Budesonide
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Budesonide
- III. Off-label Uses of Budesonide
- IV. How Budesonide Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Budesonide Formulations
- VII. Common Side Effects of Budesonide
- VIII. Serious Side Effects and Warning
- IX. Contraindications of Budesonide
- X. Careful Administration Considerations
- XI. Important Precautions with Budesonide
- XII. Administration to Special Populations
- XIII. Drug Interactions with Budesonide
- XIV. Overdosage of Budesonide
- XV. Storage Considerations for Budesonide
- XVI. Handling Precautions for Budesonide
- XVII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
The Importance of Budesonide in Medicine
Budesonide plays a role in managing different inflammatory conditions. This powerful steroid, known for its range of applications, holds immense value in clinical practice. Doctors often prescribe it because of its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, which can significantly alleviate the symptoms experienced by patients with long-term ailments.
Chemical Structure and Pharmaceutical Class
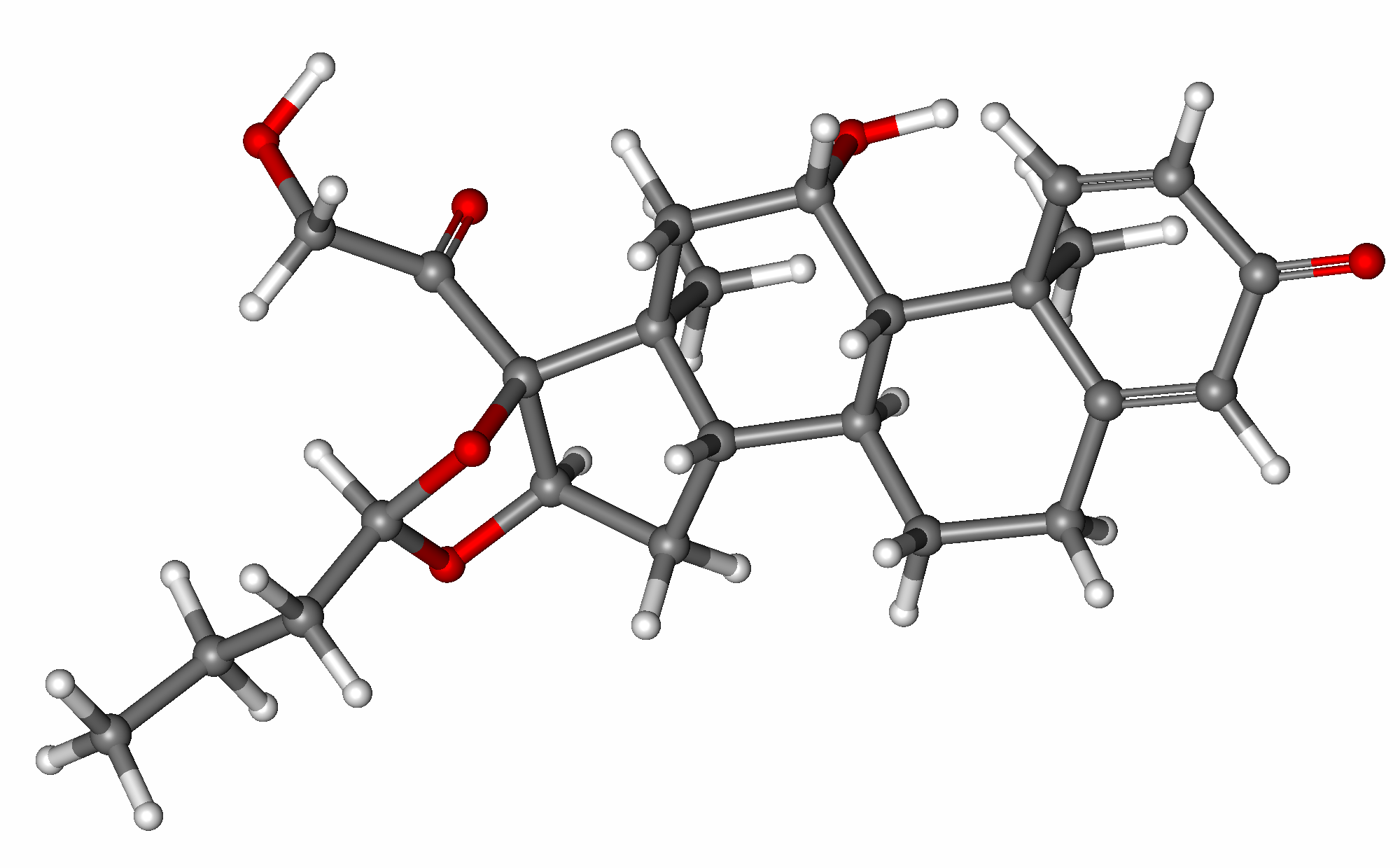
Budesonide is a type of medication that falls under the category of corticosteroids. Its chemical makeup consists of 21 carbon atoms, 27 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. This specific arrangement gives it potent anti-inflammatory properties when applied topically while minimizing potential systemic effects.
General Indications and Forms Available
Inhalers and solutions for nebulization are used to treat conditions. Medications are also available for gastrointestinal disorders and topical treatments for various skin conditions. These different formulations provide targeted relief for inflammation regardless of its location.
II. Uses of Budesonide
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Budesonide is often recommended for managing mild to moderate Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis cases. Its ability to specifically target inflamed areas in the intestines makes it a valuable treatment option as it effectively controls symptoms while minimizing the potential for absorption and any related negative effects123.
1: Budesonide for Crohn’s disease & ulcerative colitis - IBDrelief 2: Budesonide | Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation 3: Budesonide (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic
Managing Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Inhaling budesonide is a way to reduce inflammation in the airways of individuals with asthma and COPD. This helps alleviate symptoms, like wheezing, difficulty breathing, and persistent coughing, while also preventing the worsening of these conditions123.
1: Budesonide (Pulmicort) for COPD | COPD News Today 2: Budesonide Inhaler: Asthma Uses, Side Effects, Dosage - MedicineNet 3: About budesonide inhalers - NHS
Allergic Rhinitis Management
Budesonide nasal spray proves to be highly effective in managing the symptoms associated with rhinitis. It works by reducing inflammation in the nasal passages providing relief from issues like nasal congestion, runny nose, and sneezing, which can greatly affect a person's well-being123.
1: Budesonide nasal spray: a steroid used to treat cold-like symptoms caused by allergic rhinitis - NHS 2: budesonide (Rhinocort) inhaler & nasal spray: Side Effects & Dosage 3: Budesonide nasal Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
Dermatological Applications
Topical forms of budesonide, like creams and ointments, are commonly used to treat skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis. These formulations help alleviate skin inflammation and its associated symptoms, including redness, itching, and swelling123.
1: Topical Corticosteroids: Choice and Application | AAFP 2: Atopic dermatitis (eczema) - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic 3: Topical corticosteroid contact allergy | DermNet
III. Off-label Uses of Budesonide
Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
While it may not be officially approved for this use, budesonide has been utilized as a treatment alternative for autoimmune hepatitis because of its strong ability to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation123.
1: Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis | The BMJ 2: Budesonide in Autoimmune Hepatitis: The Right Drug at the Right Time for the Right Patient 3: Budesonide as first-line treatment in patients with autoimmune hepatitis
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Management
Budesonide suspension has demonstrated potential in treating eosinophilic esophagitis, a long-term inflammatory disorder affecting the esophagus. It aids in diminishing inflammation within the esophagus and relieves difficulties with swallowing and discomfort1234.
1: Safety and Efficacy of Budesonide Oral Suspension Maintenance Therapy in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis 2: Treatment of EoE with Oral Viscous Budesonide (OVB) | Eosinophilic Esophagitis 3: Oral viscous budesonide for eosinophilic oesophagitis | CUH 4: Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) - UpToDate
Other Potential Off-label Applications
Ongoing studies are being conducted to explore the advantages of budesonide in treating different ailments, including chronic rhinosinusitis and croup in children. These investigations underscore its versatility as a therapy123.
1: Croup: Diagnosis and Management | AAFP 2: Long-term Use of Budesonide Nasal Irrigation Effective for Comorbid CRS with Nasal Polyps, Asthma 3: The Long-Term Effects of Budesonide Nasal Irrigation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Asthma
IV. How Budesonide Works
Mechanism of Action
Budesonide works by attaching to receptors present in cells. This attachment changes gene transcription resulting in levels of anti-inflammatory proteins and lower levels of inflammatory mediators. As a result, it reduces inflammation and the immune response.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
One of the ways budesonide helps with inflammation is by blocking the activity of types of white blood cells and reducing the release of cytokines, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes. These substances play a role in causing inflammation.
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
After it is administered, budesonide undergoes metabolism in the liver, which helps minimize its effects throughout the body. Its pharmacokinetics exhibit local anti-inflammatory properties, quick absorption, and thorough initial metabolism.
V. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosing Guidelines
The dosage of budesonide varies depending on the condition and needs to be tailored to the severity of the disease and how the patient responds. It is crucial to use an adequate amount to minimize any possible side effects.
Route of Administration: Inhalation, Oral, Topical
Depending on the specific condition they need treatment, patients may receive types of budesonide prescriptions, such as inhalers, oral tablets, or topical creams. Each form of medication is specifically created to address inflammation in areas effectively.
Adjustment for Specific Populations (e.g. renal impairment)
Patients with liver problems may require adjustments to their budesonide dosage because the liver plays a role in metabolizing this medication. On the hand, the impact of kidney function on budesonide pharmacokinetics is relatively insignificant.
VI. Composition of Budesonide Formulations
Active Ingredients
Budesonide itself is the component in all budesonide formulations. It is a glucocorticoid steroid that has a strong affinity for receptors.
Excipients and Inactive Ingredients
Different budesonide formulations consist of nonactive components like lactose, inhalation propellants, and emollients in topical forms. These ingredients act as carriers or stabilizers for the drug.
Available Formulations and Brands
Budesonide can be found in forms and is marketed under different brand names. These include capsules that release the medication gradually in powders for inhalation solutions for nebulizers and preparations for use.
VII. Common Side Effects of Budesonide
Mild to Moderate Side Effects
Common side effects of candidiasis, also known as thrush, may include respiratory irritation if inhaled. When taken orally, it can lead to feelings of nausea and indigestion. Additionally, topical use of this medication may result in skin thinning.
Frequency and Duration of Side Effects
Although most side effects are temporary and improve with continued use or when the drug is stopped, there are instances where they might endure or even worsen. It's crucial for healthcare professionals to carefully observe patients for these effects and make any changes to their treatment plans.
VIII. Serious Side Effects and Warning
Potential for Systemic Corticosteroid Effects
While budesonide is primarily intended for localized treatment, the body can absorb it systemically. This can result in side effects, including increased blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), fluid retention, weakened bones (osteoporosis), and suppression of adrenal function. It is essential to be aware of these effects, mainly when using the medication for some time.
Risks in Long-term Usage
Long-term use of budesonide to other corticosteroids can heighten the chances of developing cataracts, glaucoma, and adverse skin and bone health effects. It is crucial to consider these risks about the therapeutic advantages when using it for extended periods.
Warning Signs and Symptoms to Monitor
Patients should be carefully observed for any changes, intense stomach pain indications of infection such as fever or persistent sore throat, and any alterations in mental well-being, like depression or mood swings. If any of these signs occur, it is imperative to seek medical attention.
IX. Contraindications of Budesonide
Absolute Contraindications
Budesonide should not be used by patients who're allergic to it or any of its ingredients. It is also not recommended for individuals with status asthmaticus or experiencing acute bronchospasm.
Relative Contraindications and Precautions
There are situations where caution should be exercised when prescribing, such as when the patient has untreated infections, peptic ulcer disease, or liver failure. Clinicians need to consider these factors before making a decision.
X. Careful Administration Considerations
Monitoring Requirements
Evaluating symptoms, adrenal function, and potential side effects is crucial. In the case of children, it is essential to monitor their growth.
Titration and Tapering Strategies
Patients should avoid stopping the use of budesonide. It is advisable to reduce the dosage to prevent adrenal insufficiency and minimize the chance of symptoms returning.
XI. Important Precautions with Budesonide
Potential for Adrenal Suppression
Long-term substance use can cause the adrenal cortex to shrink, leading to natural cortisol production. This condition needs precise handling.
Impact on Immune System and Infection Risk
Budesonide can weaken the response making individuals more prone to infections. Patients need to be aware of this risk and take necessary precautions to minimize their exposure to pathogens whenever feasible.
XII. Administration to Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals might experience a heightened sensitivity to the impacts of budesonide which may require modifications to the dosage and closer monitoring for systemic side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Budesonide should only be used during pregnancy if it is absolutely necessary. It is passed into breast milk so it's essential to be cautious when giving it to breastfeeding mothers.
Pediatric Use and Administration to Children
The effectiveness and safety of budesonide may differ in children depending on their condition and the specific form of the medication. It is crucial to monitor the growth of pediatric patients who are taking budesonide.
XIII. Drug Interactions with Budesonide
Common Drug-drug Interactions
Interactions worth mentioning involve medications such as ketoconazole, a CYP3A4 inhibitor, and certain antiretroviral drugs. These can potentially raise the levels of budesonide in the body.
Potential for Drug-food Interactions
Drinking grapefruit juice, which is known to be an inhibitor of CYP3A4 can significantly raise the levels of budesonide in the bloodstream.
XIV. Overdosage of Budesonide
Clinical Manifestations of Overdosage
Taking an amount of this medication could lead to noticeable effects such as high blood pressure, swelling, and increased blood sugar levels. It has also been noted that some individuals may experience symptoms such as extreme excitement or loss of touch with reality.
Management and Treatment Strategies for Overdosage
The management approach is generally supportive. It may involve inducing vomiting, performing stomach washouts,s and administering activated charcoal.
XV. Storage Considerations for Budesonide
Optimal Storage Conditions
Please store the medication in a place with consistent room temperature. Ensure it is protected from both light and moisture. Remember to keep medications safely out of reach of children.
Stability and Expiry Considerations
Make sure to dispose of any budesonide product that has passed its expiration date because there's no guarantee of its safety and effectiveness beyond that point.
XVI. Handling Precautions for Budesonide
Safe Handling for Healthcare Providers
To prevent exposure to the medication, healthcare professionals should avoid coming into contact, with damaged or leaking budesonide capsules or nebulizer solutions.
Disposal Considerations for Expired or Unused Product
You should follow regulations to dispose of any unused or expired budesonide properly. Typically this involves taking the medication to a pharmacy for appropriate disposal.
XVII. Conclusion
Summary of Budesonide’s Role in Clinical Medicine
Budesonide, a steroid with anti-inflammatory properties, continues to be widely used in treating different inflammatory conditions. Its distinct pharmacological characteristics, such as its local effectiveness and minimal impact on the entire body, make it an indispensable tool in patient care.
Current Research and Future Directions
Ongoing studies are investigating the possibilities of budesonide in areas of treatment, including its potential for managing inflammation caused by COVID-19. These exciting developments could provide insights into this medication's diverse uses and long-term effectiveness in real-world medical practice.