Acetyl-l Carnitine
- Introduction to Acetyl-l Carnitine
- Uses of Acetyl-l Carnitine
- How Acetyl-l Carnitine Works
- Composition and Chemical Properties
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Storage and Handling of Acetyl-l Carnitine
- Side Effects of Acetyl-l Carnitine
- Interactions with Other Substances
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Acetyl-l Carnitine Use
Introduction to Acetyl-l Carnitine
Overview of Acetyl-l Carnitine (ALC)
Acetyl L-carnitine (ALC), a compound found naturally and extracted from the amino acid L-carnitine, is recognized for its function in generating energy by aiding in the transfer of fatty acids to mitochondria for conversion into energy sources. This crucial mechanism not only boosts stamina but also enhances cognitive abilities.
History and Development of ALC in Medicine
Discovered in the 1900s and found medical uses starting in the 1950s, ALC has been recognized for its ability to boost brain function and reduce cognitive decline associated with aging. Due to its various advantages and applications, it has now become widely used in both practices and alternative treatments.
Importance of ALC in Cellular Energy Production
ALCAR is essential for the functioning of mitochondria, the energy generators; it enhances the breakdown of fatty acids to produce ATP effectively. This ability makes it valuable in reducing fatigue levels and enhancing metabolism for a boost in well-being.
Key Benefits and Role in Overall Health
- Improves cognitive function and memory
- Reduces oxidative stress and inflammation
- Supports nerve regeneration and pain management
- Enhances physical endurance and recovery
Uses of Acetyl-l Carnitine
Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimerâs Disease
Acetyl-l-carnitine for neuropathy
Acetyl-l-carnitine helps ease nerve pain linked to diabetes and neuropathy caused by chemotherapy treatments by supporting the healing of nerves and lessening sensations, like tingling and burning, while also reducing numbness.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
Improving Male Fertility and Sperm Health
Off-Label Uses
Weight Loss and Metabolism Enhancement
L-carnitine is known to help break down fats in the body. It is often used as a supplement for managing weight. It increases energy usage, which can support long-term weight loss alongside a diet and regular exercise routine.

Acetyl-l-carnitine depression and Anxiety Disorders
Acetyl l carnitine adhd
Acetyl l carnitine bodybuilding
ALC enhances stamina by optimizing energy utilization. Speeds up muscle recovery after a workout to lessen pain and tiredness.
Anti-Aging and Skin Health Applications
Acetyl-l-carnitine sleep
Acetyl L carnitine supports brain function, boosts energy levels, and enhances immune health—all crucial factors for promoting longer and more restful sleep cycles.

Acetyl l carnitine fertility
Acetyl L carnitine possesses antioxidant qualities that are especially beneficial for women's fertility compared to LC alone. Combining both ALC and LC can assist in managing PCOS and endometriosis, as well as addressing amenorrhea (the absence of a menstrual period).
How Acetyl-l Carnitine Works
Mechanism of Action in Cellular Energy Metabolism
The process facilitated by ALC involves the movement of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, which is crucial for generating ATP, the body's energy source.
Effects on Brain Function and Neuroprotection
ALC enhances acetylcholine synthesis, a neurotransmitter vital for memory and learning. Its neuroprotective effects stem from reducing oxidative stress and supporting neural repair.
Role in Fatty Acid Oxidation
By enabling efficient fatty acid oxidation, ALC helps convert fat into usable energy. This process is crucial for metabolic health and endurance.
Influence on Neurotransmitter Regulation
ALC modulates key neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. This regulation contributes to its mood-enhancing and stress-reducing effects.
Composition and Chemical Properties
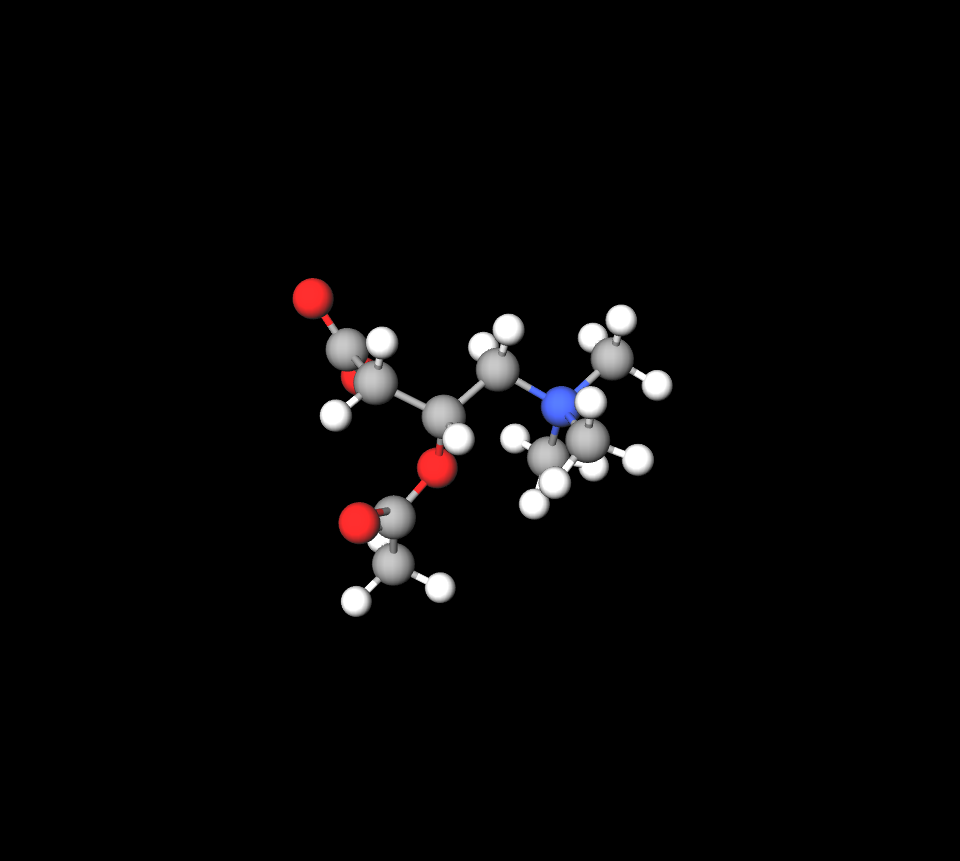
Chemical Structure of Acetyl-l Carnitine
ALC is an acetylated form of L-carnitine, making it more bioavailable. This structural modification allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively.
Forms and Preparations: Capsules, Tablets, and Liquid
ALCs are offered in forms such as capsules, tablets, and liquid solutions to meet consumers' varying preferences and requirements.
Key Ingredients in Commercial ALC Supplements
- Pure acetyl-l carnitine hydrochloride
- Stabilizers and fillers for tablet integrity
- Optional additives like B vitamins for enhanced efficacy
Acetyl l carnitine hcl
This nutritional supplement contains a type of L carnitine in its salt form. It has potential benefits for the brain, such as improving cognition and mood while also supporting the immune system.
Acetyl l carnitine alpha lipoic acid
Both acid and acetyl L carnitine have been shown to lower stress levels and enhance the functioning of mitochondria.
Acetyl l carnitine vs l carnitine
Though they have a source in commonality, both compounds differ in their effects; ALCs acetyl group boosts their ability to target the brain, while L carnitine mainly aids in energy and muscle performance.
Acetyl l carnitine vs nac
NAC is commonly utilized as a mucolytic to help loosen mucus. It is also used to treat paracetamol poisoning, while ALC has undergone trials for conditions related to aging and diabetes, like neurological disorders and neuropathy.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosage for Various Conditions
Typical dosages range from 500 mg to 2,000 mg daily, depending on the condition. Cognitive support often requires higher doses than metabolic uses.
Acetyl-l-carnitine nerve repair dosage
When individuals suffering from diabetes-related nerve pain consume 2 to 4 grams of acetyl L carnitine daily, they often experience alleviation of their symptoms.
Timing and Frequency of Administration
The effective way to consume ALC is to split the dosage into parts during the day, focusing on taking it in the morning and around midday to maximize its energy-enhancing benefits.
Best time to take acetyl l carnitine
It's best to take acetyl L carnitine in the morning on the stomach to ensure digestion and kickstart brain activity right away.
Guidelines for Adjusting Dosages
Responses, from individuals and their ability to tolerate a treatment influence the need for adjusting dosages. Start with a dose. Gradually increase it as necessary while seeking guidance from a healthcare professional.
Methods of Administration: Oral vs. Injectable
Oral forms are typically the choice; however, injectable ALC is utilized in clinical environments for specific treatments.
Storage and Handling of Acetyl-l Carnitine
Ideal Storage Conditions to Maintain Potency
Remember to keep your ALC supplements in an dry spot thats shielded from sunlight to prevent any deterioration due, to high temperatures or humidity.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Check the expiration dates on the packaging to ensure that the supplement is still effective and safe to use. Storing it correctly can help prolong its shelf life and keep the supplement strong and potent.
Proper Handling Instructions for Safety
Keep supplements tightly sealed and out of reach of children. Avoid contaminating the product with wet or dirty hands.
Side Effects of Acetyl-l Carnitine
Common Side Effects
- Nausea, vomiting, and mild gastrointestinal discomfort
- Headaches and light dizziness
- Restlessness or mild insomnia


Rare and Severe Side Effects
- Allergic reactions like rashes and swelling
- Heart palpitations or cardiovascular concerns
- Neurological symptoms such as confusion
Interactions with Other Substances
Potential Drug Interactions
Interactions, between ALC and anticoagulants can heighten the chances of bleeding occurrences. Exercise care when using it alongside thyroid hormones as it may lead to metabolic impacts.
Interactions with Dietary Supplements
By pairing ALC with antioxidants such as Coenzyme Q10 (Co Q10), you can enhance its advantages. However beware that combining may result in stimulation.
Alcohol and Lifestyle Considerations
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it may negate ALC's neuroprotective effects. Maintain a balanced lifestyle for optimal results.
Warnings and Precautions
Important Safety Warnings for Use
Acetyl L Carnitine is commonly considered safe; however it does come with some risks that should not be overlooked. It is crucial to follow expert advice to prevent any consequences. Specific groups may need monitoring as there could be reactions.

Conditions Requiring Special Attention
Diabetes Management
People who have diabetes should be careful when taking Acetyl L Carnitine as it could affect how their body processes glucose and may require monitoring of blood sugar levels to stay safe and healthy. It's important to talk to a healthcare professional, for guidance on managing any risks associated with this supplement.
Liver and Kidney Disorders
Individuals with liver or kidney issues should only take Acetyl L Carnitine under supervision as impaired organ function can affect how the compound is broken down and removed from the body and may result in potential buildup and harmful effects.
Avoidance in Specific Medical Scenarios
Avoid taking acetyll Carnitine supplements in situations involving infections or high blood pressure or when using medications that are not recommended together as its effects are not well researched in such scenarios and might worsen existing problems.
Contraindications for Acetyl-l Carnitine Use
Absolute Contraindications
Severe Allergies to Carnitine
If someone has a sensitivity, to carnitine or its derivatives that they're aware of shouldn't take Acetyl L Carnitine as it could lead to reactions like skin rashes or swelling and, in severe instances even anaphylaxis.
Acetyl-l Carnitine FAQ
- What is Acetyl-L-carnitine used for?
- Can Acetyl-L-carnitine repair nerve damage?
- Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe to take daily?
- Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe for liver?
- What are the negatives of Acetyl-L-carnitine?
- Can I take Acetyl-L-carnitine at night?
- Who needs Acetyl-L-carnitine?
- Is Acetyl-L-carnitine anti aging?
- Which is better, L-carnitine or Acetyl-L-carnitine?
- Does Acetyl-L-carnitine raise blood pressure?
- Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe for heart?
- Is Acetyl-L-carnitine good for eyes?
What is Acetyl-L-carnitine used for?
Acetyl L carnitine is occasionally utilized in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease to enhance memory and cognitive abilities and alleviate symptoms of depression to manage nerve pain in individuals with diabetes.
Can Acetyl-L-carnitine repair nerve damage?
ALCAR has demonstrated its effectiveness in protecting the system and promoting the regeneration of peripheral nerves.
Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe to take daily?
Acetyl L carnitine is recommended for maintaining brain health and function, with doses ranging from 500 to 3‚000 mg per day‚. In contrast, L carnitine L tartrate is more beneficial for enhancing exercise performance with doses between 1‚000 and 4‚500 mg, per day.
Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe for liver?
Supplementing with L Carnitine is advantageous for liver health.
What are the negatives of Acetyl-L-carnitine?
Diarrhea, nausea, stomach pain, and vomiting
Can I take Acetyl-L-carnitine at night?
Try a better night's rest with acetyl-l-carnitine
Who needs Acetyl-L-carnitine?
People with liver failure may experience impaired brain function known as encephalopathy (HE). The use of L-carnitine has shown the potential to enhance cognitive abilities in individuals dealing with HE caused by liver issues. Additionally, it could impact liver function by reducing levels in the blood.
Is Acetyl-L-carnitine anti aging?
Acetyl L carnitine, a form of the amino acid L carnitine, has demonstrated its ability to safeguard cells in the body from age-related deterioration.
Which is better, L-carnitine or Acetyl-L-carnitine?
If you focus on improving your performance and recovery time is essential, go with L-carnitine. Instead, pick Acetyl L-carnitine (ALGCM). However, if you prioritize alertness, well-being, and physical advantages, opt for ALC.
Does Acetyl-L-carnitine raise blood pressure?
Yes
Is Acetyl-L-carnitine safe for heart?
This could lead to reactions such as cardiac issues, seizures, and nausea.
Is Acetyl-L-carnitine good for eyes?
Patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) showed improvement in four aspects of function with the use of L carnitine: visual field means defect reduction and enhancement in visual acuity and sensitivity in the central part of the retina called the "fovea sensitivity" as well as changes in the structure at the back of the eye known as ocular fundus alterations.