Lovastatin
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition
- III. How Lovastatin Works
- IV. Uses of Lovastatin
- V. Off-label Use
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Administration to Special Populations
- VIII. Interaction with Other Drugs
- IX. Side Effects of Lovastatin
- X. Contraindications and Warnings
- XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XII. Overdose and its Management
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precactions
- XIV. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Brief History of Lovastatin
In the 20th century, a medication called Lovastatin emerged as a significant player in the fight against cardiovascular disease. It was developed by Alfred Alberts and his team at Merck after research and groundbreaking discoveries. Approved by the FDA in 1987, this powerful drug belongs to a class of medications known as statins. Derived from a compound found in Aspergillus terreus Lovastatin marked the beginning of a new era in lipid-lowering therapy.
General Description and Purpose
Lovastatin, which falls under the statin family, is mainly used to lower LDL cholesterol levels in the body. Its primary goal is to reduce the risk of heart-related conditions like heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Lovastatin works by blocking an enzyme that plays a role in cholesterol production. This way it helps decrease cholesterol levels and promotes a healthier balance of cholesterol in the body.
Common Brands
Lovastatin can be found under brand names worldwide. The well-known and widely used brand is Mevacor®, which Merck & Co. Other popular brands manufacture include Altocor™ Altoprev™ and Lovalip. Additionally, generic versions of the medication are easily accessible, ensuring that people can afford this medication to save lives.
II. Composition
Active Ingredients
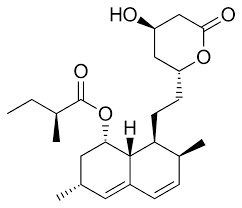
Lovastatin consists of lovastatin as its active component. Each tablet or capsule of this medication contains an active compound typically available in 10 to 80-mg doses. It's important to understand that Lovastatin, a prodrug, transforms into its form (β hydroxy acid) within the body.
Inactive Ingredients
In addition, to the component, Lovastatin also contains various inactive ingredients that assist in the delivery of the medication. These additional components may include, Are not restricted to cellulose, lactose, magnesium stearate, and starch. The specific inactive ingredients can vary depending on the brand and form of dosage. Specific versions might even include colorants and preservatives.
III. How Lovastatin Works
Biochemical Mechanism of Action
Lovastatin is a blocker of HMG CoA reductase, an important enzyme in the mevalonate pathway that produces cholesterol in the liver. When it takes on its form as β hydroxy acid Lovastatin acts like a competitor closely resembling the natural substance HMG CoA that the enzyme works with. By fitting into the enzyme active site, Lovastatin effectively hinders the conversion of HMG CoA into mevalonate, which is essential for cholesterol production. This hindrance causes a decrease in cholesterol levels, prompting an increase in LDL receptor expression and subsequently leading to greater uptake of LDL, from the bloodstream.
Influence on Cholesterol Levels
Lovastatin plays a role in managing cardiovascular risk by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the body. This decreases total cholesterol levels, particularly the "bad" LDL cholesterol. Moreover, it positively impacts increasing the "good" HDL cholesterol and reducing triglycerides, which collectively contribute to an improved lipid profile. These changes are crucial for preventing and treating conditions like atherosclerosis and its complications making Lovastatin an essential tool in risk management.

IV. Uses of Lovastatin
Primary Indications: Hypercholesterolemia and Cardiovascular Disease
Lovastatin is a medication used to lower blood levels of “bad” cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein, or LDL), to increase levels of “good” cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein, or HDL), and to lower triglycerides12. It is in a class of medications called HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)1. Lovastatin works by blocking an enzyme in the liver known as HMG-CoA reductase that is responsible for the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an important substance necessary for the synthesis of cholesterol and coenzyme Q101.
The primary purpose of using Lovastatin is to reduce the amount of cholesterol and other fatty substances in the blood. When cholesterol accumulates in our arteries, it can obstruct blood flow to organs like the heart, brain, or other body parts. This puts us at risk for serious health issues such as heart attacks or strokes13.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
Secondary Indications: Other Lipid Disorders
Lovastatin is a medication used to prevent and treat coronary heart disease. It’s also used to treat high cholesterol12. Lovastatin is used to decrease the amount of cholesterol and other fatty substances in your blood. If cholesterol builds up in your arteries, it may block blood flow to your heart, brain, or other parts of your body. This raises your risk of serious problems, such as a heart attack or stroke. Lowering your cholesterol level lowers these risks13.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
V. Off-label Use
Potential Benefits in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Studies have been conducted on the advantages of Lovastatin in treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Research suggests that Lovastatin may enhance liver function and alleviate inflammation in individuals affected by NAFLD12.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
Use in Neurological Disorders
Research has explored the potential of Lovastatin in treating conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Studies have indicated that it possesses properties and could potentially aid in reducing inflammation.
Here is a reference that you can use for your content:
Current Research and Future Perspectives
Research has explored the potential of Lovastatin in treating conditions such as cancer, osteoporosis, and autoimmune diseases12. However, more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of Lovastatin in treating these conditions.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
VI. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage for Adults
The usual initial amount of Lovastatin prescribed for adults is 20mg daily, typically taken during the evening meal. However, depending on how the patient responds and tolerates the medication, the dosage can be gradually increased to a maximum of 80mg per day. It's important to note that any dosage adjustments should be made at least four weeks between them or even longer allowing enough time to evaluate how the medication affects lipid levels.
Adjustments for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Patients with kidney problems usually don't need to change their dosage of Lovastatin because it is mostly eliminated through the kidneys. However, it's essential to be cautious if you have liver issues. Since Lovastatin is mostly broken down in the liver, people with long-term liver diseases should start with doses and be closely monitored if you have liver impairment, it's generally not recommended to use Lovastatin due to the higher risk of medication-induced liver damage.
Tablet vs. Capsule: Differences and Similarities
Lovastatin can be obtained in two forms; tablets and capsules. Although the active ingredient remains unchanged, the key distinction lies in how they release the medication. Regular tablets release Lovastatin away, whereas specific capsule variants, such as Altoprev™, have an extended-release mechanism. This slow-release formula ensures a consistent impact over 24 hours. It is recommended to take both forms with food and swallow them whole to ensure absorption.
VII. Administration to Special Populations
Elderly Patients: Considerations and Precautions
Although it is possible to give Lovastatin to patients it should be done with caution due to the higher chances of age-related kidney or liver problems. It is advisable to check liver function and use the lowest effective dose to reduce the potential for harmful side effects.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Recommendations
According to the FDA, Lovastatin is categorized as a drug that may cause harm to the fetus. Consequently, it is not recommended for women or those planning to become pregnant. Women who can conceive should ensure they use contraception while taking Lovastatin. Moreover, since its uncertain whether Lovastatin passes into breast milk, nursing mothers are usually advised to stop either taking the medication or breastfeeding to prevent any harm to their baby.
Pediatric Use: Efficacy and Safety
Lovastatin has been researched in teenagers who have hypercholesterolemia, and it has been shown to be effective in a similar way as it is in adults. However, we haven't yet determined its safety and effectiveness in children under ten. Therefore doctors should only prescribe Lovastatin to patients if the potential advantages outweigh the risks and they are under careful medical supervision.
VIII. Interaction with Other Drugs
Common Drug-Drug Interactions
Using Lovastatin concurrently with medications can lead to significant interactions. Some examples of these medications include erythromycin, itraconazole, and HIV protease inhibitors, which inhibit CYP3A4 and can increase the levels of Lovastatin in the bloodstream. This elevation in Lovastatin levels raises the risk of developing myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Additionally, combining Lovastatin with lipid-lowering drugs, like fibrates or niacin, increases the likelihood of experiencing muscular side effects. It is important to avoid consuming grapefruit juice while taking Lovastatin as it inhibits CYP3A4 can interfere with the proper metabolism of the medication.
Interactions with Food and Alcohol
To improve the absorption of Lovastatin, it is generally recommended to take the medication with food. On the hand, consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can increase the likelihood of liver damage and should be avoided. It is important to note that grapefruit juice can significantly raise the levels of Lovastatin in the bloodstream, so it's best to steer off it.
IX. Side Effects of Lovastatin
Common Side Effects: Frequency and Management
Lovastatin, similar to statins, is usually well tolerated by patients. However, there may be instances when patients experience certain common side effects such as headaches, mild muscle pain, abdominal discomfort or indigestion, nausea and diarrhea, or constipation. It's important to note that these side effects are temporary and tend to fade as the body adapts to the medication. If symptoms persist over time, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for guidance. Sometimes, adjusting the dosage or switching to a statin might be necessary.
Serious Side Effects: Signs and Immediate Actions
While it is uncommon, Lovastatin can sometimes lead to side effects, especially when taken in high doses or by more susceptible individuals. These may include experiencing muscle pain or weakness which could be a sign of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. Other possible indicators of liver dysfunction include jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), dark urine, and severe fatigue. If you notice any bleeding or bruising as well, as severe nausea, upper stomach pain, or loss of appetite while taking Lovastatin, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. In some cases, patients should discontinue Lovastatin and consult their healthcare provider without delay.
X. Contraindications and Warnings
Absolute Contraindications
Lovastatin should not be used in the following cases;
1. Patients with a known allergy or sensitivity to any ingredients in the medication.
2. Pregnant. Those who are planning to become pregnant.
3. Nursing mothers.
4. Individuals with liver disease or unexplained and ongoing high levels of certain liver enzymes in their blood.
If you fall into these categories, please consult your healthcare provider for guidance and alternative options.
Relative Contraindications
Some factors that should be considered are; People who consume amounts of alcohol and Individuals, with kidney problems. Patients taking other medications that may increase the chances of muscle-related issues when combined with Lovastatin. When faced with these situations, assessing the potential risks and benefits and exploring alternative options is essential.
FDA Black Box Warnings
Lovastatin does not have any box warnings from the FDA. However, it's essential for patients and healthcare providers to stay updated with sources since guidelines and warnings can change over time.
XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Parameters
To ensure the management of Lovastatin treatment, it is advised to monitor certain aspects regularly. This includes checking the lipid profile before starting therapy, after any dosage changes, and after that. It is also essential to measure liver function at the beginning of treatment. When clinically necessary. If there are symptoms suggesting myopathy, creatine kinase levels should be monitored. Taking action based on these monitoring parameters can help prevent complications and achieve the best therapeutic results.
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Results
Lovastatin plays a role in managing dyslipidemia effectively, especially when combined with the proper lifestyle adjustments. These adjustments include following a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, engaging in regular physical activity under the guidance of a healthcare professional, maintaining a healthy weight quitting smoking, and consuming alcohol moderately. Implementing these changes can significantly enhance the effectiveness of Lovastatin. Reduce cardiovascular risk more effectively than relying solely on medication or lifestyle modifications alone.
XII. Overdose and its Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Although there is information available on the overdose of Lovastatin taking too much of it can lead to typical symptoms associated with statin overdose. These symptoms may include muscle pain, muscle weakness, breakdown of muscle tissue (rhabdomyolysis), and potential liver damage. If you experience muscle pain or weakness, dark or reddish urine, unexplained fatigue, or jaundice, it could indicate an overdose.
First Aid Measures
If you suspect an overdose make sure the person is in a place and can breathe properly. Immediately contact the poison control center for assistance. While waiting for help, avoid inducing vomiting unless a healthcare professional explicitly advises you to do so.
Emergency Medical Treatment Options
When medical personnel arrive, they will primarily focus on providing symptomatic care for Lovastatin overdose since no specific antidote is available. This may involve procedures like lavage to eliminate unabsorbed medication and monitor the functioning of the kidneys and liver. In some instances, hospitalization might be necessary.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precactions
Appropriate Storage Conditions
Store Lovastatin at room temperature between 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). Ensure the medication is kept in a container away from heat, moisture, and direct light. Also, make sure to keep it out of reach and sight of children to avoid ingestion.
Safe Disposal Methods
It is essential to dispose of any unused or expired Lovastatin to avoid causing harm to others. Please do not flush it down the toilet. Pour it into the drain unless specifically instructed to do so. Ideally, it would be best to utilize medication take-back programs for safe disposal. If such a program is unavailable, consulting with a pharmacist or local waste disposal company for guidance on options is recommended.
XIV. Conclusion
Recap of Lovastatin Uses, Administration, and Precautions
Lovastatin, a type of medication known as a statin, is extremely important for managing cholesterol and decreasing the risk of cardiovascular problems. It is generally well tolerated. It's essential to be aware of potential side effects and specific situations where it should not be used. To ensure the possible results from this medication, it's necessary to carefully determine the appropriate dosage monitor its effects, and make lifestyle adjustments as needed.
Importance of Regular Follow-up with Healthcare Provider
Regular checkups with a healthcare provider during Lovastatin treatment are crucial. These appointments allow for assessing the drug's effectiveness, monitoring any side effects, making dosage adjustments if necessary and underscoring the significance of lifestyle modifications. The active involvement of patients in collaboration with healthcare experts plays a role in attaining the desired outcomes of Lovastatin therapy.
Lovastatin FAQ
- Lovastatin side effects?
- Lovastatin uses?
- What is Lovastatin used for?
- Lovastatin 20 mg?
- Lovastatin 40 mg?
- Lovastatin dosage?
- Lovastatin vs Atorvastatin?
- What is Lovastatin?
- Lovastatin medication?
- Lovastatin side effects in elderly?
- Lovastatin generic name?
- Lovastatin interactions?
- Lovastatin cholesterol?
- Lovastatin for cholesterol?
- Lovastatin mechanism of action?
- Lovastatin generic?
- Lovastatin drug class?
- Lovastatin vs Rosuvastatin?
- Lovastatin other names?
- Lovastatin classification?
- Lovastatin dosage for elderly?
- Lovastatin to Atorvastatin?
- Lovastatin red yeast rice?
- Lovastatin in red yeast rice?
- Lovastatin pill?
- Lovastatin contraindications?
- Lovastatin cost?
- Lovastatin and grapefruit?
- Lovastatin vs Simvastatin?
- Lovastatin vs Pravastatin?
- Lovastatin price?
- Lovastatin and warfarin?
- Lovastatin structure?
- Lovastatin indications?
- Lovastatin Mevacor?
- Lovastatin adverse effects?
- Lovastatin vs Lipitor?
- Lovastatin intensity?
- Lovastatin tablets?
- Lovastatin class?
- Lovastatin blood pressure?
- Lovastatin brand and generic name?
- Lovastatin max dose?
- Why is Lovastatin taken with food?
- Lovastatin is used for?
- Lovastatin ER?
- Lovastatin half life?
- Lovastatin grapefruit?
- Lovastatin drug?
- Lovastatin for high blood pressure?
- Lovastatin and alcohol?
- Lovastatin side effects weight gain?
- Lovastatin should be taken when?
- Lovastatin Simvastatin?
- Lovastatin patient teaching?
- Lovastatin muscle pain?
- Lovastatin medicine?
- Lovastatin high intensity?
- Lovastatin HCTZ?
- Lovastatin high blood pressure?
- Lovastatin functional groups?
- Lovastatin long term side effects?
- Lovastatin drug interactions?
- Lovastatin action?
- Lovastatin GoodRx?
- What is Lovastatin generic for?
- Which is better Rosuvastatin or Pravastatin?
- When to take Lovastatin 20 mg?
- Can Lovastatin cause weight gain?
- Can Lovastatin be crushed?
- Can Lovastatin cause joint pain?
- Lovastatin with or without food?
- Lovastatin for blood pressure?
- Lovastatin to Simvastatin conversion?
- Lovastatin used to treat?
- Lovastatin is generic for what drug?
- Lovastatin and Atorvastatin?
- Lovastatin and grapefruit juice?
- Lovastatin and Simvastatin?
- Lovastatin vs Atorvastatin conversion?
- Lovastatin vs Crestor?
- Lovastatin vs Atorvastatin dose?
- Lovastatin side effects hair loss?
- Lovastatin strengths?
- Lovastatin side effects muscle pain?
- Lovastatin uso?
- Lovastatin ingredients?
- Lovastatin package insert?
- Lovastatin teaching?
- Lovastatin calcium?
- Lovastatin complications?
- Lovastatin blood thinner?
- Lovastatin blood pressure medicine?
- Lovastatin names?
- Lovastatin metabolism?
- Lovastatin methane SIBO?
- Lovastatin lactone?
- Lovastatin liver damage?
- Lovastatin dosage forms?






















