T-Bact Cream
- I. Introduction to T-Bact Cream
- II. Composition of T-Bact Cream
- III. Mupirocin uses
- IV. Off-Label Uses of T-Bact Cream
- V. Dosage and Administration of T-Bact Cream
- VI. Warnings and Precautions for T-Bact Cream Use
- VII. Administration to Specific Populations
- VIII. Mupirocin side effects
- IX. Contraindications for T-Bact Cream
- X. Mupirocin interactions
- XI. Handling Precautions for T-Bact Cream
- XII. Overdosage and Emergency Actions
- XIII. Storage Guidelines for T-Bact Cream
I. Introduction to T-Bact Cream
Overview of T-Bact Cream
T Bact Cream is an antibiotic created to treat various bacterial skin infections effectively. Its main component is mupirocin, which acts as an antibacterial element targeting both surface and slightly deeper skin infections. It works by hindering bacterial protein synthesis and decreasing the survival of bacteria on the skin.
Brief History and Development
Since its centuries-old inception, T Bact Cream has become a trusted remedy for bacterial skin infections during heightened worries about antibiotic resistance. The creators aimed to address skin infections with a topical solution to avoid them worsening and potentially needing systemic antibiotics.
Indications for Use
Indicated for a broad spectrum of skin infections, T-Bact Cream is often prescribed for cases of:
- Impetigo
- Folliculitis
- Minor abrasions and lacerations
Effective in treating infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, T-Bact Cream is particularly beneficial in dermatological applications.
Approval Status and Regulatory Information
The T Bact Cream has been approved for use in countries. Clinical studies have proven it effective and safe. The FDA and EMA have given their approval for its usage as an antibiotic for common infections.
II. Composition of T-Bact Cream
Active Ingredients in T-Bact Cream
The primary active ingredient in T-Bact Cream is mupirocin, a topical antibiotic that inhibits bacterial isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase, which is critical for bacterial protein synthesis. This action renders the bacteria unable to reproduce, aiding in infection control.
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation
The cream also includes ingredients such as a paraffin-based carrier and glycerol to aid in the delivery of mupirocin to the skin's affected areas. This composition allows for application and reduces irritation on delicate skin.
Mupirocin moa
T-Bact Cream disrupts bacteria's essential protein synthesis processes by inhibiting their enzymatic functions. By targeting the isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase, mupirocin blocks bacterial growth and proliferation, eventually leading to cell death and infection resolution.
Comparison to Other Topical Antibiotics
T Bact Cream distinguishes itself from antibiotics by its specific approach that effectively combats even resistant strains, like MRSA. In contrast to antiseptics, mupirocin focuses on bacteria protecting the natural skin flora and minimizing negative responses.
Mupirocin vs neosporin
Neosporin and Mupirocin are medications with purposes and properties. Neosporin is an over-the-counter product for minor wounds, while Mupirocin is a prescription antibiotic ointment specifically for treating more serious bacterial infections.
Mupirocin vs bacitracin
While mupirocin generally causes side effects overall, some individuals may encounter symptoms like headaches or nausea and may feel a burning sensation at the site of application after using it. On the other hand, bacitracin is an antibiotic cream commonly applied to prevent skin infections resulting from minor cuts, scrapes, and burns.
III. Mupirocin uses
Treatment of Skin Infections
To treat infections on skin areas effectively and swiftly, T Bact Cream helps in quick healing, stopping infection from spreading to other parts of the body, and preventing further skin complications effectively and rapidly for minor skin infections.
Mupirocin for impetigo
T Bact Cream is commonly recommended for treating impetigo in children. It helps control growth, lowers the chances of spreading the infection in community environments, and effectively relieves symptoms.
Mupirocin for folliculitis
T Bact Cream effectively treats folliculitis by alleviating inflammation at the hair follicle locations, lessening swelling and redness while providing relief from discomfort.
Mupirocin for boils
When T Bact Cream is used on injuries, like cuts and scrapes, to block bacterial entry and prevent infection, it forms a protective barrier and offers antimicrobial benefits.
Mupirocin for staph
T Bact Cream is useful for combatting Staphylococcus and Streptococcus strains commonly present in skin infections without harming skin organisms.
IV. Off-Label Uses of T-Bact Cream
Potential Use in Managing MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus) Infections
MRSA infections present a hurdle because of their resistance to antibiotics. The application of T Bact Cream has demonstrated potential in managing localized MRSA infections in their phases despite being intended for nonresistant strains.
Use for Nasal Carriers of Bacteria
Eczema with Secondary Infection
If eczema gets infected as a condition T Bact Cream can assist in handling the presence effectively by lessening inflammation and supporting the recovery of irritated skin.
Mupirocin ointment for ingrown hair
If an ingrown hair gets swollen and irritated, a doctor might recommend using a cream or gel containing antibiotics such as mupirocin. This can help eliminate hair follicle bacteria and alleviate discomfort, like itching and pain.
Other Dermatological Conditions with Bacterial Infection
In addition, T Bact Cream is utilized to treat infections associated with acne and various skin conditions that are hindered by its presence during the healing process.
Mupirocin for dogs
Doctors sometimes recommend Muprocine ointment to help clear up skin infections. Dogs and other animals may also receive this prescription from their veterinarian.

V. Dosage and Administration of T-Bact Cream
Recommended Dosage for Adults and Adolescents
For adults and teenagers, the T Bact Cream is used two to three times a day after cleaning the area properly without surpassing the recommended amount to prevent resistance buildup.
Dosage Instructions for Children
The application is generally more limited in frequency and area coverage for children, ensuring safety and reducing sensitivity reactions.
Guidelines for Use in the Elderly
Elderly individuals may have a more sensitive skin response; hence, reduced frequency and close monitoring are advised. The application should be as minimal as needed for effective results.
Application Method and Frequency
Cleanse the affected area gently, apply a thin layer of T-Bact Cream, and cover lightly if necessary. Avoid excessive layering, as this could impact absorption and efficacy.
Duration of Treatment: When to Expect Results
Typically, you'll start seeing results in about 3 to 4 days of using it. If the infection persists or you don't notice any improvement after a week, it's a good idea to seek medical advice.
VI. Warnings and Precautions for T-Bact Cream Use
Important Safety Information Before Use
It's important not to apply T Bact Cream on skin areas or severe burns to prevent toxicity from systemic absorption.
Allergy and Sensitivity Considerations
Those with a history of antibiotic or preservative allergies should consult a healthcare provider before use. Skin sensitivity tests may help prevent adverse reactions.
Application on Open Wounds and Sensitive Areas
Using T Bact Cream on cuts and wounds could lead to irritation and discomfort for some individuals. It is advisable to be careful when applying the cream to areas such as the face; it's important to steer clear of the eyes and mucous membranes.
Precautions for Long-Term or Repeated Use
Using T Bact Cream for a period may cause bacteria to become resistant to it; hence, it is meant for short-term usage. It should only be used repeatedly as advised by a medical professional.
VII. Administration to Specific Populations
Safe Use in Pregnant Women
It's important to talk to a healthcare provider about using T Bact Cream during pregnancy to make sure it's safe for both the mother and the baby even though it doesn't get absorbed into the system.
Guidelines for Nursing Mothers
While generally safe, nursing mothers should apply T-Bact Cream with caution, avoiding areas close to breastfeeding sites. Wash hands thoroughly after application to prevent infant exposure.
Considerations for Children and Infants
When recommending the use of T Bact Cream, for children, it is usual to suggest a dosage and apply it frequently to reduce the chances of causing irritation or unwanted reactions in young ones.
Recommendations for Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may exhibit heightened skin sensitivity; hence, careful monitoring and adherence to lower dosage guidelines are recommended to ensure therapeutic efficacy without complications.
VIII. Mupirocin side effects
Common Side Effects: Mild Reactions
T-Bact Cream is generally well-tolerated, but certain individuals may have mild side effects. Common side effects include:
- Localized itching or pruritus
- A mild burning sensation upon application
- Redness or erythema around the treated area
These reactions are often temporary and subside as the skin adjusts to the treatment. However, monitoring is advised if discomfort persists or intensifies.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Although rare, T-Bact Cream can provoke more serious side effects in certain cases. These may include:
- Severe skin irritation or blistering
- Swelling at the application site
- Systemic symptoms such as dizziness or respiratory distress
Serious reactions may indicate sensitivity or an adverse response to mupirocin, the active ingredient. Discontinuation and immediate medical evaluation are advised.
Signs of Allergic Reactions to Watch For
Allergic responses, though uncommon, warrant vigilance. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Rash formation or hives around the treated area
- Swelling of the lips, face, or throat
- Difficulty breathing or tightness in the chest
Allergic reactions should be treated as medical emergencies. Discontinue use and seek immediate assistance if these symptoms occur.
How to Manage Side Effects at Home
For mild reactions, simple home remedies can alleviate discomfort:
- Applying a cold compress to soothe irritation
- Keeping the area dry and ventilated
- Avoiding further topical treatments until the skin calms
Should symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is prudent for alternative management options.
When to seek Medical Help for Side Effects
Medical intervention is essential if:
- Severe pain, swelling, or discoloration arises
- Allergic signs manifest (hives, difficulty breathing)
- Symptoms persist beyond a few days of cessation
Professional guidance ensures the proper course of action and, if necessary, alternatives to T-Bact Cream.
IX. Contraindications for T-Bact Cream
Conditions That Prevent T-Bact Cream Use
Certain conditions contraindicate the use of T-Bact Cream, including:
- Known hypersensitivity to mupirocin or its components
- Severe renal impairment, especially with large applications
- History of recurrent severe skin allergies
In these cases, alternative treatments are advisable to avoid adverse reactions.
Medical Conditions Requiring Caution
Caution is recommended for patients with:
- Compromised immune systems
- Extensive skin conditions, such as severe eczema
- Pre-existing skin infections resistant to topical treatment
Consultation with a healthcare provider ensures safe and effective treatment when contraindications are present.
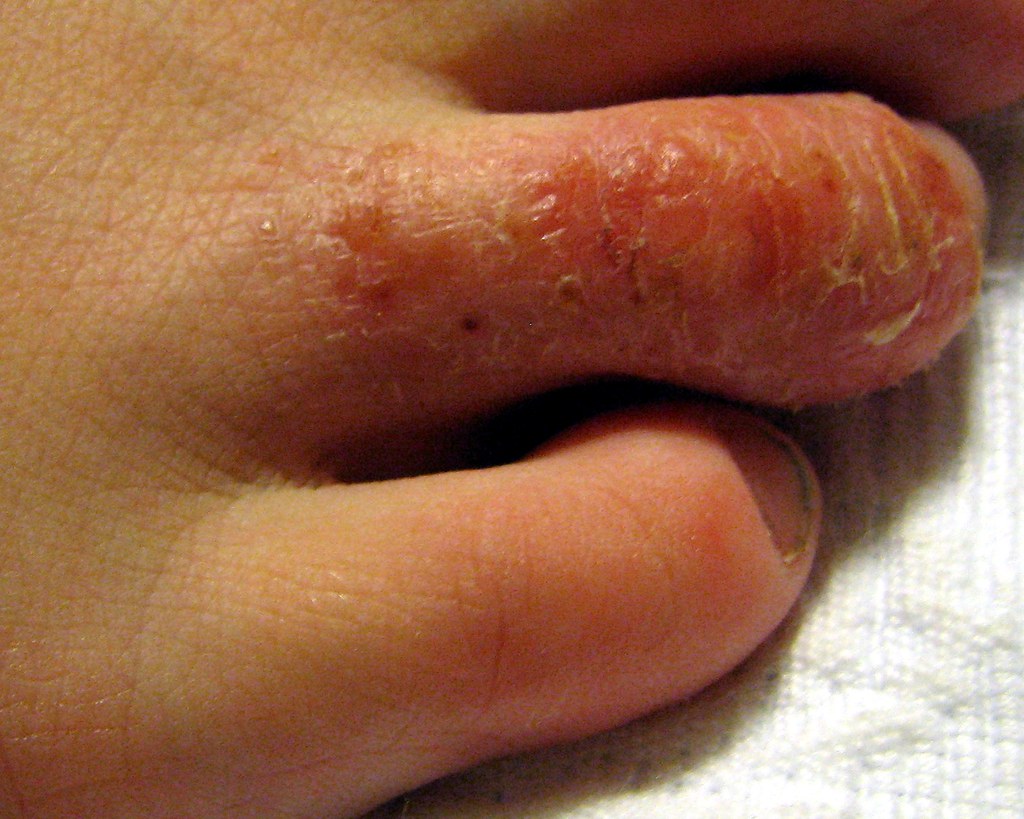
Contraindications with Known Allergies
People who are allergic to antibiotics should be careful when using T Bact Cream. A known sensitivity to antibiotics, like neomycin or polymyxin, could increase the risk of experiencing negative reactions.
Known Drug or Ingredient Interactions
Interactions with systemic medications may impact the effectiveness of T Bact Cream, so patients are advised not to use it in conjunction with potent corticosteroids or other topical antibiotics without consulting a healthcare professional.
X. Mupirocin interactions
Drug Interactions: Topical and Systemic Medications
Before using T Bact Cream alongside antibiotics or certain systemic medications that may affect its effectiveness or cause more side effects than usual, consult with a healthcare provider for guidance on the best course of action.
Interaction with Other Skin Care Products
Using T Bac Cream with some skincare items that contain acids or alcohol could lead to irritation on your skin's surface area, so it's best to skip combining it with topical treatments unless you've got the green light from a skin doctor.
Use in Combination with Other Antibiotics
Sometimes T Bact Cream might be utilized alongside antibiotics for a thorough treatment plan; nonetheless, this pairing should be overseen by a healthcare professional to prevent resistance or hypersensitivity issues.
Effects on Immunocompromised Patients
Immunocompromised individuals might have increased sensitivity to T Bact Cream. They should be closely monitored for any reactions or side effects requiring adjustments to the application frequency or dosage.
XI. Handling Precautions for T-Bact Cream
Proper Storage Conditions and Requirements
Remember to keep T Bact Cream in a place at room temperature and away from sunlight and heat to maintain its effectiveness. This prevents the ingredients from degrading due to exposure to light and extreme temperatures.
Safe Disposal of Expired or Unused Product
Make sure to dispose of any unused T Bact Cream by not flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into drains; instead, securely wrap it up and throw it in the household trash or seek advice from a pharmacy on safe disposal methods.
Avoiding Contamination of Cream During Use
- To avoid pollution, please use your hands or gloves when you apply the cream.
- Avoid placing the applicator tip in contact with your skin.
- Remember to seal the tube after every use.
- By taking these measures, you can lower the chance of bacteria getting into the cream and keep it sterile.
Tips for Clean and Safe Application
Prior to applying any product to your skin, wash the area with soap and water, dry it gently by patting, and then use a quantity of T Bact Cream. Do not use it on areas unless specifically directed to do so.
XII. Overdosage and Emergency Actions
Recognizing Symptoms of Overuse
Overuse may present as heightened skin irritation, itching, or a burning sensation. In extreme cases, systemic absorption can lead to unusual fatigue or flu-like symptoms, necessitating immediate discontinuation.
Possible Effects of Accidental Ingestion
Ingestion of T Bact Cream by mistake can lead to feelings of nausea or stomach unease and may cause dizziness. If this happens to you, take sips of water to help ease the discomfort in your stomach; however, it is advisable to seek advice as a measure.
What to Do in Case of Overdose
If much cream is used and there's an overdose risk, the skin area should be washed well after application to get rid of the extra cream residue. Then, depending on the symptoms observed, consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the next steps.
Seeking Emergency Help: Signs to Watch For
Emergency assistance should be sought if severe symptoms appear, including:
- Extreme skin pain or blistering
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe dizziness or fainting
Prompt medical evaluation ensures safety and mitigates any adverse effects of overuse.
XIII. Storage Guidelines for T-Bact Cream
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Make sure to store T Bact Cream at a temperature, under 25°C (77°F) to maintain the effectiveness of the ingredient and extend its shelf life avoiding heat or cold conditions.
Protecting T-Bact Cream from Light and Moisture
To maintain the effectiveness of T Bact Cream, avoid exposing it to moisture or light by storing it in a dark cabinet away from bathrooms or humid places.
Shelf Life and Expiration Information
Make sure to look at the expiry date on the package before using it, as expired T Bact Cream might not work well and could result in ineffective infection management.
Safe Storage Around Children and Pets
Remember to keep T Bact Cream where children and pets can't reach it to avoid ingestion or misuse. A cabinet or a high shelf works best for safekeeping.
T-Bact Cream FAQ
- Which is better t-bact or betadine?
- What is the use of T Bact cream?
- Does T-Bact heal wounds faster?
- What is the difference between T Bact and Betadine?
- Can T-bact be used for insect bites?
- Can I use T Bact on rashes?
- Can we apply T-bact on a wound?
- Can we use T-bact ointment for insect bites?
- Can we use T Bact ointment for eczema?
- Where to apply T-bact ointment?
- Is T BACT antibacterial?
- Does T-bact heal wounds?
- Can T-bact be used for itching?
Which is better t-bact or betadine?
The success of betadine ointment compared to T-bact ointment varies depending on the ailment it's used for treating. Betadine contains an antiseptic called Povidone Iodie, while T Bact contains Mupirocin, which is an antibiotic.
What is the use of T Bact cream?
The T Bact Cream is applied to address skin infections like impetigo.
Does T-Bact heal wounds faster?
It can also be applied to address infections in cuts or wounds on the skin. This therapy typically results in side effects and is expected to resolve infections within days; however, it is important to continue using it for the entire prescribed duration.
What is the difference between T Bact and Betadine?
Betadine includes a compound called Povidone Iiodine for its properties. T Bact contains Mupirocin as an antibiotic ingredient.
Can T-bact be used for insect bites?
Skin infections can include impetigo, folliculitis, furunculosis, and ecthyma, which affect areas like abrasions from injuries or insect bites that do not need hospital treatment, along with minor wounds and burns.
Can I use T Bact on rashes?
It can aid in easing issues, like skin irritations such, as redness and swelling and pain and itching usually linked to a skin infection.
Can we apply T-bact on a wound?
Small skin cuts and wounds can be protected from infection by using T-bact ointment, which works to eliminate bacteria on the skin and aid in the healing process.
Can we use T-bact ointment for insect bites?
Treatment, with T bact ointment is effective for treating skin infections such as impetigo and folliculitis and subsequent infections, like infected dermatitis (e.g. eczemarelated infections) and infected minor injuries (e.g. small wounds and insect bites).
Can we use T Bact ointment for eczema?
T-Bact is commonly employed to treat skin ailments, such as folliculitis (inflammation of the skin around hair follicles), impetigo (manifesting as a scratch or itchy area of eczema), and furunculosis (an abscess under the skin resulting from infected and inflamed hair follicles).
Where to apply T-bact ointment?
Clean and dry the area that's affected, and remember to apply the medicine three times daily.
Is T BACT antibacterial?
The product includes mupirocin, which has antibacterial properties.
Does T-bact heal wounds?
T Bact cream is effective in treating infections that develop from wounds and cuts. If left untreated, growth can quickly spread to other parts of the body. T Bact cream targets growth directly and helps prevent further spreading.
Can T-bact be used for itching?
T-Bact cream is applied to treat skin conditions like folliculitis, impetigo, and furunculosis. Folliculitis causes skin inflammation around hair roots, impetigo manifests as a scratch or itchy eczema patch, and furunculosis results in pus-filled bumps due to hair follicles.

























