Voriconazole Injection
- Introduction
- Composition of Voriconazole Injection
- Voriconazole uses
- Off-Label Uses of Voriconazole Injection
- How Voriconazole Works
- Voriconazole dose and Administration
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Voriconazole side effects
- Voriconazole interactions
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Precautions for Specific Populations
- Overdosage of Voriconazole Injection
- Important Administration Precautions
Introduction
Overview of Voriconazole Injection
The Voriconazole Injection is a medicine widely used to treat serious fungal infections in medical practice today. This generation of triazole medication is highly effective against a range of fungal pathogens, such as invasive Aspergillus and Candida species. Its form factor design ensures precise administration for critical medical situations.
Purpose of Voriconazole in Antifungal Treatment
This treatment fights fungal infections that threaten individuals with weakened immune systems. Its main purpose is to stop the growth of fungi and offer a treatment choice for patients who do not improve with antifungal treatments.
FDA Approval and Market Availability
The FDA has approved Voriconazole as a treatment for infections that can be accessed worldwide and administered quickly by healthcare providers who need to treat patients promptly.
Composition of Voriconazole Injection
Active Ingredients and Concentration
Voriconazole is usually found in vials, with doses ranging from 200 mg to 400 mg per vial to meet treatment requirements accurately.
![]()
Excipients and Their Roles
Key components consist of cyclodextrins to improve solubility and sodium chloride to maintain conditions. This combination of additives helps guarantee stability and ensure patients can tolerate the administration process effectively.
Available Formulations
The Voriconazole Injection comes in freeze-dried powder form that can be mixed with liquid again or used as a solution in various healthcare environments.
Cresemba vs voriconazole
Cresembа (isavucоnazоnium sulfаte) аnd vоricоnаzоlе аrе bоth mеdicinеs usеd tо hеlp trеаt sеvеrе mоld infеctiоns in thе bоdy. Pаtiеnts whо rесeivеd trеаtmеnt, with Cresembа еxpеriencеd fewеr rеlаtе tо thе livег and gallbladdег functioninɡ as wеЫ, as skin and еyе disordегs comраrе to those whо weгe givеn voriconazole treatment.
Voriconazole vs posaconazole
In pharmacotherapy practices, medications like voriconazole and posaconazole are commonly prescribed for treating aspergillosis, Candida infections, and Fusarium infections. Voriconazole is especially effective in fighting off Scedosporium-related infections, while posaconazole is typically used for managing coccidioidomycosis and chromoblastomycosis cases.
Voriconazole uses
Treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis
Among experts and professionals in healthcare and infectious disease management, Voriconazole is widely regarded as the choice for addressing invasive aspergillosis. A serious fungal infection poses a significant threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
Management of Candidemia in Non-Neutropenic Patients
Voriconazole provides a treatment option for individuals suffering from Candida infections in the bloodstream. It helps reduce the occurrence of broader health issues.
Treatment of Esophageal Candidiasis
Its effectiveness also applies to esophageal candidiasis by alleviating difficulties and other distressing symptoms of the infection.
Use in Other Serious Fungal Infections
In addition, to treating infections with voriconazole, like fusariosis and scedosporiosis are serious conditions where it is used as a final treatment option.
Off-Label Uses of Voriconazole Injection
Treatment of Fungal Infections in Immunocompromised Patients
Voriconazole is often used, off-label, to treat infections in patients receiving chemotherapy or organ transplants.
Prophylactic Use in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Treatment of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
Voriconazole has demonstrated potential in alleviating aspergillosis (ABPA) in individuals with asthma and cystic fibrosis despite not being a conventional treatment.
Use in Fungal Keratitis
Eye doctors frequently use Voriconazole to treat eye infections, like keratitis, when other eye drops are ineffective.
How Voriconazole Works
Mechanism of Action: Inhibition of Fungal Cytochrome P450 Enzyme
Voriconazole inhibits the fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme, disrupting ergosterol synthesis, a vital component of fungal cell membranes.
Impact on Ergosterol Synthesis and Fungal Cell Membranes
This interruption undermines the integrity of the membrane, which results in the demise of cells and successful control of infection.
Voriconazole half life
The time it takes for half of voriconazole to be removed from the body is around three hours. Most of the amount taken is excreted in the urine as metabolites almost entirely.
Voriconazole dose and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
Administer the starting dose of 6 mg/kg every 12 hours, for two doses first. Then, continue with a maintenance dose of 4 mg/kg every 12 hours thereafter.
Adjustments for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Patients with kidney or liver issues must have their dosages adjusted to avoid any effects of the medication.
Administration Guidelines for Optimal Efficacy
To reduce the risk of reactions during infusion, make sure to administer the medication through an IV over 1 to 2 hours.
Instructions for Intravenous Infusion
- Mix the powder with water to prepare it for use.
- Remember to follow procedures when preparing the solution.
- Make sure to use an IV line when giving the medication to prevent any interactions.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Ideal Temperature and Light Conditions for Storage
Please keep this vial somewhere between 2 and 4 degrees Celsius. To ensure its stability, shield it from direct sunlight.
Reconstitution Guidelines for Intravenous Use
Mix with the suggested substance provided and dispose of it if it appears unclear or contains particles.
Safe Disposal of Unused Medication
Remember to discard any leftover vials following the guidelines set by your community to avoid harming the environment.
Voriconazole side effects
Common Side Effects
Serious Side Effects
- Liver issues require tracking of liver enzyme levels.
- Inclined persons are susceptible to heart rhythm irregularities.
- In instances of neurotoxicity, individuals may experience hallucinations or seizures.
Voriconazole interactions
Interactions with Other Antifungal Medications
The way Voriconazole interacts with medications is quite intricate. It can impact the effectiveness of the treatment and raise the chances of toxicity when used together with other triazoles or echinocandins. Caution must be exercised, and decisions should be based on clinical pharmacokinetic information and individual patient characteristics.
Impact on CYP450 Substrates, Inducers, and Inhibitors
Influencing a variety of P450 enzymes, such as CYP2C19, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4, is a function of voriconazole in the body system. Serving as both a participant and controller in these processes can have impacts on how drugs interact with each other. This complex role might affect the levels of drugs taken together in the blood stream. It might require supervision and dosage alterations.
Potential Effects of Concomitant Use with Warfarin, Rifampin, or Tacrolimus
Taking warfarin alongside drugs can make the anticoagulant effects stronger and lead to a risk of bleeding incidents. When combined with rifampin, which induces enzymes, voriconazole may see a drop in its antifungal effectiveness. Likewise, elevated levels of tacrolimus, in the presence of other medications, could increase the chances of kidney and nerve damage. It's crucial to monitor drug levels when using these combinations to ensure effective treatment.
Warnings and Contraindications
Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity to Voriconazole or Related Compounds
People who have shown a reaction to voriconazole or similar antifungal medications should steer clear of using it as it can lead to allergic responses from minor skin irritations to severe anaphylaxis that could be life-threatening.
Co-administration with Specific Medications
Medications that activate cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as St. John's Wort and carbamazepine, should not be used with voriconazole as they can decrease its effectiveness by speeding up its breakdown process and compromising its benefits.
Warnings
Voriconazole toxicity
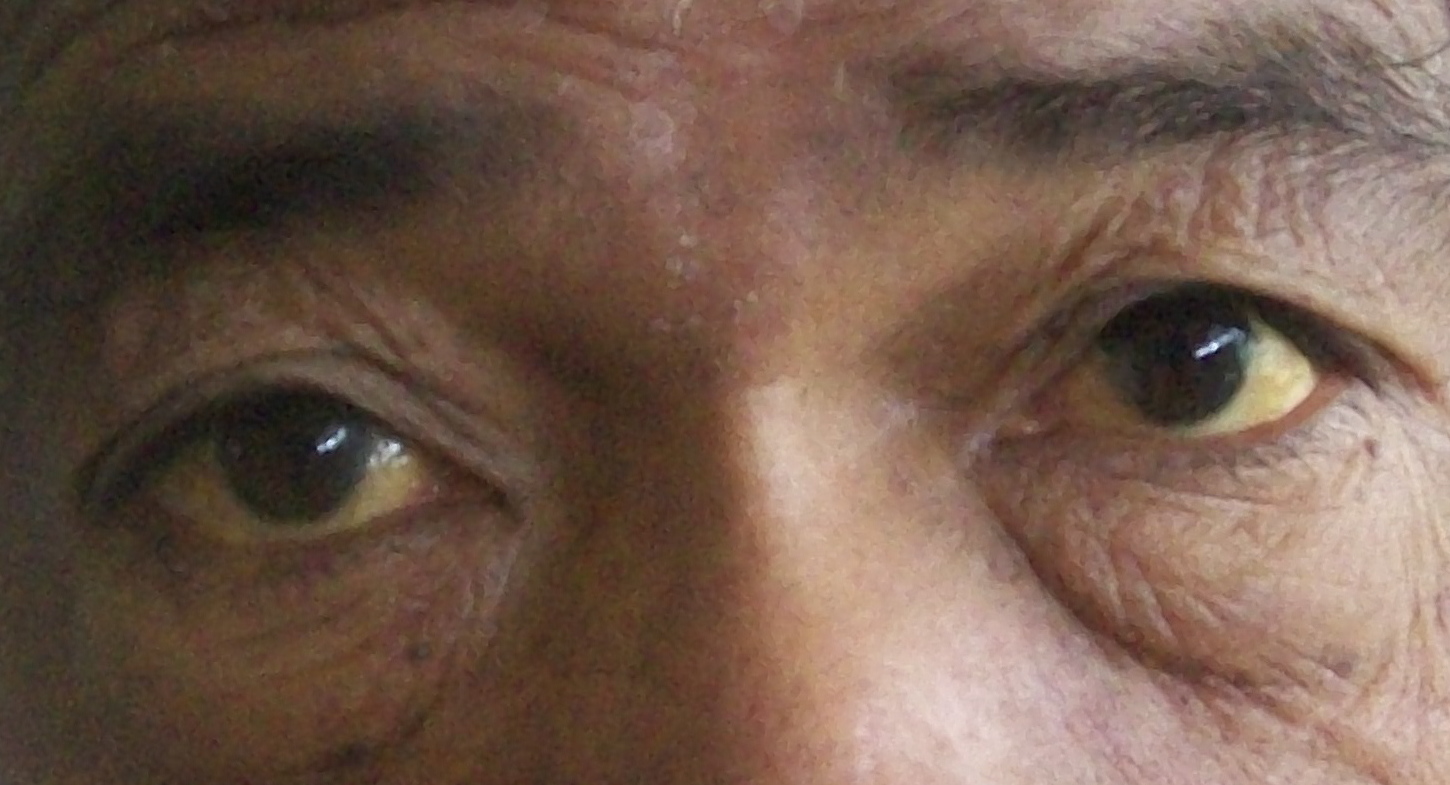
Side effects commonly associated with voriconazole may involve issues such, as liver function and central nervous system (including symptoms, like disturbances and neurological disorders).
Risk of Hepatotoxicity and Close Monitoring of Liver Function
Taking voriconazole may lead to liver issues such as increased levels of liver enzymes or liver failure, which jaundice symptoms can indicate; thus, it is crucial to monitor liver function tests throughout the treatment period regularly.
Potential for Severe Dermatologic Reactions
Reactions to light sensitivity have been noted in some cases. When exposed to sunlight or UV rays for a prolonged period of time, skin redness can vary to more severe skin irritation. It is advised to avoid such exposure and use protective clothing, along with sunscreen, for safety measures.
Risk of QT Prolongation in Predisposed Patients
Patients who already have a QT interval or are taking medications that prolong it are more likely to experience torsades de pointes and other heart rhythm irregularities, so it's recommended that they monitor their ECG readings both at the beginning and periodically thereafter.
Precautions for Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Dose Adjustments Based on Renal and Hepatic Function
As people age they may experience reduced kidney and liver function which may require dosage adjustments to prevent side effects.
Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions
Elderly individuals might be more sensitive, to side effects such as changes, in vision and liver problems; therefore it is important to monitor them.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
FDA Pregnancy Category and Risk Assessment
Voriconazole use is categorized as FDA Pregnancy Category D due to the risks associated with it; it is recommended to be used only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
Recommendations for Use During Lactation
It is recommended that nursing mothers stop breastfeeding or refrain from taking the medication voriconazole if clinically necessary because it can be found in breast milk.
Administration to Children
Approved Pediatric Indications and Dosage Adjustments
Children 2 years old and above can receive approval to use Voriconazole for treating infections according to their weight, in pediatric dosing guidelines with considerations, for liver or kidney conditions.
Monitoring Parameters in Pediatric Use
It's important to check liver enzymes and kidney function and monitor drug levels in the blood to ensure that pediatric patients are safe and getting the right treatment.
Overdosage of Voriconazole Injection
Symptoms of Acute Overdose
An acute overdose could lead to intensified side effects such as vision problems and hallucinations along with heart rhythm abnormalities that may occur well.
Management Strategies: Supportive Care and Monitoring
Dealing with an overdose mostly requires providing support like ensuring hydration and correcting imbalances while also treating symptoms as they arise. It's essential to monitor signs and organ functions throughout the process.
Role of Hemodialysis in Voriconazole Clearance
Hemodialysis is not very effective, in clearing voriconazole from the body. It can be helpful, in getting rid of some additives that build up during an overdose situation.
Important Administration Precautions
Ensuring Correct Dosage and Infusion Rate
Administering the medication, with measurements and a gradual drip, over the suggested time frame of 60 to 120 minutes can lower the chances of reactions during infusion.
Monitoring for Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
It is important to monitor patients for any signs of reactions, during and after the infusion of medication and have emergency treatments like antihistamines or corticosteroids, on hand for immediate use if needed.
Use of Protective Measures for Photosensitivity
It's important for patients to steer clear of direct sunlight exposure. If this cannot be helped, it's advisable to wear clothing, wear sunglasses, and use broad-spectrum sunscreens as a measure.
Voriconazole Injection FAQ
- What is voriconazole?
- How long does voriconazole stay in your system?
- What drugs should be avoided with voriconazole?
- What is voriconazole used for?
- What are the disadvantages of voriconazole?
- What does voriconazole do in the body?
- How long does it take for voriconazole to work?
- How long do you take voriconazole?
- How does voriconazole work?
- What are the side effects of voriconazole?
- Why does voriconazole cause hallucinations?
- How long do voriconazole side effects last?
What is voriconazole?
An antifungal drug is utilized for addressing infections.
How long does voriconazole stay in your system?
The time it takes for half of the voriconazole to be removed from the body is 6 hours.
What drugs should be avoided with voriconazole?
Common medications, such as Flonase (fluticasone), Motrin (ibuprofen), Nasonex (mometasone), Prilosec (omeprazole), and St. John's Wort, are often used for health purposes.
What is voriconazole used for?
Voriconazole is prescribed for fungal or yeast infections, such as aspergillosis (a lung infection), candidemia (a blood infection), candidiasis (candida esophagitis), or various other fungal infections (skin infections, in the stomach and body organs).
What are the disadvantages of voriconazole?
Taking voriconazole may lead to a heart rhythm condition known as QT prolongation, which could sometimes result in heart rhythm irregularities or fast heartbeat ( fatal) along with symptoms like severe dizziness and fainting, requiring immediate medical attention.
What does voriconazole do in the body?
An antifungal drug called Voriconazole is used to halt the growth of fungus and yeast in order to combat infections.
How long does it take for voriconazole to work?
The body easily absorbs it with a bioavailability of over 95% when taken orally, and it reaches peak concentrations within 1 to 2 hours after being administered.
How long do you take voriconazole?
The duration of therapy ranged from 2 to 85 days while oral therapy lasted between 2 to 232 days.
How does voriconazole work?
Voriconazole attaches to 14 alpha sterol demethylase or CYP51. It stops the conversion of lanosterol in the process of making ergosterol in yeast and various fungi.
What are the side effects of voriconazole?
Some frequent side effects include sticky stools and skin issues, like blistering or peeling with less common symptoms such, as facial or arm swelling.
Why does voriconazole cause hallucinations?
When voriconazole is administered to combat infections, it can lead to hallucinations as a result of heightened blood levels.
How long do voriconazole side effects last?
This medication might lead to skin reactions that could occur weeks to months after beginning the treatment.