Azathioprine
- I. Introduction to Azathioprine
- II. Azathioprine: Composition and Pharmacology
- III. How Azathioprine Works: Mechanism of Action
- Authorized Uses of Azathioprine
- Off-Label Uses of Azathioprine
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Azathioprine
- VII. Special Considerations in Azathioprine Administration
- VIII. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions to Azathioprine
- IX. Interaction of Azathioprine with Other Substances
- X. Contraindications and Warnings for Azathioprine Use
- XI. Dealing with Overdosage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Conclusion: Balancing Efficacy and Safety in Azathioprine Use
I. Introduction to Azathioprine
1.1 Brief History and Development of Azathioprine
Azathioprine, found in the 1950s, was a significant advancement in immunosuppressive treatment. Initially developed as a medication for cancer, its ability to regulate the body's response was discovered by chance. This unexpected finding led to its groundbreaking application in organ transplantation and the management of diseases. Since then, this remarkable drug has become a component of treatment plans worldwide.
1.2 Azathioprine: Overview and Purpose
Azathioprine, a derivative of 6 mercaptopurine called imidazolyl, plays a role in various treatment approaches that aim to suppress the immune system. Its primary function is to prevent rejection of organs by reducing the immune response. Moreover, it assists in managing and controlling conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease. By regulating the body's response, Azathioprine helps maintain a balance where it prevents self-inflicted harm while preserving defense against foreign entities.
II. Azathioprine: Composition and Pharmacology
2.1 Chemical Composition and Properties of Azathioprine
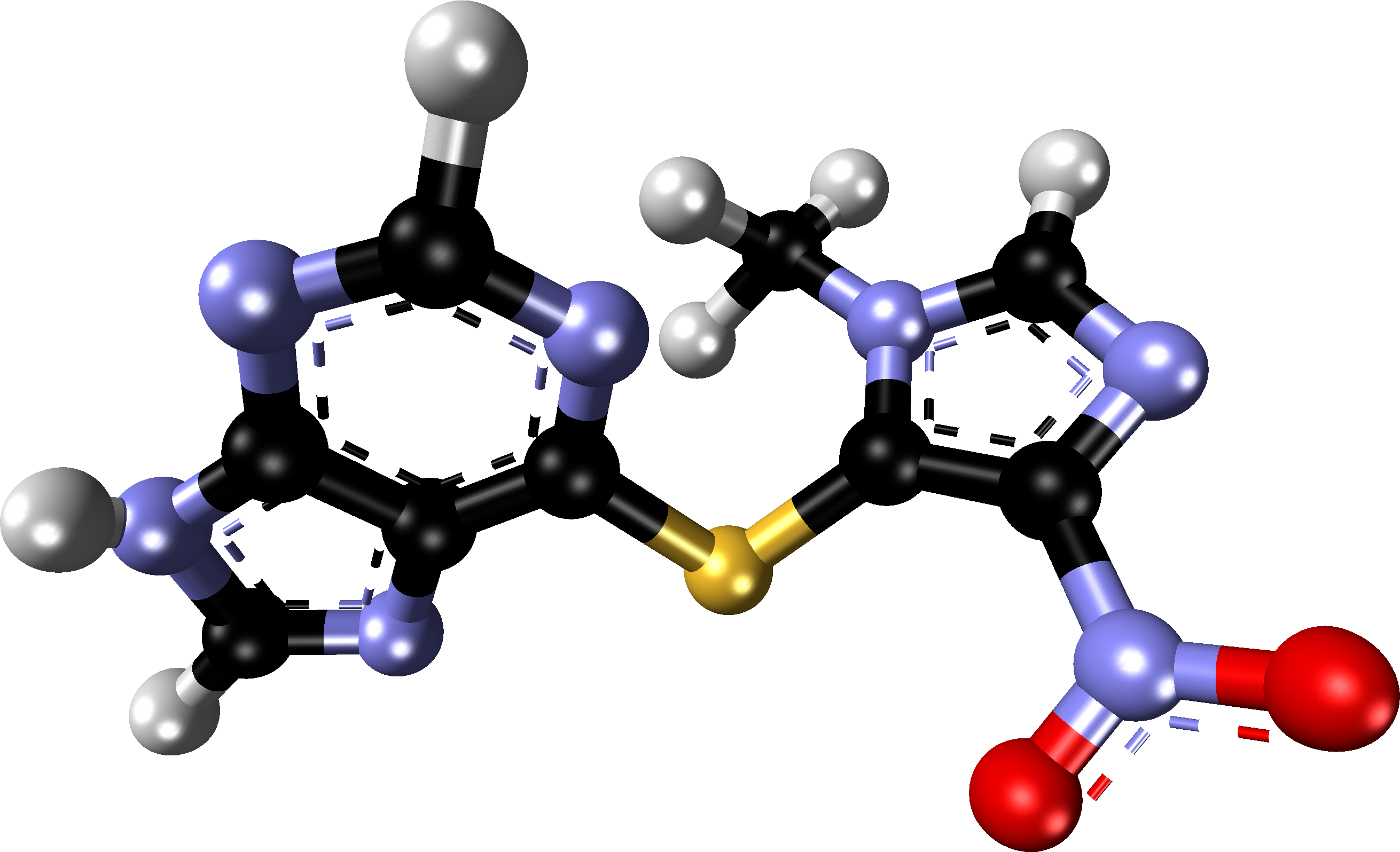
Azathioprine, chemically known as 6 [(1 methyl 4 nitro 1H imidazole 5 yl)thio] 1H purine, acts as a prodrug and a purine analog. Unlike being active, Azathioprine undergoes metabolism in the body to produce its active metabolites, mainly 6 mercaptopurine (6 MP). This particular metabolite goes through biochemical changes within the body and plays a crucial role in Azathioprine's ability to suppress the immune system.
2.2 Understanding the Pharmacokinetics of Azathioprine
Studying how the body interacts with Azathioprine, a compound, offers fascinating insights into its pharmacokinetics. When taken orally, Azathioprine is quickly—metabolized by the liver, blood and other tissues through the action of the enzyme glutathione resulting in the formation of 6 mercaptopurine. Subsequently, various metabolic pathways influence how 6 MP is processed in the body, including methylation, oxidation, and its incorporation into acids. Some important points to note about Azathioprines pharmacokinetics are as follows; It is rapidly absorbed after ingestion. Reaches its highest concentration in the bloodstream within 1 2 hours. The active metabolite 6 MP remains detectable in plasma for some time. The elimination half-life of Azathioprine may extend up to 10 hours. The drug and its metabolites are primarily eliminated from the body through kidney excretion.
III. How Azathioprine Works: Mechanism of Action
3.1 Azathioprine in the Human Body: Pharmacodynamics
Azathioprine, being a prodrug, functions using its metabolites. It hinders purine production, which's crucial for synthesizing DNA and RNA. Consequently, this impairs the growth and reproduction of cells within the immune system. Azathioprine and its metabolites possess an attraction towards rapidly dividing lymphocytes, disrupting their division and propagation. As a result, an overall immunosuppressive effect occurs.
3.2 Unpacking the Immunosuppressive Mechanism of Azathioprine
The primary way Azathioprine suppresses the immune system is through its metabolite, 6 mercaptopurine. It works by blocking enzymes in the production of purines, which are essential for DNA and RNA creation. This disruption slows down cell growth, specifically targeting dividing cells like those found in the immune system. Here's how it works; 6 MP imitates naturally occurring purines and becomes part of the DNA and RNA strands during their formation. This deceptive integration disrupts synthesis processes, leading to a halt in cell division. In particular, lymphocytes, which play a role in immune responses are affected, resulting in immunosuppression. By suppressing responses, this medication reduces the risk of organ rejection in transplant patients and helps manage overactive immune systems seen in autoimmune disorders.
Authorized Uses of Azathioprine
Role of Azathioprine in Autoimmune Diseases
Azathioprine is a medication that helps treat autoimmune diseases by suppressing the immune system. Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its healthy cells and tissues. Some common examples of these diseases include arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. Azathioprine is often used alongside medications like corticosteroids to provide a holistic approach to managing autoimmune conditions.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about azathioprine and its use in treating autoimmune diseases:
- Azathioprine: a medicine for conditions affecting the immune system - NHS
- Azathioprine - Wikipedia
- Association between - PLOS
Azathioprine in Organ Transplantation
Azathioprine is also utilized to safeguard against organ rejection in individuals who have undergone an organ transplant. When someone receives an organ, their immune system may perceive it as foreign and launch an attack. This can result in the rejection of the organ, necessitating another transplant. Azathioprine functions by suppressing the system, thereby preventing it from assaulting the transplanted organ. It is commonly employed alongside medications, such as corticosteroids and cyclosporine, to ensure a comprehensive approach, to preventing rejection of transplanted organs.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about azathioprine and its use in preventing organ rejection:
- Azathioprine Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
- Azathioprine - Transplant Living
- Azathioprine: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
Off-Label Uses of Azathioprine
Exploring Off-label Therapeutic Applications
Azathioprine is a drug that is commonly prescribed to treat various medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, and to prevent organ transplant rejection. However, there is increasing curiosity about alternative uses of azathioprine for other states. Off-label use refers to the practice of utilizing a medication for a purpose that it has not been officially approved for. It’s worth noting that while off-label use is both legal and widespread it should always be done under the supervision and guidance of a healthcare professional.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about azathioprine and its off-label uses:
- Azathioprine: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
- Azasan, Imuran (azathioprine) dosing, indications, interactions … - Medscape
Evidence-based Review of Azathioprine in Dermatology
Azathioprine has been studied to explore its advantages in treating various skin conditions. For instance,, research indicates it may offer benefits for managing psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Although further investigation is required to comprehend the potential benefits of azathioprine in dermatology,, initial findings show promise. It is essential to emphasize that azathioprine should only be utilized under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
- Azathioprine for Dermatologic Disease: A Review
- Azathioprine for the treatment of skin disease
- Azathioprine - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Azathioprine in the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Azathioprine is commonly prescribed for the treatment of bowel disease (IBD), including conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. IBD is a long-term condition that causes inflammation in the system resulting in symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea. Azathioprine works by suppressing the system, thereby reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. It is frequently used alongside medications, such as corticosteroids and biologics, to provide a holistic approach to treating IBD.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about azathioprine and its use in treating IBD:
- Azathioprine for inflammatory bowel disease
- Azathioprine - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Azathioprine (Imuran) - IBDrelief
VI. Dosage and Administration of Azathioprine
6.1 General Dosage Guidelines for Azathioprine
The dosage of Azathioprine depends on why it's being administered and the person's body weight. Typically it starts with doses and is increased gradually based on how well it works and how well the individual tolerates it. For example, in organ transplantation, the usual daily dose is 3 5mg/kg, while in rheumatoid arthritis, it usually begins at 1mg/kg per day. It's important to note that Azathioprine may take a week to fully show its therapeutic effects, so being patient and carefully monitoring its dosage adjustment phase is crucial.
6.2 Adjustments for Specific Patient Populations
Dosage adjustments are carefully considered for groups of patients. For instance, individuals with kidney problems may need doses because their bodies clear the drug more slowly. Similarly, patients with liver issues might require a reduction in dosage due to decreased metabolism. Some people have a variation that results in low levels of the TPMT enzyme, which plays a crucial role in Azathioprine metabolism. To prevent any effects, these individuals may need much smaller doses.
6.3 Best Practices for Safe and Effective Administration
To ensure safety and optimal results, it is recommended to take Azathioprine after meals in order to minimize any stomach discomfort. Regular monitoring of blood counts is crucial as there is a risk of bone marrow suppression. It's also essential to assess liver and kidney function. Additionally when administering Azathioprine alongside allopurinol caution should be exercised as the latter can significantly elevate Azathioprine levels thus necessitating dosage adjustment.
VII. Special Considerations in Azathioprine Administration
7.1 Administration to Elderly: Risks and Adjustments
As people age, their organs may not function well, impacting how Azathioprine is processed and eliminated from the body. Older individuals may also be more sensitive to the effects of this medication. Therefore it's essential to monitor blood counts and organ function, and starting with a lower dose might be advisable.
7.2 Safety Profile of Azathioprine in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Azathioprine can pass through the placenta and can also be present in breast milk. It is essential to exercise caution. When it comes to using Azathioprine during pregnancy, healthcare professionals need to weigh the potential risks and benefits of a mother who is breastfeeding needs to take Azathioprine. The decision regarding whether to continue nursing or stop taking the medication should consider how vital the drug is, for the mothers well being.
7.3 Pediatric Use of Azathioprine: Efficacy and Safety
Azathioprine can be prescribed to children for organ transplantation and specific autoimmune disorders. However, it is essential to ensure that professionals closely supervise the administration. It is crucial to select the dosage as there is a potential for adverse reactions associated with the dose. Regular monitoring of blood counts and thorough evaluation of growth parameters are vital aspects that need to be considered.
VIII. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions to Azathioprine
8.1 Understanding Common Side Effects of Azathioprine
Azathioprine is usually well tolerated, although it can have some effects. Some of the ones are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (feeling nauseous, vomiting experiencing abdominal pain), skin rash, and increased liver enzymes. Although less frequent, there are severe side effects, such as pancreatitis, a significant reduction in bone marrow function resulting in anemia susceptibility to infections or bleeding, and the potential development of malignancies like skin cancer or lymphoma.
8.2 Recognizing Serious Adverse Reactions: A Comprehensive Overview
Azathioprine has been linked to a few side effects. It can cause myelosuppression, leading to white blood cell count, anemia, or low platelet count. This is why regular blood count monitoring is necessary. However, rare acute pancreatitis is a reaction that requires immediate discontinuation of Azathioprine. Additionally, using Azathioprine for a time may increase the risk of developing malignancies. Therefore doctors should be highly vigilant when monitoring patients on long-term Azathioprine therapy.
IX. Interaction of Azathioprine with Other Substances
9.1 Azathioprine and Drug Interactions: What Clinicians Need to Know
The effectiveness and how the body processes Azathioprine can be affected by taking medications simultaneously. For example, Allopurinol, used to treat gout, blocks an enzyme that plays a role in Azathioprine metabolism. This could potentially result in possibly harmful levels of Azathioprine in the body. Warfarin, a medication, may have its effects intensified when taken with Azathioprine. Additionally, drugs like ACE inhibitors that can cause bone marrow suppression may worsen this side effect when used with Azathioprine. Therefore, understanding your medication history when undergoing Azathioprine therapy is crucial to prevent any potential drug interactions.
9.2 Impact of Food and Lifestyle on Azathioprine Efficacy
The consumption of food does not affect the absorption of Azathioprine. However, to minimize any stomach discomfort, taking Azathioprine with a meal is recommended. Limiting sun exposure when using Azathioprine is essential as it can increase the risk of skin malignancies. It is advisable to consume alcohol since it can enhance the liver toxicity associated with Azathioprine.
X. Contraindications and Warnings for Azathioprine Use
10.1 Identifying Contraindications to Azathioprine Therapy
Before starting Azathioprine therapy it is crucial to identify any conditions that would make its use unsuitable. These include having a hypersensitivity to Azathioprine or any of its components being pregnant (unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks) breastfeeding, suffering from liver or kidney problems and experiencing significant suppression of bone marrow function. If you have previously been treated with alkylating agents like cyclophosphamide or chlorambucil it may not be advisable to use Azathioprine due, to the increased risk of developing malignancies.
10.2 Crucial Warnings and Precautions for Azathioprine Use
When using Azathioprine, it's essential to take precautions. It is necessary to monitor blood counts to watch out for potential myelosuppression. Patients should be informed to report any signs of infection, uncommon bleeding or bruising, or other indications of bone marrow suppression. Regular liver function tests are also essential as there is a risk of liver toxicity. Additionally, healthcare providers must remain attentive for signs of malignancies, specifically skin cancer and lymphoma.
XI. Dealing with Overdosage and Handling Precautions
11.1 Azathioprine Overdosage: Symptoms, Management and Prevention
An excessive amount of Azathioprine can have impacts, such as suppressing bone marrow function, damaging the liver, and causing gastrointestinal problems. If someone overdoses on Azathioprine, they may experience symptoms like increased vulnerability to infections, bruising or bleeding, feelings of nausea, and yellowing of the skin (jaundice). In such a situation, it is crucial to discontinue the use of Azathioprine and initiate supportive measures. It is also essential to monitor blood counts and watch for signs of infection in patients. To prevent an overdose, patients should receive counseling on the correct dosage and understand the importance of adhering to it.
11.2 Handling and Storage Precautions for Azathioprine
Azathioprine should be stored in a dry place away from direct sunlight. It is essential to keep it out of the reach of children and pets. Pregnant women should avoid handling crushed or broken tablets due to the risks associated with their properties. If there is any contact with the skin or eyes, make sure to wash them with water. In case of swallowing or inhaling it is advisable to seek medical attention.
XII. Conclusion: Balancing Efficacy and Safety in Azathioprine Use
12.1 The Importance of Informed Use of Azathioprine
Therapy involving Azathioprine can be beneficial. It's essential to consider the potential side effects and interactions. To maintain an effective treatment, it is crucial to regularly check blood counts and organ function, follow dosage guidelines, and understand how this drug interacts with other medications or lifestyle factors. Adequate counseling of patients is essential to help them understand the risks and benefits of Azathioprine, the importance of sticking to prescribed dosages and schedules, and the need for regular follow-up appointments to monitor their progress.
12.2 Future Research Directions in Azathioprine Therapy
Azathioprine has been a used immunosuppressant for many years, but there is still much more to discover about its potential applications and the best way to administer it. Future research will likely focus on Azathioprine therapy, investigating how genetic variations can impact its metabolism and effectiveness. Additionally, there will be efforts to explore therapeutic uses, refine dosing guidelines and develop strategies to reduce adverse side effects. The ultimate aim is to maximize the benefits of Azathioprine treatment while minimizing any risks in order to improve patient outcomes and enhance their quality of life.
Azathioprine FAQ
- Azathioprine side effects?
- Azathioprine uses?
- Azathioprine brand name?
- Azathioprine mechanism of action?
- Azathioprine 50 mg?
- Azathioprine dog, Azathioprine in dogs, Azathioprine for dogs?
- Azathioprine pronunciation?
- Azathioprine drug class?
- Azathioprine tab 50mg?
- Azathioprine toxicity symptoms?
- Azathioprine warnings?
- Azathioprine Imuran?
- Azathioprine cost?
- Azathioprine dosage, Azathioprine dose?
- Azathioprine for Crohn's, Azathioprine Crohn's?
- Azathioprine pregnancy, Azathioprine in pregnancy?
- Azathioprine for ulcerative colitis, Azathioprine ulcerative colitis?
- Azathioprine lupus, Azathioprine for lupus?
- Azathioprine and allopurinol?
- Azathioprine long term side effects?
- Azathioprine interactions?
- Azathioprine for myasthenia gravis, Azathioprine myasthenia gravis?
- Azathioprine side effects in dogs?
- Azathioprine tpmt?
- Azathioprine class?
- Azathioprine for autoimmune hepatitis?
- Azathioprine side effects eyes?
- Azathioprine side effects eyes?
- Azathioprine generic name?
- Azathioprine metabolism?
- Azathioprine metabolites?
- Azathioprine autoimmune hepatitis?
- Azathioprine adverse effects?
- Can Azathioprine affect your teeth?
- Azathioprine and pregnancy?
- Azathioprine and alcohol?
- Azathioprine tablets?
- Azathioprine immunosuppression?
- Azathioprine contraindications?
- Azathioprine classification?
- Azathioprine medication?
- Azathioprine hair loss?
- Azathioprine Crohn's disease?
- Azathioprine GoodRx?
- Azathioprine for rheumatoid arthritis, Azathioprine rheumatoid arthritis?
- Azathioprine price?
- Is Azathioprine an immunosuppressant?
- Azathioprine package insert?
- Azathioprine pancreatitis?
- Azathioprine reviews?
- Azathioprine weight gain?
- Azathioprine indications?
- Azathioprine mechanism?
- Azathioprine for sarcoidosis, Azathioprine sarcoidosis?
- Azathioprine vs Methotrexate?
- Azathioprine side effects eyes?
- Azathioprine generic name?
- Azathioprine metabolism?
- Azathioprine metabolites?
- Azathioprine autoimmune hepatitis?
- Azathioprine adverse effects?
- Can Azathioprine affect your teeth?
- Azathioprine and pregnancy?
- Azathioprine and alcohol?
- Azathioprine tablets?
- Azathioprine immunosuppression?
- Azathioprine contraindications?
- Azathioprine classification?
- Azathioprine medication?
- Azathioprine hair loss?
- Azathioprine Crohn's disease?
- Azathioprine GoodRx?
- Azathioprine for rheumatoid arthritis, Azathioprine rheumatoid arthritis?
- Azathioprine price?
- Is Azathioprine an immunosuppressant?
- Azathioprine package insert?
- Azathioprine pancreatitis?
- Azathioprine reviews?
- Azathioprine weight gain?
- Azathioprine indications?
- Azathioprine mechanism?
- Azathioprine for sarcoidosis, Azathioprine sarcoidosis?
- Azathioprine vs Methotrexate?
- Azathioprine toxicity?
- Azathioprine pill?
- Azathioprine rash?
- Azathioprine drug interactions?
- Azathioprine fatigue?
- Azathioprine cats?
- Azathioprine monitoring?
- Azathioprine half life?
- Azathioprine cost without insurance?
- Is Azathioprine a DMARD?
- Azathioprine vs Mycophenolate?
- Azathioprine skin cancer?
- Azathioprine liver?
- Azathioprine withdrawal symptoms?
- Azathioprine brand?
- Azathioprine nursing considerations?
- Azathioprine for eczema?
- Azathioprine eczema?
- What is Azathioprine used for in dogs?
- Azathioprine alternatives?
- Is Azathioprine a biologic?
- Azathioprine vs 6MP?
- Azathioprine vs Mercaptopurine?
- Azathioprine vs Cellcept?
- Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine?
- Azathioprine and breastfeeding?
- Azathioprine and prednisone?
- Azathioprine side effects liver?
- Azathioprine structure?
- Azathioprine side effects weight gain?
- Azathioprine liver toxicity?
- Azathioprine lymphoma?
- Azathioprine leukopenia?
- Azathioprine liver side effects?
- Azathioprine withdrawal?
- Azathioprine generic?
- Azathioprine DMARD?
- Azathioprine drugs?
- Azathioprine breastfeeding?
- Azathioprine blood test monitoring?
- Azathioprine cancer?
- Azathioprine cancer risk?
- Azathioprine anemia?
- Azathioprine for MS?
- Azathioprine and myasthenia gravis?
- Azathioprine ulcerative colitis reviews?
- Azathioprine for psoriasis?
- Azathioprine and lupus?
- Azathioprine for dogs cost?
- Azathioprine copay assistance?
- Azathioprine cost USA?
- What is Azathioprine 50 mg used for?
- Azathioprine for RA?
- Can Azathioprine cause skin problems?
- Can Azathioprine cause liver damage?
- Can Azathioprine cause high blood pressure?
- Azathioprine vs prednisone?
- Azathioprine vs cyclosporine in dogs?
- Azathioprine and skin cancer?
- Azathioprine and Remicade?
- Azathioprine and sun exposure?
- Azathioprine and hair loss?
- Azathioprine side effects kidney?
- Azathioprine sodium?
- Azathioprine skin rash?
- Azathioprine trade name?
- Azathioprine thrombocytopenia?
- Azathioprine vasculitis?
- Azathioprine renal toxicity?
- Azathioprine weight loss?
- Azathioprine gout?
- Azathioprine during pregnancy?
- Azathioprine bone marrow suppression?
- Azathioprine multiple sclerosis?
- Azathioprine overdose?
- Azathioprine hypersensitivity syndrome?
- Azathioprine headache?
- Azathioprine action?
- Azathioprine used for Crohn's disease?
- Can Azathioprine cause weight gain?
- Can Azathioprine cause depression?
- Can Azathioprine cause cancer?
- Can Azathioprine cause pancreatitis?
- Can Azathioprine cause anemia?