficulties or swelling of the face and throat.
Potential Liver Toxicity
Rarely in some instances, Ethambutol has been linked with liver damage causing symptoms such, as skin and eyes (jaundice) dark urine coloration, and higher levels than normal liver enzymes showing up in test results. It is recommended for patients who are on long-term treatment, with this medication or have a medical record involving liver issues to undergo routine liver function tests for monitoring purposes.
Rare Side Effects
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is not very common. It can occur as a side effect of Ethambutol usage and typically shows up as tingling or numbness in the extremities due, to nerve damage caused by the drug affecting nerve cell function. Either seek advice upon experiencing these symptoms for dosage adjustments or consider stopping the use altogether as needed.
Effects on Kidney Function
Ethambutol is mainly eliminated from the body through the kidneys. Can sometimes cause issues, with kidney function in cases – especially for people, with existing kidney problems. The signs to watch out for include decreased urine output swelling in the limbs or increased creatinine levels which should be investigated promptly.Regularly checking kidney function is advised when undergoing extended treatment.
Interaction of Combutol (Ethambutol) with Other Drugs
Interaction with Other Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs (e.g., Rifampin, Isoniazid)
Ethambutol is often prescribed alongside medications, for treating tuberculosis, such as Rifampin and Isoniazid to improve treatment effectiveness although this may raise the likelihood of side effects, like liver damage (hepatotoxicity). Regular monitoring of liver enzyme levels is crucial to avoid any complications.
Effects on Antacids Containing Aluminum Hydroxide
People should steer clear from using antacids that have aluminum close, to taking Ethambutol as it can disrupt its absorption in the body and decrease its effectiveness, in treating health conditions.
Potential Interaction with Certain Antibiotics
When using Ethambutol alongside antibiotics, like aminoglycosides like gentamicin or tobramycin there is an increased risk for kidney or nerve damage due to drug interactions This requires monitoring and consideration for other treatment options if needed to minimize these risks, in patients.
Safe Combinations and Monitoring Requirements
Ethambutol can be used in conjunction, with medications under the care and guidance of a healthcare professional following established safety protocols such, as;
- Routine examinations to check your eyesight and kidney function regularly.
- Steer clear of mixing things that could make the situation worse in terms of toxicity risks.
Following the recommended doses and timing to reduce the risk of interactions. These safety measures are put in place to keep patients safe and optimize the effectiveness of treatments.
Ethambutol Adverse Effects
The side effects caused by Ethambutol can vary from mild, to severe. Require monitoring, throughout the treatment process. Typical problems may include troubles; however serious consequences can result in vision impairment or neurological issues. It is essential to address these side effects to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and the well being of the patient.
Ethambutol Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Certain situations prevent the use Ethambutol completely because it may lead to side effects or lower the effectivenessof the drug.
Hypersensitivity to Ethambutol
People who have a history or experience, with being very sensitive to Ethambutol should avoid taking this medicine at all costs.Any allergic responses to it can vary from a skin irritation to a reaction requiring immediate discontinuation and the exploration, for substitute treatments.
Pre-Existing Optic Neuritis
Ethambutol should not be used in patients, with optic neuritis because it can worsen vision problems associated with this condition—a situation where the optic nerve becomes inflamed and can result in vision loss if not addressed promptly.
Warnings for Patients with Pre-Existing Medical Conditions
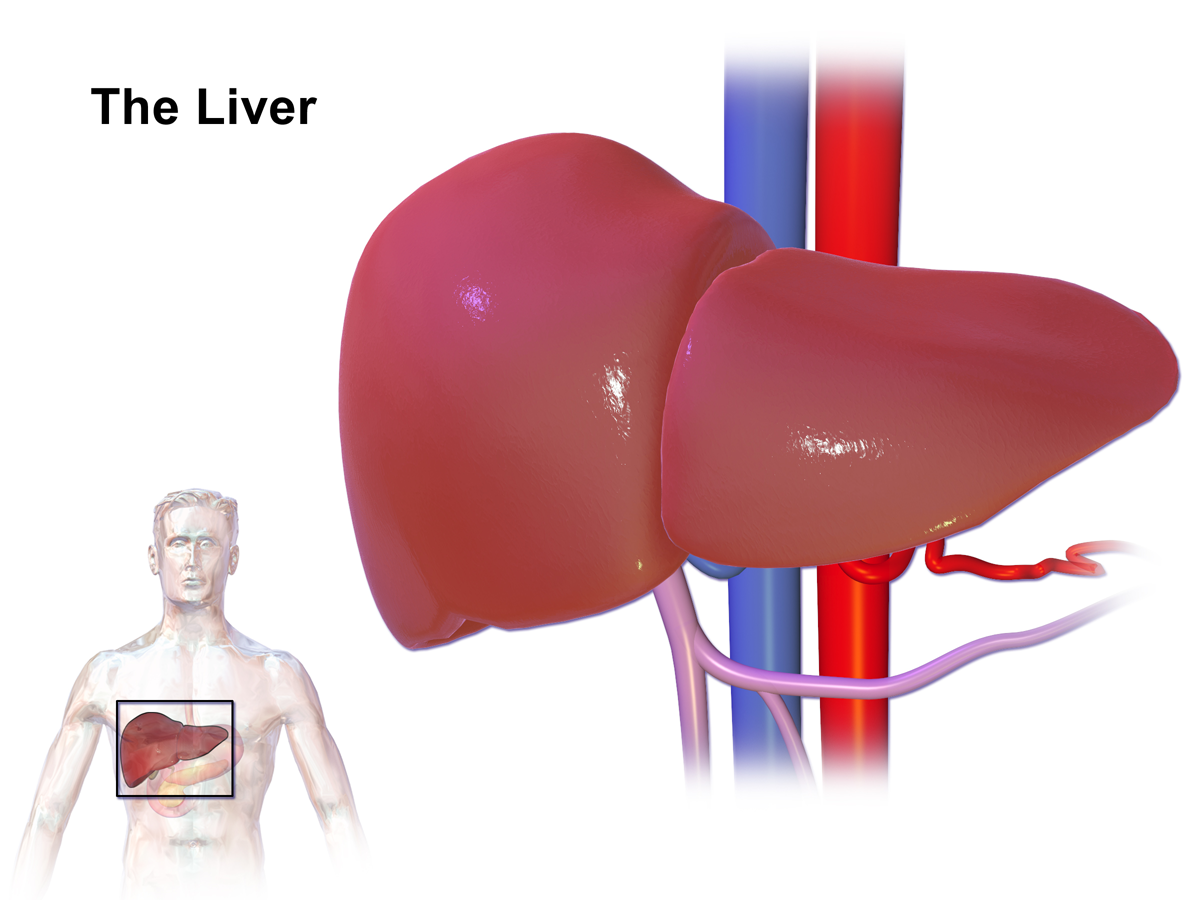
Liver or Kidney Disease
Patients, with liver or kidney issues need to have their medication doses modified and be closely monitored while receiving Ethambutol treatment. It is crucial to tailor treatment plans to each individual in cases as these health conditions can lead to drug buildup and potential harm from toxicity concerns.
Vision Problems
People who already have vision issues, like macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy need to be careful when using Ethambutol medication. It's important for them to have eye checkups to catch any problems early and deal with them promptly.
Precautions for Use
Careful Administration
Monitoring Visual Acuity During Treatment
It is essential to check clarity when on Ethambutol treatment to catch optic neuritis early—a severe yet avoidable adverse reaction patients must promptly notify their healthcare provider if they experience blurred vision or difficulty seeing colors or changes in their visual field.
Adjustments for Renal Impairment
Ethambutol is mostly eliminated from the body through the kidneys; therefore it is important to adjust the dosage, for individuals with kidney issues to prevent drug build up and harmful side effects due, to toxicity levels rising in the body system over time.
Importance of Regular Liver Function Tests
Liver damage, from Ethambutol is uncommon. Has been documented in some patients using the medication.It is crucial for individuals undergoing long-term treatment or, with existing liver issues to undergo liver function tests that include checking ALT and AST levels to detect any liver-related complications early.
Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly
Elderly individuals may need to use Ethambutol due, to the decline in function that occurs with age. Reduced renal clearance can result in drug levels, in the body. Increase the chances of experiencing side effects. It is advisable to monitor them and tailor the dosage accordingly to ensure their safety.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Throughout pregnancy, it is important to consider the risks and benefits associated with using Ethambutol. While studies, on animals have not shown any effects on offspring there is limited information available on its effects in humans. It is worth noting that nursing mothers should be cautious as Ethambutol can pass through breast milk and may impact the baby. Seeking guidance, from a healthcare professional is recommended in these situations.

Children
The safety record, for using Ethambutol in children is well known. It's important to be careful when administering it to them because the dosage usually depends upon their body weight to avoid giving too much or too little medication. Children might face a chance for side effects while undergoing treatment, with this medication, and thats why it's crucial for them to have frequent eye check ups.
Overdosage
Symptoms of Ethambutol Overdose
An excess intake of Ethambutol could cause effects such, as intense queasiness, dry heaving, muddled thinking, dizziness and vision problems. In situations, where toxicity might trigger seizures or breathing difficulties promptly necessitating intervention.
Immediate Management and Treatment Protocols
The key, to handling an overdose is quickly clearing the stomach using activated charcoal or gastric lavaging as the method of decontamination. To support the patient's stability during this time of treatment, intravenous fluids and electrolyte adjustments are administered. If a patient experiences issues hemodialysis might be required to speed up the process of removing harmful substances from their system.
Long-Term Effects of Overdose and Supportive Care
Extended exposure, to amounts of Ethambutol, may lead to enduring neurological issues. The emphasis in long term care lies in observing and addressing these consequences to prevent any lasting impact on the patients well being. Rehabilitation and ongoing consultations with specialists, in ophthalmology and neurology are frequently necessary.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
It's important to store Ethambutal to maintain its effectiveness, over time The medicine should be stored in a dry place away, from sunlight and excessive moisture These conditions help prevent the medication from degrading and ensure its potency throughout its shelf life.
Temperature, Light, and Moisture Considerations
The best storage conditions, for Ethambutol usually range from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Exposing it to heat or freezing temperatures may affect the drug's quality adversely. It is crucial to shield the medication from moisture by keeping it in its original tightly sealed packaging to prevent any potential contamination or clumping issues.
Proper Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
When you no longer need Ethambutol or it has expired make sure to dispose of it to avoid ingestion or harm to the environment. It's best not to flush the medication down the toilet or throw it in the trash. Instead, you can take advantage of pharmacies and healthcare facilities that offer programs, for returning medications, which is a safe and reliable way to get rid it.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare workers who are dealing with Ethambutol need to follow safety measures to prevent any accidents as they work with the medication tablets – such, as wearing gloves and avoiding skin contact to reduce the chances for absorption through the skin or triggering allergic responses. It is important to follow protocols when dispensing this medication, in clinical environments.
Important Precautions
Monitoring for Early Signs of Optic Toxicity
Detecting toxicity early is crucial to avoid vision loss risks associated with the Ethambutol treatment regimen require routine eye checkups, for patients experiencing blurred vision or color perception issues to seek immediate medical attention, for evaluation if symptoms persist.
Ensuring Proper Hydration to Minimize Renal Impact
It's crucial to stay well hydrated while undergoing Ethambutol treatment to help your kidneys function properly and lower the chances of kidney damage, from toxicity issues. Remember to drink plenty of fluids during the treatment process especially if you have existing kidney problems as you may need extra supervision and personalized hydration strategies.
Patient Education on Adherence and Recognizing Side Effects
Inform patients about why following the treatment plan is crucial, for achieving the results from their medication regimen.Tell them about side effects like feeling sick or tired or experiencing vision problems and advise them to let you know away if they notice anything unusual. Open and clear communication helps patients stick to their treatment and encourages them to take a role, in managing their health journey.
Combutol, Ethambutol FAQ
- What is ETHAMBUTOL?
- What are ETHAMBUTOL tablets used for?
- What is the main side effect of ETHAMBUTOL?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL cause blindness?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL be crushed?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL cause hearing loss?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL be given in IV?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL cause diarrhea?
- Can ETHAMBUTOL be taken with food?
- How does ETHAMBUTOL work?
- How does ETHAMBUTOL cause optic neuritis?
- How to take ETHAMBUTOL?
- What is ETHAMBUTOL used for?
- What does ETHAMBUTOL do?
- What does ETHAMBUTOL treat?
- When to take ETHAMBUTOL?
- When to give ETHAMBUTOL?
- When should ETHAMBUTOL be taken?
- When was ETHAMBUTOL discovered?
- When to stop ETHAMBUTOL?
- When to discontinue ETHAMBUTOL?
- Where is ETHAMBUTOL metabolized?
- Which group of drugs does ETHAMBUTOL belong to?
- Why is ETHAMBUTOL contraindicated in children?
- Why is ETHAMBUTOL used?
- Is ETHAMBUTOL a high-risk medication?
- What are the toxic effects of ETHAMBUTOL?
- Why does ETHAMBUTOL cause blindness?
- Is ETHAMBUTOL toxic to the liver?
- What does ETHAMBUTOL do to your eyes?
- How long do you take ETHAMBUTOL for TB?
- Can TB be treated without ETHAMBUTOL?
- What do you monitor for ETHAMBUTOL?
- What are the benefits of ETHAMBUTOL?
- Are ETHAMBUTOL side effects reversible?
- What is an alternative to ETHAMBUTOL?
- What should be monitored when taking ETHAMBUTOL?
- How long should I take ETHAMBUTOL?
- When to stop ETHAMBUTOL?
- What is the success rate of ETHAMBUTOL?
What is ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is a type of antibiotic mainly utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB). It falls under the category of agents which work to impede the proliferation of bacteria.
What are ETHAMBUTOL tablets used for?
ETHAMBUTOL tablets are prescribed alongside drugs to help combat tuberculosis infections caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria.
What is the main side effect of ETHAMBUTOL?
The primary negative impact of ETHAMBUTOL is neuritis—a condition that may lead to vision issues, like blurry eyesight or trouble, with color perception.
Can ETHAMBUTOL cause blindness?
Extended or excessive use of ETHAMBUTOL may cause neuritis. If not treated promptly could lead to permanent vision loss.
Can ETHAMBUTOL be crushed?
ETHAMBUTOL tablets can be crushed if its hard to swallow them; however it's important to have a healthcare provider oversee this process to ensure the correct dosage is maintained.
Can ETHAMBUTOL cause hearing loss?
Loss of hearing isn't frequently mentioned as a side effect of ETHAMBUTOL; however other drugs prescribed for tuberculosis treatment could possibly lead to problems, with hearing.
Can ETHAMBUTOL be given in IV?
ETHAMBUTOL is usually given by mouth and its intravenous version is not commonly used or easily accessible.
Can ETHAMBUTOL cause diarrhea?
ETHAMBUTOL can sometimes cause diarrhea as a side effect; however; some patients may experience issues.
Can ETHAMBUTOL be taken with food?
You can choose to take ETHAMBUTOL with or, without food; however having it with a meal might alleviate any stomach discomfort you may experience.
How does ETHAMBUTOL work?
ETHAMBUTOL functions, by stopping the formation of the cell wall through a focus on the arabinosyl transferase enzyme crucial, for the Mycobacterium tuberculosiss survival.
How does ETHAMBUTOL cause optic neuritis?
ETHAMBUTOL disrupts the functioning of mitochondria in the nerve which could cause inflammation and harm leading to neuritis.
How to take ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is typically ingested by mouth a day as instructed by a physician. Its important to follow the recommended dose and duration precisely.
What is ETHAMBUTOL used for?
ETHAMBUTOL is commonly prescribed for treating cases of tuberculosis infections. Is usually integrated into a combination therapy approach, to combat drug resistance effectively.
What does ETHAMBUTOL do?
ETHAMBUTOL hinders the multiplication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis which aids in managing and treating the infection efficiently.
What does ETHAMBUTOL treat?
ETHAMBUTOL is used to treat tuberculosis and in situations helps with infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).
When to take ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is typically consumed once a day at the time as directed by a healthcare professional.
When to give ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is typically recommended as a component of the first line therapy, for treating tuberculosis or MAC infections. Is commonly used alongside other antibiotics, in the treatment regimen.
When should ETHAMBUTOL be taken?
Make sure to follow your doctors instructions, for taking ETHAMBUTOL daily or, as part of your TB treatment plan.
When was ETHAMBUTOL discovered?
Since its discovery, in 1961 ETHAMBUTOL has played a role in the treatment of tuberculosis.
When to stop ETHAMBUTOL?
It is recommended to stop taking ETHAMBUTOL after consulting with a healthcare professional; typically when the infection clears up or if there are adverse reactions.
When to discontinue ETHAMBUTOL?
If optic neuritis or severe adverse reactions occur during treatment stopping ETHAMBUTOL may be necessary.
Where is ETHAMBUTOL metabolized?
ETHAMBUTOL undergoes some metabolic processes, in the liver. Is mainly eliminated through the kidneys.
Which group of drugs does ETHAMBUTOL belong to?
ETHAMBUTOL is classified as part of the drug category. Is mainly utilized in combating Mycobacterium species.
Why is ETHAMBUTOL contraindicated in children?
ETHAMBUTOL is used carefully in children because it can be challenging to monitor side effects such, as neuritis.
Why is ETHAMBUTOL used?
ETHAMBUTOL is prescribed for tuberculosis treatment by slowing down growth in strains of the infection.
Is ETHAMBUTOL a high-risk medication?
ETHAMBUTOL is generally not classified as risk; however it does need monitoring, for potential side effects such, as optic neuritis.
What are the toxic effects of ETHAMBUTOL?
Why does ETHAMBUTOL cause blindness?
ETHAMBUTOL has the potential to lead to vision loss as it can trigger nerve inflammation, which affects nerve function.
Is ETHAMBUTOL toxic to the liver?
ETHAMBUTOL has potential, for causing liver damage although it is recommended to approach its use in individuals, with existing liver issues.
What does ETHAMBUTOL do to your eyes?
Ethambutol has the potential to result in neuritis which may lead to alterations, in vision, like blurry eyesight or difficulty identifying colors.
How long do you take ETHAMBUTOL for TB?
ETHAMBUTOL is usually prescribed for a period of 2 months, during the stage of tuberculosis treatment; although the length of treatment may differ depending on cases.
Can TB be treated without ETHAMBUTOL?
Tuberculosis can be addressed without the need, for Ethambutol by utilizing medications; however its incorporation diminishes the likelihood of developing resistance.
What do you monitor for ETHAMBUTOL?
What are the benefits of ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is quite effective, in treating tuberculosis as it works to stop the growth of bacteria and the development of resistance, against them.
Are ETHAMBUTOL side effects reversible?
Most adverse reactions can be reversed when noticed enough; however prolonged inaction may lead to harm such, as lasting visual alterations.
What is an alternative to ETHAMBUTOL?
Instead of using ETHAMBUTOL as treatment options consider using streptomycin or fluoroquinolones based on the case and resistance characteristics.
What should be monitored when taking ETHAMBUTOL?
It's important to check your vision and kidney function and make sure you're following your treatment plan when using ETHAMBUTOL.
How long should I take ETHAMBUTOL?
ETHAMBUTOL is typically recommended for a span of 2 months, as a component of a treatment regimen; however the length may vary based on the treatment strategy, in place.
When to stop ETHAMBUTOL?
Please discontinue the use of ETHAMBUTOL away if you experience vision issues or any serious side effects and seek advice from a professional.
What is the success rate of ETHAMBUTOL?
The effectiveness of ETHAMBUTOL, in treating tuberculosis is quite high long as patients follow the treatment regimen consistently.


























