Ibandronic acid injection
- Introduction to Ibandronic Acid Injection
- Uses of Ibandronic Acid Injection
- How Ibandronic Acid Injection Works
- Ibandronic acid dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Composition of Ibandronic Acid Injection
- Storage and Handling Instructions
- Ibandronic acid side effects
- Ibandronic acid interactions
- Ibandronic acid warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Ibandronic Acid Injection
- Guidelines for Careful Administration
- Administration in Special Populations
- Overdosage and Management
- Important Precautions for Handling and Disposal
Introduction to Ibandronic Acid Injection
Overview of Ibandronic Acid
Ibandronic acid is a potent bisphosphonate used to manage bone-related conditions. It is specifically designed to inhibit bone resorption, ensuring the maintenance of bone density and strength. Targeting osteoclast activity stabilizes bone turnover, promoting healthier skeletal structures.
Brief History and Development
The introduction of ibandronic acid marked a significant advancement in the treatment of osteoporosis and metastatic bone disease. Developed in the late 20th century, it became an integral component of modern therapeutics, approved globally for its efficacy in preventing skeletal complications.
Classification: Bisphosphonates Group
Ibandronic acid belongs to the bisphosphonate family, characterized by dual phosphate groups. This class of drugs specifically binds to hydroxyapatite in bone, providing targeted therapy for bone-related disorders.
Key Benefits in Medical Treatment
- Helps lower the chances of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis.
- Helps address issues with the bones that commonly occur due to cancer spreading in the body.
- Enhances the density and strength of bones for integrity.
Uses of Ibandronic Acid Injection
Primary Uses
Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Postmenopausal women undergo bone depletion due to decreasing estrogen levels in their bodies. Ibandronic acid is successful in alleviating this condition by enhancing bone density and lowering the chances of fractures occurring.
Treatment of Paget's Disease of Bone
Paget's disease is known for its bone restructuring process. It shows great improvement with the use of ibandronic acid, which helps regulate bone structure by reducing excessive osteoclast activity.
Off-Label Uses
Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
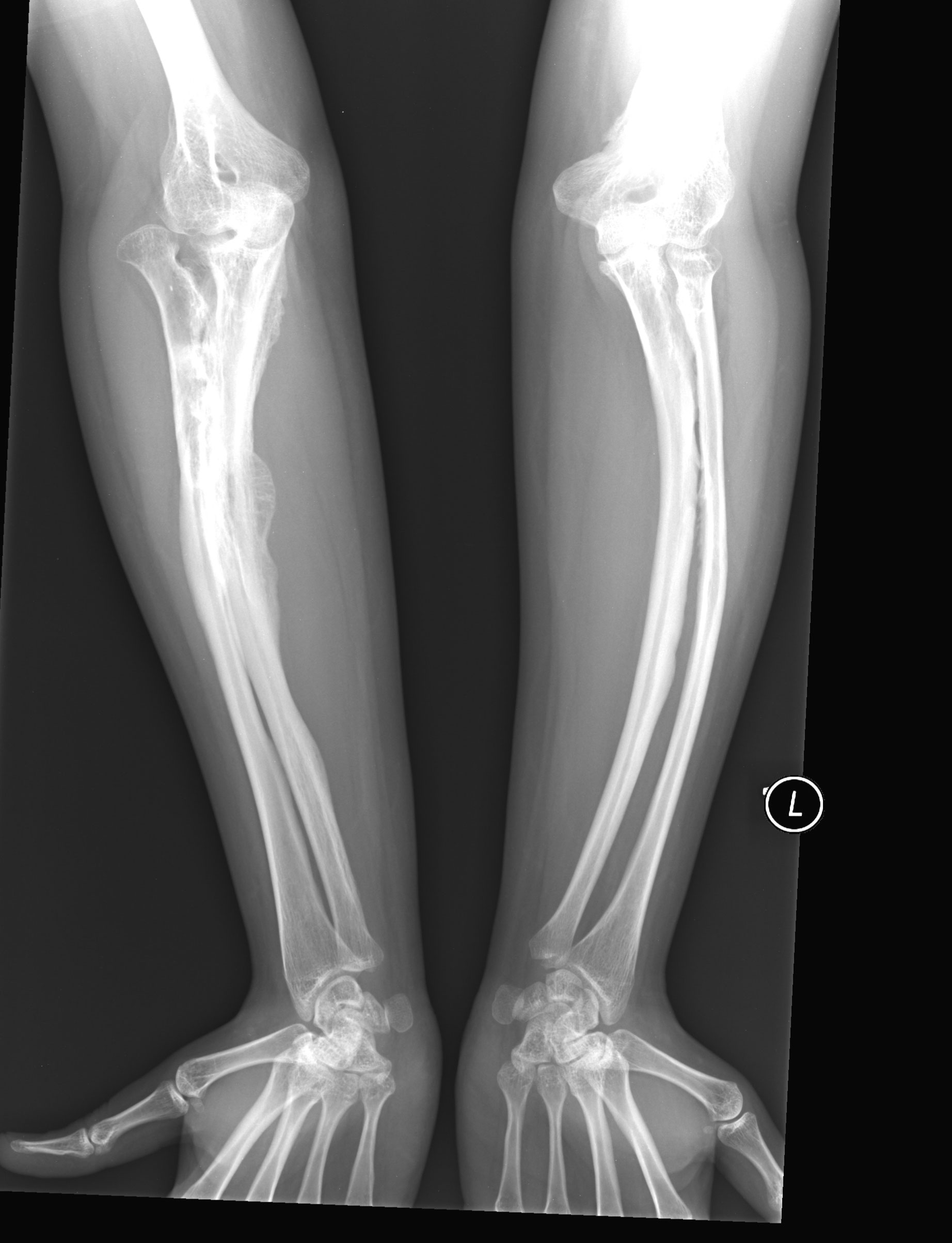
Ibandronic acid breast cancer
Prevention of Bone Loss in Prolonged Steroid Therapy
Long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to bone weakening over time. Taking acid as a measure can help protect bone health and counteract this negative impact.
How Ibandronic Acid Injection Works
Mechanism of Action: Bisphosphonate Pathway
When Ibandronic acid attaches to bone minerals in the body system, it targets osteoblast cells to create balance in the process of bone reconstruction by impeding their activities that lead to bone breakdown.
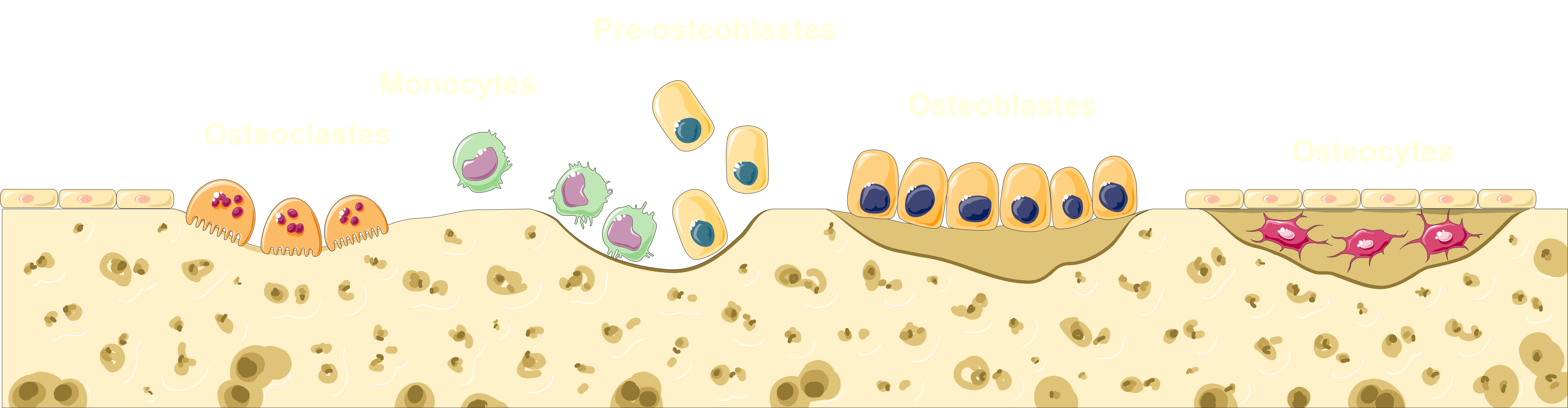
Impact on Bone Resorption and Formation
The medication reduces the breakdown of bone without affecting bone growth processes, resulting in an increase in bone strength and density.
Duration of Action in the Body
Ibandronic acid retains its effectiveness over time, which enables frequent administration while providing lasting advantages for safeguarding bones.
Ibandronic acid dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosages for Approved Uses
The recommended amount changes depending on the reason for use: a 3 mg injection every three months for osteoporosis and custom dosages for cancer treatment purposes.
Frequency of Administration
The prolonged period of effectiveness enables osteoporosis patients to receive doses for convenience without sacrificing effectiveness.
Route of Administration: Intravenous Infusion
Administering acid through infusion allows for quick and thorough delivery of the medication.
Dose Adjustments for Specific Populations
Renal function must be assessed before administration. Adjustments are necessary for patients with compromised renal function to avoid toxicity.
Guidelines for Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, it should be administered immediately, ensuring the schedule resumes without compromising therapeutic outcomes.
Composition of Ibandronic Acid Injection
Active Ingredients
The key component in play here is ibandronic acid, in the form of sodium salt, which provides anti-bone loss effects.
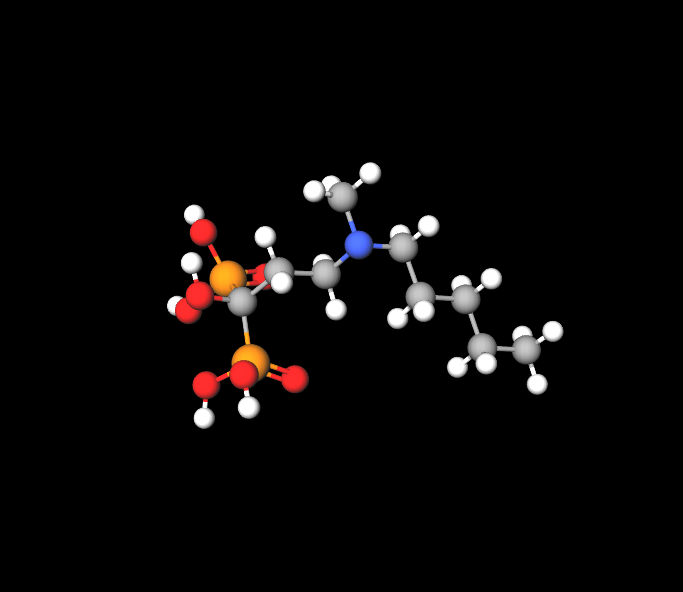
Inactive Components
Inactive components, including saline buffers, stabilize the formulation for effective delivery.
Available Forms and Concentrations
Pre-filled syringes or vials of acid injection come in concentrations to meet different medical requirements.
Ibandronic acid vs alendronic acid
Both ibandronic and alendronic acid are bisphosphonates commonly prescribed for osteoporosis treatment. Compared to acid and its side effects, in the gastrointestinal tract, ibandronic acid is known to have fewer adverse events, possibly due to its lower dosage administration.
Storage and Handling Instructions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Please keep the product in a place at room temperature (15°C. 25°C) away from sunlight and moisture.
Stability and Shelf Life
Seal everything to keep it stable, and remember to follow the expiration dates for maximum effectiveness.
Special Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare workers must adhere to a procedure to avoid contamination while administering treatment.
Ibandronic acid side effects
Common Side Effects
- Redness and swelling may occur at the site where the injection was administered.
- Feeling sick and tired after taking the medication.
- Initial doses may cause symptoms resembling those of the flu.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Patients with risk factors need to be monitored due to the uncommon complication known as ONJ.
Atypical Femur Fractures
While not frequently occurring, it is important for individuals who use the drug for periods to remain attentive to these types of fractures.
Severe Hypocalcemia
It's important to keep an eye out for any changes in patients' calcium levels and pay attention if there are concerns about existing deficiencies.
Ibandronic acid interactions
Potential Interactions with Other Medications
Calcium Supplements and Antacids
It's important to note that taking these medications together can impact how well your body absorbs acid, so it's essential to space out the doses.
NSAIDs and Corticosteroids
Using both medications simultaneously might worsen stomach discomfort, calls for careful attention to this issue.
Aminoglycosides and Loop Diuretics
These mixtures increase the likelihood of calcium levels and kidney problems that require observation.
Effects of Concomitant Use with Other Bisphosphonates
Using more than one type of bisphosphonate is unnecessary. This could lead to more side effects without any extra advantages.
Ibandronic acid warnings and Precautions
Key Warnings for Patients and Healthcare Providers
Patients and healthcare professionals need to be careful when using acid injection as it comes with risks that can result in severe complications if not taken seriously, and overlooked warnings should be heeded, such as refraining from administering it to patients allergic to the drug and conducting necessary screenings beforehand.
Monitoring for Renal Function and Bone Mineral Density
It is crucial to monitor kidney function because ibandronic acid could worsen kidney issues in some vulnerable people. Regularly tracking bone mineral density (BMD) helps ensure that the medication is working as intended and not causing any disruptions.
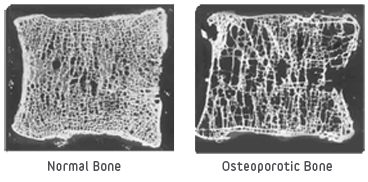
Importance of Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
Maintaining levels of calcium and vitamin D is essential to ensure that ibandronic acid works effectively and to prevent the occurrence of calcium levels during treatment.
Contraindications for Ibandronic Acid Injection
Hypersensitivity to Ibandronate or Related Compounds
Patients who have previously experienced hypersensitivity reactions to ibandronate or other similar bisphosphonates should steer clear of the medication upon experiencing symptoms, like a rash or anaphylaxis, to ensure their safety and well-being.
Severe Renal Impairment (Creatinine Clearance <30 mL/min)
Individuals with kidney problems should avoid taking acid as it can be harmful due to how the body eliminates the drug through the kidneys, potentially leading to toxicity in these patients.
Guidelines for Careful Administration
Pre-treatment Assessment of Renal Function
Before giving acid, it's crucial to assess kidney function, which involves checking serum creatinine levels and determining creatinine clearance.
Ensuring Adequate Hydration Before Injection
Monitoring for Early Signs of Adverse Effects
Patients need to be monitored for signs of potential side effects, like muscle cramps or stomach discomfort to prevent serious complications through timely intervention.

Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Adjustments for Age-Related Renal Decline
Older people frequently encounter a decline in kidney function, which requires dosage modifications to prevent any effects.
Specific Monitoring Protocols
Regularly checking skeletal health markers is essential to ensure efficient treatment for this group of individuals.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Potential Risks During Pregnancy
The FDA categorizes Ibandronic acid as a pregnancy category C medication, indicating that it should be administered when the advantages, for the mother, exceed the risks to the developing baby.
Excretion in Breast Milk and Safety for Infants
The certainty of acids' presence in breast milk is still unclear, so it is advisable for nursing mothers to seek advice from their healthcare providers to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages involved.
Administration to Children
Limited Data on Pediatric Use
There is information from trials about the safety and effectiveness of ibandronic acid in children; therefore, it should be used with caution in pediatric populations.
Experimental and Off-label Considerations
Treating conditions like imperfect requires assessment and continuous monitoring in experimental settings.
Overdosage and Management
Symptoms of Ibandronic Acid Overdose
Severe Hypocalcemia and Hypophosphatemia
Experiencing an overdose may lead to decreases in calcium and phosphate levels in the body, which can show up as muscle spasms (tetany), seizures, or irregular heartbeats (cardiac arrhythmias).
Renal Dysfunction
Taking too much can make your kidneys work harder. It may cause sudden kidney problems or long-term kidney damage.
Emergency Interventions and Antidotes
Supportive Care and Monitoring
For effective support, it is recommended that calcium be administered and electrolyte imbalances corrected while the patient's condition is closely monitored under medical supervision.
Role of Dialysis in Management
Dialysis might help eliminate medication in instances of kidney impairment; however, its efficacy is constrained by the drug's strong attachment to bone tissue.
Important Precautions for Handling and Disposal
Safe Handling Practices for Healthcare Workers
Healthcare professionals should always wear gloves. Practice procedures when preparing and administering treatments to reduce the chances of contamination.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Please dispose of any acid according to your local regulations; avoid pouring it down drains or throwing it away with household waste.
Guidelines for Avoiding Environmental Contamination
Ensuring the safety of the environment is crucial, so it's important for institutions to have protocols for managing pharmaceutical waste responsibly.
Ibandronic acid injection FAQ
- When to take ibandronic acid?
- What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
- What is ibandronic acid?
- What is ibandronic acid used for?
- How long should i take ibandronic acid?
- How does ibandronic acid work?
- How to use ibandronic acid?
- How to take ibandronic acid tablet?
- How to take ibandronic acid injection?
- How ibandronic acid works?
- Can ibandronic acid cause joint pain?
- What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
- How to give ibandronic acid?
- How to administer ibandronic acid?
When to take ibandronic acid?
Make sure to take it in the morning before consuming food or drinks or taking medications.
What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
Treatment for osteoporosis includes the use of medication, which improves bone strength and reduces the risk of fractures.
What is ibandronic acid?
Ibandronic acid belongs to a class of medications known as bisphosphonates, commonly used to prevent bone fractures in individuals with bone-related cancer conditions
What is ibandronic acid used for?
It is effective for addressing elevated calcium levels in the bloodstream due to bone metastases from cancer (secondary bone cancer) as bone fragility or discomfort resulting from breast cancer metastasizing to the bones.
How long should i take ibandronic acid?
It is usually taken for 6 months to achieve the maximum effect. After that, it can be taken as long as it is effective.
How does ibandronic acid work?
It's known that ibandronic acid can lower activity, which may lessen pain and improve bone strength by reducing calcium loss from the bones, thus bringing calcium levels in the blood back to normal.
How to use ibandronic acid?
In the morning you should have your ibandronic acid tablets with a glass of water.
How to take ibandronic acid tablet?
In the morning you should have your ibandronic acid tablets with a glass of water.
How to take ibandronic acid injection?
Administer the Ibandronic acid concentrate solution through an infusion lasting 2 hours.
How ibandronic acid works?
Ibandronic Acid slows down cells that brek down bone.
Can ibandronic acid cause joint pain?
Symptoms of the condition could involve elevated body temperature, shaking or shivering spells, headaches, or discomfort in muscles, joints, or bones.
What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
Ibandronate is commonly prescribed to treat osteoporosis by enhancing bone strength and reducing the risk of fractures.
How to give ibandronic acid?
Remember to take the tablet in the morning on an empty stomach and swallow it whole with a glass of water—no chewing or crushing is allowed! Make sure to sit or stand upright when you gulp down the tablets.
How to administer ibandronic acid?
The infusion of ibandronic acid concentrate for solution should be given over 2 hours.













