Cisplatin
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Cisplatin
- III. How Cisplatin Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Cisplatin
- V. Off-label Uses of Cisplatin
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Careful Administration
- VIII. Important Precautions
- IX. Over Dosage
- X. Administration to Special Populations
- XI. Common Side Effects of Cisplatin
- XII. Less Common Side Effects
- XIII. Drug Interactions
- XIV. Warnings
- XV. Contraindications
- XVI. Storage Guidelines for Cisplatin
- XVII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Cisplatin, a platinum chemotherapy medication, is commonly used to treat types of cancers. It was first discovered in the 1960s and gained recognition for its effectiveness in eliminating cancer cells, earning it the nickname "penicillin of cancer drugs." Its crucial role in cancer treatments solidifies its status as one of the cytotoxic agents.
II. Composition of Cisplatin
Cisplatin, chemically represented as PtCl2(NH3)2 has a planar structure. Platinum is the element in Cisplatin, and it is often combined with other compounds that help enhance its solubility or stability. Cisplatin forms are available, including those for intravenous injection and oral tablets. However, intravenous injection is generally the most frequently used method.
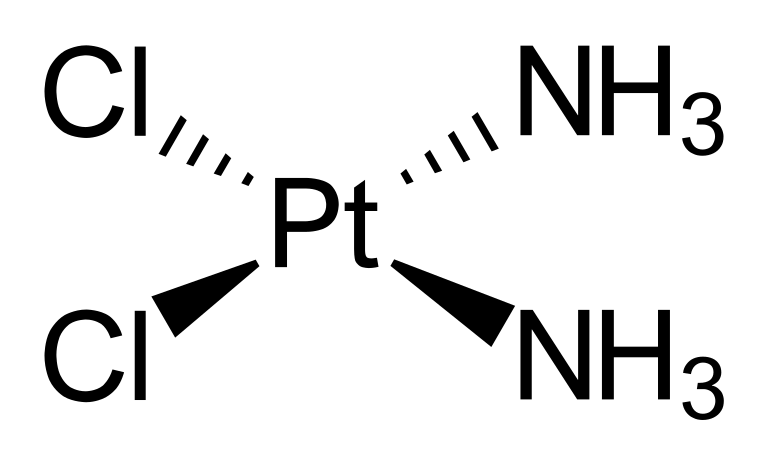
III. How Cisplatin Works
IV. Approved Uses of Cisplatin
The management of cancer is crucial in the curative approach. Doctors often employ treatment options for cancer, either as a single therapy or in combination with other medications1. Cisplatin is one such chemotherapy medication that has been used to treat various types of cancers, including testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors, and neuroblastoma2. It is administered intravenously as a short-term infusion in normal saline for the treatment of solid and hematological malignancies2. The FDA has approved cisplatin for indications such as cervical and head and neck cancers2.
Here are some references that provide more information about cisplatin:
V. Off-label Uses of Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication that has been used to treat various types of cancers, including testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors, and neuroblastoma1. It is also recognized for its effectiveness in addressing lung cancer and is commonly used as a treatment in palliative care to alleviate symptoms1. Certain cancer specialists recommend using it as part of combination therapies for types of cancers like melanoma although this is still an area that researchers are actively studying1.
Here are some references that provide more information about cisplatin:
VI. Dosage and Administration
The amount of Cisplatin given to a patient is usually customized to their needs but typically falls between 50 and 100mg/m2 per treatment cycle. The drug is commonly administered through a route where it is mixed with either saline or dextrose solution. The timing and frequency of doses depend on the treatment plan and can range from weekly to every three weeks.
VII. Careful Administration
When it comes to calculating the dose, accuracy is paramount. Factors like body surface area and renal function are typically taken into account. Healthcare professionals must be meticulous in handling Cisplatin, ensuring they wear clothing and follow safety protocols to prevent accidental exposure.
VIII. Important Precautions
Before giving Cisplatin, it is essential to assess the patient to ensure no contraindications. This typically involves checking the patient's kidney function, blood counts, and liver function. Throughout the treatment process, monitoring the patient for any possible complications, like kidney damage or blood-related issues, is crucial. This way, any necessary actions can be taken promptly if needed.
IX. Over Dosage
Excessive consumption of Cisplatin can lead to consequences resulting in severe damage to the kidneys, suppression of bone marrow function, and neurological issues. Acting quickly is essential in cases. Urgent hemodialysis and supportive treatments can help reduce the severity of these problems. In addition, providing antiemetics and hydration solutions as part of the treatment plan can often provide benefits.
X. Administration to Special Populations
For the elderly, It's essential to monitor geriatric populations because their kidneys may not function as well, and they are more prone to experiencing side effects. It is strongly advised for women and nursing mothers not to use this medication during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to the potential harm it can cause to the fetus and newborn. For children, The effectiveness and safety of this medication in patients have not been extensively studied, so it should be used cautiously.
XI. Common Side Effects of Cisplatin
The common negative impacts of Cisplatin include gastrointestinal discomfort, which can range from feeling nauseous to experiencing severe vomiting. It also affects the system, causing symptoms like peripheral neuropathy and can lead to kidney problems such as acute kidney injury.

XII. Less Common Side Effects
While Cisplatin is not as common it can still cause changes in blood cell counts, such as platelet and white blood cell levels. Allergic reactions, although uncommon, should be taken seriously. Require stopping the medication right away. Additionally, prolonged use of Cisplatin has been linked to the development of hidden and long-lasting complications, like chronic kidney disease.
XIII. Drug Interactions
When Cisplatin is taken together with chemotherapy drugs, it may increase their harmful effects. Using Cisplatin alongside cancer medications, such as medicines for high blood pressure, can lead to unexpected reactions. Additionally, consuming alcohol or recreational drugs at the time as Cisplatin can worsen its damaging effects on the kidneys and nerves.
XIV. Warnings
Patients with impaired kidney function should be extra careful due to the potential for kidney damage. Additionally, individuals with heart problems, like heart failure, may find that their condition worsens.
XV. Contraindications
There are situations where the use of this treatment is not recommended. These include having existing kidney problems, being known to have a sensitivity to platinum compounds, and being pregnant at the same time. There are also cases where caution is advised. This includes being older, having health conditions, and taking medications that are harmful to the kidneys or ears.
XVI. Storage Guidelines for Cisplatin
Cisplatin needs to be kept in an environment within a temperature range of 20 25°C (68 77°F). If you follow the storage guidelines, the drug will maintain its effectiveness until its expiration date. Make sure to dispose of it according to local environmental regulations to minimize any negative environmental impact.
XVII. Conclusion
To sum up, Cisplatin continues to be a part of the treatment options for various types of cancer. Due to its pharmacological nature, it is vital to have a comprehensive understanding and strictly follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines. Although it plays a role, it is essential to note that associated risks highlight the need for expert medical guidance. Continuous research efforts are focused on broadening its applications and finding ways to minimize any effects it may have.
















