Naproxen
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Naproxen
- III. Uses of Naproxen
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Naproxen
- V. How Naproxen Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Naproxen
- VII. Side Effects of Naproxen
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications of Naproxen
- IX. Special Considerations for Naproxen Administration
- X. Overdose and Handling Precautions of Naproxen
- XI. Storage Guidelines for Naproxen
- XII. Important Precautions while Using Naproxen
I. Introduction
A. Brief Overview of Naproxen
Naproxen is a well-known nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) widely used in medicine. It has been proven to effectively manage pain and inflammation, making it a valuable medication. Additionally, it relieves various conditions that contribute to patient discomfort and inconvenience.
B. Historical Background of Naproxen
The pharmaceutical company Syntex initially introduced Naproxen as a prescription drug in 1976. Its safety and effectiveness led to the FDA's approval for over-the-counter sale in the United States in 1994.
C. Why Naproxen is Prescribed
To bring relief from ailments like arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, bursitis, and tendonitis, Naproxen is primarily prescribed. Its crucial function is curbing the production of certain substances that instigate inflammation and cause pain. By doing so, it successfully grants patients much-desired comfort.
II. Composition of Naproxen
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Naproxen contains the active ingredient known as the titular compound derived from propionic acid. The chemical structure of Naproxen is composed of a six-membered ring and a five-membered ring, with a carboxyl group (COOH) and a methyl group (CH3). This specific arrangement allows Naproxen to effectively inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, namely COX 1 and COX 2. That plays a role in generating inflammatory substances within the body.
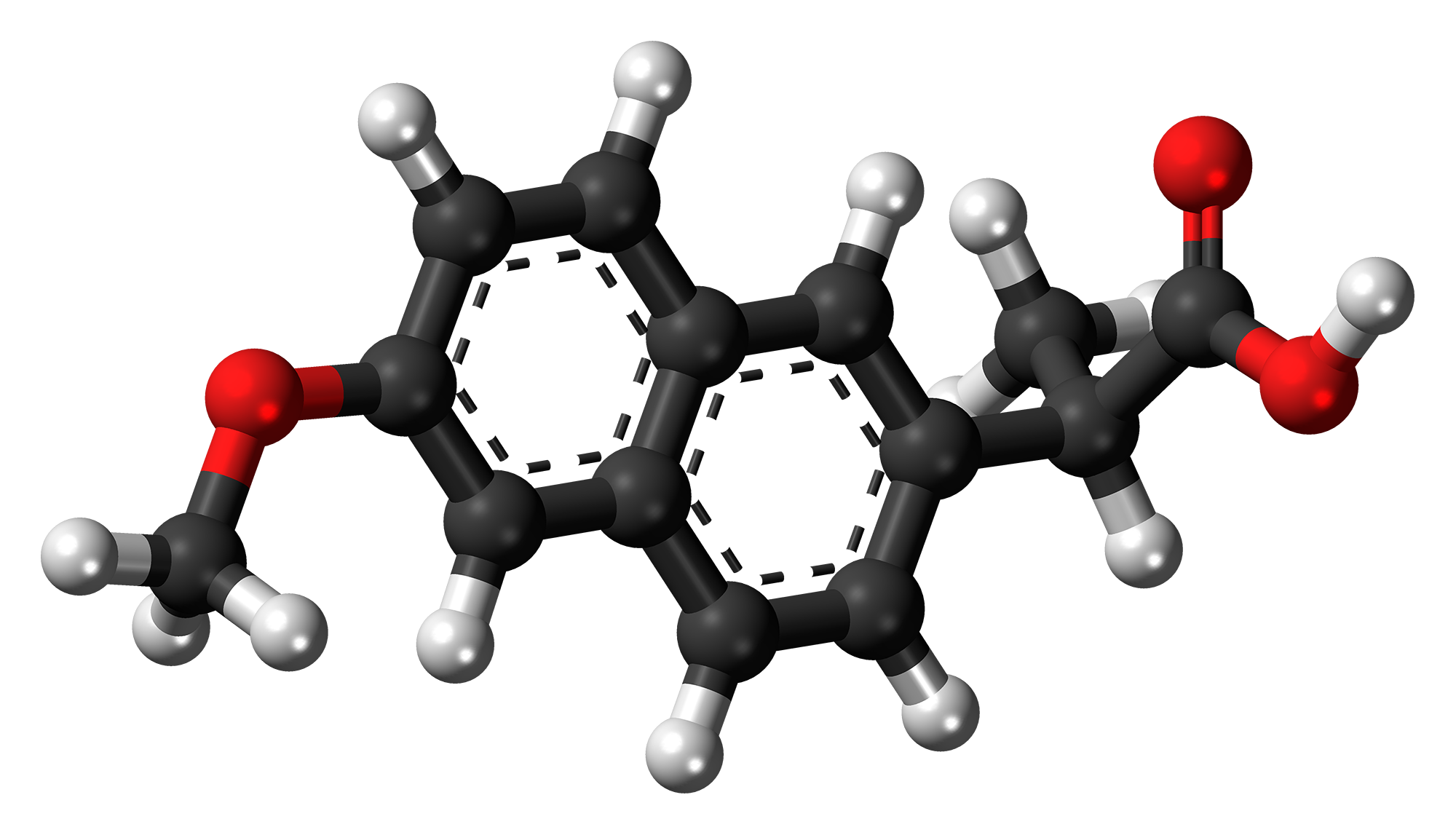
B. Active and Inactive Ingredients
Naproxens' active ingredient is Naproxen itself. As previously mentioned. This compound directly interacts with the body to produce its therapeutic effects. On the other hand, inactive ingredients, referred to as excipients, do not possess any therapeutic effects. Instead, they aid in drug delivery, improve stability and enhance the patient experience. Excipients may include fillers, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, and coating agents. It is important to note that their specific composition can vary depending on the manufacturer.
III. Uses of Naproxen
A. Standard Uses in Medical Practice
Naproxen, a widely used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is extensively utilized in numerous medical situations. It is commonly prescribed for conditions that involve both pain and inflammation, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout attacks, tendinitis, and bursitis.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
B. How Naproxen Relieves Pain and Inflammation
Naproxen's remarkable ability to alleviate pain and inflammation is primarily attributed to its ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX 1 and COX 2). These enzymes are responsible for producing prostaglandins. Lipid compounds are crucial in triggering pain and inflammation by reducing their production. Naproxen effectively reduces pain and inflammation.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
C. The Role of Naproxen in Managing Arthritis Conditions
Both rheumatoid and osteoarthritis involve an excess production of prostaglandins that causes inflammation, pain, and joint damage. Naproxen inhibits prostaglandin production, consequently alleviating these symptoms and improving patient mobility. Consequently enhancing their quality of life significantly. These reasons highlight why naproxen has established itself as a pivotal treatment option for arthritis.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
IV. Off-Label Uses of Naproxen
A. Use in Migraine Management
While Naproxen is not primarily indicated for this purpose, it has been proven effective in managing migraines as a preventive measure. It can help decrease the frequency and severity of migraine attacks. It offers respite to individuals burdened by debilitating headaches.
Here are some references for you:
2. Cochrane
3. Drugs.com
B. Application in Menstrual Pain Control
Naproxen has established itself as an effective solution for relieving menstrual pain called dysmenorrhea. Its ability to suppress the production of prostaglandins helps reduce the intensity of uterine contractions, which are the leading cause of discomfort during menstruation, as a result. It provides significant relief for those experiencing such pain.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
2. Mayo Clinic
3. AAFP
4. Drugs.com
C. Other Non-Standard Uses
Naproxen, known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, has proven helpful in acute muscle strains and sprains, toothaches, and post-surgical pain management.
Here are some references for you:
2. Mayo Clinic
3. NHS
V. How Naproxen Works
A. Naproxen's Mechanism of Action
Naproxen functions by impeding the activity of COX enzymes, which play a crucial role in converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. This inhibitory action on COX Naproxen disrupts the normal pathway resulting in decreased levels of prostaglandins. Consequently, this helps alleviate inflammation and pain.
B. Its Role in the Inflammatory Response
The body's defense against injury or infection involves a complex series of actions known as the inflammatory response. It is worth mentioning that when this response goes unchecked, it can result in both tissue damage and discomfort. As such, Naproxen becomes invaluable thanks to its ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins—critical players in inflammation—a feature that positions it as an indispensable modulator within this intricate mechanism.
C. Understanding the Pain-Relief Process
Pain is a symptom that arises from various conditions is frequently associated with inflammation and injury to tissues. Prostaglandins have the capacity to magnify the responsiveness of pain receptors thereby intensifying their reaction to stimuli. Naproxen on the other hand has the ability to diminish the levels of prostaglandins in the body. Consequently diminishing the sensitivity of these pain receptors and resulting in a significant reduction in perceived pain.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Naproxen
A. General Dosage Guidelines
The appropriate dosage of Naproxen depends on factors such as the patient's medical condition, age, and response to treatment. In cases of arthritis, the typical initial adult dose is approximately 500 1000 mg per day divided into 1 2 doses. However, it is essential to follow the prescribing physicians' instructions at all times.
B. Dosage Adjustments in Specific Conditions
Patients afflicted with kidney or liver impairment ought to receive a smaller dosage of Naproxen, considering their diminished ability to effectively process and eliminate the medicinal substance. Similarly, older individuals characterized by reduced physiological viability should be subjected to lower doses to curtail any likelihood of unfavorable repercussions.
C. Proper Administration Techniques
Taking Naproxen concurrently with food is highly advised to decrease the likelihood of encountering gastrointestinal discomfort. The tablets should be swallowed whole without crushing, chewing, or dissolving them. When utilizing the suspension variant of this medication, ensuring uniformity by vigorously shaking the bottle before every usage becomes imperative.
VII. Side Effects of Naproxen
A. Understanding Common Side Effects

Although Naproxen is known to be generally well tolerated, it is important to note that specific individuals may encounter adverse effects, including but not limited to nausea, vomiting, heartburn, headache, and dizziness.
B. Differentiating Between Mild and Severe Side Effects
Although most individuals only experience mild side effects. It is important to note that certain patients may encounter more severe ones that necessitate prompt medical attention. These severe side effects encompass intense abdominal pain, impaired hearing, unexplained weight gain, and indications of kidney issues (such as alterations in urine output).
C. What to Do If Side Effects Occur
Should you experience any undesirable effects. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider promptly. They may opt to make necessary adjustments in your dosage or medication regimen or implement alternative measures to effectively address and mitigate these side effects.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications of Naproxen
A. Comprehensive List of Contraindications
Individuals who have a known hypersensitivity to Naproxen should refrain from its use. Moreover, those with a history of severe allergic reactions to aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ought to avoid Naproxen. Additionally, individuals who currently have active or recent gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcer should not take this medication. Lastly, Naproxen is contraindicated in individuals with severe heart failure.
B. Potential Drug and Food Interactions
It is important to note that Naproxen has the potential to interact with various other medications, including anticoagulants, other NSAIDs, and specific blood pressure medicines. This interaction can alter these medications' effectiveness or even increase the chances of experiencing side effects. Additionally, it is essential to be aware that consuming alcohol while using Naproxen can elevate gastrointestinal bleeding risk. To ensure your safety and well-being. It is always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider before initiating any new medication.
C. Warning Signs to Watch for While Taking Naproxen
If signs such as chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurred speech arise while on the Naproxen medication regime, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Such symptoms can serve as potential indicators of severe and life-threatening conditions, including heart attack or stroke.
IX. Special Considerations for Naproxen Administration
A. Administration to the Elderly
It is important to note that the elderly population may be more susceptible to the effects of Naproxen and therefore. It may be necessary to administer lower doses. It is crucial to closely observe these patients for any indications of kidney or gastrointestinal issues.
B. Usage in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
While considering the use of Naproxen during pregnancy. Utmost caution should be exercised and only be employed when absolutely necessary. It is crucial to note that administering Naproxen in the last trimester has been found potentially harmful to fetal development. For nursing mothers, there exists a likelihood of transfer of Naproxen into breast milk hence warranting careful consideration before use.
C. Pediatric Use and Considerations
Although Naproxen can be prescribed to children for specific conditions, such as juvenile arthritis, it must be administered under the careful guidance of a healthcare professional. The dosage should be carefully determined based on the child's weight and age to ensure its safe usage.
D. Careful Administration to Patients with Specific Conditions
Suppose someone has pre-existing health issues such as heart disease, liver disease, kidney disease, or an experience with stomach ulcers. They should adopt cautiousness while contemplating using Naproxen since it can potentially exacerbate these conditions. Ensuring regular scrutiny under a healthcare provider's supervision is crucial to maintain their well-being and mitigate potential risks.
X. Overdose and Handling Precautions of Naproxen
A. Recognizing Symptoms of Naproxen Overdose
Overdosing on naproxen can lead to severe health complications. It is crucial to promptly identify the symptoms as they can significantly impact the outcome. These symptoms may include severe stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, or lethargy, dizziness, fainting, and slow or difficult breathing.
B. Emergency Procedures and Antidotes
If there is suspicion of an overdose, it is imperative to seek emergency medical assistance promptly. At the same time, there is no specific antidote for Naproxen. Healthcare professionals can offer vital supportive care, such as administering activated charcoal to minimize the absorption of the drug and considering dialysis for severe instances.
C. Precautions in Handling and Storing Naproxen
To uphold an environment that ensures children's safety. Take care by keeping Naproxen concealed and away from their reach. To preserve its potency efficiently. Store this medication at room temperature while preventing exposure to extreme heat or direct sunlight. Be mindful not to place it inside bathrooms as an alternative location would be more suitable. Properly sealing the container when Naproxen is not in use is imperative. Lastly, when disposing of this medication, remember that doing so through wastewater or household garbage can potentially harm the environment.
XI. Storage Guidelines for Naproxen
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain the quality of Naproxen, it is recommended to store it at a temperature ranging from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Keeping it away from excessive heat and moisture is essential as storing it in such conditions may lead to its deterioration. Additionally, it is advisable not to store this medication in a bathroom due to the high humidity. To ensure its effectiveness. It should be stored in its original packaging until the scheduled time for consumption.
B. Handling and Disposal of Expired Naproxen
Prioritizing your safety and well-being entails refraining from expired medications due to their diminished effectiveness and potential risks. When dealing with expired, Naproxen, kindly adheres to the appropriate procedures established by your local guidelines for disposing of medications or consider participating in a take-back program. It is imperative to note that flushing Naproxen down the toilet must only be undertaken if expressly directed.
C. Safeguarding Naproxen From Children and Pets
For safety purposes, it is imperative to securely store Naproxen in an area that children and pets cannot access or see. In the event of unintentional ingestion by either a child or pet. Seeking immediate emergency aid should be prioritized.
XII. Important Precautions while Using Naproxen
A. Precautions with Long-Term Use
Using Naproxen for a prolonged period can heighten the chances of experiencing severe cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes, especially in individuals with existing risk factors. When faced with such circumstances, it is crucial to receive regular checkups and diligent monitoring from a healthcare professional. Furthermore, long-term use of this medication may also lead to the development of gastric ulcers and kidney complications, among other health issues.
B. Interaction with Other Medications and Substances
It is crucial to always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are presently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements. This is because Naproxen may interact with these substances, potentially leading to adverse effects. Additionally, it is essential to note that consuming alcohol and tobacco while taking Naproxen can increase the risk of experiencing stomach bleeding.
C. Lifestyle Changes to Consider While Using Naproxen
Patients who are using Naproxen should take into consideration making changes to their lifestyle. These changes include reducing the consumption of alcohol and refraining from smoking, and maintaining a balanced diet to prevent stomach issues. Additionally, regular exercise can contribute to better overall health and well-being, potentially enhancing the patient's response to the medication.