Tetrabenazine
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Tetrabenazine
- III. Off-label Use
- IV. How Tetrabenazine Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition
- VII. Common Side Effects
- VIII. Severe Side Effects and Warnings
- IX. Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration
- XI. Important Precautions
- XII. Administration to Specific Populations
- XIII. Drug Interactions
- XIV. Overdosage
- XV. Storage Requirements
- XVI. Handling Precautions
- XVII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
The. Past of Tetrabenazine; Tetrabenazine was initially developed in the 1950s as a medication for treating conditions. However, its effectiveness in managing movement disorders led to reevaluating its uses. The current significance and applications: Tetrabenazine plays a crucial role in alleviating hyperkinetic movement disorders in medicine. It is considered a treatment for conditions like Huntingtons' disease and tardive dyskinesia.
II. Uses of Tetrabenazine
Approved Uses; Tetrabenazine is approved for treating movement disorders such as choreiform movements in Huntingtons Disease12, hemiballismus secondary to stroke3 and tardive dyskinesia caused by term neuroleptic use45. The mechanism of action of Tetrabenazine involves reducing the levels of dopamine, which is believed to be excessive in these conditions12. Effectiveness in Managing Huntingtons Disease; Tetrabenazine has shown efficacy in reducing chorea, the erratic and involuntary movements that are characteristic of Huntingtons' Disease124. Role in Treating Dyskinesia; Tetrabenazine has also been effective in mitigating the involuntary and repetitive body movements associated with tardive dyskinesia, a condition often triggered by prolonged use of specific antipsychotic medications35. This offers relief to individuals affected by this condition.
1: Tetrabenazine: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Interactions & more - Drugs.com 2: Tetrabenazine - Wikipedia 3: Tetrabenazine: A strategy for Levodopa-induced dyskinesia? 4: AUSTEDO. AUSTEDO DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS WITH HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE … 5: FDA Approves Extended-Release Deutetrabenazine for Huntington's Disease Chorea, Tardive Dyskinesia
III. Off-label Use
Psychiatric Conditions; Depression and Anxiety In the past, Tetrabenazine was used as a medication. It is sometimes used off-label to treat severe anxiety and depression, although with caution due to its significant side effects1. Treatment of Other Movement Disorders Apart from its approved uses, Tetrabenazine has shown effectiveness in addressing other movement disorders, including Tourettes syndrome2 and different types of dystonias13. Current Research and Potential Future Applications Ongoing research explores the potential of Tetrabenazine in areas such as treatment-resistant depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). These emerging applications demonstrate the drug's versatility.
1: Tetrabenazine therapy of dystonia, chorea, tics, and other dyskinesias … 2: Tetrabenazine in the Treatment of Tourette Syndrome 3: Dystonia and leveraging oral pharmacotherapy | SpringerLink
IV. How Tetrabenazine Works
Tetrabenazine works by inhibiting a protein called monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2). By blocking VMAT2, it reduces the uptake of chemicals called monoamines into small storage units in the brain. This results in levels of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the central nervous system. Tetrabenazine primarily affects the system, specifically targeting the VMAT2 receptor. However, it also has some influence on the noradrenergic systems. In contrast, to antipsychotic medications that work by blocking dopamine receptors, Tetrabenazine acts differently by affecting how these chemicals are stored. This unique mechanism helps minimize the risk of motor side effects commonly associated with antipsychotics.
V. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Recommendations To manage chorea in individuals with Huntingtons' disease, the usual initial dose is 12.5 mg daily. This dose can be adjusted as required, considering the patient's response to treatment and ability to tolerate it. Individualized Dosage Adjustments Physicians should carefully monitor their patients. Make necessary adjustments to the dosage to achieve optimal symptom control while minimizing any potential side effects. Different Administration Methods and Options There are two forms of medication for this condition; tablets and oral solutions. Both options are intended for administration providing patients with flexibility and convenience.
VI. Composition
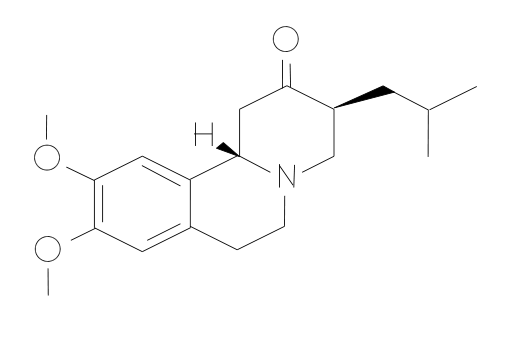
The active substance in Tetrabenazine is called tetrabenazine. It comes in different strengths like 12.5 mg and 25 mg tablets. The inactive ingredients may include lactose, cellulose, and dextrose, although the specific components might differ between brand name versions. Xenazine is the brand-name version of this medication. Generic versions are also available that are chemically the same and often more affordable.
VII. Common Side Effects
Some possible mild side effects of the medication include feeling tired, having trouble sleeping, feeling nauseous, and experiencing sadness. To manage these side effects, you can try taking the medicine with a meal to help reduce nausea. Additionally, maintaining a sleep pattern might help alleviate insomnia.
VIII. Severe Side Effects and Warnings
Recognizing and Managing Serious Side Effects Both patients and healthcare professionals must monitor for signs of worsening depression, acute dystonia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Although rare, these complications can be severe. Black Box Warning; Explanation and Implications Tetrabenazine comes with a black box warning due to an increased risk of depression and suicidality. Using this medication only under strict medical supervision is crucial, especially for patients with mental health problems. Patient Monitoring and Follow-up Given the effects and risk profile of Tetrabenazine, it is essential to have stringent patient monitoring throughout the treatment process. This includes appointments and potentially even laboratory tests.
IX. Contraindications
Tetrabenazine should not be used in patients allergic to the drug or its ingredients. It is also not recommended for patients who have suicidal tendencies or untreated/debilitated depression. Individuals with liver problems, a history of QT prolongation or significant heart conditions, and those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may need to consider treatments due to the potential risks associated with tetrabenazine therapy.
X. Careful Administration
When dealing with patients with kidney or liver problems, starting tetrabenazine at a dose and using a cautious approach when increasing the dosage is essential. Doctors should begin with an amount and gradually increase it while closely monitoring its effectiveness and potential adverse reactions. Regular consultations with the patient are crucial during this period.
XI. Important Precautions
The risk of drug abuse and dependency associated with tetrabenazine is relatively low. It is crucial to use this medication responsibly and closely monitor patients. Regarding health, healthcare providers should be particularly attentive to any signs of depression or suicidal thoughts that may arise. If such symptoms are identified, prompt intervention is necessary.
XII. Administration to Specific Populations
Special Considerations for Patients; Elderly patients may have a higher sensitivity to tetrabenazine and are more prone to experiencing adverse reactions. It is recommended to be cautious with the dosage starting at the end of the range. Risks and Recommendations for Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers; The use of tetrabenazine in women should only be considered if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks. Nursing mothers are advised to either discontinue the medication or stop breastfeeding, taking into account its importance for the mother. Safety and Efficacy in Children; The safety and effectiveness of tetrabenazine have not been established in patients. Therefore its use in this population should be approached with caution.
XIII. Drug Interactions
Significant Drug Interactions: MAOIs, Reserpine, and Strong CYP2D6 inhibitors. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects or significantly impact the effectiveness of tetrabenazine. Precautions to Take with Medications; Before starting tetrabenazine, doctors should thoroughly evaluate a patient's current medications. It is essential to review these medications during treatment. How to Avoid Interactions; Patients need to be honest about all the medicines they are taking, and doctors should refer to a comprehensive drug interaction database before starting any new medication for a patient already on tetrabenazine.
XIV. Overdosage
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of an overdose is essential. When someone experiences an overdose, they may show signs such as increased sedation, agitation, low blood pressure, and extrapyramidal symptoms. Immediate medical attention is crucial in case of an overdose. Treating an overdose mainly involves supporting the individual since there is no specific antidote for tetrabenazine overdose. Based on the patient's condition, it may be necessary to have ongoing medical supervision. The patient's kidney and liver function should be assessed as part of follow-up care.

XV. Storage Requirements
It is recommended to keep Tetrabenazine at room temperature to ensure storage conditions while avoiding excessive moisture and heat. It is essential to prevent exposure to light, heat, and moisture. Avoid storing it in areas with humidity, like bathrooms or direct sunlight. Remember to follow the expiration date mentioned on the label and dispose of any medication through a take-back program or by following the instructions in the medication guide.
XVI. Handling Precautions
Healthcare professionals are advised to handle tetrabenazine tablets using dry hands and avoid touching broken or crushed tablets. Patients need to be educated on the medication's techniques, including the administration timing and whether it should be taken with food. It is also crucial for patients to understand the significance of consistent use.
XVII. Conclusion
Tetrabenazine continues to hold a position in medicine due to its specific and crucial role. It remains a choice for treating certain movement disorders.