Acebrophylline Syrup
- Introduction
- Composition of Acebrophylline Syrup
- Acebrophylline uses
- How Acebrophylline Syrup Works
- Acebrophylline dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Acebrophylline Syrup
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Interactions of Acebrophylline Syrup
- Important Precautions
- Administration in Special Populations
- Administration to Elderly Patients
- Dosage Considerations and Monitoring
- Risks Associated with Comorbidities
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Safety Profile During Pregnancy
- Risk of Transfer Through Breast Milk
- Administration to Children
- Safety and Efficacy in Pediatric Populations
- Adjustments in Dosage Based on Weight and Age
- Overdosage of Acebrophylline Syrup
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Careful Administration Guidelines
Introduction
Overview of Acebrophylline Syrup
Acebrophylline Syrup is a medication designed to effectively treat respiratory issues. It offers a comprehensive solution for improving breathing problems, as recommended by healthcare professionals.
Role of Acebrophylline in Respiratory Health
Acebrophylline is essential for keeping the system healthy. It helps decrease inflammation, boost mucus clearance, and enhance airflow efficiency, all of which are aspects of effectively managing chronic respiratory conditions.
Importance of Acebrophylline in Managing Chronic Respiratory Conditions
Chronic respiratory disorders, such as COPD and asthma, demand long-term care. Acebrophylline Syrup is pivotal in providing symptomatic relief and improving the quality of life for patients.
Composition of Acebrophylline Syrup
Active Ingredients and Their Roles
Acebrophylline is an element that improves function through its dual effects: bronchodilation and anti-inflammatory actions, which help lower airway resistance and make breathing easier.
Inactive Ingredients and Preservatives
Crafted with stabilizing agents and taste enhancers, these components guarantee the product's effectiveness and taste appeal, meeting a range of patient requirements.
Variants and Strengths Available
Acebrophylline Syrup comes in strengths to cater to the dosage needs of both children and adults.
Acebrophylline and acetylcysteine
Acebrophylline and acetylcysteine are mainly employed to help manage and alleviate pulmonary disease symptoms (known as COPD), including breathing difficulties and coughing fits or wheezing (an audible sound during breathing).
Acebrophylline montelukast
Acebrophylline montelukast is a medicine mainly used to manage asthma attacks and prevent respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (commonly known as COPDs) and allergic rhinitis (also called hay fever).
Theophylline vs acebrophylline
Theophylline has been used for a time as a bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory agent, whereas Acebrophylline is a recent addition to the field of medicine for similar purposes in treating patients with stable COP (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). They are both considered treatments alongside LAMA medications such as Tiotropium in respiratory healthcare practices.
Acebrophylline uses
Primary Uses in Respiratory Conditions
This syrup is a cornerstone treatment for respiratory challenges. Its primary applications include:

Off-Label Uses of Acebrophylline Syrup
Emerging studies suggest potential benefits in treating inflammatory airway diseases, broadening its therapeutic scope.
How Acebrophylline Syrup Works
Mechanism of Action
Acebrophylline works by reducing inflammation and relaxing the muscles to help improve function.
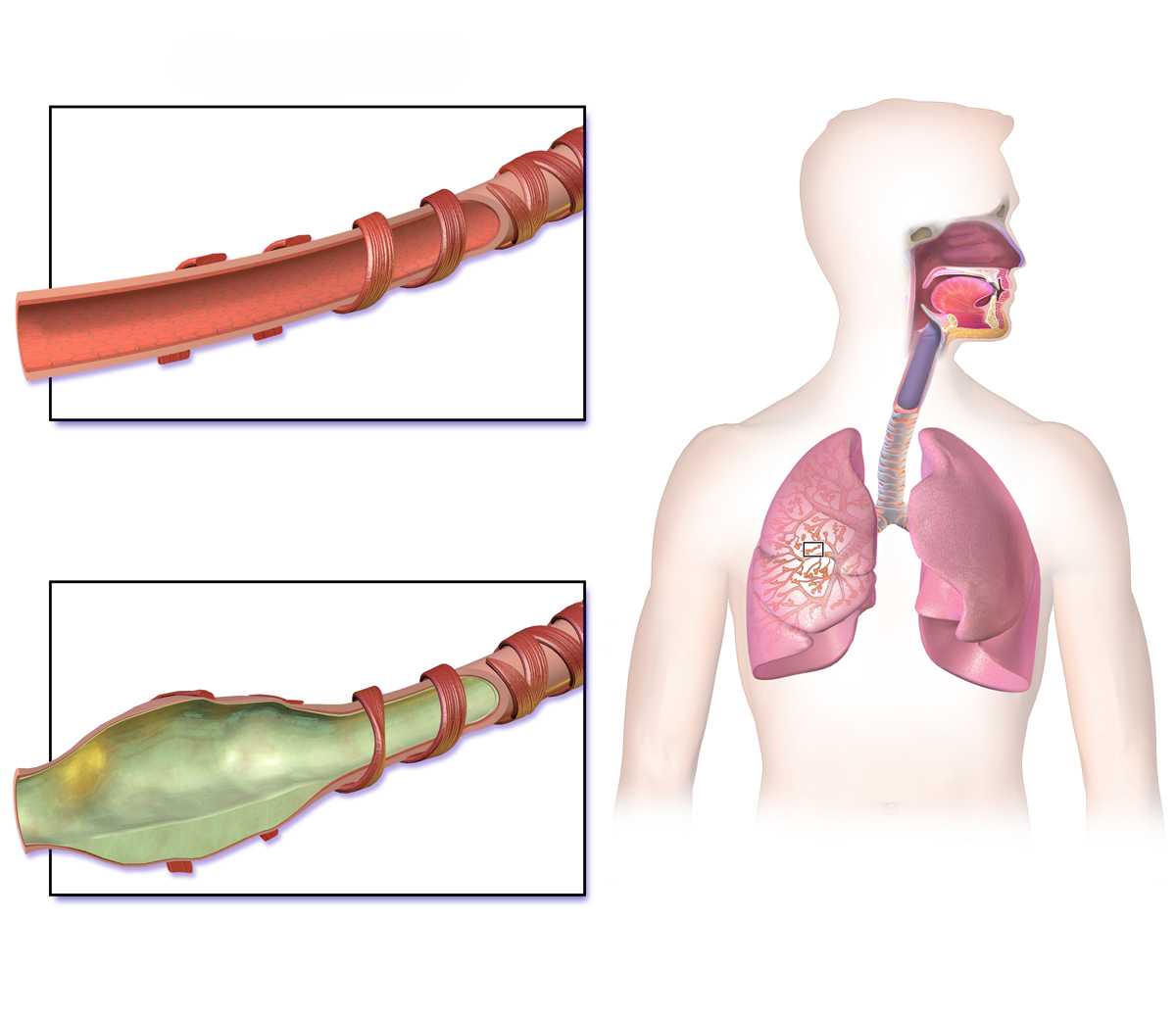

Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Acebrophylline reduces inflammation by blocking substances that cause swelling and increased sensitivity, in the airways.
Bronchodilator Effects
Its ability to open up the airways helps to relax them when they are constricted and offers relief in situations.
Mucolytic Properties for Improved Airway Clearance
Breaking down mucus to ensure air passage is a beneficial effect of the medication's mucolytic properties.
Acebrophylline solubility
Acebrophyllines solubility profile suggests that the drug dissolves to an extent in water and methanol while it dissolves well in ethanol.
Acebrophylline dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
Usually, for adults, 200 mg per day, split into two doses, is enough. However, everyone's needs can be different.
Dosage Recommendations for Children
Pediatric doses are determined based on the child's weight and usually range from 50 to 100 milligrams, depending on their healthcare requirements.
Timing and Frequency of Administration
Its recommended to take Acebrophylline after meals to reduce stomach discomfort and follow the prescribed timing intervals.
Adjustments in Specific Populations
It is important to adjust the dosage for patients who have kidney or liver issues to prevent any reactions.
Side Effects of Acebrophylline Syrup
Common Side Effects
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mild gastrointestinal discomfort
- Drowsiness or headache
Rare but Serious Side Effects
In instances urgent medical attention is required for allergic reactions and heart related issues.
Warnings and Contraindications
Medical Conditions to Disclose Before Use
Patients who have had reactions in the past or have a history of stomach ulcers should let their doctor know before starting to take Acebrophylline Syrup.

Contraindicated Conditions
This syrup should not be used by people who are highly allergic to its ingredients or those who have recently had a heart attack.
Risk of Interaction with Certain Medications or Substances
It's important to be careful when mixing Acebrophylline with medications, like corticosteroids or beta blockers.
Interactions of Acebrophylline Syrup
Drug-Drug Interactions
Concurrent use with other bronchodilators may amplify therapeutic effects but could also heighten side effects.
Impact of Combining with Antihypertensive or Antiepileptic Drugs
Using these medications together might require changing the dosage or trying treatment options.
Food and Alcohol Interactions
Alcohol could make you feel more tired, and some types of food might change how quickly your body absorbs medication.
Interaction with Herbal Supplements
Using herbal supplements that have properties alongside Acebrophylline could result in an over-relaxation of the airways.
Important Precautions
Monitoring Symptoms and Progress
It's really important to watch for any symptoms when taking Acebrophylline Syrup, keep track of how the treatment is working, and let your healthcare provider know if your respiratory problems aren't getting better or are getting worse over time. It might also be an idea to have regular lung function tests done, especially if you have a chronic respiratory condition.
Recognizing Signs of Adverse Reactions
Detecting impacts at a stage plays a crucial role in ensuring well-being and health maintenance. It's important to be mindful of any skin irritations, rash episodes, sudden swellings, or breathing challenges. These symptoms could indicate concerns. Seek advice and guidance when observing such signs to avoid further complications or health risks.
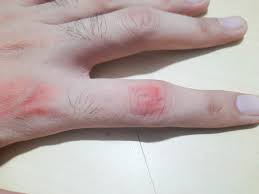
Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Dosage
It's crucial to stick to the dosage prescribed by your doctor to ensure the medication works as intended. Skipping doses or taking too much can cause ineffective outcomes or harmful side effects.
Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
As people age, they may need higher doses of medication because their bodies change. It's important to watch for any side effects, like heart strain or stomach issues, to make sure the medication is safe.
Dosage Considerations and Monitoring
The amount of medication given needs to be changed depending on how the patient's kidneys and liver are working properly, and frequent evaluations can reduce the potential dangers linked to using it for an extended period of time.
Risks Associated with Comorbidities
Patients who have health conditions, like diabetes or hypertension need to be monitored to prevent any complications or worsening of their existing health problems.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
While Acebrophylline has exhibited effects on fetuses, moms to be should only take it when the advantages outweigh the possible risks. It's crucial to seek advice from a healthcare provider before using it.

Risk of Transfer Through Breast Milk
The medicine has the possibility of transferring to breast milk and potentially impacting a baby who is breastfeeding. Based on requirements and considerations that arise during the treatment decision-making process, it might be necessary to look into treatment options or stop breastfeeding altogether.
Administration to Children
Safety and Efficacy in Pediatric Populations
Acebrophylline Syrup is deemed to be safe, for children when used as instructed with clinical research backing its effectiveness, in treating issues in kids.
Adjustments in Dosage Based on Weight and Age
Dosages for kids are usually determined based on their weight to make sure they're just right. Keeping an eye out for changes in growth and development throughout the treatment is important for safety and effectiveness.
Overdosage of Acebrophylline Syrup
Symptoms and Signs of Overdose
Taking much of the medication can lead to symptoms, like nausea and vomiting or even seizures and severe stomach pain which need urgent care.
Immediate Steps to Manage Overdose
- Inducing vomiting only if instructed by a healthcare provider
- Administering activated charcoal to limit absorption
- Providing supportive care in a clinical setting
Importance of Seeking Emergency Medical Attention
Overdosing can quickly lead to life-threatening emergencies, so it's crucial to get in touch with emergency services for the timely help.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Ideal Storage Conditions
To ensure its stability, store acebrophylline syrup in a dry place away from sunlight at 15°C to 30°C.
Shelf Life and Expiration Considerations
Make sure to look at the expiration date before using any medication. Using expired medicine may decrease its effectiveness and possibly cause side effects.
Safe Handling to Avoid Contamination
Remember to seal the bottle every time you use it and take care to protect the medication from moisture and contaminants by handling it with cleanliness, in mind.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Avoiding Abrupt Discontinuation
Suddenly stopping Acebrophylline could result in a return of symptoms, so it's advisable to reduce the dosage under the guidance of a healthcare professional when discontinuing its use.
Monitoring for Therapeutic Effectiveness
Regular medical checkups are essential to evaluate how well the treatment is working and make any needed changes to medication dosage. If lung function improvement is needed, doctors may use spirometry tests.
Importance of Regular Follow-Ups
Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider help ensure that treatment objectives are achieved while reducing the chances of experiencing side effects. These visits allow for modifications and patient education.
Acebrophylline Syrup FAQ
- What is acebrophylline used for?
- What is the difference between Acebrophylline and ambroxol?
- Is acebrophylline a theophylline?
- Does acebrophylline cause a cough?
- Is acebrophylline acetylcysteine good for coughing?
- Is acebrophylline an antihistamine?
- Is Acebrophylline a steroid?
- Is acebrophylline anti-inflammatory?
- Is acebrophylline an antibiotic?
- Does Acebrophylline affect the kidneys?
- Does Acebrophylline help with cough?
- What is side effects of acebrophylline?
- What are the benefits of Acebrophylline?
- How many days should I take acebrophylline?
- Who should not take acebrophylline?
What is acebrophylline used for?
Acebrophylline is prescribed to help manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What is the difference between Acebrophylline and ambroxol?
Acebrophylline functions as both a mucolytic and bronchodilator by soothing the airway muscles and thinning mucus to facilitate breathing. Ambroxol is a medication that aids in mucus thinning in the system for cough expectoration in the nose and lungs.
Is acebrophylline a theophylline?
Acebrophylline is made up of theophylline and ambroxol.
Does acebrophylline cause a cough?
Acebrophylline functions by calming the muscles in the airways, facilitating the loosening of mucus, and aiding in cough expulsion.
Is acebrophylline acetylcysteine good for coughing?
It mainly manages and alleviates symptoms linked to pulmonary disease (the acronym COP), like difficulty breathing or coughing.
Is acebrophylline an antihistamine?
No
Is Acebrophylline a steroid?
No
Is acebrophylline anti-inflammatory?
Acebrophylline works as a regulator for mucus in the airways. It has anti-inflammatory properties.
Is acebrophylline an antibiotic?
No
Does Acebrophylline affect the kidneys?
Diminished kidney function can impact the elimination of substances from the body.
Does Acebrophylline help with cough?
Acebrophylline is a mucolytic and bronchodilator.
What is side effects of acebrophylline?
After consuming acebrophylline medication you might encounter effects such, as feeling sleepy or dizzy and experiencing nausea or stomach problems like vomiting or discomfort having issues, like diarrhea or constipation.
What are the benefits of Acebrophylline?
Acebrophyllline is commonly prescribed for managing symptoms related to asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (commonly known as COP). These symptoms may include wheezing sounds during breathing, feeling breathless, tightness in the chest area, and persistent coughing problems. The medication functions by easing the pathways for air to flow freely in the lungs while also diminishing inflammation levels and aiding in the clearance of mucus build-up from the system, ultimately facilitating breathing for individuals affected by these conditions.
How many days should I take acebrophylline?
An allocation of time for this activity should be made every day without fail, in the evening following meals.
Who should not take acebrophylline?
It's advisable to avoid acebrophylline in case you have any allergies to it or related substances, like ambroxol or theophylline; experience heartbeats; have hemodynamic instability (unstable blood pressure) or low blood pressure; suffer from liver or kidney disorders; or have a history of heart attack.