Valproate
- I. Introduction to Valproate
- II. Composition and Properties of Valproate
- III. How Valproate Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Valproate
- V. Off-label Uses of Valproate
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Valproate
- VII. Special Considerations in Administration
- VIII. Potential Side Effects of Valproate
- IX. Interactions of Valproate
- X. Warnings and Contraindications for Valproate
- XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XII. Handling Overdosage Situations
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Valproate
I. Introduction to Valproate
A. Brief Overview of Valproate
Valproate holds a role in the medical field, being a go-to treatment for neurologists and psychiatrists. Its anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing effects make it invaluable for managing psychiatric disorders, such as epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and sometimes even for preventing migraines. The effectiveness of this medication stems from its intricate and diverse mechanism of action, which is still not fully understood.
B. History and Development of Valproate
Valproates' path to becoming relevant traces back to 1962, when it initially received approval in France for managing epilepsy. Interestingly it was discovered by chance while being used as a solvent. Scientists observed its anticonvulsant properties, and this fortunate discovery marked the beginning of Valproate's journey in medical history. Since then, extensive research has been conducted, leading to its growing range of uses and applications, solidifying its position as a trusted presence in neuropharmacology.
II. Composition and Properties of Valproate
A. Chemical Structure and Characteristics
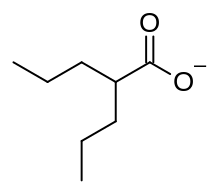
Valproate, also known as 2 propyls pentanoic acid, is a type of fatty acid with a structure. Its main structure consists of a backbone of acid, making it a derivative of valeric acid. Valproate is well known for its ability to control seizures effectively due to its broad spectrum capabilities. The lipophilic nature of valproate allows it to enter the nervous system (CNS) quickly.
B. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
The way valproate is processed in the body is quite interesting. When taken orally, it is quickly and fully absorbed in the tract. Once absorbed, it firmly attaches to proteins in the blood, leaving a small portion available in its free form. This free portion, responsible for its effects, readily crosses the brain's protective barrier and brings about its therapeutic benefits. Valproate is primarily broken down in the liver through a process known as beta and omega oxidation. It's important to understand that differences in these metabolic pathways among individuals can affect the drug levels in their blood, requiring monitoring. Usually, peak valproate levels in the bloodstream are reached between 1 to 4 hours after taking it. It has a life of approximately 9 to 16 hours, resulting in steady levels in the blood when taken twice a day. It should be noted that as the dosage increases, the rate at which valproate is eliminated from the body decreases due to its pharmacokinetic behavior.
III. How Valproate Works
A. Mechanism of Action
The way Valproate works is quite complex and not completely understood. It is believed to affect various channels, receptors, and enzymes, contributing to its wide range of effectiveness in clinical settings. Its primary actions involve enhancing the function of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, and interfering with T-type calcium channels. Each of these actions helps to control neuronal activity, which is often the cause of seizures and mood disorders.
B. Impact on Neurotransmission and Neural Activity
The impact of valproate on neurotransmission and neural activity is quite significant. It helps to enhance the effect of GABA, which slows down the firing of neurons. At the time, it blocks sodium channels, which helps prevent the spread of abnormal electrical activity often observed in seizure disorders. Furthermore, its influence on T-type calcium channels makes it effective in managing seizure types and neuropathic pain. All these effects combine to create a stable and less hyperactive environment for the neurons.
IV. Approved Uses of Valproate
A. Use in Epilepsy Management
Valproate is a medication that is commonly used to manage epilepsy. It falls under the category of drugs and works by lowering the occurrence of seizures in individuals with epilepsy. Valproate effectively treats seizure types, including absence, myoclonic, and generalized tonic-clonic1. The precise mechanism of action of valproate is unclear. Proposed mechanisms include affecting GABA levels, blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, and inhibiting histone deacetylases2. GABA is a neurotransmitter that aids in reducing the activity of nerve cells in the brain. Elevating GABA levels, valproate effectively minimizes the frequency of seizures experienced by individuals with epilepsy1.
Moreover, it is also utilized to address seizures in adults and children aged ten or above. Valproate is typically taken orally, either in tablet or capsule form. The specific dosage of valproate depends on the type of seizure being treated well as the age and weight of the patient. It’s crucial to adhere to the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when taking valproate1.
Here are some references that you can check out:
B. Role in Bipolar Disorder Treatment
Valproate is also prescribed for treating bipolar disorder, a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings encompassing manic and depressive episodes. It effectively addresses both the highs and lows experienced by individuals with bipolar disorder. Valproate functions by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain, including GABA and glutamate. This regulation helps achieve mood stabilization and alleviates symptoms associated with bipolar disorder1. The precise mechanism of action of valproate is unclear. Proposed mechanisms include affecting GABA levels, blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, and inhibiting histone deacetylases1.
The preferred valproate administration method is orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The specific dosage depends on the severity of the condition and factors such as the age and weight of the patient. Adhering to the prescribed instructions given by a healthcare professional is crucial when taking valproate1.
Here are some references that you can check out:
C. Utility in Migraine Prevention
Valproate is also prescribed for preventing migraines. Migraines are a type of headache that can cause pain, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. Valproate effectively reduces the frequency and intensity of migraines in individuals who experience them frequently. Valproate works by regulating chemical messengers in the brain, such as GABA and glutamate. This regulation helps decrease the occurrence and severity of migraines.
Typically valproate is taken orally, either in tablet or capsule form. The dosage relies on the severity of migraines and the patient’s age and weight. It’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when taking valproate.
Here are some references that you can check out:
V. Off-label Uses of Valproate
A. Potential in Schizophrenia Management
Valproate is a prescribed medication for treating epilepsy and bipolar disorder. Researchers have discovered that it might also have benefits in managing schizophrenia. Some studies indicate that valproate can potentially alleviate the intensity of symptoms associated with schizophrenia, like delusions and hallucinations. Moreover, it impacts cognitive function and may help reduce negative symptoms such as social withdrawal and apathy. While further research is still necessary to comprehend the extent of valproates’ benefits in managing schizophrenia, these initial findings are encouraging and suggest that it could be a valuable addition to the existing treatment options.
Here are some references that you can check out:
B. Exploration in Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Alzheimer’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions worldwide, currently lacks any definitive cure or method to stop its progression. However, some evidence indicates valproate’s usefulness in managing the disease. Certain studies have shown valproate can alleviate the severity of Alzheimer’s symptoms like agitation and aggression. Furthermore, it may also aid in improving function and reducing the risk of falls in older individuals with dementia.
While further research is necessary to comprehend the benefits valproate may offer for treating Alzheimer’s, these initial findings are quite promising, suggesting it could be a valuable addition to the current treatment options.
Here are some references that you can check out:
C. Potential Role in Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain is a condition that impacts millions of people worldwide. Although there are treatments currently accessible for managing chronic pain, there is some evidence indicating that valproate might be effective in reducing pain severity and enhancing the quality of life for individuals grappling with chronic pain. Some studies have discovered that valproate has the potential to mitigate pain intensity and enhance the quality of sleep among patients with pain. Moreover, it could alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression connected to pain.
Although further research is necessary to comprehend the potential advantages of valproate in managing chronic pain, these initial discoveries are encouraging and suggest that it could serve as a valuable addition to the existing treatment alternatives.
Here are some references that you can check out:
VI. Dosage and Administration of Valproate
A. Standard Dosing Guidelines
Valproate dosage can vary depending on the condition being treated. Typically it starts with a range and is gradually increased until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved. For example, when treating epilepsy, the initial dose could be as low as 10 15 mg/kg/day. Then slowly increased to 60 mg/kg/day as tolerated. The frequency of taking the medication can vary from a day to multiple times a day, depending on the specific needs of the patient and the type of formulation used. It's worth noting how the drug is taken can affect its bioavailability and behavior in the body. Compared to immediate-release forms, extended-release tablets may result in peak concentration in the blood, which can help reduce potential side effects. However, both forms have been found to offer control over seizures.
B. Adjustments for Special Populations
People with changes in their body's ability to process drugs, such as those with kidney or liver problems, often need adjustments in their medication dosage. Individuals with liver issues may have a decreased ability to break down valproate, resulting in drug levels in their blood. As a result, they may need dosages. On the hand, kidney dysfunction can affect how the drug is eliminated from the body, which may require changes in dosage to prevent any harmful effects.
VII. Special Considerations in Administration
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals need attention because their bodies undergo physiological changes as they age. They frequently experience reduced liver and kidney function, so starting with a dose and proceeding with caution when adjusting the dosage may be necessary. It is important to monitor their liver function, blood count, and drug levels to prevent any adverse effects.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Valproate administration during pregnancy and lactation presents challenges. Valproate has been linked to causing birth defects and is classified as a category D drug for pregnancy, indicating strong evidence of potential fetal harm. Therefore its use in women should only be considered if the potential benefits outweigh the risks. In breastfeeding women, valproate is secreted into breast milk. The risk to nursing infants seems to be minimal. Nonetheless, it is advisable to monitor for any effects in breastfeeding infants.
C. Administration to Pediatric Patients
The administration of valproate to children requires monitoring. This medication has been authorized for use in seizure disorders for children who are at least 2 years old. However, younger patients, those under the age of two as well as those with metabolic disorders or birth defects, are at a higher risk of experiencing liver failure. Therefore it is generally avoided to use valproate in these patients. If it is essential extreme caution and frequent monitoring should be exercised.
VIII. Potential Side Effects of Valproate
A. Overview of Common Side Effects
Valproate, a medication with effectiveness, does have the possibility of causing side effects. However, these side effects are typically mild. Tend to lessen with prolonged use. Some common side effects to be aware of include nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and CNS effects like drowsiness, dizziness, and tremors. Other potential effects may include weight gain, changes in appetite, temporary hair loss, or alterations in hair texture. Patients need to communicate any worsening effects to their healthcare providers.
B. Serious and Uncommon Side Effects
Although Valproate is generally well tolerated in cases, it can lead to serious side effects that should not be ignored. These may include liver toxicity, which can present as yellowing of the skin, persistent vomiting, or abdominal pain. Another possible complication is pancreatitis, which will exhibit itself through abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Additionally, low platelet counts, known as thrombocytopenia, could result in bruising or bleeding. Lastly, hyperammonemia can cause confusion, decreased consciousness, and sometimes, even coma. It is crucial to seek medical attention if these side effects occur, as they can be potentially life-threatening.
IX. Interactions of Valproate
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
Valproate has the potential to interact with medications, which can impact how effective and safe it is. Some notable examples include Aspirin: It may increase the amount of Valproate, potentially leading to more toxicity. Carbamazepine: This medication can speed up the removal of Valproate from the body reducing its desired therapeutic effects. Warfarin: Valproate can displace Warfarin from its protein binding sites, which can enhance Warfarin's blood-thinning effects. It's crucial for patients to constantly communicate with their healthcare providers about any prescription drugs, over-the-counter products, or supplements they are using.
B. Food and Lifestyle Interactions
Food does not impact the absorption of Valproate; it only delays the absorption process. Therefore it is possible to take Valproate with or without food. However, it is advisable to refrain from consuming alcohol as it can amplify effects and increase liver toxicity.
X. Warnings and Contraindications for Valproate
A. Identification of High-Risk Populations
Some groups of people are more susceptible to experiencing consequences when taking Valproate. These include individuals with liver problems, metabolic disorders, mitochondrial disorders, and those who have shown hypersensitivity to Valproate. It is also essential to be cautious when prescribing Valproate to patients with bleeding disorders or ongoing liver disease.
B. Specific Medical Contraindications
Individuals with liver disease or substantial liver dysfunction should not use valproate. It is also not recommended for those with known cycle disorders as it may increase the risk of hyperammonemia encephalopathy. Furthermore, Valproate is unsuitable for women as it can potentially harm the fetus when used in migraine management. This underscores the significance of examining one's medical history before starting Valproate therapy.
XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
A. Monitoring Requirements During Treatment
Careful monitoring is crucial when therapy achieves the desired treatment benefits and minimizes possible adverse effects. This includes evaluating the patient's clinical response monitoring the levels of the drug in their blood, assessing liver function, and conducting complete blood counts. It is important to check serum ammonia levels in patients with urea cycle disorders. Additionally, it is necessary for women to monitor the fetus's health to identify any potential risks as early as possible.
B. Tips for Safe Administration
It is crucial to educate patients on the correct ways to administer Valproate. Following these guidelines is essential as it significantly influences the drug's safety and effectiveness. Here are some crucial tips: Stick to the dosage without making unauthorized changes. Take the doses at times to maintain stable drug levels in the bloodstream. Consume the medication with food to reduce the chances of experiencing discomfort. Inform your healthcare provider immediately if you notice any side effects or symptoms.
XII. Handling Overdosage Situations
A. Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Taking much Valproate can result in significant health problems. Signs of an overdose can vary from stomach discomfort, feeling lightheaded and sleepy to severe life-threatening conditions like slowed breathing, unconsciousness, and failure of multiple organs. Sometimes there might be an increase in seizure episodes. These symptoms require medical attention.
B. First Aid and Medical Interventions
When someone has taken much Valproate, it's essential to prioritize the patient's safety by maintaining their airway, breathing, and circulation. If the patient comes in within an hour of ingestion, gastric lavage may be done as a precaution. Another option to consider is using activated charcoal. After that, it's essential to provide supportive care, which involves regularly monitoring vital signs, electrolytes, and liver function. In some situations, hemodialysis may be helpful.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Valproate
A. Proper Storage Conditions
Valproate should be kept in its packaging at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. It is best to store it between 15 to 30 degrees Celsius. Avoid storing it in bathrooms or areas with humidity, and ensure it is out of reach for children and pets to prevent accidental consumption.
B. Precautions for Safe Handling and Disposal
It is essential to handle valproate with hands and dispense it carefully. Avoid crushing or chewing tablets. Do not open capsules if they are used. Properly dispose of any expired medication appropriately. It is not recommended to flush it down toilets or pour it into drains unless specifically instructed. It would be wise to consult waste disposal services or a pharmacist for guidance on safe disposal methods.
Valproate FAQ
- Valproate Sodium
- Valproate Brand Name
- Valproate Side Effects
- Valproate Level Timing
- Valproate vs Valproic Acid
- Valproate Mechanism of Action
- Valproate Sodium Side Effects
- Valproate Moa
- Valproate for Bipolar
- Valproate Bipolar
- Valproate in Pregnancy
- Valproate Pregnancy
- Valproate Sodium Brand Name
- Valproate Mood Stabilizer
- Is Valproate the same as Valproic Acid
- Valproate Dose
- Valproate Toxicity
- Valproate Dosage
- Valproate for Migraines
- Valproate Migraine
- Valproate Medication
- What is Valproate used for
- Valproate Semisodium
- Valproate Reviews
- Valproate Generic Name
- Valproate IV
- Valproate Teratogenic
- Valproic Acid Withdrawal
- Valproate IV to PO
- Valproate vs Depakote
- Valproate vs Divalproex
- Valproate and Lamotrigine
- Valproate Plus Lithium
- Valproate Therapeutic Levels
- Valproate Uses
- Valproate Class
- Valproate Cost
- Valproate Adverse Effects
- Valproate for Anxiety
- Is Valproate the Same as Depakote
- Valproate is an Example of What Type of Medication
- Valproate vs Lithium
- Valproate and Pregnancy
- Valproate Valproic Acid
- Valproate Syndrome
- Valproate Pregnancy Category
- Valproate Pancreatitis
- Valproate Thrombocytopenia
- Valproate Contraindications
- Valproate Anxiety
- Valproate Birth Defects
- Valproate Package Insert
- Valproate and Valproic Acid
- Valproate Weight Gain
- Valproate Sodium vs Valproic Acid
- Valproate Monitoring
- Valproate Metabolism
- Valproate Loading Dose
- Valproate Indications
- Valproate Half Life
- Valproate Hyperammonemia
- Valproate Hyponatremia
- Valproate Depacon
- Valproate Trade Name
- Valproate Blood Test
- Valproate Brand
- Valproate for Depression
- Are Valproic Acid and Divalproex Interchangeable?
- Are Valproic Acid and Depakote the Same?
- Is Valproate a Mood Stabilizer?
- Valproate for Agitation
- Valproate vs Lamotrigine
- Valproate Same as Valproic Acid
- Valproate Structure
- Valproate Side Effects Usmle
- Valproate Seizure
- Valproate Mechanism
- Valproate Liver
- Valproate Level Toxicity
- Valproate Overdose
- Valproate Interactions
- Valproate Induced Hyperammonemia
- Valproate Injection
- Valproate Nursing Considerations
- Valproate Neuroplasticity
- Valproate Perfect Pitch
- Valproate Definition
- Valproate Depression
- Valproate Tremor
- Valproate Test
- Valproate Classification
- Valproate CYP450
- Valproate Ammonia
- Valproate Autism
- Valproate Black Box Warning
- Valproate Bipolar Depression
- Valproate Dosage for Bipolar
- Valproate Dose for Bipolar
- How Does Valproate Work
- How Long Does Valproate Take to Work
- Does Sodium Valproate Help Depression
- What Does Valproate Do
- Are Valproate and Valproic Acid the Same
- Valproate Alternatives
- Valproate for Seizures
- Valproate for Schizophrenia
- Valproate Vs Levetiracetam
- Valproate and Valproic Acid the Same
- Valproate and Platelet Count
- Valproate and Olanzapine
- Valproate and Carbamazepine
- Valproate and Lithium