Pilocarpine
- I. Introduction to Pilocarpine
- II. Composition and Chemical Structure of Pilocarpine
- III. How Pilocarpine Works
- IV. Clinical Uses of Pilocarpine
- V. Dosage and Administration of Pilocarpine
- VI. Pilocarpine Interactions
- VII. Common and Rare Side Effects of Pilocarpine
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications for Pilocarpine Use
- IX. Careful Administration of Pilocarpine
- X. Overdosage and Emergency Management
- XI. Pilocarpine Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Pilocarpine: Understanding the Important Precautions
I. Introduction to Pilocarpine
A. Brief Overview of Pilocarpine
Pilocarpine, an alkaloid that mimics the nervous system, has significant pharmacological characteristics. It is obtained from species within the Pilocarpus family with a primary focus on Pilocarpus microphyllus. This plant thrives naturally in Central and South America.
B. Historical Background and Development
Pilocarpine has been in use since the 1800s. The name comes from the words 'pilos which means ball and 'karpus which means fruit, referring to how the plant looks. Its beneficial effects were found when eye specialists started using it as a treatment for glaucoma acting as an agent. Eventually, it was artificially produced in labs. Became widely accessible for medical applications.
C. Pilocarpine's Significance in the Medical Field
Pilocarpine has proven its worth in the field over the years. Its robust safety record and effectiveness as a treatment make it an essential tool for managing conditions like glaucoma and xerostomia. It remains a subject of research in pharmacology with researchers exploring its potential uses beyond its approved applications.
II. Composition and Chemical Structure of Pilocarpine
A. Chemical Components and Formula
Pilocarpine, which is a compound with a chemical formula of C11H16N2O2 is a sophisticated tertiary amine structure. This small and flexible molecule can interact with receptor sites in the body thanks to its distinct adaptability in shape.
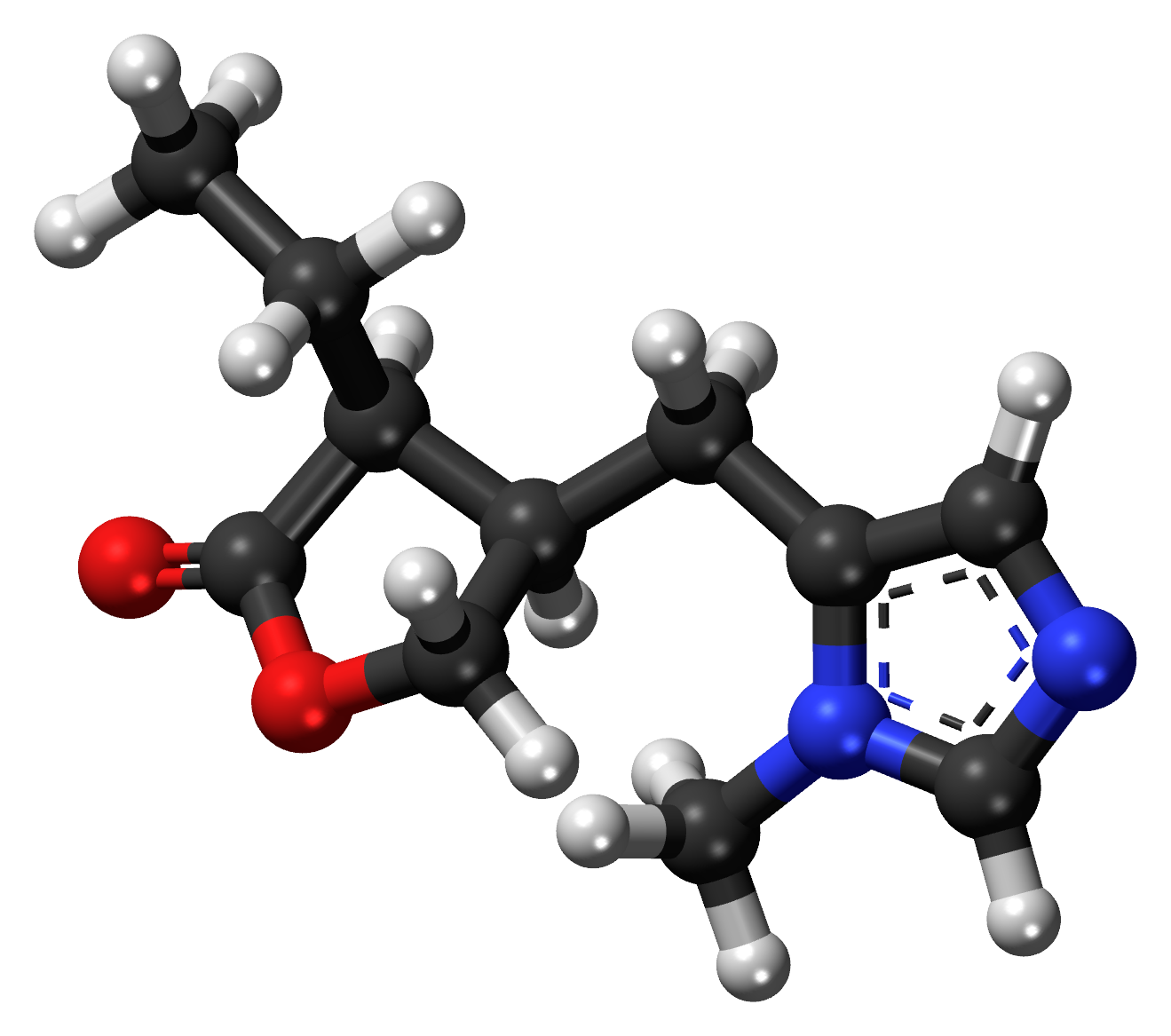
B. Synthesis and Production
Obtained initially from plants belonging to the Pilocarpus genus the synthesis of pilocarpine has undergone advancements. Nowadays the production of pilocarpine involves procedures, for extraction, isolation, and purification. This results in a stable compound that can be efficiently utilized in different pharmaceutical formulations.
C. Biological Properties
The distinctive structure of Pilocarpine gives rise to its biological properties. It acts as a stimulant for selective muscarinic receptors, contributing to its various physiological effects. These effects include the stimulation of exocrine glands resulting in increased secretion of saliva and sweat. Additionally,, it impacts specific eye conditions by causing pupil constriction or miosis. Moreover, it also plays a role in regulating heart rate and blood pressure through its interaction with cardiac muscarinic receptors.
III. How Pilocarpine Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Pilocarpine functions by imitating the actions of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Its primary mechanism involves attaching to and activating receptors that are present in the parasympathetic nervous system. This activation triggers a cascade of processes that ultimately produce the observed therapeutic effects in clinical settings.
B. Impact on the Nervous System
When pilocarpine connects with receptors it sets off a series of reactions in the parasympathetic nervous system. This results in responses such as increasing secretion in exocrine glands causing smooth muscle contraction, reducing heart rate and promoting movement in the gastrointestinal tract. These diverse effects on the system make pilocarpine an essential tool for treating numerous medical conditions.
C. Role in Saliva and Tear Production
The use of pilocarpine influences the production of saliva and tears. When it activates the receptors in the salivary and lacrimal glands it stimulates an increase in their secretion. This particular effect proves to be beneficial in cases like Sjögren's syndrome and xerostomia where the absence of saliva and tears can cause discomfort and potential complications.
IV. Clinical Uses of Pilocarpine
Approved Uses in Medicine
Glaucoma Treatment
Pilocarpine is a medication commonly used to reduce pressure inside the eye and treat different forms of glaucoma. It is also utilized to cause constriction of the pupil.
Here is a reference that you can use for your content:
Xerostomia Relief
Pilocarpine is commonly prescribed for managing xerostomia, a condition characterized by dry mouth, which can be caused by Sjogren's syndrome or as a side effect of radiation therapy used to treat head and neck cancer123.
Here is a reference that you can use for your content:
Off-label Uses
Cystic Fibrosis Management
Pilocarpine has been used to manage fibrosis even though it is not officially approved for this purpose1.
Here is a reference that you can use for your content:
Pupil Constriction in Diagnostic Procedures
Pilocarpine has been frequently employed for the purpose of constricting the pupils in procedures, although its usage is not officially approved for this particular indication1.
Here is a reference that you can use for your content:
V. Dosage and Administration of Pilocarpine
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
To ensure treatment, it is crucial to adjust the dosage of pilocarpine based on the patient's specific clinical condition. In the case of glaucoma, it is typically recommended to begin with one drop (1% to 4% solution) applied to the affected eye(s) three to four times daily. For xerostomia, a typical starting dose is usually 5 mg taken three times a day.
B. Different Forms of Pilocarpine
Pilocarpine is produced in formats to meet different medical requirements. It is available as eye drops primarily used for treating glaucoma. Oral tablets are commonly prescribed for managing the mouth associated with Sjögren's syndrome. Additionally, a gel formulation is occasionally employed in ophthalmological situations.
C. Instructions for Proper Administration
It is essential to follow the instructions given by a healthcare professional when using pilocarpine. When applying eye drops, look and avoid touching the eye or any surface with the dropper tip to prevent any potential contamination. If you are prescribed pilocarpine, take it as your physician advises, either with or without food. Lastly, do not discontinue the medication suddenly without consulting a healthcare provider.
VI. Pilocarpine Interactions
A. Interaction with Other Drugs
Pilocarpine has the potential to interact with types of medications which can affect how well it works or lead to undesired side effects. Some medicines might interact with pilocarpine. Are not limited to; drugs that have anticholinergic properties as they may counteract the effects of pilocarpine; beta blockers, which may increase the risk of bradycardia or a low heart rate; and medications used for Parkinson's' disease as they could interfere with pilocarpines effectiveness.
B. Dietary and Lifestyle Interactions
One's diet and lifestyle can influence the effectiveness of pilocarpine. A balanced diet promoting overall health can help improve the body's response to the medication. Additionally, engaging in exercise can have a positive impact as well. However, it is essential to note that certain lifestyle factors, such as stress, could potentially hinder the effects of pilocarpine.
C. Effects of Alcohol and Tobacco on Pilocarpine Efficacy
The use of alcohol and tobacco can affect how well pilocarpine works. These substances can affect the body, especially the nervous system, where pilocarpine has its action. Therefore it is advised to avoid or limit alcohol consumption and quit using tobacco while undergoing pilocarpine therapy.
VII. Common and Rare Side Effects of Pilocarpine
A. Common Side Effects and their Management
Pilocarpine may cause side effects, such as sweating, nausea, rhinitis, and diarrhea. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. If they continue or become bothersome, it's advisable to seek advice. It's important to note that the positive impact of pilocarpine typically outweighs these side effects.

B. Less Common and Rare Side Effects
Some uncommon adverse effects of pilocarpine may include; Breathing difficulties, heartbeats Severe allergic reactions Although these occurrences are rare, they require prompt medical attention.
C. Understanding the Risk-to-Benefit Ratio
Similar to any medication, the utilization of pilocarpine involves weighing its advantages and drawbacks. When deciding whether to prescribe pilocarpine, it is crucial to consider whether its potential benefits in managing a condition outweigh the potential risks of side effects. Therefore, patients must openly communicate with their healthcare providers regarding any concerns or discomforts they may experience during pilocarpine therapy.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications for Pilocarpine Use
A. Pre-existing Conditions and Pilocarpine Use
Patients who have pre-existing conditions should exercise caution when using pilocarpine. These conditions include asthma, cardiovascular disease, and gastrointestinal disorders. Additionally, individuals with a history of detachment or chronic bronchitis may require careful monitoring while undergoing pilocarpine therapy. It is always advisable to provide your healthcare provider with a medical history.
B. Drug Allergies and Sensitivity to Pilocarpine
If you have any allergies to pilocarpine or any of its ingredients, it is advised to refrain from using it. Allergic reactions may manifest as hives, breathing difficulties, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat. In case of a response, stop using pilocarpine and promptly seek medical assistance.
C. Specific Contraindications
Individuals with conditions including; 1 should not use pilocarpine. Acute. Inflammation of the iris. 2. Uncontrolled asthma. 3. Certain types of glaucoma such as angle closure glaucoma, without iridectomy.
IX. Careful Administration of Pilocarpine
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals may be more prone to experiencing the effects of pilocarpine and its side effects. As a result, it is crucial to monitor and adjust the dosage for these patients to ensure their safety and the effectiveness of their treatment.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
It is advisable to use pilocarpine during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks to the unborn baby. It is important to note that pilocarpine can be found in breast milk. Caution should be taken when administering it to breastfeeding mothers. It's always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss any risks and advantages.
C. Administration to Children
At present there isn't comprehensive research on the safety and effectiveness of pilocarpine, in children. As a result, it is advisable to exercise caution and ensure medical oversight when administering it to this age group.
X. Overdosage and Emergency Management
A. Signs and Symptoms of Pilocarpine Overdosage
An excessive amount of Pilocarpine can lead to symptoms, including low blood pressure, slow heart rate, stomach cramps, excessive sweating and drooling, difficulty in breathing, and, in severe cases, seizures, narrowing of the airways (bronchospasm), and irregular heartbeats (cardiac arrhythmias).
B. Immediate Steps and Medical Intervention
If someone overdoses on pilocarpine, it is essential to stop taking it and seek urgent medical help. The treatment for an overdose focuses on providing support and addressing the symptoms. In some cases, medications, like atropine, may be administered to treat bradycardia. It is worth noting that activated charcoal could potentially be given within an hour of ingestion to help reduce the absorption of the drug.
C. Prevention of Future Overdose Incidents
To prevent overdose, it is essential to educate patients on the proper dosage and timing of pilocarpine and emphasize the importance of not surpassing the prescribed amount. It is crucial to store the medication in a place inaccessible to children and vulnerable individuals. If a dose is missed, it should be taken promptly upon remembering. However, if it is close to the time for the scheduled dose, it is advisable to skip the missed one and resume with the regular dosing schedule. Under no circumstances should two doses be taken simultaneously to compensate for a missed dose.
XI. Pilocarpine Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Guidelines for Safe Storage
Store pilocarpine at room temperature, between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius away from direct sunlight and heat. Keep the medication in its packaging until you need to use it. Also, store pilocarpine where children and pets cannot access it to avoid accidental ingestion.
B. Handling Precautions and Safety Measures
When using pilocarpine significantly eye drops, it's essential to ensure your hands are clean and dry to avoid contamination. Avoid touching the tip of the dropper or letting it touch your eye or any surface. If the dropper gets contaminated, it could lead to an eye infection.
C. Proper Disposal of Unused or Expired Pilocarpine
Make sure to dispose of any pilocarpine you don't need or have adequately expired. It's important not to flush the medication down the toilet or pour it into the drain unless someone specifically tells you to do. Instead, take it back to a pharmacy that participates in a program for bringing back medicines or follow the disposal instructions provided on the packaging of the medication.
XII. Pilocarpine: Understanding the Important Precautions
A. Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Patients who are undergoing pilocarpine treatment should be closely observed. Regular appointments enable healthcare professionals to evaluate the medication's effectiveness and potential side effects and make any dosage adjustments. In some cases, individuals with glaucoma may need to undergo regular tests, such as monitoring their intraocular pressure.
B. Potential Lifestyle Adjustments
Patients prescribed pilocarpine may need to change their lifestyle to optimize the effectiveness of the medication and minimize any side effects. These adjustments could involve maintaining a balanced diet engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and practicing moderation when consuming alcohol. Furthermore, acquiring stress management techniques can also prove advantageous.
C. Importance of Adherence to Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Following the prescribed dosage and administration instructions is crucial when using pilocarpine therapy. Patients must take the medication as directed by their healthcare provider at the designated times each day. It is important not to discontinue or change the dosage without consulting a healthcare professional. Remember, pilocarpine therapy must be consistent and uninterrupted for it to be most effective.