Dexamethasone Injection
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Dexamethasone Injection
- III. Uses of Dexamethasone Injection
- IV. Off-label Uses of Dexamethasone
- V. How Dexamethasone Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Dexamethasone
- VIII. Important Precautions
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Special Considerations in Administration
- XI. Contraindications
- XII. Handling and Storage
- XIII. Overdosage
I. Introduction
Overview of Dexamethasone:
Dexamethasone, an artificial drug belonging to the glucocorticoids category, is well known for its ability to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. This medication is used to treat a range of conditions, from severe allergies to disorders characterized by significant inflammation.
Brief History of its Development and Approval:
Since the 1950s, dexamethasone has been widely used in medical treatments for many years due to its effectiveness and adaptability, resulting in quick approval and widespread adoption in healthcare facilities worldwide.
II. Composition of Dexamethasone Injection
Active Ingredients:
The main ingredient in dexamethasone injection is dexamethasone sodium phosphate. This substance works quickly to offer relief from swelling and discomfort.
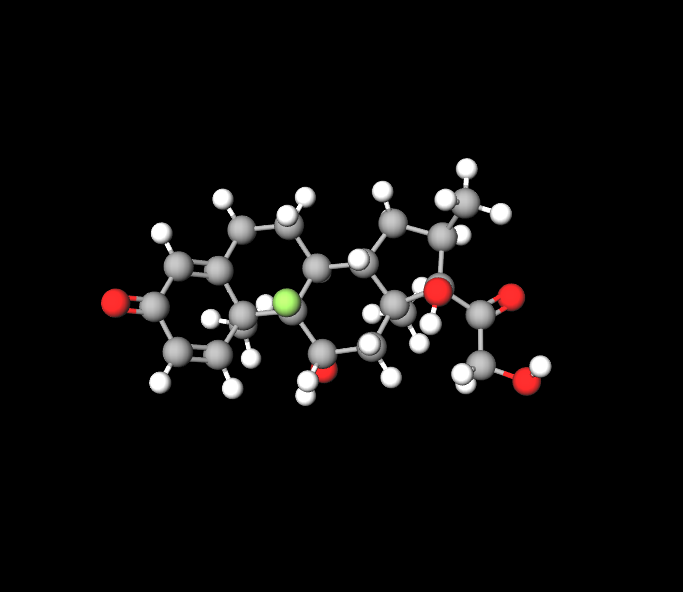
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate
Dexamethasone is prescribed for health issues, like arthritis, blood and hormone imbalances, allergies, skin ailments, eye conditions, respiratory challenges, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer treatment and immune system disorders.
Dexamethasone acetate
Dexamethasone acetate, also referred to as decadron is a type of glucocorticosteroid that was once sold in the United States for managing inflammatory respiratory, allergic, autoimmune and other health issues. It was created in 1957. Shares similarities in structure with corticosteroids, like hydrocortisone and prednisolone.
Dexamethasone vs prednisone
Dexamethasone can be administered for a period of 1 to 5 days at a dosage ranging from 0.3 to 0.6 mg per kilogram per day. It is worth noting that Dexamethasone is classified as a lasting glucocorticoid with a half life spanning from 36 to 72 hours and is approximately six times stronger, than prednisone. In comparison prednisone has a duration of action with a half life of 18 to 36 hours.
Dexamethasone vs methylprednisolone
Dexamethasone decreases inflammation. Soothes are an overactive immune system that shows greater potency than prednisolone. Methylprednisolone manages inflammation and an overactive immune system effectively. It may not be suitable for everyone. Based on the research it can be inferred that 8 mg of dexamethasone is more effective, in managing swelling and trismus compared to 40 mg of methylprednisolone. However, both medications exhibit pain-relieving capabilities.
Tobramycin dexamethasone
Tobramycin and dexamethasone are an antibiotic and a corticosteroid. They are applied to the eye to safeguard against harm that could arise from specific eye issues.
Iontophoresis with dexamethasone
Dexamethasone, a type of medication is commonly paired with iontophoresis to help alleviate pain, swelling and inflammation. During this process a patch is applied to the skin to target areas of discomfort. The primary goal is to reduce swelling and provide pain relief. The patch contains a pouch filled with medication and both are linked to an ionto machine, for administration.
Excipients and Their Functions:
Ingredients such as benzyl alcohol, sodium citrate, and water for injection are essential for maintaining the stability of the formulation and improving the solubility of the ingredient.
III. Uses of Dexamethasone Injection
Indications in Anti-inflammatory Treatments:
Applications in Allergic Reactions:
Role in Cancer Therapy Protocols:
Utility in Cerebral Edema Management:
Reducing inflammation around tumors or lesions in the brain can improve comfort and treatment results.
IV. Off-label Uses of Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is useful for more than what it's officially approved for.
Use in Severe COVID-19 Cases:
Dexamethasone for cough
Dexamethasone tablets are a type of medicine used to address skin, joint, lung, and organ inflammation. They work by lessening swelling and improving breathing. While most children may find relief after one dose, some may require multiple doses for better breathing.
Applications in Advanced Therapeutics for Autoimmune Disorders:
Experimental Uses in Rare Diseases:
Ongoing research is being conducted on its application, in medical conditions providing hope in situations where treatment options are scarce.
Dexamethasone for dogs
It is employed to manage and address immune related conditions like immune mediated anemia or thrombocytopenia certain types of cancer allergic responses such, as asthma, hives and itching inflammatory disorders and some neurological ailments. Dexamethasone is also applied externally to address skin and eye issues.

V. How Dexamethasone Works
Mechanism of Action at the Cellular Level:
Dexamethasone moves through cell walls. Attaches strongly, to glucocorticoid receptors changing how genes work and reducing the immune response.
Impact on Inflammatory Pathways:
It suppresses inflammatory cytokines, which helps lessen the indications and effects of inflammation.
Effects on Immune System Modulation:
Dexamethasone can help reduce immune-related harm by adjusting the functions of both the acquired immune systems.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines:
The amount of dexamethasone prescribed can differ depending on the ailment being addressed, usually beginning with a higher dosage that is gradually reduced based on how the treatment progresses.
Dexamethasone suppression test
The dexamethasone suppression test assesses how the adrenal glands react to ACTH. Dexamethasone is. Cortisol levels are monitored. Ideally cortisol levels should decrease after dexamethasone is given.
Dexamethasone for adult dose
Initially the daily dosage ranges from 0.75, to 9 milligrams (mg). Your physician may make adjustments based on your requirements.
Dexamethasone for child dose
The dosage is calculated according to your body weight. Should be prescribed by your physician. Initially the recommended dose ranges from 0.02 to 0.3 milligrams per kilogram (kg) of body weight daily divided into 3 or 4 doses throughout the day. Your doctor may make changes, to your dosage as necessary.
Dexamethasone in pregnancy
It's safe to take Dexamethasone during pregnancy. Its best to consult your doctor or specialist first. They might recommend switching to a type of steroid like prednisolone, which is less likely to affect your baby. Remember not to stop taking Dexamethasone without discussing it with your doctor. Dexamethasone helps the lung development reduces the risk of respiratory distress syndrome in newborns and increases survival rates for premature babies. The recommended time for starting Dexamethasone therapy is, between 31 to 34 weeks of pregnancy.
Adjustments for Specific Conditions:
Patients, with health conditions or who are receiving multiple treatments may need to have their dosages adjusted accordingly.
Dexamethasone for croup
Research has demonstrated that using dexamethasone at a dosage of 0.15 mg/kg is just as beneficial as doses of 0.3 mg/kg or 0.6 mg/kg (up to a daily dose of 10 mg) in alleviating symptoms of mild to moderate croup. However it appears that healthcare providers continue to lean towards the dosage of 0.6 mg/kg when initiating treatment, for croup.
Dexamethasone elixir for mouth sores
You can also use a 0.5mg/ml bottle of dexamethasone elixir (12 oz.) as a mouth rinse, swishing one tablespoon for two minutes, four times daily. For serious situations this rinse can be paired with Clobetasol gel.
Dexamethasone for sinus infection
Dexamethasone, a type of corticosteroid, is commonly used to treat sinusitis through oral medication. These corticosteroids help manage inflammation, in the airways and can quickly shrink polyps thereby alleviating symptoms associated with them.
Dexamethasone multiple myeloma
Steroids, which are inflammatory medications commonly prescribed for ailments like hay fever and arthritis that result in discomfort and inflammation, play a significant role in the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM). Drugs like prednisone and dexamethasone are utilized in MM therapy due to their effectiveness, in eradicating myeloma cells.
Methods of Administration:
Dexamethasone can be given by mouth through a vein or by injection into a muscle, depending on the situation, in the field.
VII. Side Effects of Dexamethasone
Common Adverse Effects:
Patients might encounter side effects such as trouble sleeping, gaining weight, and higher blood sugar levels.
Potential Long-Term Consequences:
Continued use over a period may result in issues like osteoporosis, suppression of the adrenal glands, and a decrease in muscle strength.
Managing Side Effects in Clinical Practice:
Being proactive in monitoring and adjusting the treatment can help reduce these impacts, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients.
Dexamethasone weight gain chemo
Chemotherapy may lead to tiredness, making you less inclined to be active. Steroids like prednisone and dexamethasone can trigger hunger, potentially leading to consuming more calories than necessary. Additionally steroids may result in water retention and a bloated sensation while also increasing the bodys tendency to store fat.
VIII. Important Precautions
Before Starting Dexamethasone
To start using Dexamethasone it's important to review your medical history and current medications to avoid any possible issues.
low-dose dexamethasone suppression test results interpretation
The dexamethasone suppression test evaluates if the glands cortisol secretion can be reduced. It also aids in determining the cause of cortisol levels in the body such as an overproduction of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), by the pituitary gland.
Monitoring Needs During Treatment
- Regular blood tests are conducted to check blood sugar and electrolyte levels.
- Periodic evaluations are also carried out to watch for any rise, in blood pressure and signs of infection.
Very low cortisol level after dexamethasone
Dexamethasone decreases the release of ACTH in individuals without any health issues. As a result, using dexamethasone is expected to lower the ACTH levels and cause a reduction in cortisol levels. If your pituitary gland produces amounts of ACTH you may show an unusual reaction during the low dose test. However, you may exhibit a response during the high-dose test.
Signs of Adverse Reactions to Watch For
Patients need to stay alert for signs, like swelling, rapid weight increase, intense headaches and vision issues that could signal significant adverse reactions.
Dexamethasone withdrawal
Withdrawal from dexamethasone quickly can lead to symptoms like bone and muscle pain, tiredness, weight loss, queasiness, and vomiting. It's advisable to control or avoid alcohol consumption while using dexamethasone to reduce the risk of developing stomach ulcers.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions
Dexamethasone could have interactions with medications, like NSAIDs, specific antidiabetic drugs, and vaccines, so it's important to handle them with care.
Impact on Pharmacokinetics
The existence of dexamethasone may change how other medications work in the body, leading to a decrease in their effectiveness or an increase in their side effects.
Dexamethasone to prednisone
Dexamethasone is six times more powerful than prednisone and prednisolone in reducing inflammation. Therefore, 6 mg of prednisone/prednisolone is equal to 1 mg of dexamethasone. Fludrocortisone has the sodium retaining effects being 150 times more potent, than prednisone.
Avoiding Harmful Combinations
Thoroughly examining the medications a patient is currently taking is crucial to avoid interactions between drugs and to maintain a safe treatment plan.
dexamethasone and alcohol
Alcohol and dexamethasone may individually cause irritation to your stomach. When combined, the likelihood of this effect is increased. It is advisable to refrain from consuming alcohol while undergoing dexamethasone treatment to reduce the chances of experiencing stomach related issues.
X. Special Considerations in Administration
To Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals might need doses of medication and careful supervision because they are more prone to experiencing side effects like osteoporosis and high blood pressure.
To Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before taking medications while pregnant or breastfeeding, weighing the benefits against the risks to the baby. Exploring treatment options and discussing potential risks with a doctor is important.
To Children
When giving children dexamethasone, it's important to calculate the dosage accurately, considering their weight and the seriousness of their condition. Regular monitoring is necessary to watch for growth suppression and other side effects that may affect children specifically.
XI. Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Patients with fungal infections or those who have had live or live attenuated vaccines should avoid using dexamethasone.
Relative Contraindications
Patients who have diabetes, ulcers, or heart failure should be careful when using dexamethasone and should do so under close medical monitoring.
Risk Assessment Guidelines
Before starting treatment for patients with risk factors, it is crucial to thoroughly assess the balance between risks and benefits.
XII. Handling and Storage
Proper Storage Conditions
Make sure to keep dexamethasone in a dry place at room temperature to maintain its effectiveness away, from light and moisture.
Handling Precautions to Ensure Safety
Personnel should take care to reduce heat and sun exposure while handling. It's important to wear protective gear as needed to prevent contamination.
Disposal of Unused Medication
Make sure to dispose of any dexamethasone that is not being used or has expired in accordance with guidelines to avoid any environmental harm or accidental ingestion.
XIII. Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdosage
Common symptoms might involve feelings of happiness, difficulty sleeping changes, in mood and digestive issues. In serious instances these symptoms could escalate to potentially dangerous situations.
Immediate Actions and Antidotes
In case of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical assistance. The treatment primarily aims to alleviate symptoms and stabilize the individual.
Long-term Management of Overdose Effects
Ensuring the care includes keeping an eye out for any overall side effects and making necessary changes to medication doses to avoid future issues.
Dexamethasone Injection FAQ
- How long do side effects of dexamethasone last?
- How long does dexamethasone stay in your system?
- 1 mg dexamethasone equals how much prednisone?
- Ciprofloxacin / dexamethasone ear drops how to use?
- How long does dexamethasone last?
- How long does withdrawal from dexamethasone last?
- How can i reduce the side effects of dexamethasone?
- How long do side effects of dexamethasone last after stopping?
- How long can a cancer patient take dexamethasone?
- How long does dexamethasone take to work?
- How long does a dexamethasone injection stay in your system?
- How long can a horse be on dexamethasone?
- What is dexamethasone used for in dogs?
- Dexamethasone injection for dogs how long does it last?
- How long does dexamethasone affect blood sugar?
How long do side effects of dexamethasone last?
After taking a 20 mg dose of dexamethasone, which has a life of four hours (the time it takes the body to remove half the dose) the medication will be mostly cleared from your system in approximately 24 hours. Most of the short term side effects like changes, in mood or feelings of anxiety should subside by then.
How long does dexamethasone stay in your system?
With a life of 4 hours, it typically takes around 20 hours for the majority of dexamethasone to exit your body. This is because it generally takes five half-lives for a medication to be nearly entirely removed from your system. The process of dexamethasone exiting your system may be prolonged if you have medical conditions.
1 mg dexamethasone equals how much prednisone?
Dexamethasone is six times powerful than prednisone and prednisolone in fighting inflammation; therefore 6 mg of prednisone/prednisolone is equal to 1 mg of dexamethasone. Fludrocortisone exhibits the sodium retention properties being 150 times more potent, than prednisone.
Ciprofloxacin / dexamethasone ear drops how to use?
Lie on your side with the ear facing upward. Put in the number of drops, into the ear. Keep the ear tilted upward for a minute. To maintain the cleanliness of the medicine avoid touching the applicator tip to any surface, including the ear.
How long does dexamethasone last?
Dexamethasone, a medication with a prolonged effect, remains in the bloodstream for 5 to 11 hours, varying based on the form of the drug ingested. It is important to note that using Dexamethasone during pregnancy can pose risks to the developing fetus. As such, it is advisable to discontinue Dexamethasone intake at least one month before planning conception.
How long does withdrawal from dexamethasone last?
The intense withdrawal symptoms usually subside within a week once you stop taking prednisone and other corticosteroids.
How can i reduce the side effects of dexamethasone?
Remember to take dexamethasone with a meal or snack to lessen the likelihood of experiencing stomach issues. It could be beneficial to steer of rich or spicy foods as well. If these symptoms persist make sure to consult your doctor. They might prescribe a medication to safeguard your stomach.
How long do side effects of dexamethasone last after stopping?
A 20 mg dose of dexamethasone which has a life of four hours (the time it takes for the body to get rid of half the dose) will be removed from the body in approximately 24 hours. Most of the short term effects of dexamethasone like changes, in mood or feelings of anxiety typically subside within that timeframe.
How long can a cancer patient take dexamethasone?
If you've been prescribed than 4mg of Dexamethasone daily for under 3 weeks you can stop the steroids suddenly. However it might be better to decrease the dosage to lower the chances of symptoms coming back. On the hand if you've been taking Dexamethasone for more than 3 weeks or at a dose higher than 4mg, per day its recommended to gradually reduce the dosage.
How long does dexamethasone take to work?
The. Efficiency of dexamethasone. The maximum effects of dexamethasone typically occur within 10 to 30 minutes after taking it; although it might require a days for inflammation to be adequately managed.
How long does a dexamethasone injection stay in your system?
Dexamethasone, a medication with a lasting effect remains in the bloodstream for 5 11 hours varying based on the form of the drug used. It is important to note that Dexamethasone can pose risks, to a baby if taken during pregnancy. Hence if you are considering pregnancy it is advisable to discontinue Dexamethasone intake least one month prior.
How long can a horse be on dexamethasone?
The dosage can be given again for three to five days or until a reaction is observed. For horses, the recommended intravenous dose is 2.5 to 5 mg, based on a concentration of 3 mg per mL of dexamethasone. If a lasting corticosteroid effect is needed, switching to treatment, with dexamethasone is an option.
What is dexamethasone used for in dogs?
Dexamethasone, a type of steroid is known to be stronger than the usual steroid prednisone. It acts faster. Stays in your dogs system, for a longer duration. Dexamethasone is utilized for diagnosing diseases and managing conditions like inflammation, allergies and certain types of cancer.
Dexamethasone injection for dogs how long does it last?
Dexamethasone, a type of steroid commonly used for dogs, is known to be more potent than prednisone, with a strength that is six to seven times greater. Steroids are utilized in ways for canine health, such, as managing autoimmune conditions and addressing allergic reactions, inflammation and cancer.
How long does dexamethasone affect blood sugar?
Patients who were given dexamethasone experienced an increase in their average blood sugar levels. This increase was consistently significant over the duration of up to 72 hours. Among those patients, 10.7% (8 out of 75) had blood sugar levels exceeding 180 mg/dl, necessitating insulin treatment.