Irbesartan/ Hydrochlorothiazide
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- III. How Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- V. Off-label Uses of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- VII. Special Administration Instructions
- VIII. Common Side Effects and Serious Adverse Reactions
- IX. Interactions with Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- X. Contraindications and Warnings of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
- XI. Handling Precautions and Storage Conditions
- XII. Overdosage: Identification and Management
- XIII. Important Precautions When Using Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
From the realm of exploration, Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide, a well-regarded fixed-dose combination therapy for hypertension, has significantly influenced the field of medicine. This sophisticated formulation brings together the properties of two active substances, Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide, each contributing its own distinct approach to tackling the complex condition known as high blood pressure.
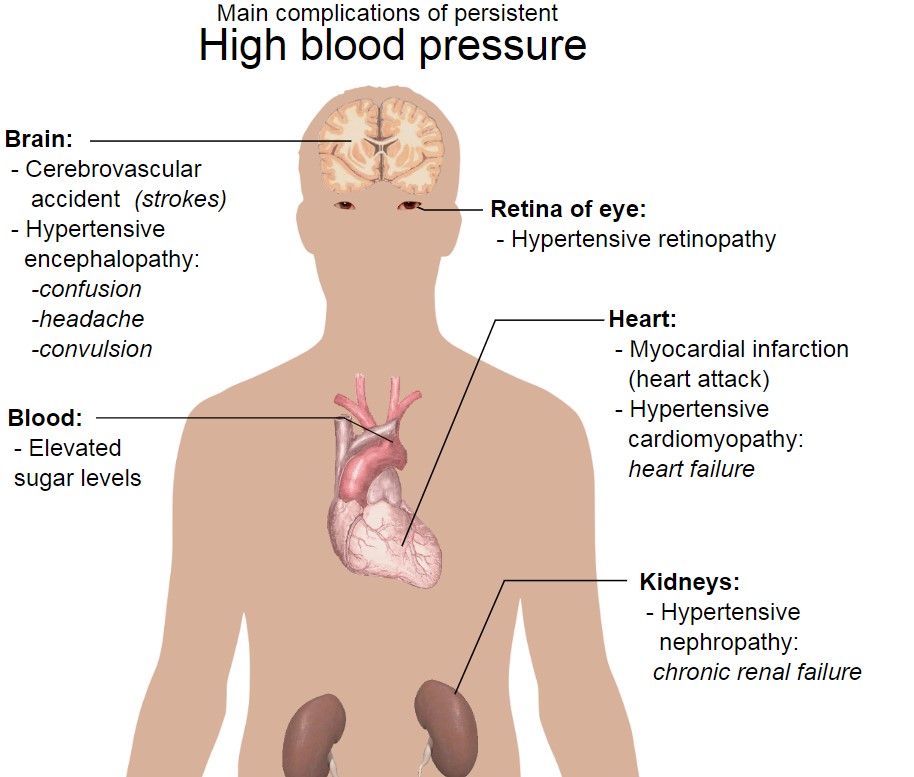
Hypertension Complications
B. Importance in the Medical Field
In the world of treatments, the significance of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide has been steadily increasing. This drug plays a role in managing the common condition of hypertension, acting as a strong protector against the gradual advancement of cardiovascular disease. Its crucial contribution to alleviating symptoms related to blood pressure makes it an essential tool for healthcare professionals globally.
II. Composition of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Irbesartan: The Active Ingredient
Irbesartan, the active ingredient in this formulation, belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin II receptor antagonists. These drugs are known for their ability to skillfully interact with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). The benefits of using irbesartan include ;
- Counteracting the effects of angiotensin II
- Widening blood vessels which ultimately help lower blood pressure.
B. Hydrochlorothiazide: The Secondary Component
Hydrochlorothiazide, which is another ingredient, falls under a category of drugs called thiazide diuretics. These medications are well-regarded for their diuretic and antihypertensive properties.
They work by inhibiting the kidney's reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions. This leads to an increase in the elimination of water from the body resulting in a decrease in blood volume and subsequently lowering blood pressure.
C. Role of Inactive Components
The components that aren't active, commonly referred to as excipients, have an often overlooked role in the entire formulation process. These include binders, fillers, disintegrants, and lubricants. Their purpose is to maintain stability, improve the absorption of ingredients and ensure effective delivery for the enhanced therapeutic effectiveness of the formulation.
III. How Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Works
A. Mechanism of Action
The way Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide works is truly remarkable. It combines the effects of its components in a harmonious manner. Irbesartan counteracts the angiotensin II receptors, which helps dilate blood vessels and reduce the production of aldosterone. On the other hand, Hydrochlorothiazide promotes increased urination by preventing the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the kidneys resulting in lower blood volume and pressure. Together these substances work together to effectively manage hypertension creating a symphony of benefits.
B. Role of Irbesartan in Controlling Hypertension
Irbesartan, a medication that blocks the angiotensin II receptors, plays a vital role in combating hypertension. By preventing vasoconstriction and reducing the release of aldosterone, it helps improve blood flow and lower blood pressure. This demonstrates the connection between scientific advancements and effective treatment for managing high blood pressure.
C. Hydrochlorothiazide's Function in Diuretic Therapy
Hydrochlorothiazide serves as a thiazide diuretic which helps to promote diuresis. It works by preventing the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the convoluted tubule leading to increased fluid excretion. As a result, it reduces blood volume. Ultimately lowers blood pressure. This diuretic effect contributes, to the comprehensive management of hypertension.
D. Synergistic Effect of the Combined Drugs
The true beauty of the Irbesartan/ formulation lies in how its different components work together. While Irbesartan widens the blood vessels Hydrochlorothiazide lowers the amount of blood in circulation. These simultaneous actions result in a decrease in blood pressure showing a truly harmonious effect. This strong combination exemplifies the idea, behind polypharmacy, which is using multiple drugs to create a therapeutic outcome that goes beyond what each drug can achieve individually.
IV. Approved Uses of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Treatment of Hypertension
Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide stands out as a powerful solution in the world of therapeutic options for hypertension(1). This combination drug has received approval for treating blood pressure, which speaks to its effectiveness and safety. Combining Irbesartan's properties with Hydrochlorothiazide's diuretic effects directly tackles hypertension by reducing blood pressure(2). These two components work together to ;
- Counteract the effects of angiotensin II, promoting blood vessel dilation and facilitating better blood flow.
- They encourage the elimination of fluid and sodium from the body resulting in reduced blood volume and lower blood pressure.(3)
This drug's significant impact in managing hypertension is supported by clinical trials solidifying its role in this crucial therapy area.
1. Mayo Clinic - Irbesartan And Hydrochlorothiazide (Oral Route)
2. Cleaveland Clinic - Irbesartan; Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets
Hypertension
B. Management of Heart Failure
Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide goes beyond treating blood pressure and offers significant therapeutic benefits in managing heart failure. While it is mainly known for its ability to lower blood pressure, it has also shown effectiveness in reducing hospitalization and mortality rates among patients with heart failure. Its valuable role in managing heart failure stems from its ability to address two challenges;
- Reducing the resistance the heart encounters as it pumps blood through the system is achieved primarily through Irbesartan vasodilatory effects.
- Controlling accumulation in the body is a common complication of heart failure thanks to Hydrochlorothiazide's strong diuretic action.
By addressing these issues, Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide provides crucial support for patients with heart failure highlighting its versatility and vital role in the field of medicine.
V. Off-label Uses of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Treatment of Edema
Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide shows potential in the field of off-label uses, particularly in treating edema. Edema is a condition characterized by a buildup of fluid in the body tissues. The remarkable effectiveness of this combination lies in Hydrochlorothiazide's diuretic properties.
By aiding the elimination of water and salts, it helps reduce fluid accumulation alleviating swelling and discomfort often associated with edema. Although not officially indicated for this purpose, its widespread use for edema highlights the versatility of this combination therapy.
B. Potential Uses in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Another interesting possible use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide is in the context of kidney disease. Irbesartan, by blocking angiotensin II receptors, has shown promise in reducing kidney damage, which's a significant complication for diabetic patients. This protective effect is evident through its ability to decrease proteinuria, an indicator of kidney damage.
Additionally, it can slow down the progression of kidney disease by controlling blood pressure and providing renal protection. Although more research is required to confirm this application, initial evidence suggests that Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide could play a beneficial role in managing diabetic kidney disease.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Initial Dosing Guidelines
The skill of pharmacotherapy involves not selecting the right medication but also determining the correct dosage. In the case of starting treatment with Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide for adults, it is generally advised to take one tablet that contains 150mg of Irbesartan and 12.5mg of Hydrochlorothiazide once a day by mouth. This method guarantees benefits;
- It allows for an initial lower dose to assess how each patient responds
- Minimizes the likelihood of any possible side effects.
B. Titration and Maximum Dose
After assessing the response, the dosage can be adjusted as per the individual patient's requirements. It is recommended not to exceed a dose of one tablet containing 300mg of Irbesartan and 25mg of Hydrochlorothiazide. The purpose of titration is to achieve therapeutic effectiveness while minimizing the risk of potential adverse reactions that may occur with higher initial doses.
C. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
Some groups of people, such as those with kidney problems, older individuals, and children, may require adjustments in how medicine they should take. This personalized approach ensures that the medication is given safely and effectively to these populations while minimizing the chance of harmful side effects.
VII. Special Administration Instructions
A. Administration to the Elderly
When giving Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide to patients, it is crucial to exercise caution and closely monitor their condition. The possibility of reduced kidney function in this age group requires consideration when determining the dosage, considering the higher likelihood of decreased liver, kidney, or heart function as well as any existing medical conditions or concurrent medication.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide during pregnancy is categorized as harmful to the fetus so it should only be prescribed if the benefits outweigh the risks. Moreover considering the negative effects on a nursing baby a careful decision should be made whether to continue breastfeeding or stop taking the medication considering its importance, to the mother.
C. Administration to Children
The use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide in children has not been proven to be safe and effective. As a result, it is generally discouraged to prescribe this medication to patients unless no other options are available and the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks.
VIII. Common Side Effects and Serious Adverse Reactions
A. Most Frequently Reported Side Effects
While Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide has its advantages, it's important to note that it may cause some side effects. The frequently reported ones are
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
However, these effects are typically mild and temporary as the body adapts to the medication.

Dizziness
B. Rare but Serious Adverse Reactions
Although they are uncommon, there can be side effects such as angioedema (an allergic reaction that causes swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat) issues with the kidneys, and imbalances in electrolytes. If any of these symptoms are suspected it is important to seek medical attention.
C. What to Do in Case of a Severe Reaction
If you experience a negative response, the initial action should be to stop taking the medication immediately and seek urgent medical help. It is important to provide your healthcare provider with information about the reaction, including when it began, how severe it was, and any other symptoms that may have occurred at the same time. This will assist them in diagnosing the issue and determining the appropriate treatment.
IX. Interactions with Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
In the changing world of pharmaceutical treatments, it is not uncommon for different medications to interact with each other. When it comes to Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide, certain drugs have the potential to affect how well it works or cause side effects.
These include; antihypertensive drugs, which could amplify the blood pressure-lowering effect and lead to low blood pressure. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs might reduce its ability to lower blood pressure and harm kidney function. Understanding possible interactions between medications is crucial for ensuring that therapy is safe and effective.
B. Food-Drug Interactions
Although there are usually no food interactions, it is advisable to be cautious when consuming alcohol while undergoing Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide therapy. This is because alcohol can act as a vasodilator and may potentially worsen the drugs hypotensive effect.
C. Interactions with Herbal Supplements and OTC Medications
Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide has the potential to interact with over-the-counter (OTC) medications and herbal supplements. For example, prescription cough, cold, and allergy medications can potentially raise blood pressure levels and disrupt the antihypertensive impact of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide. Additionally, herbal supplements such as St. Johns Wort might influence how the body metabolizes this medication.
X. Contraindications and Warnings of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Conditions that Prohibit Usage
Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide should not be used in patients who have anuria, which's a condition where urine production is absent. It is also not recommended for individuals with a hypersensitivity to Irbesartan, Hydrochlorothiazide, or any other ingredient in the medication.
B. Potential Risks and Safety Measures
Although this medication is usually well tolerated it's important to be aware of risks. These risks may include levels of potassium (known as hyperkalemia) reduced kidney function and imbalances in electrolyte levels. To ensure safety, it is advised to monitor serum electrolytes and kidney function.
C. Warning for Specific Patient Populations
Women should refrain from taking this medication as it may pose risks to the developing fetus. Similarly, nursing mothers are advised against using this medication due to the potential for adverse reactions in breastfeeding infants. As for patients, the safety and effectiveness of this drug have not been established yet.
XI. Handling Precautions and Storage Conditions
A. Proper Storage Techniques
Store Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide at room temperature, ensuring it is kept away from moisture and heat. Additionally, make sure to keep it out of the reach of children.
B. Stability and Shelf Life
The medication remains stable throughout its recommended shelf life if stored as instructed. You can find the expiration date on the packaging. It's important not to use the medication beyond that date.
C. Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
You should avoid throwing away any medication that you are not using or that has expired by putting it down the drain or in your trash. Instead, the best course of action is to return it to a pharmacy or a local waste disposal company so that it can be properly disposed of and help protect the environment.
XII. Overdosage: Identification and Management
A. Symptoms of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Overdose
Taking much Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide can lead to various symptoms. These symptoms may include experiencing ;
- Dizziness
- Fainting due to drops in blood pressure
- Muscle cramps
- Weakness
- Irregular heart rhythms as a result of an imbalance in levels
- Decreased urine output.
- Swelling in the lower limbs could indicate potential kidney problems.
It is important to recognize these symptoms for timely and effective treatment.
B. Immediate Steps for Management
When someone experiences an overdose, the main goal is to eliminate any remaining unabsorbed medication from their body. This is commonly done through a procedure called lavage, which is also known as stomach pumping.
Additionally, symptomatic treatment is provided to address issues such as blood pressure and imbalances in electrolytes.
C. Long-term Consequences and Follow-up
If someone experiences an overdose of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide, it can potentially have long-lasting effects on their kidney function and electrolyte balance. That's why it is crucial to monitor and schedule follow-up visits, for individuals who have gone through an overdose.
XIII. Important Precautions When Using Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide
A. Monitoring Response to Therapy
Regularly monitoring the response to Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide is crucial. This includes checking blood pressure and occasionally conducting blood tests to keep an eye on electrolyte levels and kidney function. Consistent monitoring serves purposes; it helps assess the effectiveness of the treatment and allows for early identification of any potential side effects.
B. Precautions for Long-Term Use
To ensure the effective use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide over an extended period, it is important to take certain precautions. Make sure to stay properly hydrated promptly, inform your healthcare provider about any symptoms you may experience and avoid stopping the medication abruptly without consulting a medical professional.
C. Understanding the Risks and Benefits
Like any medication, Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide has its set of risks and benefits. While it provides a way to manage high blood pressure, there are potential side effects to consider. Therefore it's important to have an understanding of these risks and benefits and engage in open discussions with your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcome for your treatment.