Acetazolamide
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
- Is Acetazolamide Over the Counter?
- Does Acetazolamide Help You Lose Weight?
- Acetazolamide for Altitude Sickness
- Acetazolamide and Alcohol: What You Need to Know
- FAQs in Relation to Buy Acetazolamide
- Buy Acetazolamide: Comprehensive Guide on Usage and Safety
Acetazolamide is a medication classified as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It has a range of uses in the treatment of various medical conditions. In this article, we will explore acetazolamide and its typical applications.
Understanding the Medication and Its Uses
Acetazolamide is an anticonvulsant and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that functions by blocking the activity of an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase, which plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance within our bodies. By inhibiting this enzyme, acetazolamide aids in reducing the accumulation of fluid and pressure in organs or tissues 1.
Acetazolamide has several applications in the medical field. Some of them are:
- Glaucoma: Acetazolamide is used in managing open-angle and secondary glaucoma. This medication helps decrease pressure by reducing the production of aqueous humor in the eye, thereby preventing vision loss caused by damage to the optic nerve 2.
- Epilepsy Management: Acetazolamide can also be used as a therapy for certain types of epilepsy when other medications are ineffective or produce intolerable side effects. It may help control seizures by influencing the balance of electrolytes within brain cells 3.
- Preventing Altitude Sickness: Individuals traveling to high altitude locations often receive prescriptions for acetazolamide to prevent mountain sickness (AMS). Acetazolamide aids faster adaptation to altitudes by increasing respiratory rate and reducing fluid buildup, thus alleviating symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and nausea 4.
- Management of Edema: In some instances, doctors may prescribe acetazolamide off-label to treat edema caused by congestive heart failure or other medical conditions. The medication promotes increased urine production, which can help reduce the buildup of fluid in the body 5.
For more information on these applications, please refer to the following sources:
2: Drugs.com 1: Medscape 3: Epilepsy Foundation 4: CDC 5: [Mayo Clinic]
Dosage and Administration
It is essential to understand the correct dosage and how to take Acetazolamide to achieve the best possible outcomes. This section will provide information on dosages important factors to consider, and helpful tips, for administering the medication.
Standard Acetazolamide Dosages
The initial dosage of Acetazolamide varies depending on the condition being treated. For instance, when addressing glaucoma, a standard starting dose would range from 250 mg to 1 g per day divided into doses. On the other hand, for altitude sickness prevention, a lower dosage of 125 mg twice daily might be recommended. It is crucial to adhere to your healthcare provider's instructions regarding the appropriate dosage.
Adjusting the Dose: Special Considerations and Precautions
Patients with kidney or liver problems may need to adjust their dosage of Acetazolamide because their bodies may not clear the drug efficiently. It's essential to consult your doctor before taking this medication if you have kidney or liver impairment if you are elderly, or if it will be used in a child. For adults, starting with a lower dose of Acetazolamide is recommended due to the increased risk of side effects, like dizziness or confusion. When it comes to children, the safety and effectiveness of Acetazolamide depends on their age and weight. It is essential to consult with a pediatrician before giving this medication to patients.
Tips for Optimal Use
To ensure Acetazolamide is adequately absorbed into your bloodstream, taking it with food is recommended. Remember to swallow the tablet whole and avoid crushing or chewing it. Take your doses at evenly spaced intervals throughout the day for medication levels in your system. If you experience stomach upset, you can try taking this medication with milk or antacids. Consult your doctor first, as some antacids may not interact well with Acetazolamide. In summary, it's essential to understand and follow the dosage and administration instructions for Acetazolamide to maximize its benefits while minimizing any potential side effects. Before starting any treatment with Acetazolamide, always seek advice to ensure safe and effective use. If you have any questions regarding the dosage and administration of Acetazolamide, it is advisable to consult a physician. It's also important to be aware of this medication's side effects. Key Takeaway: It is crucial to adhere to dosage and administration guidelines when using Acetazolamide to achieve optimal results. The initial dose varies depending on the condition being treated, taking into account considerations for patients with kidney or liver issues, elderly patients, and pediatric use. Helpful usage tips include taking the medication alongside meals and spacing out doses evenly throughout the day.
Side Effects
Like any medication, it's essential to know the side effects of Acetazolamide. Some people may experience mild reactions, while others may not have any adverse effects. Knowing these side effects can help you recognize and effectively deal with them.
Common Side Effects to Watch Out For
The adverse reactions of Acetazolamide often consist of dizziness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, tingling sensation in the hands and feet (paresthesia), as well as increased urination (diuresis). Fortunately, these typical side effects are usually mild. They tend to subside as your body becomes accustomed to the medication. However, it is advisable to seek guidance from your healthcare provider if they persist or worsen over time.
Serious Side Effects: When to Seek Medical Attention
Acetazolamide, although rare, can sometimes lead to severe side effects that need immediate medical attention. These can include reactions like rash or swelling of the face, tongue, or throat as well as intense dizziness or difficulty breathing. Other potential complications may involve blood disorders such as anemia and hearing problems, like hearing loss or ear ringing. If you encounter any of these side effects, it is crucial to seek medical help promptly. To obtain details regarding the prescription or prophylactic use of Acetazolamide, it's advisable to consult your healthcare provider. Additionally, it's essential to be aware that this medication might interact with drugs or substances you are currently using. When purchasing Acetazolamide, consider its side effects, which may include dizziness, fatigue, and nausea, whereas rare but serious ones should immediately prompt medical attention.
Drug Interactions
It is essential to be aware of drug interactions when using Acetazolamide. These interactions can impact the effectiveness of the medication. Lead to adverse effects. In this section, we will explore medicines that may interact with Acetazolamide and offer suggestions on how to avoid any harmful drug interactions.
Common Medications That Interact with Acetazolamide
When you take aspirin together with Acetazolamide, there is a chance of experiencing side effects such as dizziness and imbalances in electrolyte levels. Combining digoxin with Acetazolamide may increase digoxin levels in your bloodstream, increasing the risk of toxicity. If you use lithium and Acetazolamide at the time it can reduce the excretion of lithium, leading to an increased risk of lithium toxicity. Diuretics (like furosemide) alongside Acetazolamide can enhance their diuretic effect and potentially increase the chances of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. Certain anticonvulsant medications, like phenytoin or carbamazepine, may have reduced effectiveness when taken concurrently with Acetazolamide.
How to Avoid Dangerous Drug Interactions
To reduce the chances of any interactions between different medications, it's important to follow these guidelines; 1. Make sure to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications, supplements, and over-the-counter products you are currently taking or planning to take. 2. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication. It's crucial to seek their guidance and not make any decisions alone. 3. If you are prescribed a medication while already taking Acetazolamide it is advisable to check with your pharmacist for any known interactions between the two drugs. 4. Regularly schedule checkups with your healthcare provider. This will help them monitor for any drug interactions and make necessary adjustments to dosages if required. By following these steps, you can minimize the risk of drug interactions. Ensure your medications work effectively without causing any harm.
What to Do If You Suspect an Interaction
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any symptoms or side effects while using Acetazolamide. They will be able to assess if there might be a drug interaction going on and make any adjustments to ensure that your treatment remains safe and effective. Remember, it's important to act when managing potential drug interactions. Before starting a regimen with Acetazolamide, it's crucial to consider the possibility of drug interactions. Carefully review any contraindications and safety measures. Key Takeaway: When taking Acetazolamide, it's essential to be aware of drug interactions that could impact its effectiveness or lead to adverse effects. Some common medications that may interact with Acetazolamide include aspirin, digoxin, lithium, diuretics, and certain anticonvulsants. To avoid any dangerous drug interactions, make sure you inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking or plan to take and have regular checkups with them for monitoring purposes.
Contraindications and Precautions
It is essential to know the conditions that might impact the usage of Acetazolamide before using it. This section will cover who should avoid taking Acetazolamide and the precautions to be aware of before starting the treatment.
Who should not take Acetazolamide?
Specific individuals with medical conditions or allergies should refrain from taking Acetazolamide. For instance, if you have a known allergy to sulfa drugs (a class of antibiotics), there is a risk of experiencing an allergic reaction when using Acetazolamide. It is advisable for patients with renal function to avoid this medication as it may worsen their condition. Individuals with liver disease should also steer clear from taking Acetazolamide due to adverse effects on liver function. Regarding pregnancy and breastfeeding, the safety of using this medication has not been established. If you are pregnant or nursing, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
Medical conditions to consider before using Acetazolamide
It is essential to exercise caution when taking Acetazolamide, especially if you have medical conditions. Ensure to inform your doctor if you have any of the following: 1. Low sodium levels (hyponatremia): This medication can further decrease sodium levels, leading to complications. 2. High potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia); Acetazolamide can increase potassium levels, so individuals with hyperkalemia should use this medication cautiously. 3. Issues: If you have severe respiratory problems, it is advisable to be cautious when using this medication, as it may worsen your condition.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and Acetazolamide
The safety of using Acetazolamide during pregnancy or while breastfeeding is not well established. Studies conducted on animals have indicated risks to the fetus, but there is insufficient evidence from human studies. If you are expecting or nursing, it is advised to consult with a healthcare provider before starting treatment with this medication. For information regarding the use of drugs during pregnancy and lactation, please visit the MotherToBaby website. It is crucial to be aware of the restrictions and precautions associated with Acetazolamide before beginning therapy. When deciding if this treatment suits you, considering its effectiveness should be considered. Key Takeaway: Before taking Acetazolamide, it is essential to understand the contraindications and precautions involved. Individuals who are allergic to sulfa drugs have kidney or liver disease. Are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid using this medication. Patients with hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, or respiratory issues need to exercise caution when considering Acetazolamide.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
When using Acetazolamide, it's crucial to monitor your progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. To ensure that the treatment is yielding results, it is essential to keep track of your progress and make any necessary adjustments.
How to Track Your Progress While Using Acetazolamide
Here are some tips to help you track your symptoms and manage your medication: 1. Keep a diary; Take note of any changes in your symptoms like fever, severe headaches, or improvements in your vision. This information can be valuable for understanding how well Acetazolamide works for you. 2. Pay attention to side effects; It's essential to monitor any side effects you may experience while taking this medication. If they become bothersome or severe, consult your doctor away. 3. Schedule regular checkups; Regular visits with your healthcare provider are essential when using medications like Acetazolamide. They can assess your health and adjust the dosage or treatment plan. Remember, it's crucial to communicate with your doctor throughout the process to manage your condition effectively.
Adjusting Your Treatment Plan: When to Consult Your Doctor
If you notice that your condition doesn't improve after starting Acetazolamide treatment, discussing potential adjustments with your doctor might be an idea. Some reasons that may call for a change include side effects, insufficient relief of symptoms, the emergence of new medical issues, or possible interactions with medications you are currently taking.
Evaluating Success: Signs That Acetazolamide Is Working for You
The effectiveness of an individual's treatment plan depends on factors like age, weight, medical history, and the specific condition being treated. However, some indications suggest Acetazolamide is effectively managing symptoms. These include experiencing less severe headaches, improved vision, reduced swelling in the extremities, and better breathing for individuals with respiratory conditions. It's important to note that each patient's experience with Acetazolamide may vary. Maintaining communication with your healthcare provider throughout the treatment process is crucial to ensure optimal results. For information on prescribing Acetazolamide and its use as a precaution, you can refer to a comprehensive Acetazolamide guide. To ensure the prescribed medication has the desired effect it is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of your treatment. This can be done by maintaining a symptom diary noting any side effects experienced and scheduling checkups with your healthcare provider. If symptoms do not improve within a week of starting the therapy or if there are persistent side effects, it may be necessary to make adjustments in consultation with your doctor.
Is Acetazolamide Over the Counter?
Suppose you're thinking about using acetazolamide for its medical uses. In that case, it's essential to know if this strong medication can be obtained without a prescription (OTC) or if it requires a doctor's approval. In this section, we will talk about the accessibility of acetazolamide. Share some helpful advice on how to acquire it safely.
Prescription vs. OTC Medications
There are generally two types of medications: those that require a prescription and those that can be purchased over the counter. Prescription drugs need a doctor's approval because they are potent and may have side effects. Have specific usage guidelines. On the side over-the-counter medications can be bought without a prescription since they are considered safe for general use when used as directed on the label.
Acetazolamide Availability
Acetazolamide cannot be purchased without a prescription; you need to get it prescribed by your healthcare provider. This restriction is, in place to ensure that patients receive the dosage, proper administration instructions, and necessary monitoring while using this powerful medication. If you are thinking about using acetazolamide for prophylaxis purposes, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider.
Tips for Obtaining Acetazolamide Safely:
Make sure to get in touch with your healthcare provider. Suppose you think that acetazolamide could be beneficial for you based on your symptoms or specific condition(s). In that case, it's essential to consult with your doctor before attempting to purchase the medication online or from any other source. Be cautious about where you buy it from. Obtaining prescribed medicines like acetazolamide from reputable pharmacies either in person or through verified online platforms is crucial, ensuring both safety and authenticity. For information, take a look at our section on comparing online pharmacies. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully. Once you have obtained a prescription, adhere to the recommended dosage and administration guidelines. This will help minimize side effects and maximize the effectiveness of the treatment. To summarize, acetazolamide cannot be purchased over the counter due to its nature and specific usage requirements. Before taking acetazolamide, consult with a healthcare professional and acquire the medication from a source. Remember that obtaining any medication without a prescription can be risky. Now, let's explore whether acetazolamide can aid in weight loss. Key Takeaway: Acetazolamide requires a prescription from a healthcare provider. It cannot be obtained without one due to side effects and specific usage requirements. Before obtaining acetazolamide, it is essential to consult with your doctor and ensure that you purchase it from reliable sources.
Does Acetazolamide Help You Lose Weight?
In this section, we will explore the impact of acetazolamide on weight reduction.

Potential Mechanism for Weight Loss
Acetazolamide is categorized as an anhydrase inhibitor, a type of medication. Its mechanism of action involves promoting the elimination of bicarbonate in urine, resulting in increased excretion of water and sodium. This diuretic effect might lead to weight loss by reducing fluid retention. However, it's crucial to understand that this weight loss may not be sustainable or beneficial for long-term health, as supported by research on acetazolamides' direct influence on body weight.
Evidence on Acetazolamide and Weight Loss
There have been a few studies conducted to examine the direct effects of acetazolamide on body weight. A recent study published in The American Journal of Medicine discovered that individuals who took acetazolamide experienced decreased body weight compared to those who received a placebo treatment. However, further research is necessary before any definitive conclusions regarding its efficacy as a weight loss aid can be made.
Risks Associated with Using Acetazolamide for Weight Loss
Side effects; Like any medication, acetazolamide can have potential side effects such as feeling dizzy, tired, nauseous or experiencing tingling sensations in your hands or feet (source; WebMD). These side effects need to be considered about the benefits of weight loss. Off-label use: It's important to note that acetazolamide is not FDA-approved for weight loss, and using it for this purpose would be considered off-label. Before starting any medication or treatment plan, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. Limited long-term effectiveness; acetazolamide may only provide weight loss due to its diuretic properties. This means that the weight reduction achieved might not lead to results or improvements in overall health. To summarize, while some evidence suggests that acetazolamide could contribute to weight loss through its diuretic effects, further research is necessary before recommending it as a reliable solution for losing weight. If you are considering using acetazolamide for this purpose, you must discuss your options with a healthcare provider who can guide you toward effective strategies customized to your specific needs. Therefore it is not recommended to use acetazolamide for weight loss. It should be avoided. Additionally, acetazolamide has been proven effective in treating altitude sickness when taken as prescribed by a professional. The main point to remember is that acetazolamide, a medication that inhibits carbonic anhydrase, might lead to weight loss because of its diuretic properties. However, no studies are available on the direct effects of acetazolamide on body weight. Using it as a weight loss solution is considered off-label. It may have side effects that outweigh any potential benefits. It's crucial to consult with healthcare before relying on this option as a reliable way to lose weight.
Acetazolamide for Altitude Sickness
When traveling to altitudes, many people experience a condition known as acute mountain sickness (AMS). AMS can cause headaches, nausea, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. It has been proven through studies that acetazolamide is an effective treatment and preventive measure for altitude sickness.
How Acetazolamide Helps with Altitude Sickness
Acetazolamide promotes the excretion of bicarbonate in the urine, aiding your body in adapting to altitude variations efficiently. This mechanism alleviates the symptoms commonly linked to mountain sickness (AMS) and facilitates a quicker adjustment when ascending to higher altitudes.
Dosage Recommendations for Altitude Sickness Prevention
For adults, the recommended amount is 125 mg taken twice a day. Take it one day before going up to altitudes and continue until two days after reaching the highest point. As for children, the dosage is determined based on their weight. It's usually 5 mg per kilogram of body weight divided into two daily doses for children aged two years or older. To get personalized guidance based on your child's age and weight, it's best to consult with a professional.
Treatment Considerations When Prescribing Acetazolamide for Altitude Sickness
Make sure to prioritize acclimatization. While acetazolamide can help prevent symptoms of acute mountain sickness (AMS), it shouldn't be seen as a replacement for essential practices like gradually ascending and taking rest days during climbs. Stay well hydrated; Acetazolamide may cause urination, so keeping yourself adequately hydrated while taking this medication is essential. Take note of side effects. Common side effects may include tingling sensations in the hands and feet, changes in taste perception, and mild diuresis. These are generally well tolerated. It should be closely monitored during treatment. In addition to using acetazolamide as a measure, other steps such as proper acclimatization techniques, maintaining hydration, and recognizing early signs of altitude sickness can help ensure a safe and enjoyable experience at high altitudes. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any medications or treatments for altitude sickness prevention or management. Acetazolamide can indeed be an option for altitude sickness; however, it is essential to consider potential interactions with alcohol before using this medication. Now let's explore how acetazolamide and alcohol may interact when taken together. Key Takeaway: Acetazolamide is a medication for preventing and treating altitude sickness. It works by increasing the excretion of bicarbonate in urine, allowing the body to adapt quickly to changes in altitude. However, it is important to follow appropriate acclimatization techniques and closely observe any potential side effects, including the possibility of increased urination.
Acetazolamide and Alcohol: What You Need to Know
If you are prescribed acetazolamide, it is essential to be aware of how alcohol might interact with this medication. Combining acetazolamide and alcohol can result in side effects or diminish the effectiveness of the drug. This section will explore the hazards of mixing these substances and offer guidelines for safe consumption.
Potential Risks of Combining Acetazolamide and Alcohol
Possible Increased Side Effects: When you take acetazolamide and consume alcohol, it can cause feelings of dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, or headaches. Combining them may make these side effects more intense. Potential Reduced Effectiveness of the Medication: If you drink alcohol while taking acetazolamide, it could potentially hinder its ability to treat your condition effectively. This is because increased urine production caused by the combination might lower the medication levels in your blood. Impact on Liver Function: Excessive consumption could strain your liver function over time since the liver processes both substances. Potentially lead to damage.
Tips for Safe Consumption While Taking Acetazolamide
It's essential to be mindful of your alcohol intake while undergoing acetazolamide treatment. Talk with your doctor to determine an amount based on your circumstances. If you do choose to drink during your treatment, it's best to pace yourself and sip slowly over an extended period rather than consuming large amounts quickly. Since acetazolamide and alcohol can lead to dehydration, it is essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. This will help minimize any side effects and maintain proper kidney function. Keep an eye on any changes in your condition if you experience any side effects while taking acetazolamide with alcohol. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice worsening symptoms or new issues. To sum up, understanding the risks associated with combining acetazolamide and alcohol is crucial. It is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before mixing these substances. Always seek guidance from healthcare before deciding whether or not it's safe to combine them during treatment. If you are considering using acetazolamide prophylaxis or being prescribed this medication, it is essential to take into account the risks involved in incorporating it with alcohol. Key Takeaway: Combining acetazolamide and alcohol can heighten side effects, reduce the effectiveness of the medication, and put a strain on liver function. To ensure consumption when using acetazolamide, it is advisable to moderate alcohol intake, drink beverages gradually over an extended duration, maintain proper hydration by consuming water, and closely monitor any symptoms for potential worsening or the emergence of new issues.
FAQs in Relation to Buy Acetazolamide
What are the problems with acetazolamide?
Some individuals may experience symptoms when taking acetazolamide, including dizziness, tiredness, feelings of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or tingling sensations in the hands and feet. In some cases, it can also result in metabolic acidosis or the formation of kidney stones. It is important to note that prolonged usage is not advised due to hazards such as liver toxicity and blood disorders.
What is an alternative to acetazolamide?
Dexamethasone is a kind of medicine that can prevent altitude sickness. This corticosteroid is known to reduce the symptoms of acute mountain sickness (AMS) when taken as a preventive measure. However, it's important to note that it should only be used under a professional's guidance because potential side effects may be associated with its use.
What is the generic substitute for acetazolamide?
Diamox Sequels (extended-release capsules) are an alternative to Acetazolamide. While both medications have the active ingredient, their release mechanisms differ, which could impact how often they need to be taken.
Can you buy altitude sickness tablets over the counter?
No, you won't be able to buy altitude sickness tablets like Acetazolamide or Diamox at a pharmacy without a prescription from a healthcare provider. It's crucial to consult with your doctor for the correct dosage and guidelines for using these medications.
Buy Acetazolamide: Comprehensive Guide on Usage and Safety
Acetazolamide is a medication that can be used to treat conditions like altitude sickness, glaucoma, and epilepsy. It helps reduce the body levels, potentially alleviating symptoms associated with these disorders. It is crucial to follow dosage and administration guidelines when taking Acetazolamide, and it is essential to monitor for side effects and potential drug interactions. Additionally, being aware of any contraindications or precautions is essential for usage. When looking for a source to purchase Acetazolamide, Buy Pharma. md is an excellent choice. They have a reputation for providing customers with high-quality medications at competitive prices. With over 10 years of experience serving customers, they offer a range of affordable medicines. Start your treatment plan by purchasing Acetazolamide from Buy Pharma. md today. Remember to consult your healthcare provider before starting any medication.
Acetazolamide FAQ
- What are the side effects of Acetazolamide?
- What are the uses of Acetazolamide?
- What is the mechanism of action of Acetazolamide?
- What is the brand name of Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used for altitude sickness?
- What is Acetazolamide's MOA?
- What is the dosage of Acetazolamide?
- What are the interactions of Acetazolamide?
- What is the class of Acetazolamide?
- What is Acetazolamide 250 mg?
- Can Acetazolamide be purchased over the counter?
- What are the warnings associated with Acetazolamide?
- What is the dose of Acetazolamide for altitude sickness?
- What is the drug class of Acetazolamide?
- What are the adverse effects of Acetazolamide?
- What is Acetazolamide Diamox?
- What is Acetazolamide tablet 250 mg?
- What is Acetazolamide ER 500 mg?
- How is Acetazolamide used for metabolic alkalosis?
- Is Acetazolamide a diuretic?
- What are the contraindications for Acetazolamide?
- How is Acetazolamide used for glaucoma?
- What causes the tingling side effect of Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used in heart failure?
- How is Acetazolamide pronounced?
- Can Acetazolamide be used in patients with a sulfa allergy?
- How does Acetazolamide work?
- What are the indications for Acetazolamide?
- Is there an eye drop formulation of Acetazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide be bought over-the-counter (OTC)?
- Is Acetazolamide used for metabolic acidosis?
- What is the mechanism of action of Acetazolamide?
- What is the cost of Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used for idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH)?
- Can Acetazolamide be taken with alcohol?
- Is Acetazolamide effective against mountain sickness?
- What is the form of Acetazolamide?
- What is the generic name for Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used for central sleep apnea?
- Can you buy Acetazolamide over the counter?
- How does Acetazolamide compare to Methazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide be used if there's a sulfa allergy?
- What is the maximum dose of Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used for migraines?
- Does Acetazolamide cause weight loss?
- Is Acetazolamide safe during pregnancy?
- Does Acetazolamide affect potassiumlevels?
- What are the possible drug interactions with Acetazolamide?
- Where can I buy Acetazolamide?
- What is the price of Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used for headaches?
- Is Acetazolamide used for sleep apnea?
- What is the role of sodium in the function of Acetazolamide?
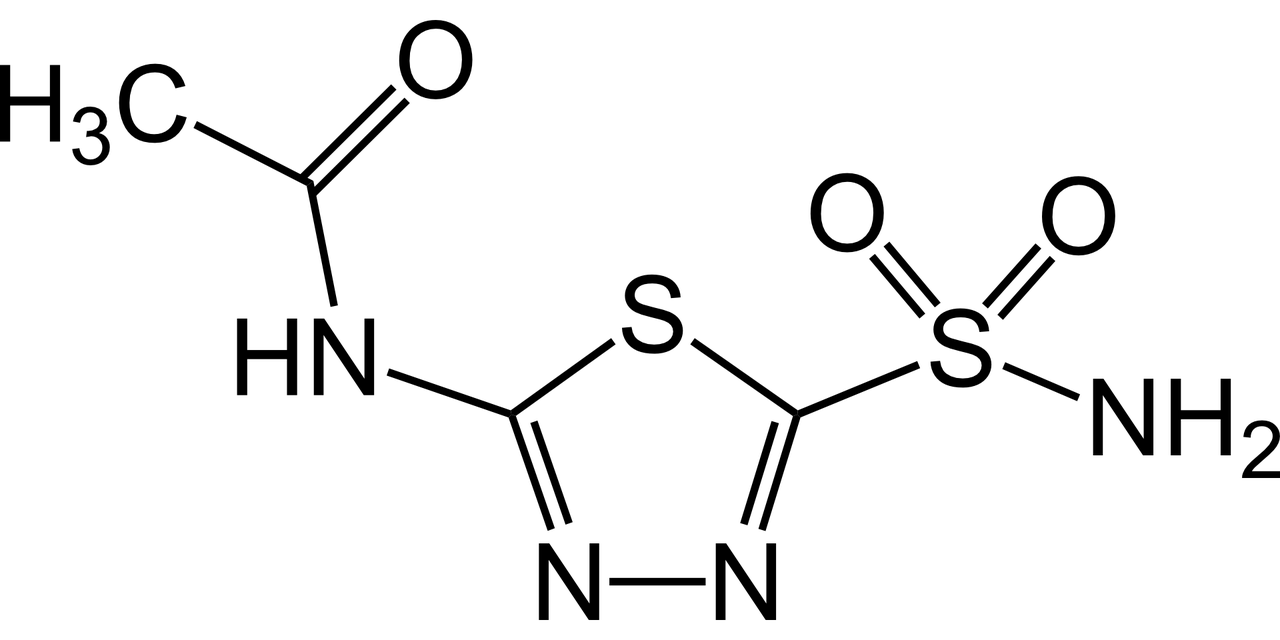
- What is the chemical structure of Acetazolamide?
- Does Acetazolamide cause acidosis?
- Is Acetazolamide available as an IV formulation?
- What are some nursing considerations when administering Acetazolamide?
- Where can I find the package insert for Acetazolamide?
- Does Acetazolamide cause hypokalemia?
- Is Acetazolamide used for high altitude?
- Can Acetazolamide cause headaches?
- What are the brand names for Acetazolamide?
- Does Acetazolamide affect bicarbonate levels?
- Is Acetazolamide a prescription medication?
- What class of medication is Acetazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide be used for metabolic alkalosis?
- What is the mechanism of action of Acetazolamide?
- What are some alternatives to Acetazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide cause tingling?
- Can Acetazolamide be used to prevent kidney stones?
- What are other names for Acetazolamide?
- How is Acetazolamide administered orally?
- Can Acetazolamide be used for increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
- How do patients review Acetazolamide?
- Is Acetazolamide used as a prophylaxis?
- What are the side effects of Acetazolamide ER 500 mg?
- What is the half-life of Acetazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide cause hyponatremia?
- Is Acetazolamide used for hydrocephalus?
- Where can one buy Acetazolamide?
- Can Acetazolamide be used for contraction alkalosis?
- Can Acetazolamide be used for vertigo?
- Can Acetazolamide be used during pregnancy?
- Is Acetazolamide available on UpToDate?
- What is the trade name for Acetazolamide?
- Does Acetazolamide have an effect on the kidneys?
- Is Acetazolamide used for intracranial hypertension?
- Is Acetazolamide safe for pediatric use?