Etoposide Capsule
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Etoposide
- III. Off-Label Uses of Etoposide
- IV. How Etoposide Works
- V. Composition of Etoposide
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Etoposide
- VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration of Etoposide
- XI. Administration to Specific Populations
- XII. Overdose of Etoposide
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Etoposide: Origins and Development
Etoposide, which is derived from the American Mayapple, has been highly regarded in the field of oncology for a time. It is a compound that stems from podophyllotoxin showcasing the significant impact of natural substances on our medical practices. The chemical structure of Etoposide consists of rings and lactone formations, representing a delicate yet powerful balance that plays a vital role in battling cancer. One breakthrough was adding a component that significantly improved its stability and ensured its effectiveness when used as medicine. Exploring the connection between podophyllotoxin and nature's pharmacopeia highlights the potential for transforming compounds into potent treatments with optimal bioavailability for maximum efficacy.
B. FDA Approval and Current Status
During the 1980s, Etoposide gained recognition as an anticancer drug and received FDA approval for its ability to combat small-cell lung and testicular cancer. One of its features is its ability to interact with DNA and inhibit topoisomerase II, an enzyme crucial for DNA replication. This mechanism contributes to its cytotoxic effects. It is worth noting that Etoposide is currently included in the World Health Organizations List of Essential Medicines, highlighting its role in global healthcare. Its years of service have proven its value beyond FDA approval.
II. Uses of Etoposide
A. Primary Uses: Treating Testicular and Small Cell Lung Cancer
Etoposide has proven to be highly effective in treating cancer and small-cell lung cancer. It does not stop the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells but also triggers programmed cell death, known as apoptosis. When dealing with cancer, Etoposide is often used alongside other chemotherapy drugs like cisplatin, creating a combined treatment called EP or Etoposide plus cisplatin. This comprehensive approach has improved patient survival rates, firmly establishing Etoposide's role in the management of testicular cancer. The unique nature of Etoposide lies in its ability to inhibit tumor growth while promoting cell death2.
B. Other Recognized Oncological Applications
Etoposide has proven to be more than a treatment for its primary uses. It shows effectiveness against types of cancers. For example, in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Etoposide is a part of the initial treatment plan to put the disease into remission. Moreover, it has shown results in treating other cancers like Hodgkins and non-Hodgkins lymphoma, Kaposis sarcoma, and neuroblastoma. This demonstrates the range of clinical applications for Etoposide across different malignancies.
III. Off-Label Uses of Etoposide
A. Investigative Uses in Non-Oncological Conditions
Etoposide has established itself as an ally in the field of oncology. However, researchers are now exploring its potential beyond cancer treatment. They are investigating whether it could effectively address cancerous conditions characterized by abnormal cell growth. For instance, there is exploratory research into its possible use in autoimmune disorders to help regulate immune responses. These prospects need investigation to determine if Etoposide can expand its therapeutic range and open new possibilities for treatment.
B. Emerging Research and Potential Uses
Ongoing research on Etoposide is continuously advancing, exploring its applications in various fields. Recent studies indicate that it may play a role in addressing neurodegenerative diseases by affecting neuronal apoptosis. In the future, there is a possibility that Etoposide could be repurposed to combat conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. This highlights the journey of discovery surrounding the future of Etoposide.
IV. How Etoposide Works
A. Mechanism of Action: Inhibition of Topoisomerase II
Etoposide creates an interaction with DNA and an enzyme called topoisomerase II. This interaction leads to the breaking of stranded DNA, which effectively stops the process of cell division and ultimately causes cell death. Etoposide is classified as a type II topoisomerase inhibitor because of its ability to inhibit topoisomerase II, a classification it shares with other chemotherapy medications. It's fascinating how DNA, topoisomerase II, and Etoposide form this triad playing a crucial role in inhibiting cell division for healing purposes2.
B. Impact on Cancer Cell Growth and Division
Etoposide works by causing breaks in the stranded DNA, which helps stop the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells. It also triggers a process called apoptosis or programmed cell death, effectively reducing the size of the tumor. These two mechanisms. Inhibiting proliferation and promoting cell death. From the foundation of Etoposides cancer activity. Etoposide slows down cancer cell growth and encourages their destruction through apoptosis.
V. Composition of Etoposide
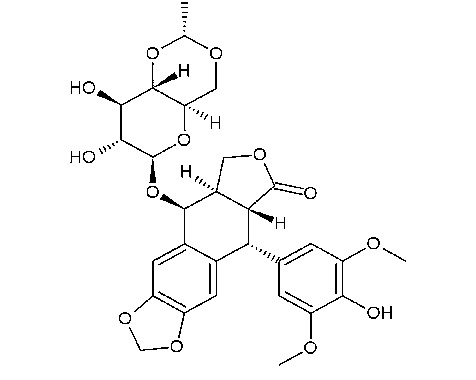
A. Active Ingredient: Etoposide
The main component in Etoposide is the compound that shares its name. Etoposide is derived from podophyllotoxin, a compound found in the American Mayapple. Scientists have changed the podophyllotoxin molecule, resulting in a more effective and safer combination for patients. From origins to laboratory advancements; The story behind Etoposides creation. Improving effectiveness; The alterations made to podophyllotoxin.
B. Role and Composition of Inactive Ingredients
The inactive ingredients or excipients in Etoposide serve functions in the formulation of the medication. They help improve solubility, enhance stability, and optimize bioavailability. These constituents can vary depending on the formulation but may include polysorbate 80 and alcohol as solvents or bulking agents for Etoposide capsules. The presence of these excipients plays a role in ensuring the medication's safety, effectiveness, and tolerability. Additionally, they contribute to optimizing its efficacy by addressing factors such as solubility, stability, and bioavailability.
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
The amount of Etoposide given depends on the type of cancer, patient characteristics, and concurrent treatment. Usually, the dosages range from 50 to 100 mg/m² per day1. It can be administered through an injection lasting 30 to 60 minutes or orally in cycles. It's crucial to remember that these dosages should be tailored to each individual under the supervision of an oncologist. When determining the dosage, personalized dosing plays a significant role. Additionally, understanding how Etoposide is administered within each cycle is essential for management.

B. Important Instructions for Safe and Effective Administration
Like any chemotherapy drug, it's essential to administer Etoposide correctly. When given through an IV, it should be administered with caution to avoid leakage. If taking it orally, make sure to take it on a stomach. Monitoring blood counts is crucial to managing potential side effects like neutropenia effectively. Since Etoposide can interact with medications, reviewing your current medications thoroughly is essential.
VII. Side Effects of Etoposide
A. Most Common Side Effects: Management and Mitigation
Etoposide, similar to chemotherapy drugs, can cause various side effects. The frequently reported ones include2
- Feeling sick
- Vomiting
- Reduced appetite
- Hair loss
These effects are usually temporary. It may improve as your body gets used to the medication. To cope with these side effects, Your doctor may prescribe nausea medications to relieve gastrointestinal discomfort. Making adjustments, like having smaller and more frequent meals, can help alleviate the loss of appetite. Using hair care products and avoiding harsh treatments that could worsen hair loss is advisable.

B. Rare but Severe Side Effects: Awareness and Action
Although uncommon, Etoposide can sometimes cause side effects like severe neutropenia, allergic reactions, and, in rare cases, secondary malignancies. It is crucial to recognize these situations and take appropriate action. Regular monitoring of blood counts can help detect neutropenia so that timely intervention can be provided. Patients should be informed to seek medical assistance if they experience symptoms that suggest an allergic reaction, such as
- Difficulty breathing
- Hives
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
It may also be necessary to screen patients receiving long-term Etoposide therapy for the development of secondary malignancies.
VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
A. Common Drug-Drug Interactions with Etoposide
Etoposide has the potential to interact with a range of other medications, which can affect how well it works and its potential side effects. For example, suppose Etoposide is used at the time as certain antibiotics like ciprofloxacin or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine. In that case, it may increase the amount of Etoposide in the blood, which could increase the risk of experiencing side effects. On the other hand, medications that activate liver enzymes, such as rifampin, may decrease Etoposide's effectiveness by speeding up its breakdown in the body. Therefore, it is crucial to review all medications taken and make any necessary dosage adjustments to optimize treatment outcomes.
B. Etoposide and Dietary Supplements: What to Know
The relationship between Etoposide and dietary supplements is still not fully understood, so caution's essential. Some accessories might impact the activity of liver enzymes. Interfere with how the drug is absorbed, which could potentially affect how well Etoposide works. Patients should talk with their healthcare provider about supplements to address possible interactions.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Health Conditions Precluding Etoposide Use
Although Etoposide can be a weapon in the fight against cancer, certain health conditions may prevent its use. Examples of these contraindications include bone marrow suppression, recent or ongoing radiation therapy, or hypersensitivity to Etoposide or its components. Patients who have these conditions might need to explore alternative treatment options. Assessing the patient's overall health status is crucial when planning for Etoposide therapy.
B. Drug, Food, and Lifestyle Factors to Avoid
During Etoposide therapy, avoiding medications that may affect liver enzymes by consuming grapefruit juice or using certain dietary supplements is essential. Additionally, if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, it is advisable to refrain from Etoposide treatment and use contraception methods. It is necessary to monitor your blood count and be cautious about coming into contact with individuals who have infectious diseases due to the possible weakening of your immune system.
X. Careful Administration of Etoposide
A. Key Precautions for Healthcare Providers
When healthcare professionals are giving Etoposide, they need to be very careful. They should. Administer the medication cautiously to prevent direct contact with the skin or mucous membranes. It is also necessary for them to wear personal protective equipment while preparing and administering Etoposide.
B. Importance of Regular Monitoring and Patient Follow-up
It is crucial to monitor blood counts and liver function to evaluate how well the treatment works, identify any possible side effects, and make any needed adjustments to the dosage. Additionally, patients should have follow-up appointments to ensure that the therapy is effective, keep an eye out for any potential secondary cancers and address any long-term side effects that may arise.
XI. Administration to Specific Populations
A. Etoposide Use in Elderly Patients
The use of Etoposide in patients requires careful consideration due to factors like age-related physiological changes, existing health conditions, and multiple medications. These factors can affect how the drug is processed in the body, which may increase the likelihood of experiencing reactions. It is essential to evaluate organ function, kidney and liver health before starting treatment and adjust the dosage if necessary. Close monitoring of side effects is crucial since older patients may be more prone to experiencing suppressed bone marrow activity and gastrointestinal issues. It is also recommended to review the effectiveness and tolerability of the therapy.

B. Considerations for Pregnant and Nursing Women
Using Etoposide in women and nursing mothers poses significant challenges due to its potentially harmful effects on the fetus or nursing infant. It is typically administered in life-threatening situations where the benefits outweigh the risks. Using contraception during treatment and for a certain period afterward is essential. If Etoposide is used during pregnancy or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving this medication, informing the patient about the harm it may cause to the fetus is crucial. As we do not know whether Etoposide is excreted in human milk, breastfeeding should be stopped if the mother is treated with Etoposide.

C. Etoposide in Pediatric Oncology: Current Understanding
Etoposide is a treatment option for various pediatric cancers, including neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, and Ewings sarcoma. However, when using this chemotherapy drug in children, carefully weigh the risks and benefits. Since kids process medications differently than adults, it's important to follow dosage guidelines based on their body size and maturity. Close monitoring of blood counts and kidney and liver function is essential to ensure the possible outcomes and minimize any potential side effects. Additionally, long-term follow-up is necessary to keep an eye out for any delayed side effects that might occur, such as secondary malignancies.

XII. Overdose of Etoposide
A. Recognizing Symptoms and Signs of Overdose
Taking much Etoposide can worsen its side effects, mainly suppressing bone marrow function and leading to neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. Signs to watch out for include fatigue, frequent infections, and unusual bleeding. It's crucial to identify these symptoms to address the consequences effectively.
B. Management and Treatment Approaches for Overdose
The primary approach for dealing with an overdose of Etoposide is to provide care2. This includes stopping the medication, monitoring blood counts and organ function closely, and effectively managing neutropenia and infections. In some cases, this may involve using colony-stimulating factors, antibiotics, or providing blood component transfusions.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Best Practices for Etoposide Storage
To ensure the effectiveness of etoposide capsules, storing them in a dry place away from direct light and moisture is recommended. It is essential to handle this medication cautiously as it is considered hazardous. Following the guidelines provided by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) will help minimize any risks associated with its handling.
B. Ensuring Safe Handling and Disposal of Etoposide Medication
Considering Etoposide's nature, handling and disposing of it with great care is crucial. Healthcare professionals must wear gloves and protective clothing while dealing with Etoposide making sure to avoid any contact with the skin or mucous membranes. In case of exposure, thoroughly wash the affected area using soap and water or rinse your eyes with water if there is eye contact. Promptly clean up any spills following the procedures. When disposing of Etoposide, ensure compliance with regulations and institutional policies regarding cytotoxic waste management.