Atropine
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Atropine
- III. How Atropine Works
- IV. Composition of Atropine
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Side Effects of Atropine
- VII. Interaction with Other Drugs and Substances
- VIII. Warnings and Precautions
- IX. Special Populations
- X. Overdosage and Management
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Historical Background of Atropine
Atropine, a known anticholinergic drug, originates from the belladonna plant. This plant has been used for centuries for its cosmetic properties. The term 'atropine' is derived from the plant's name, Atropa belladonna. This particular plant is well known for its qualities and historical use in traditional remedies.
Atropine: An Overview
Atropine, a compound, acts as a competitive antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. This vital interaction gives atropine its range of medical uses. It can be used as an agent to control salivary and bronchial secretions and as a life-saving antidote for specific poisonings.
Importance and Relevance in Modern Medicine
Atropine continues to play a role in today's medical field. It is a component in managing bradycardia, serving as a cornerstone treatment. Additionally, it is widely used in ophthalmology for purposes. Moreover, atropine is an antidote in cases of poisoning caused by organophosphates and specific types of mushrooms.
II. Uses of Atropine
a. Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Bradycardia
Atropine is commonly used to promptly address bradycardia, a condition characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate. Its mechanism involves obstructing the signals that influence the heart leading to an elevation in heart rate123.
1: Atropine - Wikipedia 2: CV Pharmacology | Atropine (Muscarinic Receptor Antagonist) 3: Atropine Induced Paradoxical Bradycardia | Epomedicine
Use as a Preoperative Medication
In environments, atropine is administered to decrease saliva, mucus, and throat secretions. It also prevents the slowing of the heart caused by the vagus nerve during the induction of anesthesia123.
1: Atropine - Wikipedia 2: Atropine injection Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com 3: Atropine (Injection) - Side Effects, Interactions, Uses, Dosage, Warnings
Treatment of Ophthalmic Conditions
Atropine sulfate ophthalmic solution is used to cause mydriasis, which refers to the pupil's dilation and cycloplegia, which involves the paralysis of the ciliary muscle in the eye. This is done to facilitate procedures12345.
1: Altropine sulfate, Statistical Review and Evaluation 2: 206289Orig1s000 - Food and Drug Administration 3: Atropine Ophthalmic Solution: Package Insert - Drugs.com 4: NDA 208151/S-003 Page 3 - Food and Drug Administration 5: Ophthalmic - Mydriatics & Cycloplegics - GlobalRPH
b. Off-label Uses
Management of Organophosphate Poisoning
In situations where there is poisoning, which leads to the inhibition of cholinesterase and causes continuous stimulation of muscarinic receptors, atropine can be a lifesaver. It works as a blocker for these receptors. Effectively counteracts the effects of excessive stimulation123.
1: Atropine - Wikipedia 2: Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Part 4 - Section 11 Management Strategy 3 … 3: Atropine: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
Reducing Saliva and Mucus Production
Atropine can also be used outside of the operating room to reduce saliva production linked to specific medical conditions123.
1: Atropine - Wikipedia 2: Safety and Efficacy of Atropine for Salivary Hypersecretion 3: Drooling: Definition & Causes - Cleveland Clinic
Other Emerging Off-label Applications
Recent studies have investigated the effectiveness of using atropine as a treatment for myopia in children. We are also exploring its potential for various other therapeutic uses123456.
1: Low-Dose Atropine for Kids with Myopia - American Academy of … 2: All about atropine | My Kids Vision 3: Atropine eye drops for myopia control in children 4: Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Atropine in Childhood Myopia 5: Efficacy and safety of atropine to control myopia progression: a … 6: How to Use Low-Dose Atropine to Slow Myopic Progression in Kids
III. How Atropine Works
Mechanism of Action
Atropine is an antagonist to the various types of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1, through M5). It attaches to these receptors. Effectively hinders the parasympathetic impact of acetylcholine.
Antagonist Effects on Muscarinic Receptors
Atropine works by attaching to receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. This action reduces the activities resulting in effects, like elevated heart rate and enlarged pupils.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Atropine is quickly and efficiently absorbed into the system. It can pass through the barriers of the brain and placenta because of its structure as a tertiary amine. In adults, the drug remains active for around 2 to 3 hours before it starts to break down.
IV. Composition of Atropine
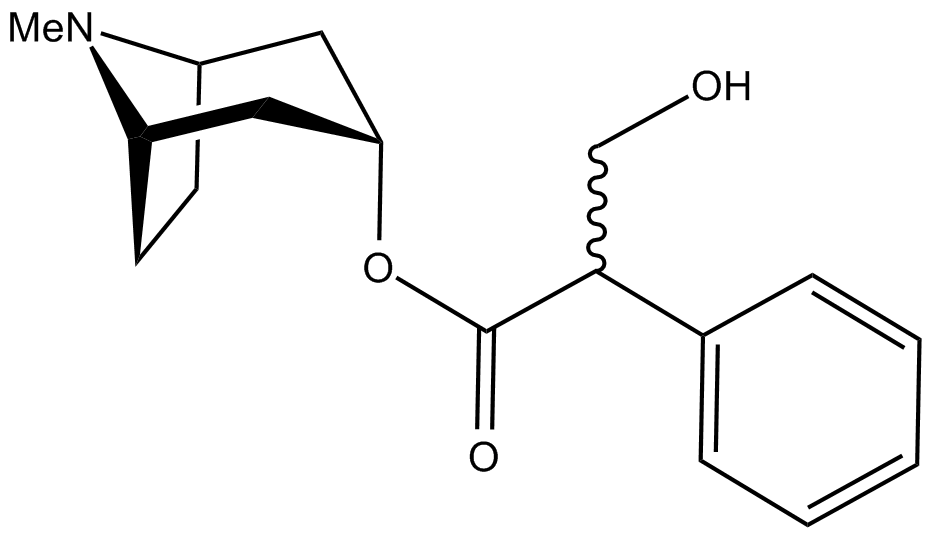
Chemical Structure
Atropine is a mixture that contains hyoscyamine as its component. Its chemical formula is C17H23NO3.
Available Formulations (Injectable, Ophthalmic, Oral)
Atropine comes in forms such as injectable solutions, eye drops, and oral preparations.
Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main component found in atropine preparations is atropine sulfate. Different formulations may contain inactive substances, such as sterile water, sodium chloride, and additional additives, for preservation or stability.
V. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages
Methods of Administration
Adjustments for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
VI. Side Effects of Atropine
Common Side Effects
- Dry Mouth
- Blurred Vision
- Sensitivity to Light
Serious Side Effects
- Tachycardia
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
Reporting Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Both patients and healthcare professionals must report any adverse reactions associated with atropine promptly. In the United States, this can be accomplished by utilizing the MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program provided by the FDA.
VII. Interaction with Other Drugs and Substances
Common Drug Interactions
Atropine is known to interact with medications. These interactions can. Increase or decrease the effects of atropine or the accompanying drug. There are some interactions to note, such as antihistamines, which may strengthen the anticholinergic effect. Additionally, antipsychotic medications could result in intraocular pressure or hyperthermia. Medicines that affect motility may also raise the risk of constipation.
Interactions with Food and Alcohol
The absorption of Atropine might be affected by types of food. For example, when there is food in the stomach, it could potentially delay the absorption process. It's important to note that consuming alcohol can intensify the effects on the central nervous system, which increases the risk when used together with Atropine.
Special Considerations for Polypharmacy Patients
When a patient takes medications, there is a higher risk of interactions, between them. It is essential to conduct a review of their medications focusing on avoiding unnecessary ones and closely monitoring for any unexpected interactions.
VIII. Warnings and Precautions
Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
There are situations where the use of atropine is strongly advised against. These include glaucoma, and narrow-angle glaucoma, as it can potentially increase pressure within the eyes. It is not recommended for individuals with uropathy, a condition that obstructs urine flow.
Relative Contraindications
It is essential to use atropine cautiously for a few reasons; 1. When dealing with patients suffering from myasthenia gravis as it could potentially worsen their condition. 2. In cases of obstructive disorders as it may increase the risks associated with reduced motility.
Important Precautions
Cardiovascular Risks
Using atropine may cause an increase in heart rate, potentially worsening conditions such as heart disease. It is crucial to monitor the heart rate in this situation.
Central Nervous System Effects
Higher amounts or heightened sensitivities can result in confusion or restlessness. Being aware of indicators and taking quick action is extremely important.
Careful Administration
Considering the impacts of atropine, it is crucial to carefully administer the correct dosage and choose the appropriate method of administration. When using injection, it is essential to avoid injecting too quickly as it could cause palpitations or other unfavorable reactions. It may also be necessary to adjust based on factors like renal function.
Monitoring Parameters and Follow-up
It is regularly keeping track of signs like heart rate, is crucial. Moreover, it can be advantageous to have eye exams and gastrointestinal evaluations.
IX. Special Populations
a. Administration to Elderly Patients
Dosage Adjustments
Elderly individuals might have decreased capacities, which could require starting with lower doses and carefully adjusting them based on how they respond to treatment.
Monitoring and Special Precautions
Elderly people may experience increased sensitivity to the side effects of medications, such as constipation, difficulty urinating, and cognitive impacts. It is essential to evaluate their condition and monitor for any potential changes.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Known Risks
While there is evidence of teratogenic effects in animal studies, the safety of atropine during human pregnancies is not well established. It should only be used if the potential benefits outweigh any risks.
Recommendations and Precautions
If a nursing mother is given atropine it is essential to monitor the baby for any side effects because atropine is excreted in breast milk.
c. Administration to Children
Age-specific Dosage Guidelines
Doctors often determine the dosage for children based on their body weight. It is crucial to ensure precise dosing to minimize the chances of any reactions.
Safety and Efficacy Profile
Children receiving treatment may display increased sensitivity to the dilation-inducing effects and may occasionally exhibit unexpected responses, such as heightened activity or restlessness.
X. Overdosage and Management
Signs and Symptoms of Atropine Overdose
Some possible signs could include having skin, experiencing blurry vision having a fever, a fast heartbeat, difficulty urinating, and even seeing things that aren't there.

Immediate Management Steps
For actions, it is essential to focus on managing the airway, administering activated charcoal, and providing symptomatic treatment. In severe situations, the use of physostigmine, an anticholinesterase agent, can be considered.
Long-term Consequences and Follow-up
It is crucial to monitor for any complications, such as irregular heartbeats or difficulty in breathing. After the delirium or agitation has subsided, it may be necessary to undergo an evaluation.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
Temperature
It is recommended to store Atropine at room temperature, avoiding any extreme temperature conditions.
Light
It's essential to store the medication in its packaging and protect it from direct sunlight.
Moisture
It is essential to keep Atropine in a place away, from any areas that are damp or humid.
Proper Disposal of Unused Atropine
You should consult with a healthcare professional. Follow local regulations to properly dispose of any atropine that is not being used or has expired.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
It is essential to take precautions like wearing gloves when dealing with atropine to avoid any accidental contact.
XII. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Atropine is a medication that works by blocking certain nerve signals in the body. It has a range of uses in medicine from being used as an antidote for poisonings to being an important tool in ophthalmology. However, it is essential to use this medication due to its potential, for causing side effects and interacting with other medications.
Current State of Knowledge and Future Research Directions
Although we understand atropine pharmacology and its applications, new research is now looking into its potential use for controlling myopia in children. It is crucial to keep exploring its range of effects and finding the best ways to utilize it effectively.
Patient Counseling and Education Highlights
It is crucial to inform patients about the side effects monitoring requirements and potential interactions of atropine. Making sure that patients understand how to take the medication and the importance of attending follow-up appointments can significantly improve the effectiveness of their treatment.