Caffeine Citrate
- Introduction to Caffeine Citrate
- Uses of Caffeine Citrate
- Composition of Caffeine Citrate
- How Caffeine Citrate Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Caffeine Citrate
- Precautions and Warnings
- Contraindications
- Drug Interactions with Caffeine Citrate
- Overdose and Handling Precautions
- Storage of Caffeine Citrate
- Administration Considerations
Introduction to Caffeine Citrate
Overview of Caffeine Citrate
Caffeine Citrate is a known drug that's highly effective in treating neonatal apnea conditions in premature babies who have underdeveloped respiratory systems. Intended to stimulate the system and respiratory centers this compound has been widely used in neonatal care facilities globally as a critical intervention for these vulnerable infants.
Historical Development and Medical Applications
Caffeine Citrate has a history dating back to when it was discovered as a stimulant in the 1800s and later recognized for its potential medical advantages in neonatology research during the late 20th century for treating premature infant apnea and gaining FDA recognition as an essential treatment method.
Key Features of Caffeine Citrate
- Highly bioavailable formulation ensuring rapid absorption.
- Dual action stimulates respiratory drive and enhances alertness.
- Proven safety profile with minimal side effects in neonates.
Uses of Caffeine Citrate
Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Apnea of Prematurity in Neonates
Apnea of prematurity is a condition characterized by intermittent cessation of breathing in preterm infants. Caffeine Citrate is the first-line treatment for this condition, effectively reducing the frequency and severity of apnea episodes.
Stimulation of Central Nervous System in Specific Conditions
Off-Label Uses of Caffeine Citrate
Treatment of Post-Dural Puncture Headache
Management of Neonatal Respiratory Depression
Sometimes, this medication is used in a way to help babies with breathing problems caused by sedatives.
Other Emerging Applications
Ongoing studies are looking into how research could be used to help with lung diseases and as a treatment for certain neurological disorders.
Composition of Caffeine Citrate
Active Ingredients and Their Functions
Caffeine is the element that works as a stimulant for the nervous system by blocking adenosine receptors and boosting alertness and respiratory functions.
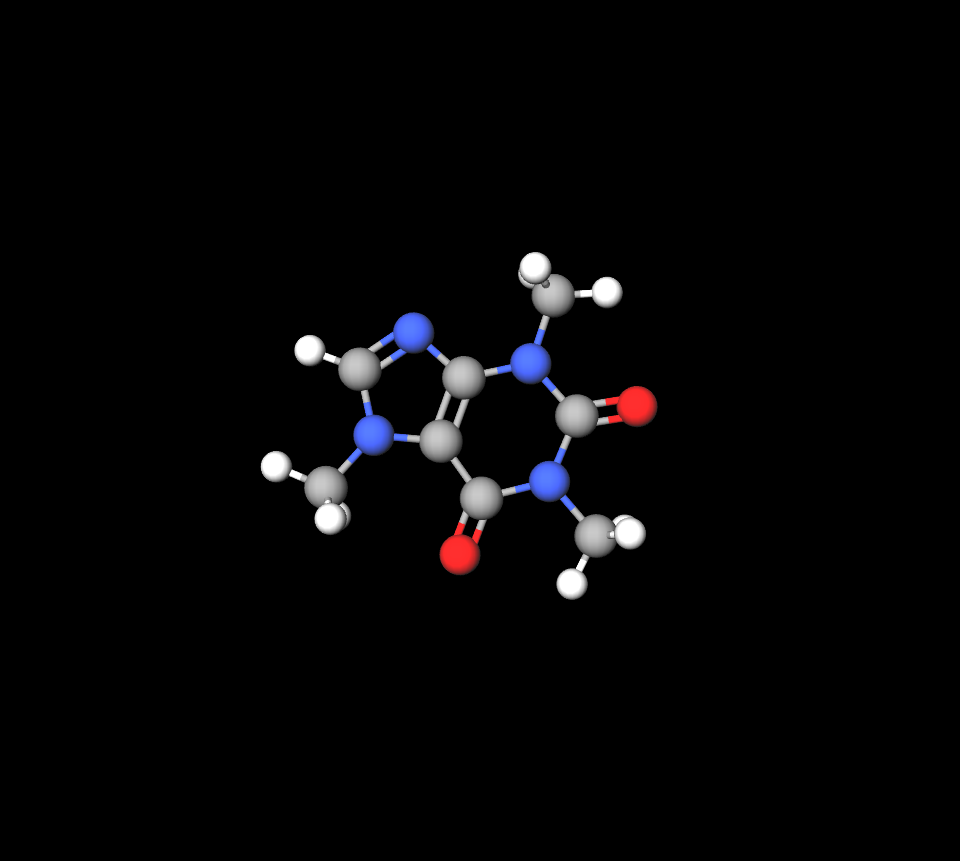
Inactive Ingredients and Their Roles
The additional substances included in the formula, like citric acid and sodium citrate, play a role in maintaining the stability and solubility of the product, which helps to extend its shelf life and improve how well it is absorbed by the body.
Caffeine citrate vs anhydrous
While caffeine citrate works quickly, caffeine anhydrous doesn't provide much active caffeine. The 20Mg of caffeine citrate yields only 10mg of active caffeine. In other words when compared gram, for gram caffeine citrate offers 50 % caffeine than caffeine anhydrous.
How Caffeine Citrate Works
Mechanism of Action
The way Caffeine Citrate works is by blocking adenosine receptors that control activity in the brain and body system. This blockage increases the release of neurotransmitters and boosts both respiratory function and central nervous system activity.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
- Absorption: Rapidly absorbed following oral or intravenous administration.
- Distribution: Widely distributed across body tissues, including the central nervous system.
- Metabolism: Primarily metabolized in the liver to active and inactive metabolites.
- Excretion: Excreted via urine, with a prolonged half-life in neonates due to immature liver enzymes.
Impact on Central Nervous System and Respiratory System
Activating the breathing control centers in the brainstem area of the body through its interaction with Caffeine Citrate facilitates improved breathing rhythms for neonates while also boosting alertness and decreasing instances of apnea episodes in newborns.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Neonates
In newborns, the initial dose is typically 20 mg per kilogram of body weight, and then a daily maintenance dose of 5 to 10 mg per kilogram is given to keep the medication at levels without causing harm.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Infants with liver or kidney issues may need their dosage adjusted to avoid buildup and potential side effects.
Methods of Administration (Oral and Intravenous)
- Oral: Preferred for stable neonates with intact gastrointestinal function.
- Intravenous: Utilized in critically ill neonates or those unable to tolerate oral administration.
Side Effects of Caffeine Citrate
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Sleep Disturbances
Trouble sleeping or disrupting your sleep may happen because of its effects.
Increased Heart Rate
An occasional rise in heartbeat is a generally harmless occurrence.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Seizures
Precautions and Warnings
Important Precautions Before Use
Before starting treatment with Caffeine Citrate, it is important to be cautious to guarantee both safety and effectiveness. It is necessary to assess a patient's medical history, including any existing medical conditions, current medications being taken, and any possible allergies. The drugs impact on the system requires close observation especially in newborns, with organs that are not fully developed.

Warnings for Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
While mainly utilized in newborns or infants, circumstances may need to be taken into account when giving it to people. Aging-related changes in liver and kidney function can affect how medications are processed and removed from the body, possibly resulting in buildup. Regular blood level checks are advised.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Caffeine Citrate is typically not recommended for women unless the advantages are greater than the disadvantages since it can affect development by crossing the placenta barrier. Breastfeeding mothers should also take care because caffeine can be transferred to breast milk and could possibly disrupt the baby's sleep patterns and behavior.

Administration to Children
For newborns, older kids with certain conditions might need custom doses of medication. In the course of treatment it's crucial to monitor their growth metrics and neurological progress.
Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Patients who are sensitive to caffeine or any of the ingredients in Caffeine Citrate should avoid using it as individuals with severe liver problems or serious heart rhythm issues.
Conditions Requiring Careful Administration
- Renal impairment, where dose adjustments may be necessary to prevent accumulation.
- Gastrointestinal ulcers or bleeding, as caffeine, can exacerbate symptoms.
- Seizure disorders, given the potential for increased excitability of the nervous system.
Drug Interactions with Caffeine Citrate
Interaction with Other Medications
Numerous medications can interact with Caffeine Citrate; this includes drugs metabolized by the P450 enzyme system, like theophylline and some antidepressants, which might enhance its effects and raise the chances of experiencing side effects.
Food and Beverage Interactions
Consuming caffeine foods and drinks, at the time can enhance its stimulating effects and cause jitters and a higher heart rate to occur more prominently. Additionally, meals high in fat might affect how quickly the body absorbs the medication.
Potential Impact of Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements, such as ginseng and guarana, are recognized for their stimulating effects. May interact with Caffeine Citrate in a way that could potentially lead to stimulation and add complexity to its pharmacological characteristics.
Overdose and Handling Precautions
Symptoms of Caffeine Citrate Overdose
Signs of an overdose may show up as feeling uneasy and nauseous with a heartbeat; in serious instances, seizures could occur, too. Newborn babies might seem fussy, than usual. Have irregular heartbeats that need urgent medical care.
Immediate Steps to Address Overdose
- Discontinuation of Caffeine Citrate therapy.
- Administration of activated charcoal to limit absorption in cases of oral overdose.
- Supportive care, including hydration and symptomatic management of cardiac and neurological effects.
Guidelines for Safe Handling and Disposal
Be cautious when handling Caffeine Citrate to avoid contamination and unintended exposure. Like Dispose of any expired medication, in accordance, with local biomedical waste disposal regulations to reduce environmental hazards.
Storage of Caffeine Citrate
Recommended Storage Conditions
Make sure to store Caffeine Citrate at room temperature and away from sunlight and moisture to maintain its effectiveness properly stored away from children's reach to avoid consumption.
Stability and Shelf Life
Storing Caffeine Citrate correctly is important, for maintaining its quality over time. Any alterations, in color or texture could signal spoilage. It's best to dispose of items right away.
Safety Precautions for Storage
- Store in a secure location, preferably in a locked cabinet.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, which can affect potency.
- Ensure the storage container is tightly sealed to prevent contamination.
Administration Considerations
Monitoring During Treatment
Regularly checking blood levels and respiratory and neurological functions is crucial when administering Caffeine Citrate therapy.It's important to make dosage adjustments based on the patients progress and test results.
Adjustments for Comorbid Conditions
Patients with comorbid conditions such as renal or hepatic impairment require individualized dosing regimens. Collaboration between neonatologists, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals is essential to optimize outcomes.
Strategies to Minimize Side Effects
- Start with the lowest effective dose and titrate based on clinical response.
- Ensure adequate hydration to mitigate gastrointestinal side effects.
- Avoid concomitant stimulants to reduce the risk of overstimulation and insomnia.
Caffeine Citrate FAQ
- What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
- How to give IV caffeine citrate?
- What class of drug is caffeine citrate?
- What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
- How much caffeine citrate is safe?
- When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
- What is the action of caffeine citrate?
- What is the function of caffeine citrate?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
- How do you make caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
- How much caffeine is in caffeine citrate?
- Does caffeine citrate need to be refrigerated?
- What does caffeine citrate taste like?
- Does caffeine citrate cause tachycardia?
- How to dilute caffeine citrate?
- What is the half life of caffeine citrate?
- What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
- How to give IV caffeine citrate?
- What class of drug is caffeine citrate?
- What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
- How much caffeine citrate is safe?
- When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
- What is the action of caffeine citrate?
- What is the function of caffeine citrate?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
- How do you make caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
- Does caffeine citrate cause tachycardia?
- What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
- How to give IV caffeine citrate?
- What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
- How much caffeine citrate is safe?
- When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
- What is the action of caffeine citrate?
- What is the function of caffeine citrate?
- What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
- How do you make caffeine citrate?
- Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate doses are typically higher than those of caffeine base because of the weight of the citrate component.
How to give IV caffeine citrate?
An initial dose of caffeine citrate, at 20mg/kg, is administered intravenously, followed by a maintenance dose of 10mg/kg after 24 hours.
What class of drug is caffeine citrate?
Methylxanthine class
What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
The caffeine citrate oral solution is a colorless medication used to address prematurity apnea episodes when premature infants have difficulty breathing.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
Injecting caffeine citrate is a practice that helps babies (those born between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age) who experience temporary pauses in breathing, often referred to as apnea of prematurity.
What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
Nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, headache, trouble sleeping, restlessness, poor feeding, increased urination, rash or dry skin may occur.
How much caffeine citrate is safe?
Reports have mentioned doses of caffeine citrate, up to 80 mg/kg ( to 40 mg/kg of caffeine base) administered intravenously or orally.
When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
Stop giving the baby caffeine after they reach 35 weeks of age unless they are still experiencing apnea episodes.
What is the action of caffeine citrate?
Coffee also interacts with calcium channels, causing the release of calcium from within cells. It has the potential to hinder the function of voltage calcium channels, which could impact neural communication.
What is the function of caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate has long been a go-to option for treating and preventing apnea in babies ever since it was first approved.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
The injection of caffeine citrate is administered to address apnea in infants born between 28 and 32 weeks gestational age when they experience breathing pauses.
Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
It is possible to find it in coffee beans; however, it also exists naturally in types of teas and cacao beans that's distinct from coffee beans.
How do you make caffeine citrate?
It is obtained by combining caffeine with citric acid.
Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
It acts as a brain stimulant that boosts the body's breathing control system by making the respiratory centers in the brain more responsive to carbon dioxide and enhancing the strength of diaphragm muscles.
How much caffeine is in caffeine citrate?
20 mg/mL
Does caffeine citrate need to be refrigerated?
It is safe to store the caffeine solution either at room temperature or in the refrigerator within the reach of children.
What does caffeine citrate taste like?
Bitter
Does caffeine citrate cause tachycardia?
The caffeine citrate also has impacts on the heart and blood pressure, leading to a rise in heart rate (known as tachycardia) as an increase in blood pressure levels.
How to dilute caffeine citrate?
Diluted in sterile solutions
What is the half life of caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate’s half-life is 100 hours when a baby is born. Decreases to 5 hours when the gestational age is over 29 weeks.
What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
The amount of caffeine citrate needed is higher compared to the caffeine base because of the weight of the citrate component.
How to give IV caffeine citrate?
An initial injection of 20mg/kg of caffeine citrate is administered once. This is followed by a maintenance dose of 10mg/kg given after 24 hours.
What class of drug is caffeine citrate?
Methylxanthine class
What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
The oral solution of caffeine citrate is a colorless medication used to address apnea of prematurity – intervals when premature infants pause breathing.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
The purpose of administering caffeine citrate through injection is to address apnea in infants who are born between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age when they experience breathing pauses.
What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
Some people may experience nausea and vomiting or have a stomach after taking this medication; others may also have headaches or difficulty sleeping. You might feel restless or have trouble eating properly.
How much caffeine citrate is safe?
Caffeine citrate doses of up to 80 mg/kg (equivalent to 40 mg/kg of caffeine when given intravenously or orally have been documented.
When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
It is recommended to discontinue caffeine intake at 35 weeks PMA unless the baby is still experiencing apnea issues.
What is the action of caffeine citrate?
Coffee also interacts with calcium channels by binding to them and releasing calcium from within cells, which can help regulate processes in the body like neurotransmission.
What is the function of caffeine citrate?
Since its approval, caffeine citrate has been widely used in the treatment and prevention of apnea in infants.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate is administered to help manage breathing pauses in babies born between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age, known as apnea of prematurity.
Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
It can be found in coffee beans in different types of teas, and in cacao beans that are distinct from coffee beans.
How do you make caffeine citrate?
Mixing caffeine with citric acid can create it.
Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
It acts as a brain booster that enhances the body's breathing control system by making the respiratory centers in the brain more responsive to carbon dioxide and enhancing the strength of the diaphragm muscle.
Does caffeine citrate cause tachycardia?
Additionally caffeine citrate may impact the system by raising heart rate (known as tachycardia) and blood pressure as well.
What is the difference between caffeine and caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate doses are typically higher, than caffeine base doses because of the weight of the citrate component.
How to give IV caffeine citrate?
An initial infusion of caffeine citrate, at a dosage of 20mg/kg is administered once through the veins. Subsequently, after 24 hours, a daily maintenance dose of 10mg/kg is given intravenously.
What is caffeine citrate oral solution used for?
The caffeine citrate oral solution is an colorless medication used to address apnea of prematurity – episodes when premature infants experience breathing pauses.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
In treating apnea in babies, caffeine citrate injection is employed when infants between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age experience breathing cessation.
What are the side effects of caffeine citrate?
You might experience nausea or vomiting along with stomach discomfort and headaches; sleeping difficulties and restlessness may also happen as changes in appetite and increased urination; skin rash or dryness are also potential effects to be aware of.
How much caffeine citrate is safe?
Dosages of caffeine citrate, up to 80 mg/kg (to 40 mg/kg of caffeine base), administered intravenously or orally have been documented.
When should I stop taking caffeine citrate?
It is recommended that caffeine intake be discontinued at 35 weeks of age unless the infant continues to experience apnea episodes.
What is the action of caffeine citrate?
Coffee also interacts with calcium channels by binding to them and releasing calcium stored inside cells while also having the ability to block voltage calcium channels, which could potentially affect the transmission of neurotransmitters in the body.
What is the function of caffeine citrate?
Using caffeine citrate has been a practice for treating and preventing apnea in babies ever since it was first approved.
What are the benefits of caffeine citrate?
Caffeine citrate injection is employed to manage apnea episodes in infants born between 28 and 32 weeks of gestational age when they experience breathing cessation.
Is caffeine citrate in coffee?
It can come from coffee beans. Be naturally present in teas and cacao beans that are distinct from coffee beans.
How do you make caffeine citrate?
Mixing caffeine with citric acid can create it.
Is caffeine citrate a stimulant?
It's a type of medication that boosts the brain's ability to control breathing by making the respiratory centers, in the brain, more sensitive to carbon dioxide and enhancing the strength of the diaphragm muscles.