Alfacalcidol
- I. Introduction to Alfacalcidol
- II. Composition of Alfacalcidol
- III. How Alfacalcidol Works in the Body
- Primary Uses of Alfacalcidol
- Off-label Uses of Alfacalcidol
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Alfacalcidol
- VII. Careful Administration of Alfacalcidol
- VIII. Special Populations and Alfacalcidol Administration
- IX. Potential Interactions with Alfacalcidol
- X. Recognizing and Managing Side Effects
- XI. Contraindications for Alfacalcidol Use
- XII. Alfacalcidol Overdose: Signs and Treatment
- XIII. Alfacalcidol Storage and Handling Precautions
- XIV. Important Warnings Related to Alfacalcidol Use
- XV. Conclusion: Integrating Alfacalcidol into Effective Medical Care
I. Introduction to Alfacalcidol
A. Overview and Historical Development
Alfacalcidol, a form of vitamin D has a captivating past and numerous applications in medical treatments. Initially created in the 1970s, it was part of an exploration into bioactive analogs of vitamin D. Its introduction represented a significant advancement in our comprehension and management of bone-related ailments. As the story of alfacalcidol unfolded, scientists discovered its potential in combating diseases associated with calcium metabolism. This led to its usage, particularly in conditions like osteoporosis and renal osteodystrophy. Today alfacalcidol is acknowledged as a component in addressing calcium disorders.
B. Understanding the Role of Alfacalcidol in the Body
Alfacalcidol plays a role in the body by primarily regulating calcium balance. It acts as a prodrug, which means it needs to undergo metabolism to become active and produce its effects. Once ingested, it is quickly converted into calcitriol in the liver, which's the most potent form of vitamin D. Calcitriol interacts with vitamin D receptors in various parts of the body, such as the intestines, bones, and kidneys. These interactions enhance calcium absorption from the gut and release calcium from bones into the bloodstream when necessary. Reduce calcium excretion through the kidneys. As a result, alfacalcidol plays a role in maintaining optimal levels of calcium in our body and contributes significantly to overall bone health.
II. Composition of Alfacalcidol
A. Detailed Breakdown of the Molecular Structure
Alfacalcidol, also known as 1α Hydroxycholecalciferol in terms, is a type of vitamin D analog with a distinct molecular structure. Its chemical formula is C27H44O2, and it weighs 400.6 g/mol. The molecular structure of alfacalcidol closely resembles that of vitamin D3, with an extra hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to the side chain at the one alpha position. This unique modification significantly enhances its effectiveness. What sets alfacalcidol apart is the presence of the hydroxyl group at the one alpha position, which allows it to bypass the need for activation in the kidneys. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for use when kidney function is impaired and regular conversion of vitamin D into its active form may be hindered.
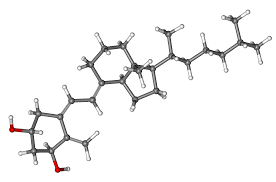
B. Comparing Alfacalcidol to Other Vitamin D Analogs
There are types of vitamin D analogs used in medical practice, each having its distinct characteristics based on its molecular structure. Alfacalcidol calcitriol and doxercalciferol are examples of these analogs. Although they all have the form of vitamin D their side chains have specific modifications that affect how they are metabolized, their effectiveness, and the conditions they can be used for. Compared to calcitriol, the biologically active form of vitamin D, alfacalcidol acts as a prodrug that needs to be activated in the liver. This difference allows for a controlled release of the active substance and lowers the risk of hypercalcemia, characterized by abnormally high calcium levels in the blood. Unlike doxercalciferol, which requires two steps of activation in both the liver and kidneys respectively, alfacalcidol only needs one step. This makes alfacalcidol a better choice for patients with kidney function. As a result, alfacalcidol's unique composition plays a role in managing disorders related to calcium metabolism.
III. How Alfacalcidol Works in the Body
A. Mechanism of Action: Absorption and Conversion
Alfacalcidol is a medicine that works in two steps to help the body maintain the right amount of calcium. First, it gets absorbed quickly from the stomach and intestines when taken orally. Then in the liver, it rapidly transforms into calcitriol, the most active form of vitamin D. This efficient process ensures that vitamin D levels are replenished effectively and promptly. Once activated, calcitriol attaches to vitamin receptors throughout the body, triggering a series of biochemical reactions that aim to increase calcium levels in the blood.
B. Understanding Its Role in Calcium Regulation
The main role of alfacalcidol in our bodies is to maintain the balance of calcium levels. It achieves this by operating through three mechanisms;
1. We are enhancing the absorption of calcium in the intestines, thus increasing the amount of calcium that enters the bloodstream.
2. Reducing calcium excretion in the kidneys helps conserve the body's calcium levels.
3. Stimulating the release of calcium from bones into the bloodstream when necessary, a process referred to as bone resorption.
By employing these mechanisms, alfacalcidol plays a part in ensuring that our bodies have sufficient calcium to sustain bone health and carry out various essential functions.
Primary Uses of Alfacalcidol
Osteoporosis Treatment: Bridging the Calcium Gap
Alfacalcidol is a form of vitamin D that is prescribed for the treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become fragile and prone to fractures. Alfacalcidol helps strengthen bones and reduce risk by improving calcium absorption from the intestines and kidneys. It is commonly used alongside calcium supplements and bisphosphonates to treat osteoporosis. Remember, it’s crucial to seek guidance from healthcare before using alfacalcidol.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about alfacalcidol and its use in treating osteoporosis:
- The combination therapy with alfacalcidol and risedronate improves the …
- Alfacalcidol in men with osteoporosis: a prospective … - Springer
- Plain vitamin D or active vitamin D in the treatment of osteoporosis: where do we stand today?
Treatment of Renal Osteodystrophy: A Chronic Kidney Disease Approach
Renal osteodystrophy is a condition that affects individuals who have kidney disease. It occurs due to an imbalance of minerals in the body, which can result in bone loss and fractures. Medical professionals often prescribe alfacalcidol as a treatment for osteodystrophy because it helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the body alfacalcidol aids in preventing bone loss and fractures among those with chronic kidney disease. It’s crucial to note that using alfacalcidol should only be undertaken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about alfacalcidol and its use in treating renal osteodystrophy:
- 1-alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol for renal osteodystrophy
- Alfacalcidol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online
- ALFACALCIDOL: Uses, Side Effects and Medicines | Apollo Pharmacy
Hypocalcemia: Restoring Calcium Levels
Hypocalcemia is a condition that occurs when the level of calcium in the blood becomes insufficient. This deficiency can result in muscle cramps, spasms, and weakness. One prescribed treatment for hypocalcemia is alfacalcidol, which aids in raising calcium levels in the bloodstream. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that alfacalcidol should only be administered under the supervision and guidance of a healthcare professional.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about alfacalcidol and its use in treating hypocalcemia:
- Treatment of hypocalcemia - UpToDate
- Alfacalcidol for the treatment of hypocalcaemia due to hypoparathyroidism in adults
- Alfacalcidol | Side Effects | Dosage | Precautions | Warnings | Medicine
Off-label Uses of Alfacalcidol
Potential Benefits in Autoimmune Disorders
Alfacalcidol, a version of vitamin D, is utilized in the treatment of various conditions such as osteoporosis and renal osteodystrophy. However, there is a growing interest in exploring the advantages of alfacalcidol for managing autoimmune disorders. These disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks cells and tissues within the body. Some common examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. Alfacalcidol has demonstrated effects meaning it can assist in regulating the immune system to prevent it from attacking healthy cells and tissues. Although further research is required to comprehend the potential benefits of alfacalcidol in treating autoimmune disorders, initial studies have shown promise. It's important to note that alfacalcidol should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
References:
Exploring Its Role in Cardiovascular Health
Alfacalcidol has demonstrated potential advantages when it comes to cardiovascular well-being. One notable benefit is its ability to regulate blood pressure and diminish inflammation within the body. Inflammation plays a role in the onset of cardiovascular disease, so by reducing it, alfacalcidol might aid in preventing or slowing down the advancement of such conditions. However, it's worth mentioning that further research is required to grasp all the potential benefits that alfacalcidol may offer for cardiovascular health.
References:
Alfacalcidol in Psoriasis Management
Psoriasis is a lasting skin condition that results in red, flaky patches on the skin. While there isn't a cure for psoriasis, various treatments exist to help control its symptoms. Alfacalcidol has shown potential in managing psoriasis. For instance, studies have demonstrated its ability to decrease inflammation and enhance skin symptoms in individuals with psoriasis. It's worth mentioning that further research is required to comprehend the advantages alfacalcidol may offer in managing psoriasis.
References:
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Alfacalcidol
A. Standard Dosages: For Osteoporosis and Renal Osteodystrophy
Like any medicine, the amount of alfacalcidol you take should be customized to meet your needs. For adults dealing with osteoporosis, it's common to start with a dose of 1 microgram and then adjust it based on how your body responds and your blood calcium levels. If you have osteodystrophy, the typical recommendation is also 1 microgram per day, but your doctor may make changes based on your unique situation and their professional judgment.
B. Adjustments in Dosage: Special Conditions and Considerations
The dosage of alfacalcidol might require adjustments in some situations. It's essential to consider factors like the patient's health condition, any existing medical conditions, and the use of other medications. In patients with liver dysfunction, starting with an initial dose may be necessary due to difficulties in converting alfacalcidol into its active form. For individuals with a history of kidney stones or cardiac disease, close monitoring and potential dose adjustments are crucial to prevent calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). Additionally, dosage adjustments may also be required when alfacalcidol is used alongside medications, like thiazide diuretics, that can raise calcium levels in the body.
C. Administration Guidelines: Ensuring Maximum Effectiveness
To ensure results, it is essential to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional when taking alfacalcidol. Typically it is taken once a day. You have the option to take it with or without food. However, taking it alongside a meal can help improve its absorption. Sticking to the dosage and avoiding adjusting or stopping the medication without consulting your healthcare provider is essential.
VII. Careful Administration of Alfacalcidol
A. Necessity of Regular Monitoring: Calcium and Phosphate Levels
Monitoring plays a role in the effectiveness of alfacalcidol treatment. Conducting blood tests to measure calcium and phosphate levels in the bloodstream is essential. These tests should be done initially during the adjustment phase and at intervals during maintenance therapy. Consistent monitoring helps prevent the occurrence of hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia ( phosphate levels) by enabling healthcare providers to adjust the alfacalcidol dosage as necessary.
B. Response to Treatment: Timely Adjustments
Since patients can have varying responses to alfacalcidol, it may be necessary to make adjustments in the dosage to achieve the desired effect while minimizing potential side effects. If serum calcium or phosphate levels become too high, reducing or temporarily stopping the alfacalcidol dosage is recommended until these levels return to normal. Afterward, the dosage can be resumed at a station. Therefore maintaining communication between the patient and healthcare provider is crucial to ensure a safe and effective treatment.
VIII. Special Populations and Alfacalcidol Administration
A. Elderly Patients: Adjustments and Precautions
Due to decreased kidney function in elderly patients, beginning with a lower dose of alfacalcidol may be necessary. This is because the drug's activation and excretion can be affected. Furthermore, elderly individuals might be more prone to experiencing side effects such as hypercalcemia. Consequently, monitoring and adjusting the dosage for this particular population is crucial.
B. Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risk vs Benefit
Alfacalcidol should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks to the baby. While studies on animals have not indicated any harm to the fetus, there is a lack of research on pregnant women. We are unsure if alfacalcidol is excreted in human breast milk. Since many medications can be passed through breast milk, it is advised to exercise caution when administering alfacalcidol to a nursing mother.
C. Administration in Children: Dosage and Precactions
Regarding children, the dosage of alfacalcidol should be tailored based on their weight, age, and overall condition. Just like with adults, it's essential to keep an eye on their blood's calcium and phosphate levels to avoid any issues with calcium or phosphate. It's especially crucial to be cautious when using alfacalcidol in infants and young kids since they may be more sensitive to the effects of having too much calcium. Parents and caregivers should also be informed about the signs that indicate calcium levels, such as difficulties with eating, throwing up, constipation, and weight loss.
IX. Potential Interactions with Alfacalcidol
A. Medication Interactions: Commonly Used Drugs
Interactions between drugs can impact how medications work and potentially lead to an increased risk of side effects. Regarding alfacalcidol, there are a few interactions that healthcare professionals and patients should be aware of. For example, taking thiazide diuretics at the time as alfacalcidol can raise the risk of hypercalcemia because they both affect calcium absorption. Additionally, if someone with hypercalcemia is also taking Digitalis or other cardiac glycosides for heart conditions, their toxicity levels may increase. Another thing to remember is that cholestyramine, a medication used to lower cholesterol levels, can decrease the absorption of alfacalcidol and thus reduce its effectiveness.
B. Nutritional and Lifestyle Interactions
Apart from medications, nutrients, and lifestyle factors can impact alfacalcidol. Consuming in quantities alongside alfacalcidol, foods, and supplements high in calcium or vitamin D can increase the risk of hypercalcemia. Additionally, it's worth noting that alcohol and tobacco, known to affect bone health, might reduce the effectiveness of alfacalcidol. To ensure the treatment results, patients should talk with their healthcare provider about their dietary habits and lifestyle choices.
X. Recognizing and Managing Side Effects
A. Common Side Effects of Alfacalcidol: Identification and Management
Like any medication, alfacalcidol can have side effects. However, it's important to note that not everyone will experience them. Some reported side effects include hypercalcemia, which can cause constipation, decreased appetite, increased thirst, and frequent urination. Nausea, headaches, and skin rashes are also frequently mentioned. If any of these effects persist or worsen, you must inform your healthcare provider.

B. Less Common but Serious Side Effects: Awareness and Response
Occasionally although not often, alfacalcidol may cause some more severe side effects. These can include changes in urine output, unexpected weight loss, and ongoing diarrhea or vomiting. These symptoms could indicate underlying health problems like kidney issues or gastrointestinal disorders. It is essential to seek immediate medical help if they occur. Patients must be aware of these side effects in order to identify them and receive appropriate treatment quickly.
XI. Contraindications for Alfacalcidol Use
A. Conditions and Situations to Avoid Alfacalcidol
Alfacalcidol should not be used in conditions and situations. These include being allergic to alfacalcidol or any of its components and having diseases linked to high calcium levels or signs of vitamin D overdose. Patients with kidney problems and those prone to developing kidney stones should also refrain from using alfacalcidol due to the increased chances of experiencing elevated calcium levels and forming calcium stones.
B. Understanding Hypercalcemia: A Major Contraindication
Excessive calcium levels in the blood, known as hypercalcemia, can pose an issue when using alfacalcidol. This condition is usually detected through laboratory tests and can manifest with symptoms like fatigue, depression, muscle weakness, abdominal discomfort, and increased urination. If left untreated, hypercalcemia can lead to health complications such as kidney stones, bone pain, and heart issues. Therefore, patients undergoing alfacalcidol treatment must have their serum calcium levels regularly monitored.
XII. Alfacalcidol Overdose: Signs and Treatment
A. Identifying Symptoms of Overdose
While alfacalcidol is generally safe when taken as directed, it is possible to overdose on it by consuming amounts, whether intentionally or accidentally. Signs of an overdose usually manifest as hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by elevated calcium levels in the blood. Some common symptoms that may indicate an overdose include; Feeling extremely thirsty and urinating, Experiencing constipation or abdominal pain, Feeling tired or weak, Experiencing nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite, Having muscle or bone pain, Feeling confused or unable to concentrate, Unexpected weight loss If you notice any of these symptoms in yourself or someone else and suspect an alfacalcidol overdose it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
B. Response and Management
Treating an overdose of alfacalcidol mainly involves addressing the condition of high calcium levels and its associated symptoms. In severe instances, it may be necessary for the patient to be hospitalized. Initially, measures may include discontinuing alfacalcidol and any other sources of vitamin D or calcium, increasing intake to help eliminate excess calcium from the body, and administering medications that can lower blood calcium levels. If the condition. It becomes life-threatening, and more aggressive treatments like dialysis may be required. The recovery process from an overdose depends on how severe the symptoms are and the patient's overall health status.
XIII. Alfacalcidol Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Best Practices for Storing Alfacalcidol
Storing alfacalcidol is essential to ensure it works well and stays safe. Keep alfacalcidol in a dry spot at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Ensure it's out of reach and sight of kids so they don't accidentally take it. And be careful not to store it in places like bathrooms or kitchens since moisture can ruin the medication.
B. Safe Handling Measures
Like any medication, it is essential to handle alfacalcidol with care. Remember to wash your hands after touching the drug to prevent any contamination. Avoid touching the medicine with your hands or placing it on unclean surfaces. It's crucial not to open, crush or chew alfacalcidol capsules; instead, swallow them whole with a glass of water. Lastly, make sure not to use the medication beyond its expiration date. If you notice any changes in color, cloudiness, or particles in the medicine, it is best not to use and dispose of it properly.
XIV. Important Warnings Related to Alfacalcidol Use
A. Specific Risks and Warnings
Despite the benefits that alfacalcidol offers in terms of therapy, there are a few important considerations for both medical professionals and patients. One major concern is the possibility of experiencing hypercalcemia, which can show symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, nausea, and kidney stones. To manage this risk, it's crucial to monitor calcium levels in the blood during alfacalcidol treatment. If someone has a known sensitivity to alfacalcidol or its components, it's best to avoid using it. Individuals with kidney disease or conditions that can cause hypercalcemia should also refrain from taking alfacalcidol.
B. Long-Term Use: Potential Complications
Regular monitoring is crucial when using alfacalcidol for a period. This is because there is a risk of developing hypercalciuria and potential kidney stone formation. Prolonged use may cause hypercalcemia, leading to calcification in blood vessels and organs, potentially damaging the heart and kidneys. It's important to have checkups and blood tests to detect any complications early on and promptly make necessary medication dosage adjustments.
XV. Conclusion: Integrating Alfacalcidol into Effective Medical Care
A. Summarizing the Role and Importance of Alfacalcidol
Alfacalcidol, a form of vitamin D, has proven to be a valuable treatment option for various bone-related conditions like osteoporosis and renal osteodystrophy. Its role in maintaining calcium balance and promoting bone metabolism is an important therapeutic agent. However, it is crucial to administer it regularly, monitor the calcium levels in the blood, and consider patient-specific factors such as age and any other existing medical conditions.
B. Future Directions for Alfacalcidol Research and Use
Although the advantages of alfacalcidol have been extensively documented, scientists are still conducting research to uncover potential uses and impacts. Recent studies indicate that vitamin D analogs, such as alfacalcidol, may have a role in treating diseases, specific types of cancer, and cardiovascular conditions. Further exploration in these areas could broaden the range of applications for alfacalcidol. Nevertheless, regardless of discoveries ensuring patient safety and implementing personalized treatment strategies will always be paramount when administering alfacalcidol.
Alfacalcidol FAQ
- Alfacalcidol vs Calcitriol?
- Alfacalcidol uses?
- What is Alfacalcidol?
- Alfacalcidol in USA?
- Why is Alfacalcidol given in renal failure?
- What is Alfacalcidol 0.25.mcg?
- Alfacalcidol for Vitamin D deficiency?
- Alfacalcidol used for?
- Alfacalcidol 1 mcg to IU?
- Alfacalcidol USA?
- Vitamin D Alfacalcidol?
- Is Alfacalcidol the same as Calcitriol?
- Alfacalcidol vs Cholecalciferol?
- Alfacalcidol vs Vitamin-D3?
- Alfacalcidol vs Calcitriol in CKD?
- Alfacalcidol vs Calcitriol equivalent dose?
- Alfacalcidol vs Cholecalciferol dose?
- Alfacalcidol vs Vitamin D?
- Alfacalcidol and Calcium capsule?
- Alfacalcidol and Calcitriol?
- Alfacalcidol and Calcium?
- Alfacalcidol and Cholecalciferol?
- Alfacalcidol and Cholecalciferol together?
- Alfacalcidol and Vitamin D3?
- Alfacalcidol vs Cholecalciferol in CKD?
- Alfacalcidol tablet uses?
- Alfacalcidol tablet?
- Alfacalcidol trade name?
- Alfacalcidol Theramex?
- Alfacalcidol hypoparathyroidism?
- Alfacalcidol dosage?
- Alfacalcidol renal failure?
- Alfacalcidol BNF?
- Alfacalcidol Bon-One uses?
- Alfacalcidol Bon One?
- Alfacalcidol buy?
- Alfacalcidol Wirkstoff?
- Alfacalcidol Wikipedia?
- Alfacalcidol equivalent Vitamin D?
- Alfacalcidol Vitamin D deficiency?
- Alfacalcidol generic name?
- Alfacalcidol oral drops?
- Alfacalcidol One Alpha?
- Alfacalcidol osteoporosis?
- Alfacalcidol over the counter?
- Alfacalcidol dose?
- Alfacalcidol drops?
- Alfacalcidol dose Medscape?
- Alfacalcidol drug?
- Alfacalcidol dose in renal failure?
- Alfacalcidol dose in pediatric?
- Alfacalcidol capsules?
- Alfacalcidol capsules 0.25 mcg?
- Alfacalcidol capsules uses?
- Alfacalcidol capsules 0.25 mcg uses?
- Alfacalcidol capsules 0.25mcg price?
- Alfacalcidol class?
- Alfacalcidol Calcitriol?
- Alfacalcidol capsules 0.25mcg side effects?
- Alfacalcidol Calcium?
- Alfacalcidol composition?
- Alfacalcidol side effects?
- Alfacalcidol soft capsules?
- Alfacalcidol soft gelatin capsules 0.25 mcg?
- Alfacalcidol soft gelatin capsules?
- Alfacalcidol SPC?
- Alfacalcidol pediatric dose?
- Alfacalcidol price?
- Alfacalcidol pret?
- Alfacalcidol Germany?
- Alfacalcidol indication?
- Alfacalcidol injection?
- Alfacalcidol in renal failure?
- Alfacalcidol in pregnancy?
- Alfacalcidol mechanism of action?
- Alfacalcidol mode of action?
- Alfacalcidol MSDS?
- Alfacalcidol medicine?
- Alfacalcidol alternatives?
- Alfacalcidol 0.25 mcg?
- Buy Alfatradiol?
- Buy Alfacalcidol online?