Gemifloxacin Mesylate
- 1. Introduction to Gemifloxacin Mesylate
- 2. Composition and Properties of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
- 3. Uses of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
- 4. Off-Label Uses of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
- 5. How Gemifloxacin Mesylate Works
- 6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 7. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- 8. Special Considerations in Administration
- 9. Interaction with Other Medications
- 10. Contraindications and Cautions
- 11. Storage and Handling Precautions
- 12. Overdosage Information
- 13. Important Precautions and Warnings
1. Introduction to Gemifloxacin Mesylate
Overview of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
Gemifloxacin Mesylate is an antibiotic from the fluoroquinolone class, known for its effectiveness in treating various bacterial infections. It is commonly used to treat infections and is valued for its wide range of antibacterial properties and ability to be taken orally.
Brief History and Development
The creation of Gemifloxacin Mesylate represented a step forward in the field of antimicrobial treatment. Launched in the 2000s, it was designed to combat the increasing resistance observed with previous fluoroquinolones, providing a better pharmacokinetic profile to improve patients' results.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Gemifloxacin Mesylate holds a place in contemporary healthcare, playing a vital role in treating community-acquired pneumonia and acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Its effectiveness in care highlights its essential position in combating bacterial infections within therapeutic treatments.
2. Composition and Properties of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
Chemical Composition and Formula
Gemifloxacin Mesylates molecular makeup, with the formula C18H20FN5O4, incorporates a fluorinated quinolone structure essential for its antibacterial properties. The addition of mesylate salt improves its solubility and stability, making it well suited for intake.
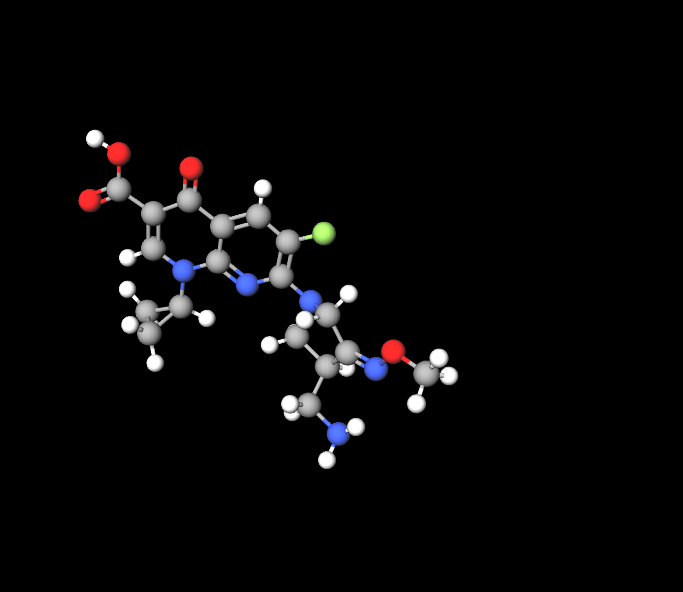
Physical and Chemical Properties
This substance is known for its crystal appearance, usually white or light yellow. It dissolves in water and has some solubility in ethanol. Its ability to remain stable under circumstances is an important aspect that guarantees its effectiveness once it is administered.
3. Uses of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
Primary Indications: Treating Respiratory Infections
-
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis (ABECB):
- Gemifloxacin is effective in treating ABECB, which refers to the sudden worsening of symptoms in patients with chronic bronchitis due to bacterial infection. It helps combat bacterial pathogens responsible for exacerbations.
- The drug acts by inhibiting DNA synthesis through the inhibition of both DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are essential for bacterial growth1.
-
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP):
- Gemifloxacin is also indicated for the treatment of CAP. CAP is a common type of pneumonia acquired outside of hospitals or healthcare facilities.
- The drug’s broad-spectrum activity targets susceptible bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Gemifloxacin’s ability to penetrate tissues effectively contributes to its efficacy in eliminating the pathogens causing CAP1.
Comparison with Other Antibiotics
4. Off-Label Uses of Gemifloxacin Mesylate
Overview of Common Off-Label Uses
Although not officially sanctioned for these purposes, Gemifloxacin Mesylate is sometimes recommended for:
- Treating urinary tract infections
- Providing preventive care for specific immunocompromised individuals
Doctors choose to use this antibiotic in such scenarios due to its wide-ranging antibacterial effectiveness and positive safety record.
5. How Gemifloxacin Mesylate Works
Mechanism of Action Against Bacteria
Gemifloxacin methylate works mainly by blocking DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are essential enzymes for DNA replication and cell division. This activity leads to a halt in bacterial growth and reproduction.
Impact on Bacterial DNA Replication
Interfering with the process of DNA replication proves fatal for bacteria, resulting in their swift demise. This action greatly enhances the drug's efficacy in treating bacterial infections, offering quicker symptom relief compared to numerous other antibiotics.
Factors Influencing Efficacy
- Bacterial resistance patterns in the community
- Patient compliance with the dosage regimen
- Pharmacokinetic variations among individuals
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage Recommendations
Gemifloxacin Mesylate is usually given in the form of a 320 mg tablet daily. The length of treatment depends on the type of infection being addressed typically lasting 5 to 7 days, for bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and 7 to 14 days for community acquired pneumonia.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Adjusting the dosage may be required for groups such as patients with kidney issues and older individuals with reduced kidney function. It is important to make these changes to avoid the buildup of the medication, which may cause effects.
Administration Techniques and Best Practices
For results, make sure to take Gemifloxacin Mesylate either 2 hours before or 3 hours after consuming antacids, multivitamins, or any products with magnesium, aluminum, iron, or zinc.
- It's crucial for patients to complete the treatment regimen even if they start feeling better to avoid the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
- Following these guidelines plays a role in reaching the intended therapeutic results and reducing potential side effects.
7. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common Side Effects: Risk and Management
The common side effects of Gemifloxacin Mesylate often consist of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, and dizziness.
- These issues are usually mild can typically be alleviated with non prescription remedies or, by modifying the medication dosage under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Severe Reactions and Long-Term Implications
In some cases, there might be serious side effects like tendonitis and tendon tears, QT prolongation, which affects the heart rhythm, and severe skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Individuals with these symptoms should promptly seek help. The lasting consequences of these effects highlight the need for careful usage, particularly among vulnerable groups.
Reporting and Managing Unexpected Reactions
Healthcare professionals need to notify the medical authorities about any unusual or serious reactions to keep track of the drugs safety. Patients should feel empowered to share any effects they encounter as this is crucial, for continuous safety monitoring and shaping future prescription practices.
8. Special Considerations in Administration
Administration to the Elderly: Precautions and Dosage Adjustments
It's important to use Gemifloxacin Mesylate in older patients as they might have changes in kidney function due, to aging.
Dosages should be adjusted appropriately to prevent the buildup of the medication and potential harm. Its advised to check kidney function to make sure the treatment is effective and safe.
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Gemifloxacin Mesylate is not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to harm to fetal development. If there is a need for this antibiotic, it should be prescribed cautiously after weighing the advantages and disadvantages. Expectant or nursing mothers should be informed about how it could affect their children.
Pediatric Use: Safety and Efficacy
The safety and effectiveness of Gemifloxacin Mesylate in children have not been definitively proven. Given worries about how fluoroquinolones may impact bone, joint, and cartilage growth, it is advised to use this medication in pediatric patients when there are no safer options. Thorough evaluations for children and careful dosing are considerations.
9. Interaction with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Management
Gemifloxacin has the potential to interact with medications, which could change how they work.
- Important interactions to note include: Antacids, iron, and zinc supplements may hinder the absorption of Gemifloxacin.
- Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) could raise the risk of CNS stimulation and seizures.
- To address these interactions, it is suggested that medications be adjusted to prevent conflicts or replaced with safer options.
Effects on Systemic Medication Levels
Gemifloxacin may impact the levels of medications in the body, like warfarin and theophylline, which could require dosage changes to ensure effectiveness and avoid potential harm.
Avoiding Adverse Interaction Scenarios
Healthcare professionals must perform a medication evaluation prior to prescribing Gemifloxacin in order to avoid potential negative interactions. Patients need to be reminded to disclose all medications they are currently taking, including prescription drugs and supplements for a well rounded approach, to their treatment plan.
10. Contraindications and Cautions
Absolute Contraindications for Use
Patients with a past of tendon issues linked to fluoroquinolone therapy should not take Gemifloxacin. It is also not suitable for individuals to any part of the medication as it may cause severe allergic responses.
Conditions Requiring Careful Administration
Patients with kidney problems, epilepsy, or a history of seizures need to be given Gemifloxacin. Dosages should be adjusted accordingly to reduce risks and closely observe for any side effects.
Precautions for Patients with Pre-existing Conditions
Patients who have heart conditions and those prone to QT prolongation should be carefully watched while taking Gemifloxacin to prevent the possibility of experiencing irregular heartbeats. It is recommended for these patients to undergo a medical evaluation and continuous cardiac monitoring.
11. Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Gemifloxacin needs to be kept in a room, with temperature shielded from light and moisture to maintain its effectiveness and extend its storage duration. It's important to store it in a place that children and pets cannot reach to avoid consumption.

Handling Precautions to Maintain Efficacy
Remember, it's important to store the tablets in their packaging until you're ready to use them and to avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures that could potentially damage the active ingredients.
Disposal and Environmental Concerns
It is important to follow the guidelines for pharmaceutical disposal to get rid of expired or unused gemifloxacin. This helps prevent pollution and lowers the chances of drug abuse.
12. Overdosage Information
Symptoms of Overdosage and Immediate Actions
In the case of taking much Gemifloxacin, one might experience symptoms like sudden kidney failure, queasiness, lightheadedness, and seizures. It is vital to seek medical attention, which may involve providing symptom relief and possibly using dialysis to help eliminate the excess drug from the body.
Long-Term Management of Overdose Patients
Continuing to observe the kidney function and neurological condition over a period is essential until the patient's condition stabilizes, providing continuous care to avoid any lasting damage.
Prevention Strategies and Education
Educating patients about the significance of following dosages and schedules is crucial in preventing overdoses. Healthcare professionals must highlight the dangers linked to straying from recommended treatments.
13. Important Precautions and Warnings
Critical Safety Information for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to stay alert and watch out for any indications of responses particularly related to tendon issues, cardiac problems, and potential tendon ruptures. It is crucial to act and make necessary treatment adjustments if the patient's well-being is at risk.
Patient Education and Awareness
Patients need to know about the side effects of Gemifloxacin, the significance of finishing the entire treatment and the importance of promptly reporting any unusual symptoms.
Legal Implications and Liability
When doctors prescribe Gemifloxacin they have obligations. It's important for healthcare providers to follow the clinical recommendations and make sure patients understand their treatment fully. This helps reduce liabilities and improve patient care.






























