Nimesulide/ Tizanidine
- I. Introduction to Nimesulide/Tizanidine
- II. Composition and Properties
- III. Mechanism of Action
- IV. Uses of Nimesulide/Tizanidine
- V. Off-Label Uses
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Administration in Special Populations
- VIII. Side Effects of Nimesulide/Tizanidine
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Important Precautions and Warnings
- XI. Overdosage and Emergency Management
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction to Nimesulide/Tizanidine
Overview of Nimesulide and Tizanidine
Nimesulide and Tizanidine are medications commonly used for their anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxing effects. Nimesulide functions as a steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), while Tizanidine is known for its role as a central alpha 2 adrenergic agonist.
Historical development and approval
The emergence of Nimesulide took place in the 1980s, followed by the introduction of Tizanidine in the early 1990s. These drugs went through clinical testing before being authorized for medical purposes in different parts of the world, meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Common therapeutic uses
Nimesulide is commonly utilized for its pain relieving and fever reducing properties while Tizanidine is mainly prescribed to help relieve muscle stiffness.
II. Composition and Properties
Chemical structure and formulation
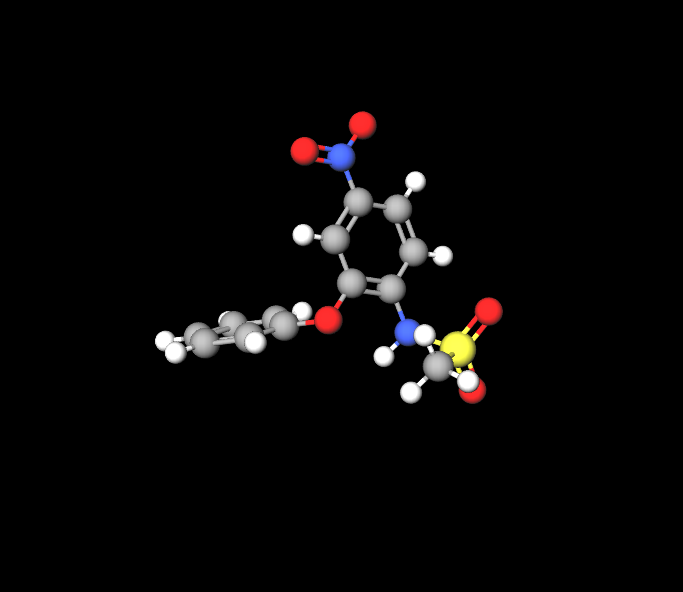
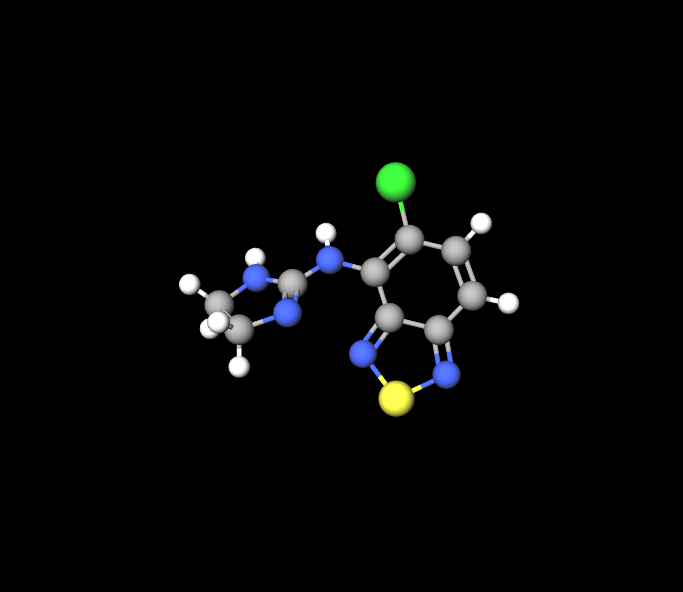
Nimesulides molecular makeup includes a sulfonanilide structure that influences how it works while Tizanidine contains an imidazoline structure that plays a role, in its ability to relax muscles.
Key ingredients and their roles
The key components in these medications highlight how they work to provide benefits. Nimesulide works by blocking cyclooxygenase, which helps decrease the production of prostaglandins. Tizanidine regulates the release of neurotransmitters, which play a role in controlling muscle spasticity.
III. Mechanism of Action
How Nimesulide works in the body
How Tizanidine affects muscle spasticity
Synergistic effects of Nimesulide and Tizanidine combination
IV. Uses of Nimesulide/Tizanidine
Approved indications for Nimesulide/Tizanidine
-
Nimesulide:
- Nimesulide is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic properties.
- It is administered orally or rectally twice daily for various inflammation and pain states.
- Nimesulide has specific affinity to inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), resulting in milder effects on the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Studies suggest that it is comparable in efficacy to other NSAIDs but better tolerated with fewer adverse reactions1.
- It may have anti-inflammatory effects without kidney and stomach side effects, making it promising for certain individuals at risk1.
-
Tizanidine:
- Tizanidine is a muscle relaxant used to manage muscle spasms and stiffness.
- It works by blocking nerve signals (alpha-2 adrenergic agonist) to reduce muscle tone.
- When combined with Nimesulide, it enhances pain relief and muscle relaxation2.
V. Off-Label Uses
Exploration of non-approved uses
Research support for off-label benefits
Recent research indicates that there may be advantages to exploring, off label applications. These claims still await confirmation through extensive clinical trials.
Legal and ethical considerations
Prescribing drugs for purposes not approved by authorities raises legal and ethical considerations requiring comprehensive patient consent and compliance with medical standards.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Recommended dosages for different conditions
The usual Nimesulide dosage is generally 100 mg taken twice daily whereas Tizanidine is typically prescribed in doses ranging from 2 mg, to 8 mg to be taken three times a day based on the seriousness of the ailment and how the patient reacts.

Guidelines on administration methods
Both drugs should be taken by mouth. It can be consumed with or without food. It is advisable to take them in relation to meals to reduce the risk of stomach discomfort.
Adjustments for specific patient groups
It's important to adjust the dosage for patients, with kidney or liver issues making sure to balance the risks and benefits of treatment.
VII. Administration in Special Populations
Elderly: Adjustments and considerations
For patients, it is recommended to use lower doses of both medications because they have a higher chance of experiencing negative effects and other health conditions that could impact how their bodies process and eliminate the drugs.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and recommendations
It is advised to use both Nimesulide and Tizanidine during pregnancy and breastfeeding since their safety has not been definitively proven.
Children: Age-specific dosage and precautions
Nimesulide is typically not advised for children under 12 years old because of the liver toxicity risks, whereas Tizanidine requires close monitoring when used in pediatric environments.
VIII. Side Effects of Nimesulide/Tizanidine
Common side effects encountered
Individuals who are prescribed Nimesulide and Tizanidine might encounter side effects. Frequently mentioned concerns consist of system discomfort, like queasiness and indigestion feeling sleepy, lightheadedness and headaches. These effects are typically mild. Can be controlled with standard medical advice.
Serious adverse reactions and their management
Serious side effects, though uncommon, may involve liver problems, severe stomach bleeding, and heart-related concerns for Nimesulide; Notable low blood pressure, hallucinations, and severe liver issues for Tizanidine. Dealing with these responses requires medical attention, potentially stopping the medication and treating symptoms with specific therapies.
Statistics on side effects prevalence
- 10% of individuals might encounter mild side effects when taking Nimesulide.
- A small percentage, less than 1%, may face severe issues requiring hospitalization.
- Tizanidine displays a trend, with around 5% of individuals noting notable drowsiness or dizziness.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
Common drug interactions and their implications
Nimesulide and Tizanidine have the potential to interact with medications either boosting or reducing their effects. Nimesulide might amplify the impact of warfarin, whereas Tizanidine could heighten the sedative qualities of alcohol and benzodiazepines.
Interaction with over-the-counter medications and supplements
Over-the-counter NSAIDs and supplements such as St. Johns Wort can also have interactions with these medications, which could result in side effects or reduced effectiveness of the treatments.
How to manage potential interactions
Keeping track of interactions requires attention to all the medications a patient is taking, including over-the-counter items and supplements. It's important for healthcare providers to offer advice on possible interactions and make any needed adjustments, to dosages or medications.
X. Important Precautions and Warnings
Contraindications for use
Patients with liver, kidney or heart issues should avoid taking both medications. It is not recommended to use tizanidine with potent CYP1A2 inhibitors because it can lead to a significant drop in blood pressure and slow heart rate.
Individuals with a past of ulcer illness or those presently utilizing other NSAIDs should approach Nimesulide cautiously. Users of Tizanidine should be informed about the potential for drowsiness and discouraged from operating heavy machinery.
Precautions for long-term use
Extended use of these medications necessitates monitoring of liver and kidney functions along with regular evaluations for cardiovascular risks, particularly for individuals taking Nimesulide over a prolonged duration.
XI. Overdosage and Emergency Management
Signs and symptoms of overdose
Symptoms of an overdose could involve gastrointestinal bleeding, sudden kidney failure, and central nervous system depression. Individuals might show signs of fatigue, slower breathing, and low blood pressure.
Immediate actions and antidotes
For treatment gastric lavage and activated charcoal are given to decrease absorption. Additional care like IV fluids and vasopressors might be needed to handle blood pressure and breathing difficulties.
Long-term health effects of overdose
People who have survived overdoses might experience lasting damage, to their kidneys or liver which could require continuous care and lead to potential long term health problems.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper storage conditions
Make sure to keep Nimesulide and Tizanidine at room temperature in a place and away, from direct sunlight to maintain their effectiveness and prevent them from breaking down.
Disposal and handling precautions
Proper disposal of unused medications is important to prevent environmental contamination. Patients should be educated on the methods, for safe disposal.
Stability under different environmental conditions
These drugs remain intact in settings but their potency could diminish if they encounter excessive humidity or are stored at temperatures, beyond the recommended range possibly resulting in decreased efficacy.