Colfosceril Palmitate
Introduction
Colfosceril Palmitate is a phospholipid-based compound classified as a synthetic pulmonary surfactant. It is designed to mimic the natural surfactants present in the lungs, essential for reducing surface tension and preventing alveolar collapse. The compound's introduction marked a milestone in neonatal medicine, revolutionizing the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).
Initially developed in the late 20th century, Colfosceril Palmitate emerged from intensive research on surfactant biochemistry. It was primarily targeted at addressing the high mortality rate associated with preterm infants suffering from RDS. Today, its significance extends to broader respiratory conditions, underscoring its pivotal role in critical care settings.
Composition and Mechanism of Action
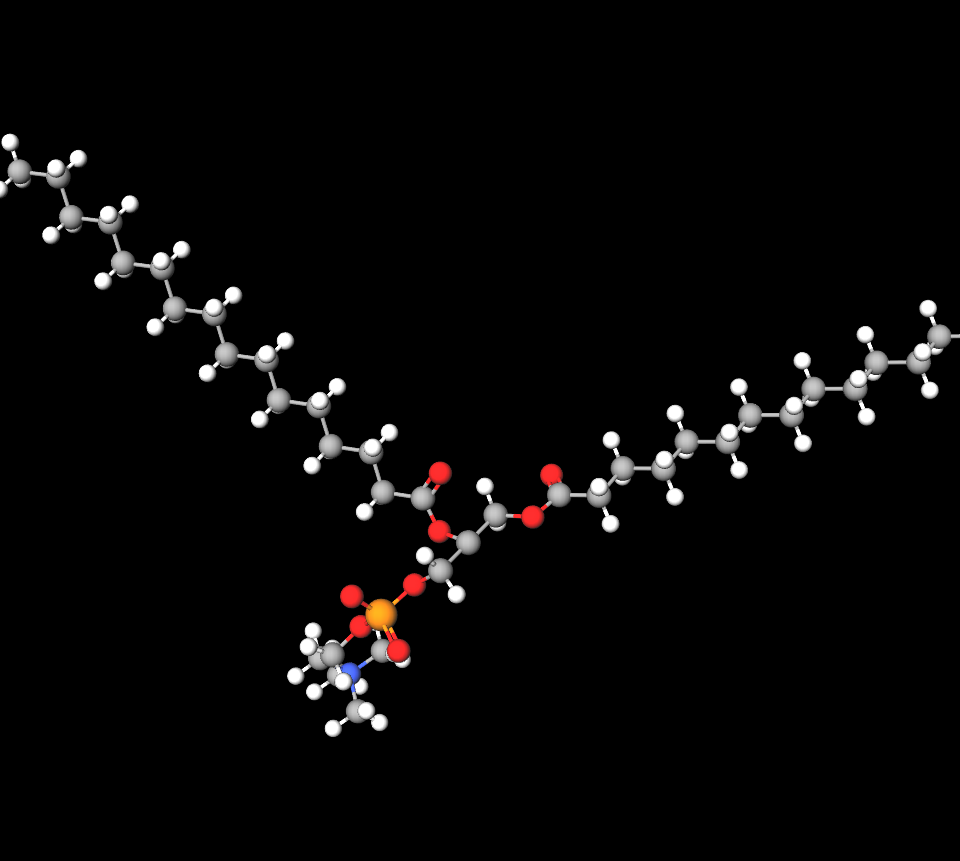
The chemical composition of Colfosceril Palmitate includes dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), a key component of endogenous lung surfactants. This phospholipid is structured to mimic natural lung surfactants, ensuring compatibility and efficacy.
Colfosceril Palmitate functions by lowering alveolar surface tension, thereby preventing alveolar collapse during exhalation. Its mechanism involves creating a stable monolayer over the alveolar lining, enhancing gas exchange and oxygenation. This process is critical in neonates with underdeveloped lungs.
- Pharmacodynamics: Rapid onset of action post-administration.
- Pharmacokinetics: Localized effect with minimal systemic absorption.
Approved Uses
Colfosceril Palmitate is primarily indicated for the treatment of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), a condition characterized by insufficient surfactant production in premature infants. It is administered shortly after birth to reduce mortality and morbidity associated with RDS.
- Facilitates lung expansion and oxygenation in preterm infants.
- Reduces the risk of chronic lung conditions associated with prolonged ventilation.
In high-risk cases, its prophylactic use helps prevent alveolar collapse, ensuring improved respiratory outcomes.
Off-Label Uses
Emerging research highlights potential off-label applications of Colfosceril Palmitate:
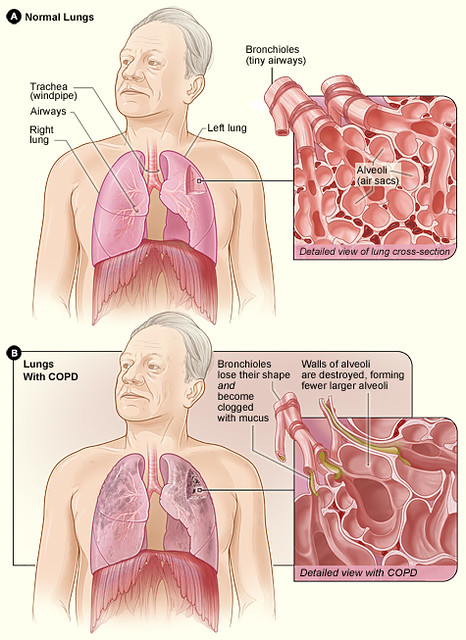
- Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Investigational trials suggest its efficacy in improving oxygenation in adults.
- Acute Lung Injuries: Preliminary studies explore its role in mitigating damage and facilitating recovery.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Potential as an adjunctive therapy in severe exacerbations.
These applications, though promising, require further clinical validation to establish widespread acceptance.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage for neonates is calculated based on body weight, typically administered via an endotracheal tube. The process includes careful preparation to ensure optimal efficacy:
- Reconstitution: Mix the powder with sterile water as per guidelines.
- Administration: Deliver in divided doses directly into the trachea.
- Frequency: Repeat doses may be given based on clinical assessment.
Proper administration requires trained personnel to minimize risks and maximize therapeutic benefits.
Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, Colfosceril Palmitate may cause side effects:
- Common: Apnea, bradycardia, cyanosis.
- Less Common: Pulmonary hemorrhage, oxygen desaturation, infection risks.
Long-term use in neonates has shown no significant adverse developmental impacts, though vigilance remains paramount during administration.
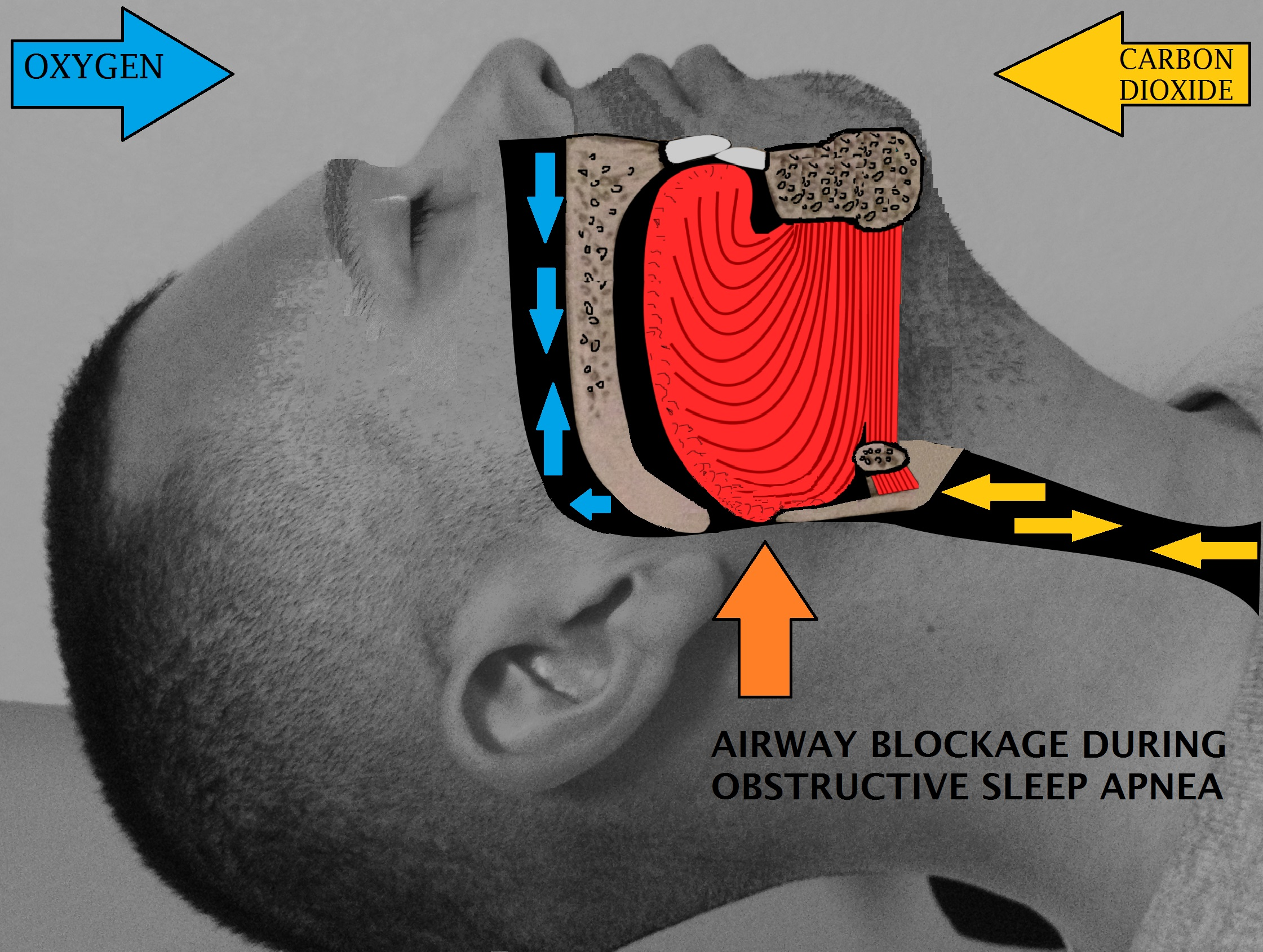
Contraindications and Warnings
Absolute contraindications include hypersensitivity to Colfosceril Palmitate or its components. Specific pre-existing conditions, such as congenital abnormalities affecting the respiratory system, warrant careful evaluation before use.
Warnings include:
- Administer only under the supervision of specialized medical professionals.
- Risks associated with improper administration, such as uneven lung distribution or airway obstruction, require thorough training and monitoring.
Interactions with Other Medications
Colfosceril Palmitate exhibits interactions with certain medications that may impact its efficacy or safety. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate co-administered treatments to mitigate potential complications.
- Corticosteroids: Co-administration may potentiate respiratory function but requires monitoring for synergistic effects that could alter lung mechanics.
- Oxygen Therapy: Excessive oxygen supplementation, when combined with Colfosceril Palmitate, may exacerbate oxidative stress, increasing the risk of lung tissue damage.
Additionally, its use alongside other respiratory treatments demands careful adjustment to ensure no interference in therapeutic outcomes.
Special Precautions
The administration of Colfosceril Palmitate requires vigilance in specific populations to ensure optimal outcomes:
- Premature Infants with Infections: Infants with systemic or localized infections may experience altered responses, necessitating close monitoring and possibly adjunctive treatments.
- Patients with Congenital Abnormalities: Structural anomalies in the respiratory system can affect the uniform distribution of the surfactant, requiring tailored approaches.
Monitoring during and after administration is critical. Ensuring appropriate oxygenation levels and avoiding prolonged mechanical ventilation is key to minimizing risks.
Administration to Specific Groups
To Elderly Patients
Data on the use of Colfosceril Palmitate in elderly populations is scarce. This limitation highlights the need for off-label studies to explore its potential benefits in age-related respiratory conditions. Until further evidence emerges, its use should be guided by clinical judgment.

To Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety profile for pregnant women and nursing mothers remains under-researched. Its administration should be considered only in critical scenarios where the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Consultation with specialists is imperative in such cases.
To Children
Specific dosages are recommended for pediatric use beyond neonates based on weight and clinical condition. Long-term studies suggest minimal developmental impact, though comprehensive safety data are still evolving.

Overdosage
Overdosage of Colfosceril Palmitate can lead to complications requiring immediate attention. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Severe oxygen desaturation.
- Airway obstruction or uneven surfactant distribution.
Emergency protocols include airway suctioning, supportive ventilation, and symptomatic management. Documented case studies have highlighted positive outcomes with timely intervention, underscoring the importance of preparedness.
Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of Colfosceril Palmitate ensure its efficacy and safety. Guidelines include:
- Temperature Requirements: Store at temperatures recommended by the manufacturer, typically refrigerated.
- Protection from Light and Contamination: Keep in original packaging to avoid degradation.
- Handling Precautions: Healthcare professionals should use aseptic techniques during reconstitution and administration.
Disposal of unused portions should follow institutional protocols to prevent contamination and misuse.
Important Clinical Considerations
Timely intervention with Colfosceril Palmitate in high-risk neonates can dramatically improve survival rates. A multidisciplinary approach, involving neonatologists, respiratory therapists, and nurses, ensures comprehensive care.
The role of this surfactant in enhancing neonatal outcomes is undeniable. Its integration into standard protocols has not only reduced mortality but also minimized long-term complications associated with respiratory distress syndrome.
Colfosceril Palmitate FAQ
What is the function of Colfosceril palmitate?
Colfosceril palmitate is a type of lung surfactant that is given to babies to help treat Respiratory Distress Syndrome (commonly known as RDS). It's a man made version of lung surfactant. It is used to help infants with breathing problems due to RDS.