Probenecid
- I. Introduction to Probenecid
- II. The Pharmacological Composition of Probenecid
- III. Detailed Explanation on How Probenecid Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Probenecid
- V. Off-Label Uses of Probenecid
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Probenecid
- VII. Special Administration Guidelines and Precautions
- VIII. Understanding Probenecid Side Effects
- IX. Probenecid Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Warnings and Contraindications for Probenecid Use
- XI. Management of Overdosage of Probenecid
- XII. Probenecid Storage Guidelines
- XIII. Important Precautions When Handling Probenecid
I. Introduction to Probenecid
A. Brief History of Probenecid
Probenecid, which emerged as a medical advancement in the mid-20th century, was initially created during World War II. The primary objective was to extend the healing benefits of penicillin and other antibiotics, which was particularly crucial during times of medical resources. Over time the uricosuric properties of Probenecid were acknowledged, leading to its application in treating gout and hyperuricemia.
B. Overview of Its Purpose and Function
Probenecid is a medication that helps the body excrete acid through urine, decreasing its levels. This is beneficial in managing gout and hyperuricemia. Additionally, it can enhance the practical effectiveness of antibiotics in situations where high antibiotic concentrations are needed to treat certain conditions.
II. The Pharmacological Composition of Probenecid
A. Chemical Components and Characteristics
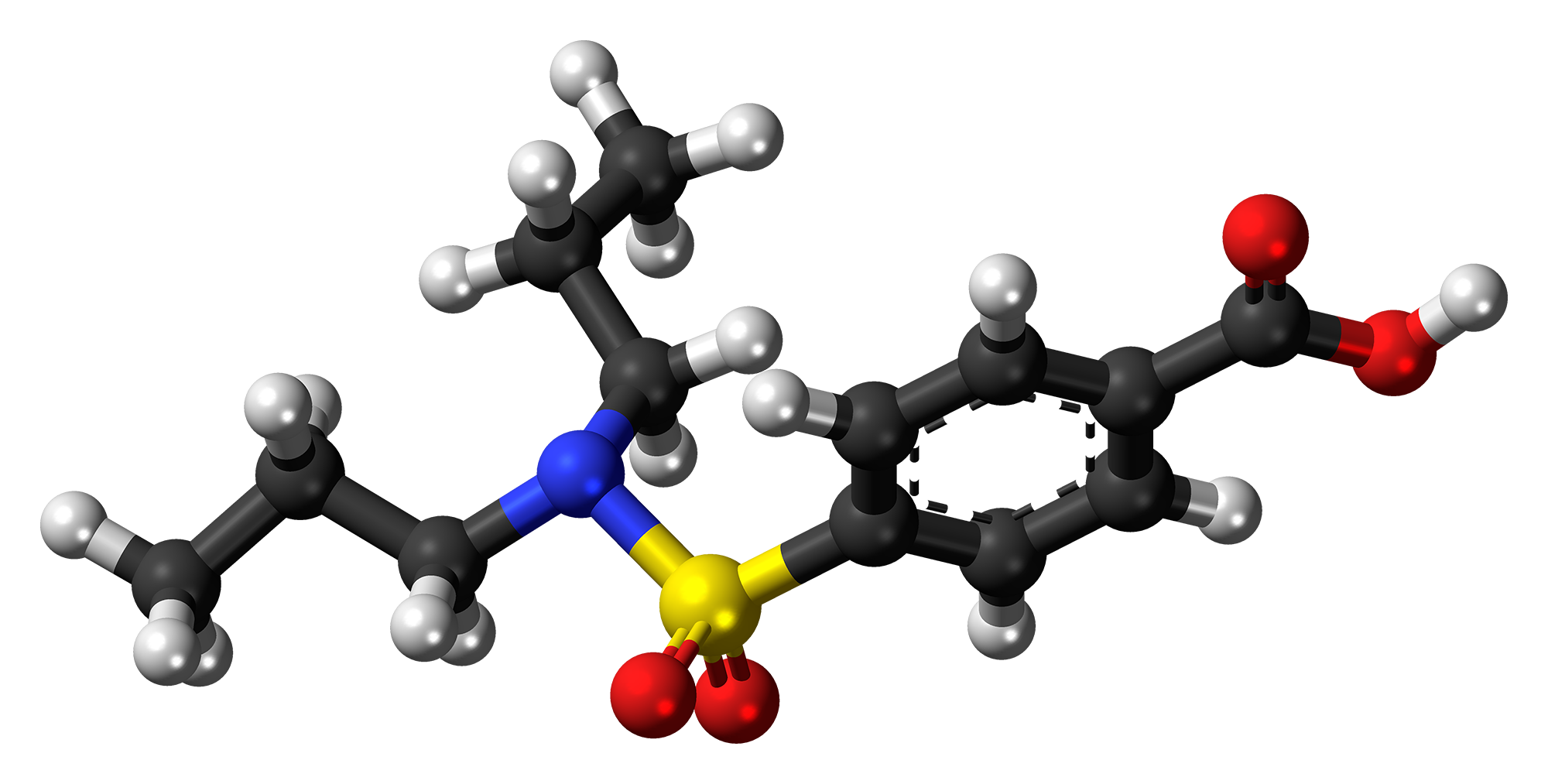
Probenecid, which is also referred to as four acid from a chemical standpoint, is an organic compound that consists of a benzene ring fused with both a carboxylic acid and a sulfonamide group. It presents itself as a powder that's either white or nearly white. The solubility of Probenecid depends on the medium it is placed in; it cannot dissolve in chloroform or ether. It can be dissolved in diluted alkaline and acidic solutions. The approximate molecular weight of Probenecid is 285.3 grams per mole.
B. Manufacturing Process and Standards
The production of Probenecid involves a series of chemical reactions, including condensation, cyclization, and sulfonation. The final product goes through quality control tests to guarantee purity, effectiveness, and safety. These tests adhere to pharmaceutical standards mandated by regulatory bodies like the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
III. Detailed Explanation on How Probenecid Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Probenecid works by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing acid. It does this by blocking a group of protein transporters called Organic Anion Transporters (OATs), OAT1, and OAT3 found in the renal tubular epithelium. When these transporters are inhibited, Probenecid reduces the amount of acid reabsorbed into the bloodstream from the renal tubule leading to increased excretion of uric acid in the urine.
B. Probenecid's Impact on the Body's Biochemical Processes
Probenecid, a medication that promotes acid excretion, plays a crucial role in regulating purine metabolism in the body. It helps control the levels of acid in the blood, improving symptoms of gout and preventing the formation of urate crystals. This medication can also affect how the kidneys handle substances and medicines due to its broad-ranging impact on organic anion transporters.
IV. Approved Uses of Probenecid
A. Treatment of Gout and Hyperuricemia
Probenecid is a medication that helps treat gout, a type of arthritis causing joint inflammation due to the buildup of urate crystals. Its main role is to enhance the elimination of acid through the kidneys, which helps reduce high levels of uric acid in the body and prevents the progression of gout. As a result, it aids in relieving inflammation and stops additional crystal formation123.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information on this topic:
- Probenecid (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic
- Probenecid Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
- Probenecid Treatment For Gout: Everything You Need To Know
- Probenecid: MedlinePlus Drug Information
B. Enhancement of Antibiotic Therapy
Initially, Probenecid was primarily used for its ability to extend the effectiveness of antibiotics. It does this by hindering the kidneys’ ability to eliminate these drugs, leading to antibiotic levels in the bloodstream and a longer duration of their effects. This characteristic proves valuable when treating severe infections that require elevated and sustained antibiotic levels, like meningitis and gonorrhea1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information on this topic:
- Probenecid Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
- Probenecid: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- Probenecid: Package Insert - Drugs.com
V. Off-Label Uses of Probenecid
A. Promising Potential in Treating Various Disorders
Over the years, researchers have been studying Probenecid for its uses in treating other health issues. For example, due to its impact on organic anion transporters, there is potential for it to affect neurotransmitter release and therefore play a role in managing certain neurological disorders. Additionally, there are suggestions that it could be helpful in conditions such as sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information on this topic:
- Probenecid Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
- Probenecid: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- Probenecid: Package Insert - Drugs.com
B. Current Research and Clinical Trials
Clinical trials aim to understand better the possible ways in which Probenecid can be used as a treatment. These trials are explicitly looking into its potential to protect against neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease, enhance muscle strength in individuals and effectively manage the symptoms of heart failure123.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information on this topic:
- Repurposing Probenecid for the Treatment of Heart Failure (Re … - Trials
- The MPTP/Probenecid Model of Progressive Parkinson’s Disease
- Parkinson’s Disease Drug Therapies in the Clinical Trial Pipeline: 2020
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Probenecid
A. Standard Dosage Recommendations
The typical starting dose of Probenecid for adults with gout or gouty arthritis is usually 250 mg taken twice a day. This dose can then be gradually increased based on how the patient responds, with a maintenance dose ranging from 500 mg to 2 g, per day. When using Probenecid alongside antibiotics, the dosage will vary depending on the antibiotic being used and the infection being treated.
B. Adjustment for Special Populations
Certain groups of people may need to have their dosage adjusted. If someone has kidney problems, it can impact how Probenecid works in their body, so the dose might need to be changed. When it comes to children, the dosage should be determined based on their weight and what condition they're being treated for. Like with any medication, it's essential to carefully consider the use of Probenecid in pregnant or breastfeeding women and weigh the possible benefits against any risks involved.
VII. Special Administration Guidelines and Precautions
A. Probenecid in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often have medical considerations due to the natural changes in their bodies as they age, including reduced kidney function that can affect how medications are processed. Therefore it is essential to use caution when giving Probenecid to this group of patients. It's advisable to start with a dosage and gradually increase it while closely monitoring potential adverse reactions.
B. Probenecid in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Probenecid should only be used in women when necessary and after carefully evaluating the balance between risks and benefits. Although animal studies have not definitively determined its safety during pregnancy, data is available from human studies. Since Probenecid can be found in human breast milk, it is essential to exercise caution when giving it to breastfeeding mothers due to the potential for adverse effects on nursing infants.
C. Probenecid in Pediatric Patients
Probenecid hasn't been thoroughly studied in children, so it's essential to be cautious in this age group. Adjust the dosage according to the child's weight and overall health condition. Regular clinical monitoring is crucial to ensure that the treatment is effective and safe.
VIII. Understanding Probenecid Side Effects
A. Common Side Effects Encountered
Like any other medication, Probenecid may have some side effects. People commonly experience gastrointestinal discomfort, which includes a loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. Sometimes individuals may also have headaches feel dizzy, or have hypersensitivity reactions, like developing a rash.
B. Potential Serious Side Effects and Risks
Sometimes there could be instances where more significant side effects may happen. These might include allergic reactions, sudden and intense gout attacks, issues with kidney function, or blood-related problems, like aplastic anemia. If any of these situations arise, seeking medical assistance is crucial.
IX. Probenecid Interactions with Other Medications
A. Drugs to Avoid While Taking Probenecid
Using Probenecid alongside medications may result in undesired drug interactions. For example, it can interfere with the effectiveness of drugs like Aspirin in reducing acid levels. Additionally, it can impact the elimination process of drugs such as Methotrexate, potentially causing concentrations in the blood and increasing the risk of toxicity.
B. Impact of Probenecid on the Efficacy of Other Drugs
Although Probenecid may affect the effectiveness of some medications, it can actually enhance the impact of other, antibiotics. It does this by inhibiting the secretion in the tubules leading to higher levels of antibiotics in the bloodstream and intensifying their effects. However, it is essential to be cautious when utilizing this interaction therapeutically due to the potential for increased toxicity associated with antibiotics.
X. Warnings and Contraindications for Probenecid Use
A. Medical Conditions that May Affect Probenecid Use
Before administering Probenecid, it is important to consider individuals with specific medical conditions. People with kidney problems or a history of kidney stones should be cautious because Probenecid can affect acid excretion. Likewise, patients who have experienced ulcer disease may face a higher risk of aggravating their condition due to potential stomach irritation caused by Probenecid.
B. When Probenecid Should Not Be Used
There are situations where Probenecid should not be used. These include patients who have a known sensitivity to Probenecid or its ingredients. It should also be avoided in people with blood disorders or kidney stones caused by acid. It is not recommended for children under the age of 2 or individuals with kidney problems that are already known.
XI. Management of Overdosage of Probenecid
A. Recognizing Symptoms of Overdosage
When someone takes much Probenecid, they may experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, or dizziness. In severe cases, they might have trouble urinating, notice blood in their urine (hematuria), or experience kidney pain. It's also possible for them to have gout attacks.
B. Emergency Care and Treatment
If an overdose happens, it is crucial to seek medical help. The treatment usually involves providing relief and supportive care. This may include using lavage to eliminate any unabsorbed medication and ensure sufficient hydration to encourage the excretion of the drug through urine. Monitoring patients for potential complications and taking necessary actions based on their clinical condition is essential.
XII. Probenecid Storage Guidelines
A. Optimal Storage Conditions for Probenecid
To maintain the effectiveness and strength of Probenecid, it is recommended to store it at room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Keep it away from moisture and direct light. Additionally make sure to keep the medication in its packaging until you're ready to use it as this helps protect it from any changes, in the environment.
B. Impact of Improper Storage on Probenecid's Efficacy
Improper storage conditions like exposure to temperatures, excessive moisture, or intense light can potentially degrade the quality of Probenecid. This can compromise its effectiveness as a drug and even cause changes in appearance or consistency. Therefore it is crucial to store the medication to ensure it remains potent and safe for use.
XIII. Important Precautions When Handling Probenecid
A. Safeguarding Against Accidental Exposure
When dealing with Probenecid it's essential to be cautious and avoid exposure, especially in people who aren't supposed to take the medication. For example, pregnant women or those who are hypersensitive to the drug should stay away from contact. Additionally, it's an idea to wash your hands before and after handling the medication to prevent unintentional swallowing or getting it in your eyes.
B. Disposal Guidelines for Unused or Expired Probenecid
It is essential to follow proper disposal methods to ensure the disposal of unused or expired Probenecid and prevent any accidental exposure or misuse. Avoid throwing it in the household trash or flushing it down the toilet. Instead, it would be best to consider returning it to a take-back program or following the regulations for its disposal. If you're unsure about the guidelines in your area, consult a healthcare professional or contact a local waste disposal company for appropriate instructions on how to dispose of it responsibly.