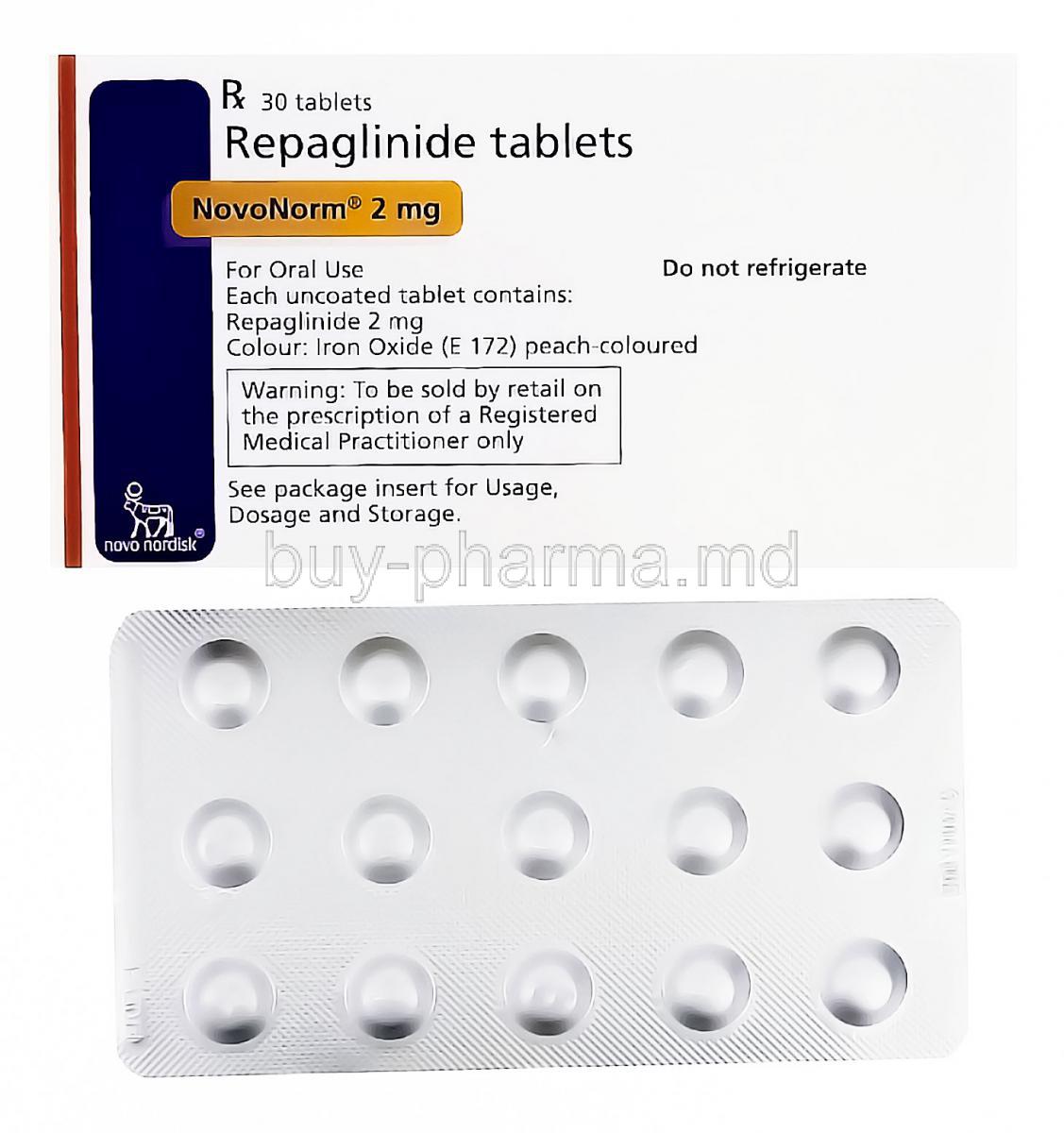
Novonorm, Repaglinide
- I. Introduction to Novonorm (Repaglinide)
- II. Uses of Novonorm (Repaglinide)
- III. Off-Label Uses of Novonorm
- IV. How Novonorm Works
- V. Dosage and Administration of Novonorm
- VI. Composition of Novonorm
- VII. Repaglinide side effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects of Novonorm
- IX. Warnings and Precautions
- X. Interactions with Other Drugs
- XI. Contraindications of Novonorm
- XII. Careful Administration of Novonorm
- XIII. Administration to Elderly Patients
- XIV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- XV. Administration to Children
- XVI. Overdosage of Novonorm
- XVII. Storage and Handling of Novonorm
- XVIII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction to Novonorm (Repaglinide)
Overview of Novonorm
What is Repaglinide?
Approval status and history
Mechanism of action
II. Uses of Novonorm (Repaglinide)
Primary use in managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
When Novonorm is prescribed
Novonorm for patients with renal insufficiency or liver dysfunction
III. Off-Label Uses of Novonorm
Investigational uses for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Potential role in preventing cardiovascular events in diabetic patients
Emerging uses in other metabolic conditions
IV. How Novonorm Works
Repaglinideâs mechanism of action on the pancreas
How it differs from other insulin secretagogues
Onset and duration of action
Impact on postprandial glucose levels
V. Dosage and Administration of Novonorm
Standard dosing guidelines based on blood glucose levels
How to take Novonorm (timing with meals)
Adjusting dosage in specific populations (e.g., renal impairment)
Missed dose recommendations
VI. Composition of Novonorm
Active and inactive ingredients
Pharmaceutical formulation (tablets)
Available strengths (e.g., 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg)
Repaglinide vs glipizide
VII. Repaglinide side effects
Common side effects (e.g., hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal issues)
Less common side effects (e.g., joint pain, upper respiratory infections)
Rare but serious side effects (e.g., allergic reactions, liver dysfunction)
VIII. Common Side Effects of Novonorm
Hypoglycemia: causes, symptoms, and prevention
Gastrointestinal discomfort (nausea, diarrhea)
Weight gain and other metabolic effects
Skin reactions (rash, itching)
IX. Warnings and Precautions
Risk of hypoglycemia and how to manage it
Use with caution in patients with liver or kidney disease
Interaction with other medications that affect blood glucose levels
Driving and operating machinery while on Repaglinide
Repaglinide nursing considerations
X. Interactions with Other Drugs
Common drug interactions (e.g., beta-blockers, corticosteroids)
How Repaglinide interacts with other antidiabetic drugs
Interaction with alcohol
Impact of herbal supplements on Repaglinide efficacy
XI. Contraindications of Novonorm
Known hypersensitivity to Repaglinide
Contraindications for use in Type 1 Diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis
When not to use Novonorm with other insulin secretagogues
XII. Careful Administration of Novonorm
Considerations for patients with impaired liver function
Monitoring blood glucose levels frequently in high-risk patients
Careful dose adjustment in elderly patients
XIII. Administration to Elderly Patients
Special considerations for elderly populations
Adjusting dosage to reduce risk of hypoglycemia
Increased sensitivity to side effects
XIV. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety profile during pregnancy (Pregnancy Category C)
Risks to the fetus and alternative treatment options
Recommendations for nursing mothers and potential effects on breastfed infants
XV. Administration to Children
Pediatric use: current guidelines and research
Risks and benefits in children with Type 2 Diabetes
Lack of established safety and efficacy data for pediatric use
XVI. Overdosage of Novonorm
Symptoms of Novonorm overdose
Emergency management of hypoglycemia
Supportive care and treatment options in case of overdose
Repaglinide max dose
XVII. Storage and Handling of Novonorm
Proper storage conditions (temperature, moisture control)
Handling precautions for pharmacies and patients
What to do if the medication is improperly stored
XVIII. Handling Precautions
How to handle and dispose of unused medication safely
What to do if a dose is missed
Handling instructions for healthcare professionals
Novonorm, Repaglinide FAQ
- Why take repaglinide with a meal?
- When should repaglinide be given?
- When should repaglinide be taken?
- Repaglinide when to take?
- Repaglinide what class?
- Repaglinide what type of drug?
- What repaglinide good for?
- What repaglinide is used for?
- How is repaglinide used?
- Repaglinide how to take?
- How repaglinide works?
- Can repaglinide cause pancreatitis?
- Can repaglinide cause weight loss?
- Can repaglinide cause hypoglycemia?
- Can repaglinide be cut in half?
- What are repaglinide pills?
Why take repaglinide with a meal?
Using repaglinide during meals has been found to be a strategy for enhancing blood sugar management in individuals with type 2 diabetes whose control is not fully optimized through changes alone.
When should repaglinide be given?
This medication is typically taken 15 minutes before eating, although it can also be taken up to 30 minutes before a meal.
When should repaglinide be taken?
Repaglinide is in tablet form for consumption. It should be taken before meals, ideally between 30 minutes before eating and just before starting the meal.
Repaglinide when to take?
Repaglinide is in tablet form. It should be consumed orally before meals—between 30 minutes before a meal and just as the meal is served. Remember to skip the dose of repaglinide should you happen to skip a meal.
Repaglinide what class?
Repaglinide is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes. It falls into the category of drugs called meglitinides alongside nateglinide.
Repaglinide what type of drug?
Repakline is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. It falls under the category of medications called meglitinides alongside nateglinide. Meglitinides function by lowering blood sugar levels through the stimulation of the body's insulin production.
What repaglinide good for?
Repaglinide is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes. It stimulates the body's natural insulin production and lowers blood sugar levels. It falls under the category of medications called meglitinides and is closely related to nateglinide.
What repaglinide is used for?
Repaglinide is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. It falls under the category of drugs called meglitinides alongside nateglinide Meglitinides function, by boosting the bodys insulin production to lower blood sugar levels.
How is repaglinide used?
Repaglinide is prescribed in combination with adjustments and physical activity to manage levels of blood sugar in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus as it prompts the pancreas to increase insulin secretion into the bloodstream. Still, it is not practical for those with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Repaglinide how to take?
Repaglinide is available in tablet form for consumption. It should be taken before meals, ideally between 30 minutes and right before eating.
How repaglinide works?
Repanglide is prescribed in conjunction with dietary and physical activity measures to manage blood sugar levels in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Its mechanism of action involves stimulating the pancreas to increase the secretion of insulin into the bloodstream. However, it is important to note that this medication is not effective for individuals with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes.
Can repaglinide cause pancreatitis?
This instance of pancreatitis caused by repaglinide is quite uncommon and exceptional; hence, we advise caution when prescribing repaglinide to individuals who have had pancreatitis before. It's important for doctors to be aware of the side effects of repaglinide and for patients to be informed well in order to reduce complications and potentially lessen the time spent in the hospital overall.
Can repaglinide cause weight loss?
Some individuals might experience weight gain as a side effect of taking Repaglinide since it boosts insulin levels in the body, which could potentially result in increased body weight.
Can repaglinide cause hypoglycemia?
Patients who are prescribed repaglinide may experience a risk of hypoglycemia similar to that associated with insulin and sulfonylureas; nevertheless, due to its action and short duration of effects, repaglinide poses a lower hypoglycemic threat compared to insulin or sulfonylureas.
Can repaglinide be cut in half?
Your physician may modify the dosage by a maximum of 4 mg to be consumed before or within 30 minutes prior to every mealtime. The daily limit is advised at 16 mg per day for Repaglinide STADA 4 mg tablets, which can be split into equal portions.
What are repaglinide pills?
Repaglinide is prescribed along with diet and physical activity to manage blood sugar levels in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes as it prompts the pancreas to produce insulin in the bloodstream effectively; however, it is not beneficial for those with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes conditions.