Mercaptopurine
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Mercaptopurine
- III. How Mercaptopurine Works
- IV. Uses of Mercaptopurine
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Side Effects of Mercaptopurine
- VII. Important Precautions
- VIII. Drug Interactions
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration
- XI. Overdosage
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Brief History of Mercaptopurine
Mercaptopurine, often referred to as 6 MP, was initially created during the 1950s in the pursuit of developing antineoplastic drugs. Its development represented progress in the realm of chemotherapy.
Importance in Modern Medicine
This medication is primarily used to treat types of blood cancers and autoimmune disorders. Its ability to effectively address medical conditions makes it an essential part of modern treatment plans.
Objective of the Article
The main purpose of this article is to provide detailed information about the pharmacological characteristics of Mercaptopurine, including its approved and off-label applications, potential side effects, and necessary precautions.
II. Composition of Mercaptopurine
Chemical Structure
Mercaptopurine falls under the category of purine analogs in terms of its chemical classification. Its molecular structure is represented by the formula C5H4N4S, which showcases a complex arrangement of atoms.
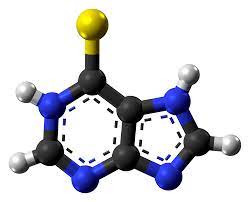
Pharmacological Class
Belonging to the category of drugs, Mercaptopurine hinders the synthesis of DNA and RNA by imitating crucial components necessary for their formation.
Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main component of this product is Mercaptopurine. Other ingredients include lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and starch.
III. How Mercaptopurine Works
Mechanism of Action
Mercaptopurine undergoes a metabolic process that results in the formation of thioinosinic acid. This compound acts as an inhibitor of purine synthesis, leading to decreased availability of DNA and RNA building blocks.
Cellular Level Interactions
At a level, Mercaptopurine has a significant influence on cells that are actively dividing as well as those in a dormant state, which makes it incredibly potent, against the diverse nature of cancer cells.
Importance in Inhibiting DNA Synthesis
Its ability to stop DNA synthesis is crucial for its effectiveness in fighting against cancer. By disrupting the process of DNA replication, it effectively slows down the growth of cells.
IV. Uses of Mercaptopurine
Approved Uses
Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Mercaptopurine is an antineoplastic agent used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) 12. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs 1.
Here are some references that provide more information about mercaptopurine:
- American Cancer Society: Treating Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- DrugBank Online: Mercaptopurine
Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Mercaptopurine is an antineoplastic agent that is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) 12. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs 1.
Here are some references that provide more information about mercaptopurine:
- American Cancer Society: Treating Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- DrugBank Online: Mercaptopurine
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management
Mercaptopurine is an antineoplastic agent that is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) 12. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs 1.
In addition to its use in blood-related cancers, mercaptopurine has also been used to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis 345.
Here are some references that provide more information about mercaptopurine:
- American Cancer Society: Treating Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- DrugBank Online: Mercaptopurine
- UpToDate: Overview of azathioprine and mercaptopurine use in inflammatory bowel disease
- UpToDate: Thiopurines: Pretreatment testing and approach to therapeutic drug monitoring for adults with inflammatory bowel disease
- National Cancer Institute: Mercaptopurine
Off-label Uses
Autoimmune Disorders
Mercaptopurine is an antineoplastic agent that is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) 12. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs 1.
While mercaptopurine has not been approved by the FDA for the treatment of lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis, it has been studied for its potential use in treating these conditions 345. However, more research is needed to determine its efficacy and safety for these purposes.
Here are some references that provide more information about mercaptopurine:
- American Cancer Society: Treating Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- DrugBank Online: Mercaptopurine
- Frontiers in Immunology: Preclinical Autoimmune Disease: a Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes
- Proceedings of UCLA Healthcare: ABATACEPT-induced Lupus Erythematosus Panniculitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- SpringerLink: Cytokine profile in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases
Other Forms of Cancer
Sometimes doctors use mercaptopurine along, with cancer fighting drugs to treat solid tumors.
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
Pediatricians sometimes use Mercaptopurine to alleviate the symptoms associated with Crohn's disease in children.
V. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage
Recommended Doses for Different Conditions
The recommended daily dosage ranges from 60 to 115 mg per meter for all conditions. In the case of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), the suggested dosage is between 1.5 and 2.5 mg per kilogram per day. For Inflammatory Bowel Disease, it is advised to take between 1 and 1.5 mg per kilogram daily.
Route of Administration
Oral tablets and liquid formulations are frequently utilized in practice.
Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly
It is crucial to proceed cautiously when adjusting the dosage to prevent any effects on the bone marrow and liver function.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Mercaptopurine falls into Pregnancy Category D. It Should not be used by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Administration to Children
Dosages, for children, are typically determined based on their body surface area and necessitate careful monitoring.
VI. Side Effects of Mercaptopurine
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
Hematologic Effects
- Leucopenia
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
Liver Function Alterations
Elevated liver enzymes have been observed.
Less Common Side Effects
Skin Reactions
- Urticaria
- Rash
Central Nervous System Effects
- Dizziness
- Malaise
Pancreatic Complications
Acute pancreatitis has been reported, although it is not an occurrence.
VII. Important Precautions
Pre-Treatment Tests
Preliminary blood counts and liver function tests are essential.
Monitoring During Treatment
Regular monitoring of blood parameters and occasional liver function tests should be included as part of the treatment plan.
Steps for Dose Adjustments
Immediate adjustments to the dosage are necessary if there is a decrease in the count of blood cells or any indication of liver toxicity.
VIII. Drug Interactions
Interaction with Allopurinol
When Mercaptopurine is combined with Allopurinol, it can amplify the effects of Mercaptopurine, which may require adjustments to the dosage. Allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase, an enzyme that affects how Mercaptopurine is metabolized. As a result, there is an increased risk of experiencing toxicity. It is essential to modify the dosage and closely monitor the situation to ensure safety.
Interaction with Blood Thinners
When Mercaptopurine and anticoagulants, like warfarin, are taken together, the anticoagulant effects may become more muscular. This can lead to an increased risk of bleeding. To manage this, it is advised to monitor the prothrombin time or international normalized ratio (INR).
Interaction with Live Vaccines
Administering vaccines to patients taking Mercaptopurine can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening infections because the drug weakens the immune system. As a result, patients become more vulnerable to conditions. Therefore, it is generally recommended to avoid administering vaccines in such cases.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
General Warnings
Risk of Secondary Neoplasms
People who are prescribed Mercaptopurine may have a risk of developing additional types of cancer, specifically skin cancers and lymphomas.
Bone Marrow Suppression
One of the serious negative consequences of Mercaptopurine is its tendency to cause myelosuppression, which is a reduction in the production of blood cells. It is essential to monitor blood counts to ensure the safety and well-being of patients taking this medication.
Hepatotoxicity Risks
Mercaptopurine carries a probability of causing liver problems, which is emphasized by the possibility of increased liver enzyme levels.
Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity
Individuals with a known sensitivity or allergy to the drug should not use mercaptopurine.
Severe Liver or Kidney Dysfunction
Individuals with liver or kidney problems should avoid taking Mercaptopurine because it can be more toxic for this group of patients.
X. Careful Administration
Guidelines for Safe Handling
Make sure to wear protective equipment (PPE) when handling tablets. Ensure your hands are dry before touching them. Be careful not to crush or break the tablet.
Patient Education Points
The significance of taking medication as prescribed and following the recommended schedule Identifying the indications of toxicity at an early stage Taking necessary precautions in terms of dietary habits and choices
Provider Responsibility
We need to keep an eye on the patient's progress, provide them with guidance and support, and make any necessary changes, to their medication dosage if required.
XI. Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms
Experiencing an amount of Mercaptopurine can result in intense feelings of nausea, throwing up, and abnormalities in the blood, among other symptoms.

Emergency Management
You should seek medical attention and consider having your stomach flushed if necessary. If required, hemodialysis may also be considered.
Supportive Measures
Administering fluids through a vein, Providing support for blood needs, observing and tracking essential indicators.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
You should keep mercaptopurine in a place where it's not too hot or humid and away from sunlight.
Shelf Life
Usually, Mercaptopurine can last for around 36 months if stored properly.
Disposal Guidelines
It is important to follow both state regulations when disposing of medication. It is crucial to avoid throwing away medication, in household waste, or flushing it down the toilet.