It is essential to be aware of the associated benefits and safety measures. This article will delve into various aspects of oral Acyclovir, including its uses in treating herpes simplex virus infections.
Throughout the article, you'll learn about different dosages and administration methods for Acyclovir and essential contraindications and precautions to consider before starting treatment. Moreover, the potential adverse effects of utilizing this drug will be discussed.
When deciding whether to buy Acyclovir or another antiviral drug, it's crucial to compare generic vs. brand-name options and explore ways of overcoming resistance issues. Furthermore, we will also examine how Acyclovir compares with other antiviral medications on the market and explain its mechanism of action.
Table of Contents: Buy Acyclovir
- Understanding Antiviral Medications
- Uses of Acyclovir
- Dosage and Administration
- Precautions and Contraindications
- Side Effects of Acyclovir
- Generic vs. Brand-Name Acyclovir
- Overcoming Resistance to Acyclovir
- Acyclovir vs. Other Antiviral Medications
- The Mechanism of Action of Acyclovir
- Buy Acyclovir
Understanding Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are drugs designed to combat viral infections by inhibiting the growth and replication of viruses within the body. Antivirals specifically target viruses, unlike antibiotics, which target bacteria and help your immune system fight off these invaders more effectively.
A significant milestone in modern medicine, antiviral medications have been developed to combat viral infections. The first successful antiviral drug was Acyclovir, discovered in 1977 by Dr. Gertrude Elion and her team at Wellcome Research Laboratories (now part of GlaxoSmithKline). Following the discovery of Acyclovir, other antiviral drugs have been developed to treat various viral diseases.
A Brief History of Acyclovir
Acyclovir's discovery was a significant milestone in developing antiviral treatments, as it enabled further exploration into treating viral infections. Its discovery can be traced back to research on nucleoside analogs - compounds that resemble natural building blocks found in DNA or RNA but with slight modifications that disrupt their normal function when incorporated into new genetic material.
In 1977, Dr. Elion's team synthesized Acyclovir after screening over 200 nucleoside analogs for potential activity against HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus type 1). After examining a large number of nucleoside analogs for their potential to battle HSV-1, Dr. Elion's team discovered that Acyclovir was the most successful; it had robust anti-HSV characteristics and did not cause any significant harm to host cells - making it an optimal choice for further research as a treatment option for herpes patients.
The Importance of Antiviral Medications
- Preventing complications: Antiviral medications can help prevent severe complications from viral infections, such as organ damage or death.
- Reducing symptoms and duration: Antivirals can lessen the severity and duration of viral infections by inhibiting the growth and replication of viruses. This allows patients to recover more quickly and resume their normal activities sooner.
- Inhibiting transmission: Some antiviral medications can also help reduce the risk of transmitting a virus to others by decreasing viral shedding - when an infected person releases infectious particles into their environment through bodily fluids like saliva or mucus.
In summary, understanding how antiviral medications work is crucial for effectively managing various types of viral infections. The development of Acyclovir has not only provided relief for millions suffering from herpes outbreaks but also paved the way for future advancements in treating other life-threatening diseases caused by viruses.
Antiviral meds can help treat specific conditions, yet it is essential to comprehend their functioning before using them. Before taking Acyclovir, it is necessary to consult your healthcare provider for advice on its use.
Antiviral medications are designed to combat viral infections by inhibiting the growth and replication of viruses within the body. Acyclovir, discovered in 1977, was the first successful antiviral drug and paved the way for future advancements in treating various life-threatening diseases caused by viruses.
Uses of Acyclovir
Acyclovir is a versatile antiviral medication with several applications in treating and managing viral infections. Its primary use lies in addressing herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections, but it also plays a significant role in managing shingles and chickenpox caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Let's delve deeper into these uses.
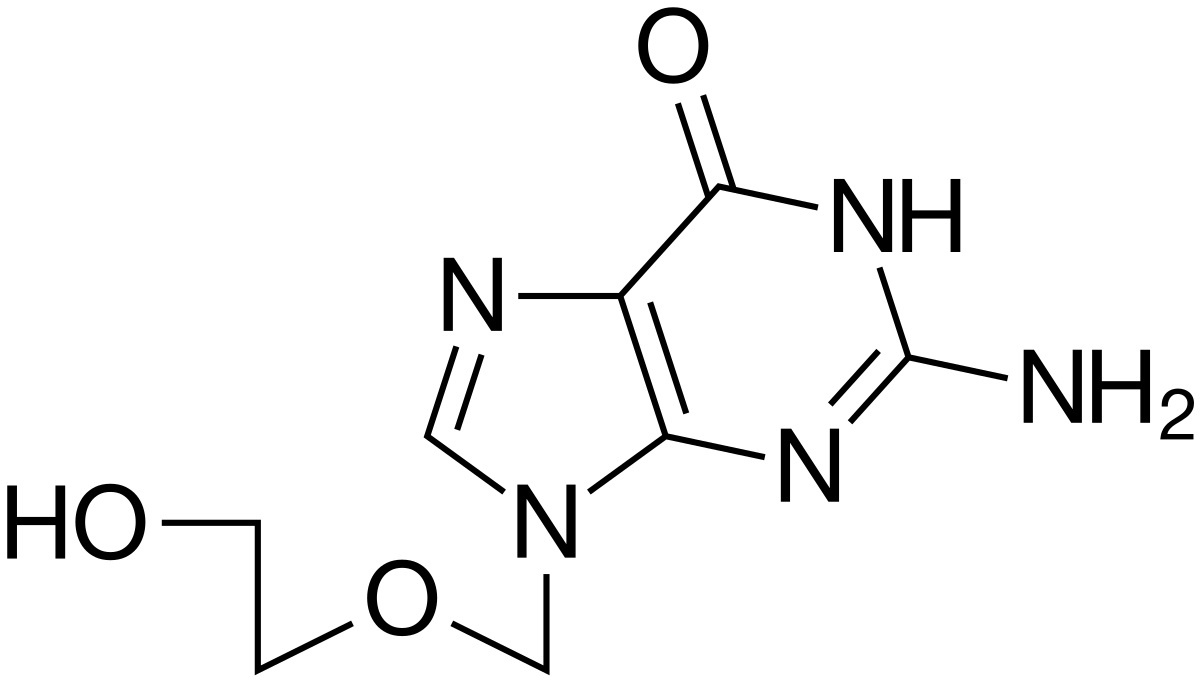
Treating Herpes Simplex Virus Infections
Herpes simplex viruses are responsible for causing oral and genital herpes. These highly contagious infections manifest as painful sores on or around the mouth (oral herpes) or genitals (genital herpes). Acyclovir effectively treats HSV outbreaks by inhibiting viral replication, thereby reducing the severity and duration of symptoms. It can also be used as suppressive therapy to prevent recurrent seizures in patients with frequent recurrences.
Managing Shingles and Chickenpox
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash caused by the reactivation of VZV that remains dormant after an initial chickenpox infection. Acyclovir is effective for relieving pain, shortening the duration of shingles, and treating chickenpox in high-risk individuals.
In addition to shingles management, Acyclovir can treat chickenpox in children and adults. Acyclovir can be especially advantageous for people with weakened immune systems or severe skin conditions. By reducing the severity of chickenpox symptoms, Acyclovir helps prevent complications like bacterial infections and pneumonia.
Other Potential Applications
Beyond its primary uses, Acyclovir has shown potential in treating other viral infections. For instance, it may be used off-label to manage Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infections that cause mononucleosis or certain types of cancer. Additionally, some studies suggest that Acyclovir could have a role in treating human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infections in immunocompromised patients.
In conclusion, while primarily known for its effectiveness against HSV and VZV infections, Acyclovir's antiviral properties also extend to other potential applications. Its versatility makes it an essential tool for managing viral illnesses and improving patient outcomes.
Acyclovir is an efficacious antiviral medicine employed to manage multiple infections due to the herpes virus. It is essential to understand how and when Acyclovir should be taken to maximize its effectiveness, which will be discussed in the next heading.
Acyclovir is a versatile antiviral medication used to treat herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections, manage shingles and chickenpox caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and potentially treat other viral infections such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). It inhibits viral replication, reduces the severity and duration of symptoms, alleviates pain, shortens rash time, and prevents complications like postherpetic neuralgia or pneumonia in high-risk individuals.
Dosage and Administration
Taking the appropriate dose of Acyclovir is crucial for effectively treating viral infections while minimizing side effects. This section will guide you through determining the proper dosage and following your doctor's instructions.
Determining the Appropriate Dose
When determining an appropriate dose for Acyclovir, a healthcare provider will consider the type and severity of infection, patient age, weight, kidney function, and overall health status. Your healthcare provider will carefully evaluate these factors before prescribing a suitable dose for you. In general, adults with herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections may be prescribed 200 mg to 800 mg tablets taken two to five times daily (source). For shingles or chickenpox treatment in adults or children over 40 kg (88 lbs), doses can range from 800 to 1000 mg three to four times daily (source). Always consult your doctor for personalized dosing recommendations.
Following Your Doctor's Instructions
- Take as directed: Following your doctor's instructions regarding when and how often to take Acyclovir is essential. Skipping doses or not completing the entire course of therapy may decrease its effectiveness or increase the risk of developing resistance.
- Maintain consistent levels: To maintain steady levels of Acyclovir in your bloodstream, try taking it at evenly spaced intervals throughout the day (e.g., every six hours).
- Avoid missing doses: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it's almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule. Do not double up on doses to make up for a missed one.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water while taking Acyclovir to help prevent kidney problems (source). This is especially important in patients with compromised kidney function or those taking high doses of the medication.
- Monitor progress: Keep track of any changes in symptoms and report them to your doctor during follow-up appointments. Adjust your dosage as needed based on how you respond to treatment.
In conclusion, determining the appropriate dose of Acyclovir and following your doctor's instructions are crucial steps toward successful viral infection treatment. Remember that individual dosing requirements vary; consult a healthcare professional before adjusting your prescribed regimen.
Dosage and administration should be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure the safest and most effective treatment plan. When using Acyclovir, it is essential to consider the potential risks and contraindications before determining an appropriate dosage regimen.
To effectively treat viral infections and minimize side effects, it is crucial to determine the appropriate dose of Acyclovir based on factors such as infection type, age, weight, kidney function, and overall health status. Following your doctor's instructions regarding when and how often to take the medication while staying hydrated and monitoring progress during follow-up appointments is essential.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before taking Acyclovir, knowing the associated precautions and contraindications is essential. This section will discuss various medical conditions that may impact your ability to use Acyclovir and potential drug interactions safely.
Medical Conditions to Consider
Before starting Acyclovir therapy, inform your healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions you have or had in the past. Some health issues can affect how your body responds to this antiviral medication. These include:
- Kidney disease: Individuals with kidney problems may require a lower dose or adjusted dosing schedule due to decreased renal function.
- Allergies: If you are allergic or hypersensitive to Acyclovir or similar medications like valacyclovir (Valtrex), let your doctor know before starting treatment.
- Weakened immune system: Patients with compromised immunity should consult their physician for proper guidance on antiviral medications such as Acyclovir.
Potential Drug Interactions
Acyclovir has the potential to interact with other medications, which could either increase side effects or reduce its effectiveness. It is essential to disclose any medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements you are taking to your healthcare provider so they can evaluate the potential for interactions. Some examples of drugs known to interact with Acyclovir include:
- Probenecid: This gout medication may increase aciclovir levels in the blood, potentially leading to increased side effects.
- Tenofovir: This antiretroviral drug used for HIV treatment can increase the risk of kidney problems when taken with Acyclovir.
- Other nephrotoxic drugs: Nephrotoxic other medicines such as NSAIDs, aminoglycoside antibiotics, and amphotericin B can increase the risk of kidney problems when taken in combination with Acyclovir.
In addition to these interactions, it is essential not to take other antiviral medications without consulting your healthcare provider. Combining multiple antiviral agents could lead to adverse reactions or reduced effectiveness of each drug. Always follow your doctor's guidance on using additional treatments alongside Acyclovir therapy.
Before taking it, it is crucial to be aware of the possible risks and contraindications related to Acyclovir, as they can substantially affect your health. Now let's explore some of the side effects of taking this medication.
Before using Acyclovir as a treatment option, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions you have or had in the past. Patients with compromised immunity should consult their physician for guidance on antiviral medications such as Acyclovir. They should also provide a complete list of all prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements they are currently taking to assess possible interactions.
Side Effects of Acyclovir
As with any medication, awareness of the potential side effects associated with Acyclovir is essential. While most individuals tolerate this antiviral drug, some may experience adverse reactions. This section will discuss common and rare but severe side effects and guide managing them.
Common Side Effects
Most people taking Acyclovir do not experience significant issues; however, some common side effects may occur. These include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headaches
- Mild skin rash or itching
If you encounter these symptoms while using Acyclovir, they are typically mild and subside as your body adjusts to the medication. However, consult your healthcare provider for advice if they persist or worsen over time.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
In addition to the more common side effects mentioned above, rare but severe reactions can also occur when taking Acyclovir, such as:
- Allergic reaction (swelling of face/lips/tongue/throat)
- Breathing difficulties
- Chest pain
- Seizures
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
- Blood in urine or stool
If you experience severe side effects, seek immediate medical attention.
Managing Side Effects
To minimize the risk of adverse reactions and manage potential side effects while taking Acyclovir, follow these tips:
- Stay hydrated by consuming sufficient fluids daily to reduce the chances of feeling dizzy and protect your kidneys while taking Acyclovir. This can help reduce dizziness and prevent kidney issues related to Acyclovir use.
- Take your medication with food if it causes stomach upset.
- Contact your healthcare provider if you develop a rash or other skin reaction, which may indicate an allergy to the medication.
In conclusion, understanding and managing potential side effects is crucial to successful treatment with Acyclovir. By proactively addressing any concerns arising during therapy, patients can optimize their health outcomes while minimizing discomfort associated with this powerful antiviral drug. Acyclovir is an effective medication for treating oral acyclovir and herpes simplex virus.
Before taking Acyclovir, being mindful of possible side effects is essential. Moving on, let us explore the differences between generic and brand-name versions of Acyclovir.
When taking Acyclovir, being aware of potential side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, and headaches is essential. While most people tolerate the medication, rare but severe reactions like allergies or seizures can occur. To minimize risks and manage any side effects, stay hydrated and take the medication with food if necessary while contacting a healthcare provider if severe symptoms occur.
Generic vs. Brand-Name Acyclovir
When choosing between generic and brand-name Acyclovir, understanding their differences is crucial in making an informed decision. Both options have advantages and disadvantages, which we will explore in this section.

Differences Between Generic and Brand-Name Acyclovir
The primary difference between generic and brand-name medications lies in their price. Generic drugs are typically less expensive than their branded counterparts because they do not require the same level of investment for research, development, marketing, and promotion as brand-name drugs. However, both generic and brand-name versions must meet the same quality standards established by regulatory agencies such as the FDA.
In terms of composition, generic Acyclovir contains the same active ingredient (Acyclovir) as its branded counterpart (e.g., Zovirax). The main distinction may lie in inactive ingredients or excipients used during manufacturing processes that can affect appearance or taste but should not impact overall effectiveness.
Evaluating Effectiveness: Are They Equally Effective?
- FDA Approval: Both generic and brand-name Acyclovir undergo rigorous testing before receiving approval from regulatory bodies like the FDA. This ensures that they are equally safe and effective for treating viral infections.
- Bioequivalence: To be approved by regulatory authorities, a generic drug must demonstrate bioequivalence with its reference listed drug (RLD), meaning it has similar absorption rates when taken under identical conditions. Therefore, generic Acyclovir is considered as compelling as its brand-name counterpart.
- Clinical Experience: Both generic and branded versions of Acyclovir have been widely used for decades, with a wealth of clinical experience supporting their effectiveness in treating viral infections such as herpes simplex virus (HSV), varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and others.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Usually, choosing between generic and brand-name Acyclovir will come down to personal preference or financial considerations. Here are some factors you may want to take into account when making your decision:
- Cost: If affordability is a primary concern, opting for generic Acyclovir can save money without compromising efficacy or safety.
- Patient Assistance Programs: Some pharmaceutical companies offer patient assistance programs that provide discounted or free medications for eligible individuals. You may wish to explore these options if cost is an issue but prefer using a brand-name medication like Zovirax.
- Talk to Your Doctor: Ultimately, it's essential to consult your healthcare provider before deciding which version of Acyclovir suits you. They can help guide your choice based on medical history, allergies, or other circumstances.
Before deciding which Acyclovir product to buy, one must know the differences between generic and brand-name versions to ensure successful treatment. To further provide the successful treatment of virus infections, it is also essential to be aware of strategies that can help overcome resistance to Acyclovir.
When deciding between generic and brand-name Acyclovir, it's essential to understand that both versions meet the same quality standards. The primary difference lies in price, with generics being less expensive due to lower investment costs. Ultimately, patients should consider factors such as cost and consult with their healthcare provider before deciding.
Overcoming Resistance to Acyclovir
Antiviral resistance is a growing concern in the medical community, as it can render medications less effective or ineffective against viral infections. To ensure the continued effectiveness of Acyclovir, it's essential to understand and implement strategies for preventing resistance.
Understanding Antiviral Resistance
Antiviral resistance occurs when viruses mutate and develop mechanisms to survive exposure to antiviral drugs like Acyclovir. This can result in reduced drug efficacy or complete treatment failure. The development of resistant strains may be influenced by incorrect dosage, poor adherence to treatment regimens, and overuse of antiviral medications.
Strategies for Preventing Resistance
To minimize the risk of developing Acyclovir-resistant strains and maintain their effectiveness, consider implementing these strategies:
- FOLLOW PRESCRIBED DOSAGE AND DURATION: Adhere strictly to your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment with Acyclovir. Taking too little medication or stopping treatment prematurely can contribute to developing resistant strains.
- ADEQUATE IMMUNE RESPONSE: A healthy immune system plays a crucial role in controlling viral infections; therefore, maintaining good overall health through proper nutrition, exercise, sleep hygiene, and stress management techniques will help your body fight off infections more effectively.
- LIMIT ANTIVIRAL USE TO NECESSARY SITUATIONS: Avoid using antiviral medications like Acyclovir unnecessarily (e.g., treating mild symptoms). Instead, reserve their use for severe or recurrent infections, as your healthcare provider advises.
- EARLY TREATMENT: Initiating Acyclovir therapy at the first sign of a viral infection can help reduce the likelihood of resistance development. Prompt treatment allows for better control over viral replication and reduces the chances of mutation.
- COMBINATION THERAPY: In some cases, using multiple antiviral medications with different mechanisms of action may be recommended to decrease the risk of resistance. For optimal viral control, your doctor may suggest a combination of antiviral drugs to reduce the risk of resistance.
In addition to these strategies, ongoing research aims to develop new antiviral agents that are less prone to resistance or can overcome existing resistant strains. For example, recent studies have explored potential alternatives like lecithin-based topical formulations, which show promise in improving drug delivery and reducing the risk of resistance development.
Maintaining Acyclovir's effectiveness against viral infections requires patient's and healthcare providers' vigilance. By understanding antiviral resistance and implementing prevention strategies, we can continue benefiting from this powerful medication while minimizing its limitations due to resistance.
Overcoming resistance to Acyclovir requires a comprehensive approach that includes monitoring the patient's response and adjusting treatment as needed. The following heading will explore how Acyclovir compares to other antiviral medications regarding effectiveness, side effects, and more.
Following the prescribed dosage and duration is essential to prevent the development of resistant strains, maintain a healthy immune system, limit antiviral use in critical situations, initiate early treatment, and consider combination therapy. Ongoing research aims to develop new antiviral agents that are less prone to resistance or can overcome existing resistant strains.
Acyclovir vs. Other Antiviral Medications
Several antiviral medications are available in the market when it comes to treating viral infections. While Acyclovir is a popular choice for managing herpes simplex virus infections, shingles, and chickenpox, it's essential to understand how it compares with other antiviral drugs.
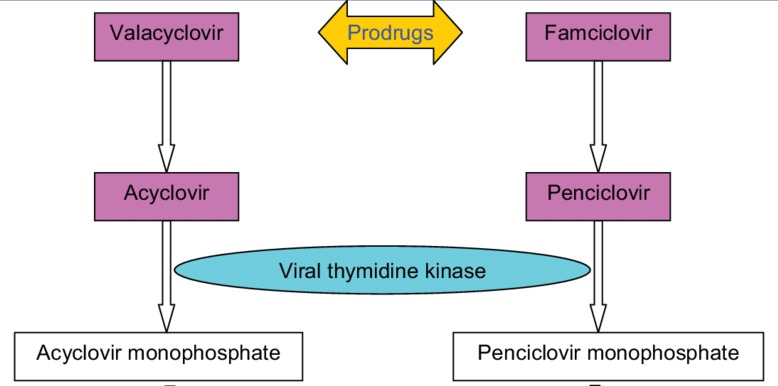
Famciclovir and Valacyclovir: Alternative Options for Herpes Infections
Famciclovir and Valacyclovir, like Acyclovir, belong to nucleoside analogs that inhibit viral replication by targeting DNA synthesis. These medications are often prescribed as alternatives or complement to Acyclovir for treating herpes infections.
- Famciclovir: This medication is used primarily for genital herpes outbreaks and suppressive therapy. It has a longer half-life than Acyclovir, allowing less frequent dosing.
- Valacyclovir: A prodrug of Acyclovir with better oral bioavailability; this means that more of the drug enters your system when taken orally compared to taking Acyclovir directly. Valacyclovir can be an effective option if you have difficulty swallowing pills or require higher doses of medication.
Oscillococcinum: Homeopathic Treatment for Flu-like Symptoms
If you're seeking relief from flu-like symptoms rather than herpes or shingles, Oscillococcinum might be an option. Oscillococcinum is a homeopathic remedy sourced from duck liver and heart that has been utilized for years to naturally relieve symptoms associated with influenzas, such as body aches, chills, feverishness, and exhaustion.
Tamiflu (Oseltamivir) and Relenza (Zanamivir): Antiviral Drugs for Influenza
For treating influenza A or B virus infections specifically, you may need antiviral medications like Tamiflu (oseltamivir) or Relenza (zanamivir). These drugs work by inhibiting the enzyme neuraminidase, which helps release new viral particles from infected cells. For optimal results, taking these medications within 48 hours of symptom onset is recommended.
In conclusion, while Acyclovir remains a powerful antiviral medication for managing herpes simplex virus infections, shingles, and chickenpox, other options like Famciclovir and Valacyclovir can also be considered depending on your specific needs for non-herpes-related viral infections, such as the flu or influenza viruses, treatments like Oscillococcinum, Tamiflu (oseltamivir), and Relenza (zanamivir) should be explored with your healthcare provider.
Acyclovir is an effective antiviral medication that can be used to treat a variety of viral infections. Acyclovir is preferred by many due to its lesser side effects compared with other antiviral medicines. By understanding how Acyclovir works in the body, we can gain further insight into its effectiveness and potential uses.
Acyclovir is a popular antiviral medication for managing herpes simplex virus infections, shingles, and chickenpox. However, Famciclovir and Valacyclovir are alternative options that can be considered depending on specific needs; for non-herpes-related viral infections such as the flu or influenza viruses, treatments like Oscillococcinum, Tamiflu (oseltamivir), and Relenza (zanamivir) should be explored with your healthcare provider.
The Mechanism of Action of Acyclovir
Acyclovir is an antiviral medication targeting HSV, VZV, and other viruses to combat viral infections. To understand how this influential drug works, it's essential to delve into its mechanism of action, which primarily involves targeting viral replication.
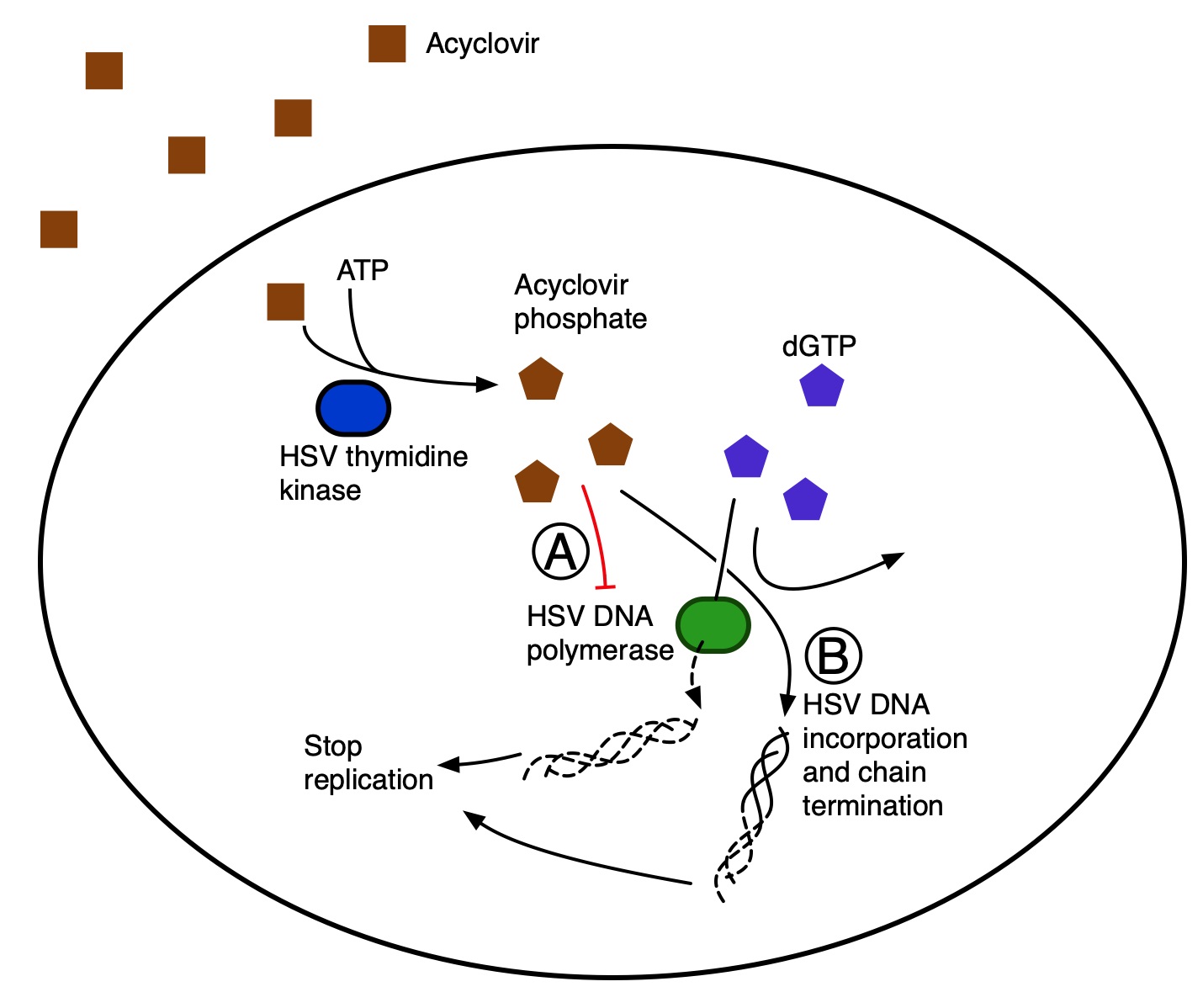
Inhibition of Viral DNA Synthesis
One key aspect of Acyclovir's mechanism lies in its ability to inhibit the synthesis of viral DNA. Acyclovir is activated within an infected cell by a virus-specific enzyme called thymidine kinase, allowing it to compete with dGTP for incorporation into the viral DNA chain during replication. The conversion is facilitated by a virus-specific enzyme called thymidine kinase.
Once activated, acyclovir triphosphate vies with deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) for insertion into the multiplying viral DNA strand during replication. When incorporated instead of dGTP, Acyclovir causes premature termination or stalling due to its unique structure lacking a 3'-hydroxyl group necessary for further elongation.
Selectivity for Infected Cells
A significant advantage Acyclovir offers is its selectivity towards infected cells rather than healthy ones. This specificity arises from two main factors:
- Virus-Specific Thymidine Kinase Activation: As mentioned earlier, Acyclovir relies on thymidine kinase produced by HSV or VZV-infected cells for activation. This enzyme is either absent or present in low amounts in uninfected cells, resulting in minimal activation of the drug and reduced toxicity to healthy cells.
- Preferential Incorporation into Viral DNA: Acyclovir triphosphate has a higher affinity for viral DNA polymerase than cellular DNA polymerases. Consequently, it preferentially targets viral replication machinery while sparing normal cellular processes.
Resistance to Acyclovir
Although Acyclovir is highly effective against HSV and VZV infections, some strains may develop resistance over time. The primary mechanisms behind this resistance include mutations in thymidine kinase (leading to reduced activation) or alterations in viral DNA polymerase (reducing drug binding). However, such resistant strains are relatively rare and typically emerge only after prolonged exposure to the medication. Strategies for overcoming resistance can be found under the heading "Overcoming Resistance to Acyclovir" within this guide.
In short, an appreciation of how Acyclovir works can be beneficial in comprehending its utility as a treatment for viral infections. By selectively targeting infected cells and inhibiting viral replication through disruption of DNA synthesis, this potent medication offers significant relief from herpes simplex virus infections and other related conditions.
Acyclovir is an antiviral medication that inhibits the synthesis of viral DNA, targeting infected cells and sparing healthy ones. It relies on thymidine kinase produced by HSV or VZV-infected cells for activation. It has a higher affinity for viral DNA polymerase than cellular DNA polymerases, making it effective against herpes simplex virus infections and related conditions.
Buy Acyclovir
It prevents the virus from multiplying and spreading, reducing symptoms and improving healing time. When taking oral Acyclovir, it's important to follow dosage instructions carefully and be aware of potential side effects. Before altering any medication regimen, seeking advice from a medical professional is recommended. If you want to buy Acyclovir online, Buy-Pharma offers a convenient and reliable option for purchasing this medication. Competitive pricing and fast shipping options make it easy to get the treatment you need without leaving your home. Herpes simplex virus is a common infection that can cause painful blisters and sores. Acyclovir is an effective treatment for managing outbreaks and reducing the frequency of future occurrences. Targeting the virus directly can help alleviate symptoms and promote faster healing. At Buy-Pharma, you can trust that you're getting high-quality Acyclovir from reputable manufacturers. They offer a range of dosages to suit your needs and can guide how to take the medication safely and effectively. Don't let the herpes simplex virus disrupt your life. Buy Acyclovir from Buy-Pharma today and start feeling better soon.