Colchicine
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Colchicine
- III. Uses of Colchicine
- IV. How Colchicine Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Side Effects of Colchicine
- VII. Interaction with Other Drugs
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Careful Administration
- X. Special Administration Concerns
- XI. Overdosage
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Brief Overview of Colchicine
Colchicine, a medication derived from alkaloids, is crucial in treating conditions such as gout and Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF). It has gained recognition in the medical field for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Historical Background: The Plant Origin and Early Uses
Colchicine, initially derived from the Colchicum autumnale plant, has a history in traditional medicine that spans thousands of years. In the past, it was used to treat gastrointestinal issues and relieve joint discomfort. This highlights its range of medicinal benefits and versatility.
Scope of the Article: What Will Be Covered
The following discussion aims to analyze Colchicine, covering its chemical makeup, approved uses by the FDA, alternative applications not officially endorsed, and possible adverse effects, among other relevant subjects.
II. Composition of Colchicine
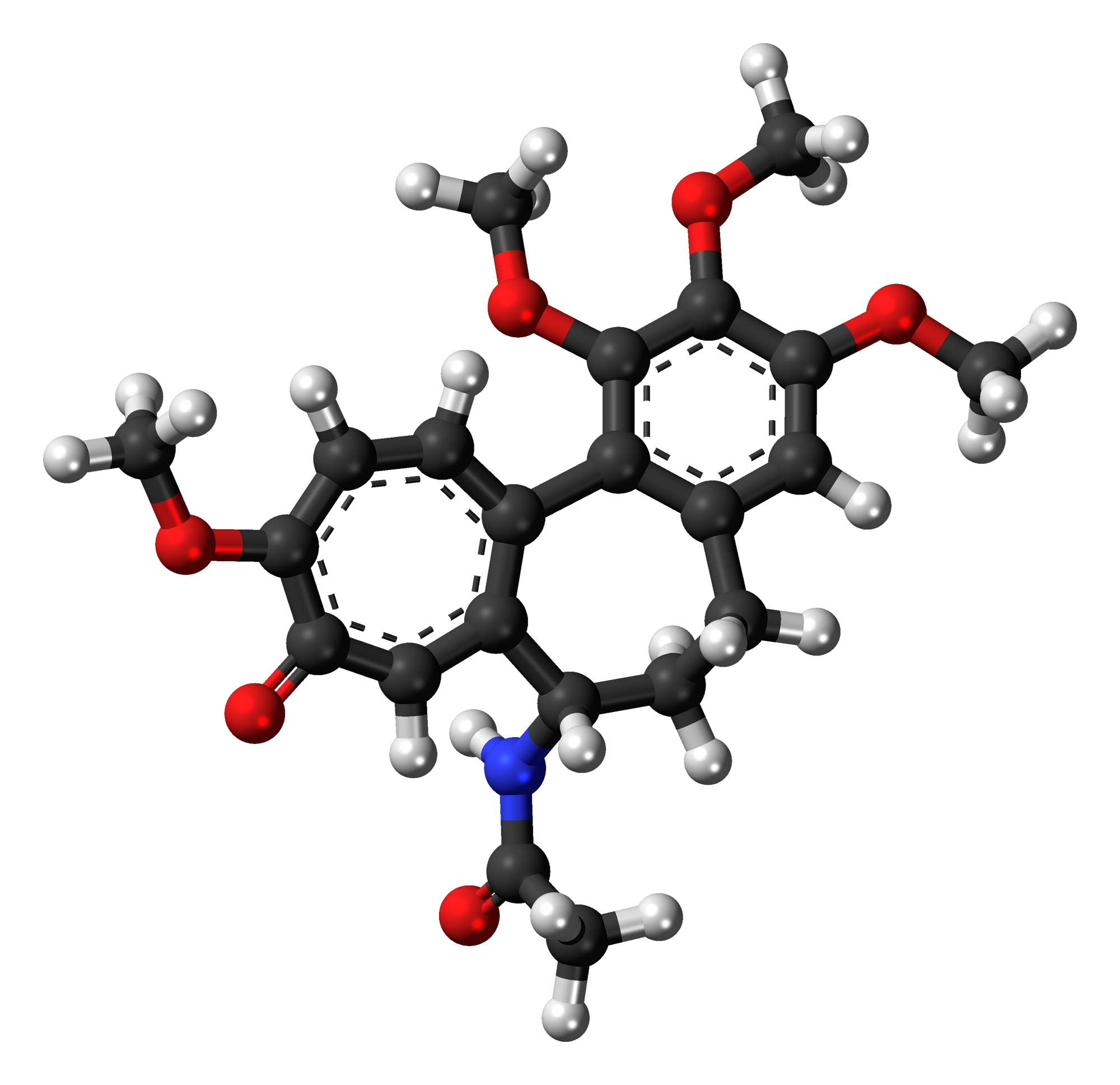
Chemical Structure and Properties
Colchicine possesses a chemical structure that includes a complex arrangement of heptalene methanol rings and various substituents. This unique structural feature contributes to its pharmacodynamic properties.
Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main component of this medication is Colchicine. It also contains substances such as lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and sodium starch glycolate, commonly used as additional medicine ingredients.
Available Forms: Tablets, Liquid, etc.
The medication comes in forms, including oral tablets, intravenous solutions, and compounded creams.
III. Uses of Colchicine
FDA-Approved Uses
Treatment of Gout
Colchicine is a medicine that is used to prevent or treat attacks of gout, a condition caused by too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid can form crystals that cause inflammation and pain in the joints. Colchicine works by decreasing swelling and lessening the build up of uric acid crystals12. It is also used to treat a rare inherited disease called familial Mediterranean fever, which causes episodes of fever, pain and swelling in the abdomen, chest or joints34.
1: Colchicine (Gout) Oral: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions … - WebMD 2: Colchicine (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic 3: Colchicine Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com 4: Colchicine | Side Effects, Dosage, Uses & More - Healthline
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
Colchicine is commonly used as a part of the treatment plan for familial Mediterranean fever (FMF). This rare inherited disease causes fever, pain, and swelling in the abdomen, chest, or joints. Colchicine effectively reduces the inflammation typically linked to this condition by interfering with the activity of a protein called interleukin-1 beta12. Colchicine also helps prevent the development and progression of amyloidosis, a severe complication of FMF that can damage the kidneys and other organs34.
1: Update on the management of colchicine-resistant Familial Mediterranean … 2: Management of familial Mediterranean fever - UpToDate 3: Colchicine Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com 4: Familial Mediterranean fever - Diagnosis & treatment - Mayo Clinic
Off-Label Uses
Pericarditis
Colchicine shows promise in the treatment of pericarditis, which is the inflammation of the protective sac around the heart known as the pericardium. Colchicine is an anti-inflammatory drug that can reduce the pain, fever and recurrence of pericarditis, especially when combined with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or aspirin12. Colchicine may also prevent the complications of pericarditis, such as constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade34. The exact mechanism of action of colchicine in pericarditis is not fully understood, but it may interfere with the production and release of inflammatory mediators23.
1: Colchicine for Treatment of Pericarditis - REBEL EM 2: Colchicine for pericarditis pain (unlicensed indication … - GMMMG 3: Acute pericarditis: Treatment and prognosis - UpToDate 4: The Use of Colchicine in Pericardial Diseases
Behcet's Disease
Colchicine is a medication that is also used to treat Behcet’s disease, which is a rare inflammatory condition that affects multiple organs in the body, such as the mouth, genitals, eyes, and joints. Colchicine may help to ease joint pain, swelling, and oral and genital sores associated with Behcet’s disease12. Colchicine is not a cure for Behcet’s disease, and it may not prevent the disease from progressing13. The exact mechanism of action of colchicine in Behcet’s disease is not fully understood, but it may interfere with the production and release of inflammatory mediators45.
1: Colchicine Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com 2: Behçet’s Disease and Mouth Ulcers 3: Colchicine - Wikipedia 4: Treatment of Behçet syndrome - UpToDate 5: Behcet’s disease - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
Other Anti-Inflammatory Applications
- Acute osteoarthritis
- Amyloidosis
- Certain types of dermatitis
IV. How Colchicine Works
Mechanism of Action
Colchicine hinders the formation of microtubules, which are crucial components of cells, thus preventing cell division and interfering with various cellular processes.
Inhibition of Microtubule Formation
Colchicine hinders the growth of microtubules, which plays a role in reducing the cell's ability to move and thereby dampening inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The medication reduces the number of neutrophils that enter the inflamed areas, which helps relieve the symptoms.
V. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosages
Gout Treatment
For flare-ups start with a dose of 1.2 mg and then take another dose of 0.6 mg after an hour. As for prevention take 0.6 mg once or twice daily.
FMF Treatment
The recommended dose for adults is usually between 1.2 and 2.4 mg per day.
Special Cases
Administration to Elderly
It is recommended to adjust the dosage for elderly patients in order to minimize the decline in renal function.
Administration to Children
Calculating dosages requires careful consideration of the child's weight and their specific medical condition.
Adjustments for Liver or Kidney Dysfunction
Individuals with liver or kidney function may require adjustments in the dosage.
Important Precautions
Please begin the treatment with the effective dose. A professional must closely monitor any increase in dosage.
VI. Side Effects of Colchicine
Common Side Effects
Feeling sick. Throwing up Tiredness or general discomfort Skin-related symptoms like rashes
Severe Side Effects
Myelosuppression refers to a condition where the bone marrow functioning is impaired. Neuromuscular toxicity can lead to muscle pain or weakness. In some cases, organ failure may occur, specifically renal or hepatic failure.
VII. Interaction with Other Drugs
List of Commonly Interacting Drugs
Some known medications that can have adverse effects when taken with Colchicine are Statins, particular antifungal drugs, and blood thinners such as warfarin.
Risks of Interaction: What Could Happen?
Combining medications can increase the effectiveness or harm caused, raising the possibility of experiencing side effects.
Tips for Safe Co-administration
It is essential to have discussions with healthcare professionals. Careful monitoring of drug levels is necessary to prevent any effects.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
Warnings
Liver and Kidney Impairment
People who have liver or kidney problems should be careful when using Colchicine. There is a chance of the medication building up in their system, which can lead to adverse side effects.
Cardiovascular Risks
Colchicine has been linked to complications affecting the heart and blood vessels. While not common, there have been cases of heart rhythms and fluctuations in blood pressure, so it's essential to closely monitor these factors.
Contraindications
Known Allergies
Patients with a known sensitivity to Colchicine should avoid using it as it can potentially trigger allergic reactions.
Severe Renal or Hepatic Dysfunction
People with liver or kidney problems should not use Colchicine because it may adversely affect how the drug is processed in their bodies.
IX. Careful Administration
Monitoring During Treatment
Monitoring routine blood work, renal function tests, and liver enzymes throughout the treatment phase is essential.
Situations Where Caution is Advised
It is important to be especially careful in the following situations; When taking medications that could potentially harm the liver or kidneys at the time if you have health conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
X. Special Administration Concerns
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Known Risks
Colchicine is able to pass through the barrier and may be present in breast milk, which could lead to adverse effects, on the developing fetus or newborn.
Recommendations and Guidelines
It is generally advised against using Colchicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosing
Calculations for dosages can be quite complex as they often depend on factors such as body weight and the specific medical condition.
Safety Precautions
It is crucial to monitor for any adverse effects. Parents should seek guidance from healthcare professionals when determining the dosage.
XI. Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdosage
Symptoms of an overdose can vary, ranging from discomfort to severe muscle and nerve issues. In some cases, it can even lead to the failure of multiple organs.
Immediate Steps to Take
If there is a suspicion of an overdose, it is essential to seek medical help. Doctors often use lavage and supportive treatments in such cases.
Treatment of Overdose Cases
Treatment options in the field may involve using activated charcoal, hemodialysis, or other appropriate interventions that align with the seriousness of the specific clinical situation.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
Keep the product stored at room temperature in a place and ensure it is not accessible to children.
Handling Precautions to Maintain Efficacy
Please avoid exposing the item to changes in temperature. Make sure the packaging is intact to prevent any form of contamination.
XIII. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Colchicine is a used medication with various applications, primarily for treating gout and FMF. However, it requires administration and monitoring due to its numerous contraindications and possible adverse reactions.
Further Research and Upcoming Developments
Scientists are currently investigating therapeutic uses of Colchicine beyond its known applications. These include inflammatory conditions and even certain types of cancer.
Resources for Additional Information
For personalized medical advice on Colchicine, it is recommended to consult reliable medical literature, healthcare professionals, or specialized pharmaceutical databases.