Chloroquine Phosphate
- What is Chloroquine Phosphate?
- Composition and Chemical Characteristics of Chloroquine Phosphate
- Pharmacological Mechanism: How Chloroquine Phosphate Works
- Primary Uses of Chloroquine Phosphate
- Off-label Uses of Chloroquine Phosphate
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Chloroquine Side Effects
- Interaction with Other Medications
- Specific Administration Considerations
- Overdose Information and Emergency Response
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Important Precautions and Patient Advisories
- Careful Administration Practices
What is Chloroquine Phosphate?
Overview of Chloroquine Phosphate
What is Chloroquine Phosphate? It is widely recognized as a medication that prevents and treats malaria. It is also used to help control disorders because of its ability to regulate the immune system.
Historical Context and Development
Chloroquine was first created in the 1930s, building upon the use of quinine, which was prevalent before the 20th century. Its invention represented an advancement in combating malaria a common issue, in tropical areas.
Composition and Chemical Characteristics of Chloroquine Phosphate
Active Ingredients and Their Properties
Chloroquine Phosphate mainly consists of chloroquine, a chemical that effectively fights against Plasmodium parasites. Its capability to block DNA replication and RNA transcription in these organisms is crucial for its effectiveness as a treatment.
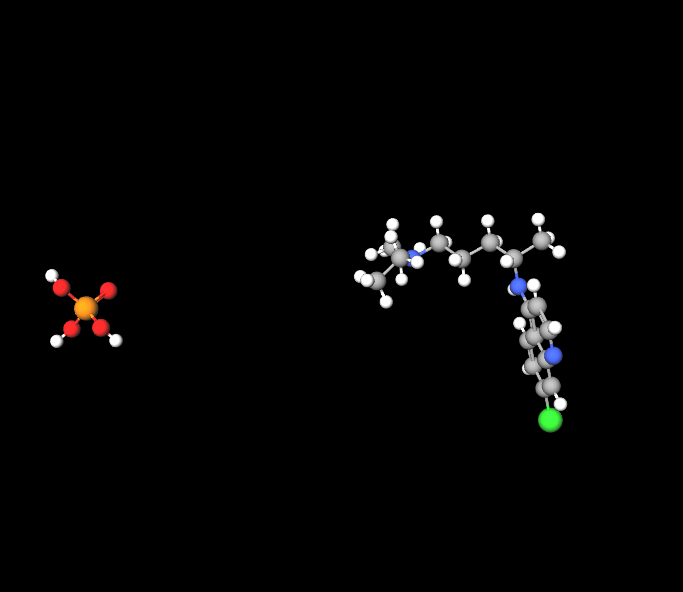
Excipients in Chloroquine Formulations
- Lactose helps to stabilize the tablet.
- Magnesium stearate functions as a lubricant during the formulation process.
- Cornstarch is utilized as a binder to provide structure to the tablet.
Pharmacological Mechanism: How Chloroquine Phosphate Works
Mechanism of Action Against Malaria
Chloroquine hinders the parasite's growth in blood cells by stopping polymerization, a harmful substance produced when hemoglobin breaks down from forming nontoxic hemozoin. This process essentially poisons the parasites with their waste.
Effects on Immune System and Anti-inflammatory Properties
Chloroquine not only works against malaria but also helps regulate the immune system by decreasing cytokine production, which in turn reduces inflammation. This approach is commonly used in treating conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Primary Uses of Chloroquine Phosphate
Treatment of Malaria: Indications and Efficacy
- Chloroquine is an antimalarial drug used to treat infections caused by Plasmodium vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and susceptible strains of P. falciparum123.
- It is also effective against extraintestinal amebiasis123.
Off-label Uses of Chloroquine Phosphate
Potential Role in Viral Infections Including COVID-19
- Beyond malaria, chloroquine has been repurposed for various conditions:
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosage for Malaria Treatment and Prevention
The typical treatment for malaria involves a chloroquine dose, then additional doses, at 6, 24, and 48 hours. To prevent it a weekly dose is suggested starting a week before contact and lasting four weeks after departing the high risk region.
Guidelines for Autoimmune Conditions
To manage conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, doctors typically prescribe lower, consistent doses depending on the patient's condition and how they respond to treatment.
Modifications in Dosage Based on Patient Condition and Response
Adjusting the dosage is essential, taking into account the patient's background, other medications being taken, and how they are responding to the treatment. This helps achieve the results with minimal side effects.
Chloroquine Side Effects
Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal, Neurological, and Dermatological
Chloroquine Side Effects may be experienced:
- Gastrointestinal issues, like feeling queasy and throwing up.
- Neurological symptoms involve experiencing headaches and feeling dizzy.
- Skin reactions may vary from itching to severe rashes.
Serious Adverse Reactions and Management Strategies
On the chance that uncommon severe outcomes such as retinopathy, significant blood conditions, and cardiomyopathy arise, it is crucial to stop the medication right away and seek thorough medical care. Essential monitoring methods like eye check-ups and blood tests are vital for reducing these dangers.
Interaction with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Potential Risks
Chloroquine Phosphate over the counter may interact with medications, leading to a decrease in its effectiveness or an increase in its side effects. For instance, antacids and laxatives with magnesium or aluminum can lower the absorption of chloroquine. Taking ampicillin at the same time may reduce its levels in the body. It is important to be cautious when using it with antimalarials or drugs that prolong the QT interval, as this can raise the possibility of cardiac toxicity.
Impact on Efficacy of Other Treatments
Specific Administration Considerations
Administration to Elderly: Adjustments and Monitoring
Guidelines for Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use: Safety and Dosage Adjustments
Overdose Information and Emergency Response
Symptoms of Overdose and Immediate Actions
Signs of taking too much Chloroquine include headaches, feeling drowsy, vision problems, heart issues, and seizures. The initial steps include providing treatment to address the symptoms and offering support, such as monitoring the heart and taking actions to stop the medication's absorption.
Long-term Management of Overdose Symptoms
Dealing with symptoms of overdose requires consistent checkups and compassionate assistance. Depending on the extent of heart-related issues, rehabilitation might be needed.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
It's best to keep Chloroquine Phosphate in a dark place, at room temperature, to ensure it stays effective and lasts longer.

Handling Procedures to Ensure Safety and Stability
To safely handle Chloroquine Phosphate it's important to follow safety guidelines to avoid exposure. Avoid touching tablets with hands and ensure that powders if necessary are handled in areas, with good ventilation.
Warnings and Contraindications
Specific Health Conditions that Preclude Use
Patients who have a known sensitivity to chloroquine or similar 4 aminoquinolines should avoid using Chloroquine Phosphate. It is also not recommended for individuals with any eye-related issues or children who require long-term treatment.
Genetic Factors Influencing Risk
Some specific genetic indicators might make certain individuals more likely to experience effects when taking Chloroquine Phosphate. Doctors may suggest testing to evaluate the chances of hemolytic anemia in people with a shortage of glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD).
Important Precautions and Patient Advisories
Monitoring Requirements during Treatment
Patients taking Chloroquine Phosphate need to have their vision, blood cell levels, and muscle function checked regularly to detect any severe side effects at an early stage.
Preventive Measures to Mitigate Side Effects
To avoid issues, it is important to make sure the correct dosage is taken, follow the prescribed treatment plan diligently, attend routine medical appointments, and educate patients on how to identify early indications of side effects.
Careful Administration Practices
Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to make sure that they prescribe medications after conducting diagnostic assessments and taking into account all individual patient factors in order to achieve the best treatment results with Chloroquine Phosphate.
Patient Education and Compliance Enhancement
It's really important to educate patients so they understand their treatment, possible side effects, and why it's crucial to stick to their prescribed medication schedule.























