Diloxanide
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Diloxanide
- III. Off-label Use of Diloxanide
- IV. How Diloxanide Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interaction
- X. Warning
- XI. Contraindication
- XII. Careful Administration
- XIII. Important Precautions
- XIV. Administration to Special Populations
- XV. Overdosage
- XVI. Storage
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Historical background of Diloxanide
Diloxanide, a medication developed in the mid-20th century, quickly became a leading treatment for protozoal infections. Pharmaceutical innovators took the lead in formulating this drug to combat the increasing number of amoebic diseases.
General overview and relevance in modern medicine
Diloxanide remains a medication in fighting amoebiasis, emphasizing its ongoing importance due to the prevalence of amoebic infections worldwide, particularly in areas with inadequate water sanitation.
II. Uses of Diloxanide
Primary indications and FDA-approved uses
Diloxanide is an anti-protozoal agent that is used to treat an infection caused by a very small living organism called Entamoeba histolytica 1. Diloxanide is mainly known for its effectiveness in treating infections that do not show any symptoms 1. It is also used as a medication after the treatment, with tissue amoebicides 2. The FDA has approved Diloxanide based on clinical trials and patient safety information 3.
2: MIMS 1: Patient 3: DrugBank
Comparisons to alternative treatments for similar conditions
While there are medications like Metronidazole and Tinidazole that also work to treat amoebiasis, Diloxanide is notable for its reduced risk of systemic side effects, its focus on luminal amoebas, and its compatibility with other amoebicides.
III. Off-label Use of Diloxanide
Overview of off-label applications
Apart from its purpose, some medical professionals have taken the initiative to utilize Diloxanide for treating other types of protozoal infections. However, it is essential to exercise caution and rely on informed judgment.
Studies and evidence supporting these applications
Diloxanide is an anti-protozoal agent that is primarily used to treat an infection caused by a very small living organism called Entamoeba histolytica 1. While Diloxanide is primarily used for treating this condition, recent research suggests that it may have applications in treating conditions like Giardiasis 2. However, it is important to recognize that these studies are still in their early stages and further rigorous trials are necessary to establish its undeniable effectiveness.
Potential risks and benefits of off-label use
There are attractive aspects and concerns when considering the use of medications for purposes other than their approved indications. On the side, it may offer broader therapeutic benefits and cost savings. However,, this practice has risks, such as side effects and potential reduction, in effectiveness.
IV. How Diloxanide Works
Mechanism of action
Diloxanide works by interfering with the metabolic processes of the amoeba. It hinders its ability to store carbohydrates, which stops its growth and reproduction.
Time to onset and duration of effect
After taking Diloxanide, it starts working, and you can start experiencing its effects within a few hours. The inhibitory properties of Diloxanide on amoebas last for a while. It's essential to follow a prescribed treatment plan to eliminate the amoebas.
Comparison to other drugs in its class
Diloxanide has an approach compared to other antiprotozoal agents as it specifically targets the intestines, resulting in fewer side effects on the rest of the body. This localized action sets it apart from its counterparts. Reduces the risk of systemic reactions.
V. Dosage and Administration
Recommended dosages for different conditions
The recommended dosage for adults with amoebic infections is 500 mg, taken three times a day for 10 days. In the case of children, the dosage should be adjusted according to their weight and age.
Dosage adjustments for specific populations
Pregnant women, older individuals, and people with liver or kidney issues might require customized doses of medication with monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Methods of administration and guidelines
Diloxanide is typically found in the form of tablets. It's essential to complete the treatment course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent any chance of relapse.
VI. Composition
Active and inactive ingredients
The main component of this drug is Diloxanide furoate. It also contains other substances like magnesium stearate and cellulose derivatives that help optimize its effects on the body.
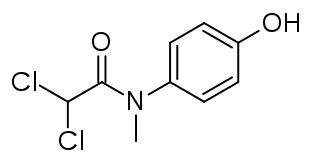
Formulations available (e.g., tablets, liquid)
Tablets may be the choice in the pharmaceutical market, but oral suspensions offer an alternative option specifically designed for pediatric populations or individuals who face difficulties in swallowing.
Potential allergens or sensitizing agents
Specific formulations may include lactose or gluten. People who have sensitivities or intolerances should refer to the medications leaflet. Seek advice from a pharmacist.
VII. Side Effects
Overview of potential side effects
Similar to any medication, Diloxanide is not entirely free of side effects. These can vary from gastrointestinal issues to less common systemic reactions.
Differentiating common versus rare side effects
Although it is expected to experience flatulence and abdominal cramps, rashes or severe allergic reactions are not as frequent. Should be taken seriously and require immediate medical attention.
VIII. Common Side Effects
List of most frequently observed side effects
Some common issues that people often complain about include gas, mild abdominal discomfort, and nausea.
Management and mitigation of these effects
Over-the-counter medications for relieving cramps can be helpful. Following dietary recommendations may reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. It's always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment to alleviate symptoms.
When to seek medical attention
If you experience symptoms like ongoing vomiting, intense diarrhea, or any indication of an allergic reaction, such as swelling or difficulty breathing, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
IX. Interaction
Common drug-drug interactions
Diloxanide, although generally considered safe, may interact with medications. This can include medicines that might enhance Diloxanide's effectiveness as a treatment. Additionally, certain antibiotics can affect how the drug is processed in the body. It is essential to inform healthcare providers about all your medications to minimize potential adverse effects.

Drug-food interactions and guidelines
While it is generally not advised to consume high-fiber diets while taking Diloxanide as they can affect its absorption, it is wise to stick to a diet throughout the treatment period.
Effects of alcohol and recreational drug use
Combining alcohol or recreational drugs can affect how medications work and increase the chances of experiencing side effects. It is highly recommended to avoid using them while undergoing treatment.
X. Warning
Situations where Diloxanide use may be hazardous
There are situations where caution is necessary. For example, if someone has severe gastrointestinal disorders or a history of allergic reactions to antiprotozoal medications. In these cases, vigilance's essential to avoid any complications.
Serious reactions and their potential outcomes
Although it is uncommon, there can be reactions like anaphylaxis. These emergencies may result in a cardiovascular failure if not promptly attended to.
XI. Contraindication
Medical conditions where Diloxanide use is not recommended
People with liver problems or a known allergy to this medication should avoid taking Diloxanide or be very cautious if they decide to use it.
Specific drugs that should not be taken alongside Diloxanide
Some antiviral and immunosuppressive medications can negatively impact the effectiveness of Diloxanide. It is essential to inform your doctor about any use of drugs before starting treatment.
XII. Careful Administration
Overview of populations needing careful dose adjustment
Some groups, like those with liver problems or kidney insufficiency, may require adjusted doses to avoid any adverse effects.
Importance of monitoring during the initial phase of treatment
Introducing a treatment can test the limits of drug tolerance and effectiveness. Monitoring patients during this phase is crucial to quickly identify any negative reactions or instances when the treatment may not be working effectively.
XIII. Important Precautions
Guidelines for safe use
It is essential to follow the recommended dosages, administer Diloxanide on time, and refrain from self-medicating to ensure medication usage.
Factors that might alter drug efficacy or increase risk of side effects
Factors like changes in diet, concurrent medication usage, or even shifts in the pH levels of the system can impact how drugs work. Awareness of these variables can help maximize the effectiveness of treatments and achieve results.
XIV. Administration to Special Populations
Elderly: Dosage considerations, potential risks, and monitoring
In patients, decreased kidney or liver function can affect how drugs are cleared from the body, so it's essential to adjust the dosage carefully. Keeping an eye on their condition can help prevent any possible complications.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety profile, considerations, and recommendations
Although no evidence indicates harmful effects on fetal development, it is advisable to minimize its use during pregnancy unless necessary. Mothers who are breastfeeding should be informed about the possibility of the drug passing into breast milk.
Children: Age-specific dosages, potential side effects, and monitoring guidelines
When determining dosages, it is crucial to calculate them according to the child's weight carefully. Since children can experience side effects, it is essential to observe them closely.
XV. Overdosage
Symptoms of Diloxanide overdose
Excessive consumption can lead to symptoms such as stomach discomfort, ongoing feelings of nausea, or even signs of neurological and mental health issues. It is essential to recognize these symptoms.
Immediate steps and treatments for management
When dealing with a suspected overdose, it is crucial to seek medical help. The primary approach for treatment involves providing care, performing gastric lavage if necessary, and managing symptoms accordingly.
Long-term consequences and prevention
Excessive and prolonged medication use can affect the liver or kidneys. To prevent these consequences, it is crucial to follow the guidelines and regularly monitor your health.
XVI. Storage
Optimal storage conditions for potency and safety
Diloxanide must be stored in a dry place away from direct sunlight to ensure its pharmacological effectiveness.
Shelf life and expiration guidelines
Expired medications may not work effectively. It could pose potential risks. It's essential for users to check and follow the expiration dates of their medications regularly.
Proper disposal methods
It's essential to handle disposal and not take it lightly. Flushing medications or casually throwing them in the bin can affect the environment. It's crucial to make use of channels for pharmaceutical disposal.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Guidelines for safe handling
Make sure your hands are clean and dry when handling tablets. This helps to maintain the integrity of the tablet and prevents any deterioration.
Preventing contamination and ensuring proper usage
It is essential to follow guidelines when handling pill bottles. Make sure your hands are dry before touching the tablets, and avoid using any tablets that have changed in color or texture. These precautions are crucial for ensuring your safety and the effectiveness of the medication.