Idarubicin. Injection
- Introduction to Idarubicin Injection
- Idarubicin mechanism of action
- Idarubicin uses
- Off-Label Uses of Idarubicin Injection
- Composition and Formulation of Idarubicin Injection
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Storage and Handling of Idarubicin Injection
- Idarubicin side effects
- Drug Interactions and Incompatibilities
- Warnings and Precautions for Idarubicin Injection
- Contraindications to Idarubicin Injection Use
- Special Considerations in Specific Populations
- Careful Administration and Monitoring Parameters
- Important Precautions When Using Idarubicin Injection
- Overdose Management and Emergency Intervention
- Safe Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Idarubicin Injection
Overview of Idarubicin
Idarubicin is a medication used to target cancers with precision by interfering with DNA intercalation to hinder cancer cell growth and replication process efficiently through injection delivery, quick absorption, and widespread impact.
Classification as an Anthracycline Antibiotic
Classified as an anthracycline antibiotic, idarubicin belongs to a group of chemotherapeutic agents known for their dual role in DNA intercalation and topoisomerase inhibition. These compounds, although originally isolated from Streptomyces, are primarily used for their cytotoxic properties rather than antibacterial effects.
FDA Approval Status and Global Availability
Idarubicin has been approved by the FDA for treating acute myeloid leukemia in the US. It is considered essential in countries worldwide due to its significant impact on healthcare systems and regulatory approvals that differ by region.
General Indications in Oncology
Idarubicin is primarily indicated for:
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- Induction and consolidation therapy
- Combination regimens with other cytotoxic agents
It remains a cornerstone in oncologic protocols, particularly in hematologic cancers.
Idarubicin mechanism of action
Cellular Target and DNA Intercalation
Idarubicin works by fitting in between the building blocks of DNA, hindering the production of acids in the process. This disruption impacts the stability of DNA and RNA strands and eventually halts the growth of cells.

Inhibition of Topoisomerase II
It hinders the action of the topoisomerase II enzyme, which is crucial for the DNA replication process by stabilizing the complex between DNA and the enzyme, thus preventing the rejoining of DNA strands, leading to stranded breaks.
Impact on Cell Cycle and Apoptosis
Idarubicin causes a pause in the cell cycle during the S phase. Then, it leads to apoptosis starting up. The substance activates caspases and makes the mitochondrial membrane more permeable, which helps in causing cell death in a way.
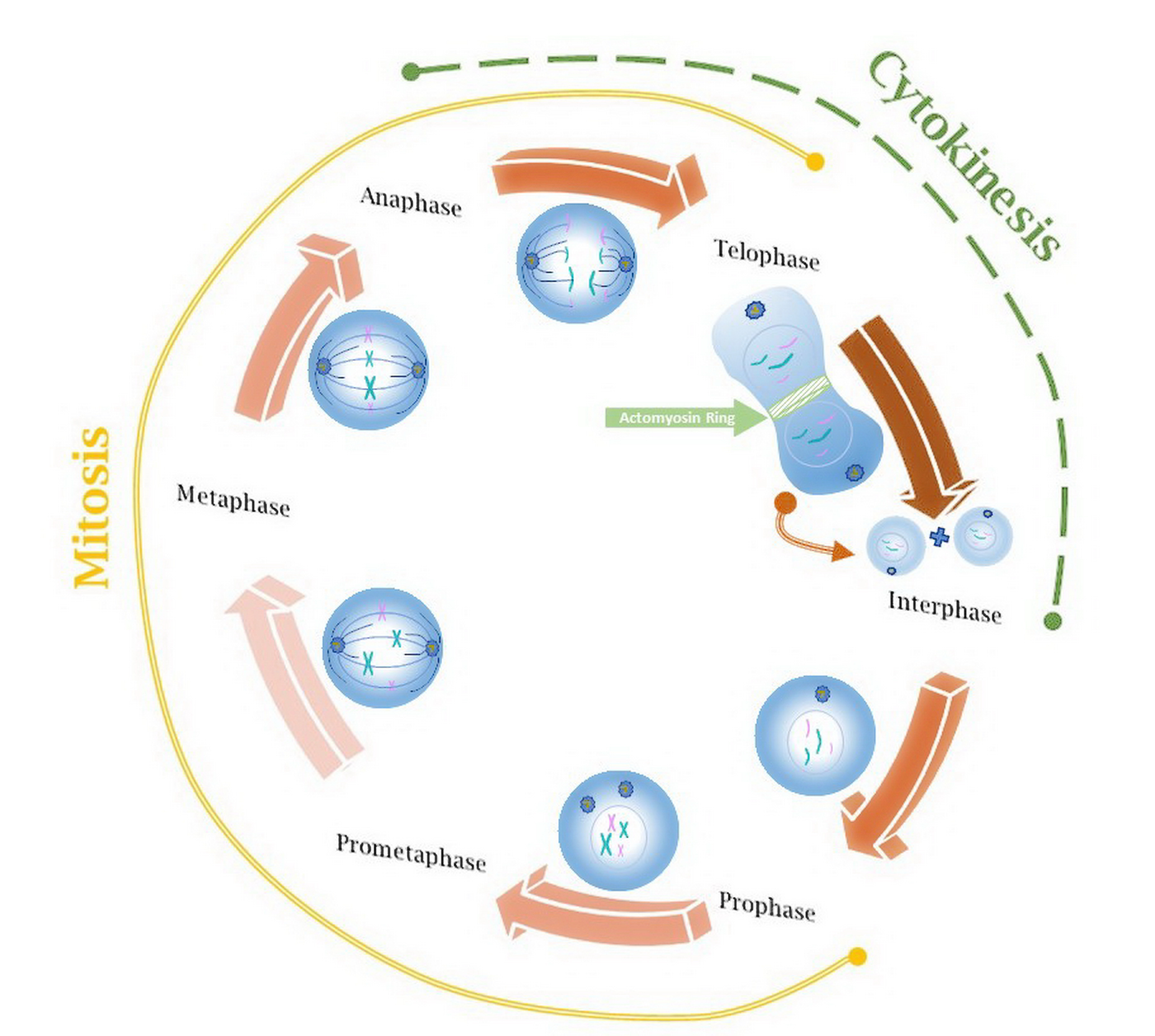
Selectivity for Rapidly Dividing Cancer Cells
Idarubicin demonstrates a preference, for dividing cells due to its mechanism of action. This targets blood cell precursors while minimizing harm to dormant cells
Idarubicin uses
Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Use in Combination Chemotherapy Protocols
The medication plays a role in combined treatments with cytarabine, etoposide, and fludarabine to improve effectiveness and lower resistance levels.
Role in Induction and Consolidation Therapy
Throughout the treatment phase for leukemia patients, known as induction therapy, Idarubicin plays a role in reducing the cancerous load within the body's system. As treatment progresses to consolidation therapy following induction phase completion, idarubicin continues its function by aiding in eradicating any remaining disease cells and acting as a measure against potential relapses.
Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Leukemia
Idarubicin is often used in follow-up treatment for individuals dealing with resistant AML, where adjustments in dosage and pairing with medications are frequently practiced.
Off-Label Uses of Idarubicin Injection
Use in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Off-label Application in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Certain types of Hodgkin's lymphoma that are aggressive have been treated with idarubicin, specifically when sensitivity to anthracycline is observed.
Investigational Use in Breast Cancer
Experimental Role in Sarcomas and Other Solid Tumors
Data from the stages of testing shows that it is effective in fighting types of soft tissue cancers, while ongoing studies are looking into how well it works against solid tumors that grow rapidly.
Composition and Formulation of Idarubicin Injection
Active Ingredient and Its Concentration
Each vial usually contains idarubicin hydrochloride at concentrations of 5 mg/mL or 10 mg/mL with an active ingredient that improves tissue penetration.
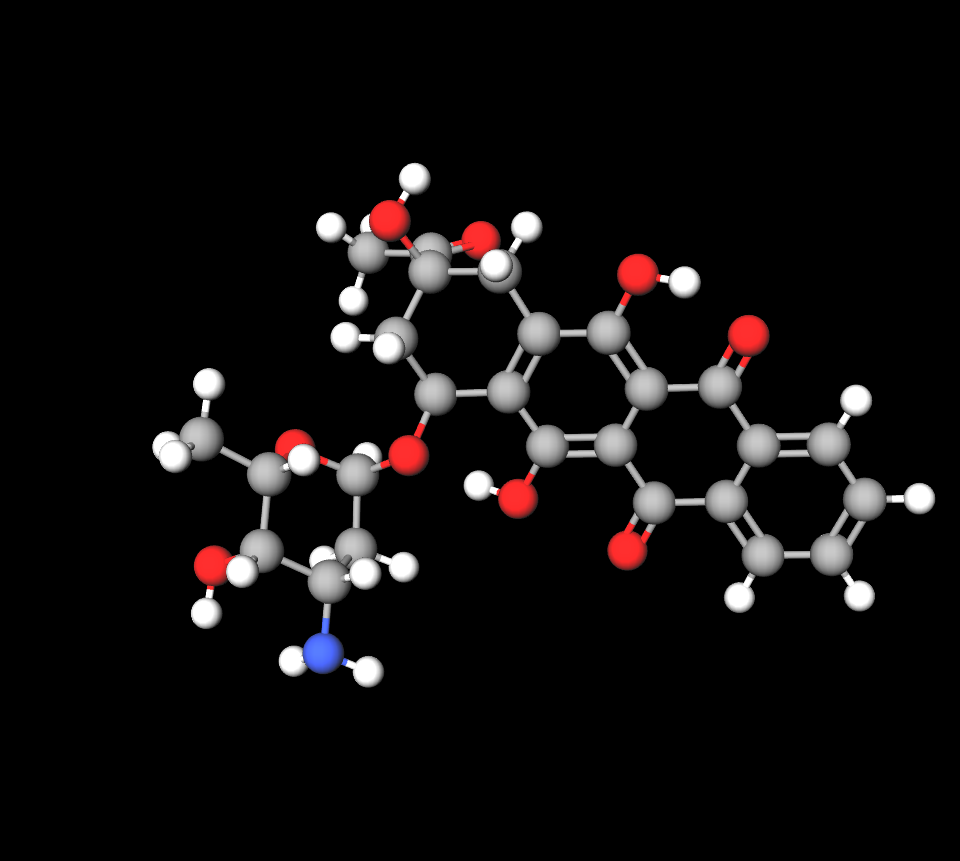
Inactive Ingredients and Their Functions
Common excipients include:
- Lactose monohydrate: stabilizer
- Water for injection: solvent
Available Dosage Forms and Packaging
Idarubicin is available in single-use glass vials, sealed under sterile conditions. Dosage presentations include 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg vials.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage for Adults with AML
Recommended dosing: 12 mg/m2 IV daily for 3 days, often in combination with 100 mg/m2 of cytarabine for 7 days.
Dosage Adjustments for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Adjustments may include:
- 50% dose reduction in moderate hepatic dysfunction
- Use contraindicated in severe renal impairment
Idarubicin administration
Given through an injection or brief infusion lasting 10 to 15 minutes, preferably using a central line to prevent leakage into surrounding tissues.
Monitoring During and After Administration
Includes:
- Complete blood counts
- Cardiac function tests (e.g., LVEF via echocardiogram)
- Liver and renal panels
Dosage in Combination with Other Chemotherapy Agents
It's important to coordinate dosing schedules to avoid many toxicities overlapping each other as the dose intensity and intervals vary depending upon the specific protocol in use.
Storage and Handling of Idarubicin Injection
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Keep the item in a place between 2°C and 8°C, away from light exposure, and make sure not to freeze it.
Shelf Life and Stability Considerations
Unused vials can be kept intact for 24 months when stored correctly, while reconstituted solutions should be utilized within a day of preparation.
Proper Handling Procedures for Healthcare Providers
Remember to use biological safety cabinets when working with chemicals and always wear equipment (PPE). Follow the protocols for handling materials and be sure to prevent aerosol generation when mixing substances.
Disposal of Unused Medication and Contaminated Materials
Please ensure disposal through authorized waste management facilities instead of throwing it in regular trash bins or sewage systems.
Idarubicin side effects
Frequently Reported Adverse Effects
Serious and Life-Threatening Side Effects
Late-Onset Side Effects and Long-Term Risks
Side Effect Management and Supportive Care
Drug Interactions and Incompatibilities
Interactions with Other Chemotherapeutic Agents
Interaction with CYP450 Enzyme Modulators
Contraindicated Drug Combinations
Impact on Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests
Warnings and Precautions for Idarubicin Injection
Idarubicin cardiotoxicity and Monitoring Requirements
Risk of Myelosuppression and Neutropenia
Secondary Malignancy Risk
Extravasation Risk and Tissue Damage
Immunosuppression and Infection Risk
Contraindications to Idarubicin Injection Use
Known Hypersensitivity to Idarubicin or Anthracyclines
Pre-existing Cardiac Conditions
Severe Hepatic or Renal Impairment
Concomitant Live Vaccination
Special Considerations in Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
Pediatric Use and Dosing Adjustments
Genetic and Ethnic Considerations in Pharmacokinetics
Careful Administration and Monitoring Parameters
Baseline Assessments Before Initiation
Ongoing Hematologic and Cardiac Monitoring
Managing Cumulative Dose Limits
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Important Precautions When Using Idarubicin Injection
Avoiding Exposure to Infections
Lifestyle Adjustments During Treatment
Recognizing Early Signs of Complications
Use of Protective Measures by Healthcare Workers
Overdose Management and Emergency Intervention
Signs and Symptoms of Idarubicin Overdose
Emergency Response and Supportive Measures
Role of Hematopoietic Support in Overdose
Reporting and Documentation of Overdose Cases
Safe Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Prevention of Drug Exposure Through Skin or Inhalation
Procedures for Spillage or Accidental Contact
Training Requirements for Handling Cytotoxic Agents
Idarubicin. Injection FAQ
- What is idarubicin used for?
- How do you give idarubicin?
- Is idarubicin a chemo drug?
- What are the long term effects of idarubicin?
- What is the difference between doxorubicin and idarubicin?
- What is the use of idarubicin injection?
- What is Idarubicin Injection used for?
- How does Idarubicin work?
- How is Idarubicin administered?
- What are the common side effects of Idarubicin?
- Can Idarubicin cause heart problems?
- Can Idarubicin cause low blood cell counts?
- How often is Idarubicin administered?
- Can Idarubicin be used during pregnancy?
- Can Idarubicin be used during breastfeeding?
- What precautions should be taken before receiving Idarubicin?
- What should patients report to their doctor while on Idarubicin?
- Can Idarubicin cause hair loss?
- How is cardiac function monitored during Idarubicin treatment?
- Can Idarubicin cause mucositis (mouth sores)?
- Can Idarubicin cause nausea and vomiting?
- What are the long-term risks associated with Idarubicin?
- How is Idarubicin dosage determined?
- What blood tests are monitored during Idarubicin treatment?
- Can Idarubicin cause changes in liver or kidney function?
- Is Idarubicin always used alone?
What is idarubicin used for?
Idarubicin is a type of medication from the anthracene group that is commonly prescribed to adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). It is taken orally. It has been found to be effective in treating breast cancer and various types of lymphomas and leukemias while also having the advantage of causing less harm to the heart.
How do you give idarubicin?
Idarubicin is typically administered via infusion or injection directly into a vein.
Is idarubicin a chemo drug?
Idarubicin belongs to a category of chemotherapy used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
What are the long term effects of idarubicin?
Serious heart conditions such as heart failure due to fluid buildup and irregular heartbeats like atrial fibrillation have been observed in individuals receiving initial treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) along with chest discomfort and asymptomatic decreases in left ventricular ejection fraction (EF).
What is the difference between doxorubicin and idarubicin?
Idarubicin is typically preferred as the anthracycline treatment for AML patients. On the other hand, doxorubicin is commonly utilized for treating other forms of cancer.
What is the use of idarubicin injection?
Idarubicin injection is typically prescribed alongside medications for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
What is Idarubicin Injection used for?
It's used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in adults.
How does Idarubicin work?
It functions by decelerating or halting the proliferation of cells.
How is Idarubicin administered?
It is given through an IV by a professional.
What are the common side effects of Idarubicin?
Typical symptoms may consist of queasiness or stomach upset along with hair thinning or loss and ulcers in the mouth area as lower levels of blood cells.
Can Idarubicin cause heart problems?
It has the potential to result in cardiotoxicity. It may lead to heart failure when administered at cumulative doses.
Can Idarubicin cause low blood cell counts?
It often results in myelosuppression which can lead to decreased blood cells (anemia), white blood cells (leukopenia), and platelets (thrombocytopenia).
How often is Idarubicin administered?
The amount and timing of the medication vary based on the treatment plan and how the patient reacts to it.
Can Idarubicin be used during pregnancy?
No, It can harm the fetus.
Can Idarubicin be used during breastfeeding?
It is advised to avoid it while breastfeeding because of the harm it could pose to the baby.
What precautions should be taken before receiving Idarubicin?
Before commencing the treatment regimen, patients should undergo cardiac function assessments and blood work, as well as other essential evaluations.
What should patients report to their doctor while on Idarubicin?
Patients need to inform the healthcare provider if they experience any signs of infection, like chest pain or shortness of breath, and any unusual bleeding, bruising or other worrying symptoms.
Can Idarubicin cause hair loss?
It's quite common for people to experience hair loss as a side effect.
How is cardiac function monitored during Idarubicin treatment?
Doctors keep track of how the heart is working by using echocardiograms or other types of heart imaging tests.
Can Idarubicin cause mucositis (mouth sores)?
Yes
Can Idarubicin cause nausea and vomiting?
Yes
What are the long-term risks associated with Idarubicin?
Potential long-term dangers consist of heart-related issues and the possibility of developing cancers.
How is Idarubicin dosage determined?
The prescribed amount is meticulously calculated according to the patient's body surface area and other relevant considerations.
What blood tests are monitored during Idarubicin treatment?
Monitoring blood counts (CBCs helps evaluate bone marrow function and the likelihood of infection or bleeding complications.
Can Idarubicin cause changes in liver or kidney function?
It has the potential to impact the functioning of the liver and kidneys, thus necessitating monitoring.
Is Idarubicin always used alone?
It's commonly paired with chemotherapy medications to address AML.



















