Cotareg (Co-Diovan)
- Introduction to Cotareg (Co-Diovan)
- Composition
- Cotareg Mechanism of Action
- Approved Uses of Cotareg (Co-Diovan)
- Off-Label Uses of Cotareg
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Valsartan hctz side effects
- Less Common and Severe Side Effects
- Drug Interactions and Risk Management
- Important Precautions and Handling Guidelines
- Administration to Special Populations
- Overdosage: Signs, Symptoms, and Management
- Storage Recommendations
- Careful Administration and Patient Monitoring
- Handling and Disposal Precautions
Introduction to Cotareg (Co-Diovan)
Co Diovan is a known product used mainly to treat high blood pressure or hypertension by combining two powerful ingredients – valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide – to effectively regulate blood pressure levels with a dual action approach endorsed by reputable medical companies in the field of healthcare products and services. Cotareg is recommended for those individuals who need management of their blood pressure to avoid health issues related to hypertension. Targeting the root causes of risk factors allows Cotareg not just to control blood pressure but also reduce the chances of experiencing heart related issues in the future.
Composition
Cotaregs effectiveness comes from the combination of its two components.
Valsartan:
A medication known as an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) works by stopping the tightening of blood vessels to improve blood flow and lower strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide work together to lower blood pressure by increasing urine output and addressing vasoconstriction, respectively, for control of blood pressure levels. These medications have an effect when combined. Valsartan reaches peak plasma concentrations within 24 hours, while hydrochlorothiazide achieves the same within 1-2 hours, ensuring absorption in the body.
Sacubitril-valsartan
Sacubitril and valsartan are combined to manage long-term heart failure in adults, aiming to lower the chances of mortality and hospital visits associated with the condition while also serving as a treatment option for children experiencing heart failure symptoms. The addition of valsartan aids in blocking angiotensin II receptors (ARB).
Lisinopril hydrochlorothiazide
A blend of lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide is prescribed to manage blood pressure issues. Lisinopril falls under a drug called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE ) inhibitors. It reduces substances that constrict the blood vessels to facilitate blood circulation.
Triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide
The blend of triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide is prescribed for managing blood pressure and edema (the accumulation of fluid in body tissues). This medication is typically recommended for patients with low potassium levels or those at risk of potassium deficiency complications.
Amlodipine and valsartan
Combining a medication called amlodipine with valsartan is often prescribed for managing blood pressure also known as hypertension as this condition can put strain on the heart and arteries.
Valsartan vs losartan
Valsartan and losartan differ mainly in the duration of their action in the body at varying dosages. Valsartan maintains activity for 24 hours of dosage, while losartan activity diminishes sooner at doses; generally speaking, valsartan is considered more potent than losartan in terms of effectiveness.
Chlorthalidone vs hydrochlorothiazide
Chlorthalidone has a duration of action and has demonstrated greater efficacy in lowering blood pressure over 24 hours compared to hydrochlorothiazide (HCT).
Cotareg Mechanism of Action
It acts selectively on the AT1 receptor subtype, which is responsible for the known actions of angiotensin II. The increased plasma levels of Ang II following AT1 receptor blockade with valsartan may stimulate the unblocked AT2 receptor, which appears to counterbalance the effect of the AT1 receptor.
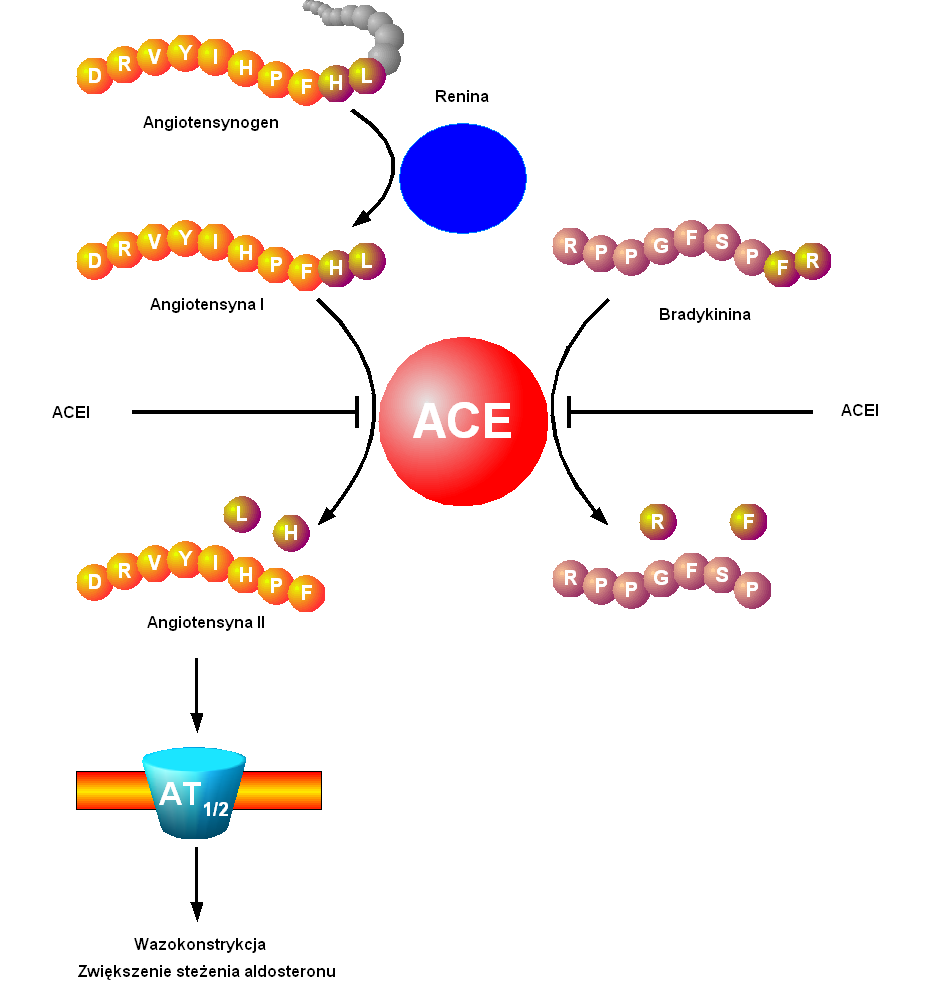
Valsartan half-life
Valsartan remains effective for around 24 hours due, to its life lasting between six to nine hours providing benefits over an extended period of time.
Approved Uses of Cotareg (Co-Diovan)
Approved for uses Cotareq has received regulatory clearance.
Hypertension Management:
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction:
Ideal for individuals with a susceptibility to heart issues or past occurrences of episodes.
Kidney Protection:
Off-Label Uses of Cotareg
While Cotaref is mainly prescribed for blood pressure treatment purposes it has shown to be effective in unapproved uses as well.
Heart Failure:
In cases where standard treatments fall short, it is employed to handle instances of heart failure.
Chronic Kidney Disease:
It helps reduce protein in urine. It may help protect kidney function.
Resistant Hypertension:
Utilized when conventional treatments are ineffective in reaching the targeted blood pressure levels. However, seeking advice before using Cotareg for purposes not specified on the label is essential.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Usually, Cotareg is taken by mouth once a day.
Adults:
The initial dose typically varies between 80mg and 160 mg per 12 hours, depending on the individual's requirements.
Renal or Hepatic Impairment:
Properly adjusting the dosage is essential to prevent any complications from arising.
Best time to take valsartan
It would be best if you typically took valsartan twice as prescribed by your doctor for the best results in managing your condition effectively and safely. If you are using the medication daily, it is advisable to take the dose before bedtime to minimize the risk of feeling dizzy.
Missed Dose
If you forget to take a dose of medication, make sure to take it as you remember, but be careful not to take two doses at once.
Warnings and Contraindications
Certain conditions and risks necessitate caution:
Contraindications:
People with kidney problems or who are unable to produce urine or have reactions to the ingredients should avoid this product.
Warnings:
Watch for blood pressure issues and imbalances in potassium and electrolytes in groups more susceptible to these conditions. Patients should also inform their healthcare providers about any existing health conditions before starting treatment.

Valsartan and alcohol
Consuming alcohol may enhance the ability of valsartan to lower blood pressure levels. It may result in feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness.
Valsartan hctz side effects
Cotareg is well-tolerated by most patients, though some may experience:
These effects are generally mild and transient. Staying hydrated and taking the medication as prescribed can help mitigate them.
Less Common and Severe Side Effects
Rare but serious adverse effects include:
- Angioedema: Swelling of the face or throat, requiring immediate attention.
- Severe Hypotension: This may occur in volume-depleted patients.
- Renal Dysfunction: Warranting regular monitoring of kidney function.
Valsartan side effects weight gain
Usually, valsartan doesn't lead to weight gain. However, there are cases where individuals might experience slight weight gain as a result of swelling or retaining fluids while taking valsartan.
Valsartan side effects anxiety
Some individuals experience mood shifts, such as anxiety, which might happen when undergoing treatment for a condition requiring attention.
Valsartan cancer
Valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker known for its ability to reduce blood pressure. It is widely regarded as safe and efficient in most cases; nevertheless, certain batches of valsartan have been found to contain N nitrosodimetilamine(NDMA), a harmful impurity classified as a human carcinogen.
Valsartan and potassium
Valsartan has the potential to elevate potassium levels to an extent, known as hyperkalemia, which can have consequences and even result in death.
Drug Interactions and Risk Management
Cotareg interacts with several medications:
- NSAIDs: Can reduce the antihypertensive effect.
- Lithium: Increased risk of lithium toxicity.
- Diuretics: Potential for enhanced diuretic effects and electrolyte imbalance.
Valsartan and ibuprofen
Mixing Valsartan and Ibuprofen could lessen the impact of Valsartan on reducing blood pressure.
Valsartan alternatives
Important Precautions and Handling Guidelines
Using Cotareq requires attention to guarantee its efficient utilization, with particular precautions tailored for different patient categories and the drug's management.
Precautions for Elderly Patients:
As people age and undergo changes associated with aging, they may find that they become more sensitive to Cotareg's effects. It is important to watch their blood pressure and kidney function to avoid any consequences and ensure their well-being.
Administration Considerations for Pregnant and Nursing Women:
During pregnancy, Cotaregi is categorized as Category D due to risks to the baby's growth and development. It's not recommended to take it during the stages of pregnancy. For breastfeeding mothers, the amount of Cotaregin in breast milk is very low. It needs to be assessed by a healthcare professional.
Guidelines for Pediatric Use:
The effectiveness and safety of Cotaregin in children under 18 years old are not clearly proven yet.It is advisable to use it after considering the child's weight and medical requirements for dosage adjustment.
Handling Precautions:
Remember to store Cotareg its packaging to shield it from moisture and light and make sure to keep it from children and pets.
Valsartan withdrawal symptoms
Sudden discontinuation of these medications may lead to a condition characterized by increased activity manifesting as feelings of unease or restlessness, heartbeat, and headaches.
Valsartan and bananas
Both valsartan and bananas have the advantage of improving blood pressure levels. Valsartan relaxes blood vessels, lowering blood pressure.Bananas are packed with potassium, which aids in maintaining blood pressure levels.

Valsartan and coffee
Drinks, like coffee that have caffeine, don't directly interact with the majority of blood pressure medications; however, they can elevate blood pressure on their own, which may heighten the likelihood of heart-related problems, like stroke or heart attack.

Valsartan and grapefruit
The presence of furanocoumarins in grapefruit can affect how your liver processes medications by raising the levels of ingredients like valsartan and causing an unexpected drop in blood pressure effectiveness.

Administration to Special Populations
The management of Cotares should be customized to address the requirements of groups.
Adjustments for Elderly Patients with Co-morbidities:
Many older patients commonly have health issues to manage at once and need adjustments to their medication doses and regular monitoring to reduce the chances of negative side effects like low blood pressure and imbalances in electrolytes.
Risks and Benefits in Pregnancy:
Cotaregist is classified as a Category D medication, with risks of causing birth defects during the stages of pregnancy; nonetheless, it could be deemed appropriate in critical situations where no safer options are available.
Safety Profile for Lactating Mothers:
While Cotaregin breast milk analysis factors are present, it's crucial to acknowledge the possible impacts on the baby. This underscores the importance for breastfeeding mothers to seek advice from their practitioner prior to usage.
Limited Data and Precautions for Pediatric Use:
It is not common for Cotaregs to be prescribed for children because there is data available on its use in pediatric patients, and any use outside the approved indications should only be done under close medical supervision.
Overdosage: Signs, Symptoms, and Management
Taking too much Cotareg can cause issues that require immediate attention.
Symptoms of Cotareg Overdose:
Common symptoms may include high blood pressure, feeling lightheaded or dizzy, and imbalances in electrolytes, like high potassium or low sodium levels.
Emergency Management Protocols:
In the beginning, it is important to adjust the patient's position to ensure blood flow to organs and provide intravenous fluids to address low blood pressure.
Role of Activated Charcoal and Supportive Care:
Using activated charcoal right after ingestion might lessen absorption while other steps involve balancing electrolytes and keeping an eye on heart and kidney functions.
Storage Recommendations
Ensuring that Cotaregre remains stable and effective throughout its storage is crucial for maintaining its quality over time.
Optimal Storage Conditions:
Remember to store Cotareg in a place with a suitable temperature, away from heat or moisture, and direct sunlight—usually, around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
Shelf Life and Packaging Details:
Always check the expiration date on Cotareg before using it, and don't use the medication after that date to ensure its effectiveness is maintained.
What to Do if the Medication is Improperly Stored:
If Cotareg has been inappropriately stored or subjected to conditions, seek advice from a pharmacist to assess its effectiveness.
Careful Administration and Patient Monitoring
It is essential to monitor progress to guarantee that Cotareg treatment is effective and safe and to minimize any risks along the way.
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure and Kidney Function Tests:
Regular evaluations offer a glimpse into how the patient is reacting to the treatment and help identify any indications of potential side effects.
Monitoring for Electrolyte Imbalances:
For patients with kidney problems, blood tests to monitor levels of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes are important.
Recommendations for Long-Term Therapy Management:
Regular assessments of how a treatment is working and any possible side effects are important for fine-tuning the dosage and dealing with any issues that may arise in advance.
Handling and Disposal Precautions
The correct management and disposal of Cotaregs protect both people and the surroundings.
Safe Handling to Prevent Accidental Exposure:
Avoid touching the medication when handling crushed or broken tablets, and remember to wash your hands afterward.
Proper Disposal Methods:
Do not throw expired or unused Cotaregs in your household trash bin; instead, refer to regulations or pharmacy disposal programs for proper disposal methods.
Cotareg (Co-Diovan) FAQ
- When does valsartan start working?
- Valsartan when to use?
- Valsartan when to take?
- What valsartan hydrochlorothiazide for?
- What valsartan treat?
- What valsartan used for?
- Valsartan how long to work?
- How valsartan and amlodipine work?
- How valsartan / hydrochlorothiazide works?
- Can valsartan cause diarrhea?
- Can valsartan cause erectile dysfunction?
- Are valsartan and metoprolol the same?
- Are valsartan and lisinopril the same thing?
- Are valsartan and diovan the same?
- Are valsartan and amlodipine the same thing?
- Are valsartan and losartan the same?
- Will valsartan make you sleepy?
- Will valsartan make you gain weight?
- Will valsartan make you tired?
- Will valsartan cause ed?
- Why take valsartan and metoprolol together?
- Why take valsartan at night?
- Will hydrochlorothiazide cause hair loss?
- Why hydrochlorothiazide for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
- Why hydrochlorothiazide and spironolactone given together?
- Who uses hydrochlorothiazide?
- Hydrochlorothiazide which type of diuretic?
- Hydrochlorothiazide when to take?
- What hydrochlorothiazide good for?
- What hydrochlorothiazide used for?
- Hydrochlorothiazide how long to work?
- How hydrochlorothiazide cause hyperglycemia?
- Can hydrochlorothiazide cause weight gain?
- Can hydrochlorothiazide cause dehydration?
- Can hydrochlorothiazide cause low potassium?
- Can hydrochlorothiazide cause gout?
- Are hydrochlorothiazide and hydralazine the same?
When does valsartan start working?
It typically takes around two hours for Valsartan to begin lowering blood pressure. Its full effects may not be felt until 2 to 4 weeks later.
Valsartan when to use?
For blood pressure, take 80 mg to 320mg daily. For heart failure, take 40mg to 160mg twice a day. After a heart attack, take 20mg to 160mg twice a day.
Valsartan when to take?
You typically need to take valsartan twice.
What valsartan hydrochlorothiazide for?
Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide are often prescribed either on their own or alongside medications to manage hypertension, also known as blood pressure.
What valsartan treat?
Valsartan is a medication used for managing blood pressure and heart failure.
What valsartan used for?
Valsartan is prescribed on its own or in combination with medications to manage hypertension, a condition characterized by elevated blood pressure that places extra strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Valsartan how long to work?
Valsartan typically takes around two hours to begin lowering blood pressure. Its full effects may not be seen until 2 to 4 weeks later.
How valsartan and amlodipine work?
Amlodipine helps to relax the blood vessels, allowing blood and oxygen to flow to the heart while reducing strain. Valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) that inhibits a substance in the body for constrictions in blood vessels.
How valsartan / hydrochlorothiazide works?
The combination of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide involves two medicines collaborating to address blood pressure by dilating blood vessels and boosting urine production.
Can valsartan cause diarrhea?
Please consult your physician immediately if you fall ill while using this medication – especially if you experience nausea, persistent vomiting, or diarrhea that does not subside, as it could result in dehydration and potentially lead to high blood pressure.
Can valsartan cause erectile dysfunction?
Valsartan did not have any impact on function or testosterone levels.
Are valsartan and metoprolol the same?
Valsartan works as a blocker for the AT (type 11) receptor system, and metoprolol functions as a beta blocker in the body.
Are valsartan and lisinopril the same thing?
In patients with mild hypertension, Valsartan and lisinopril proved to be effective in managing blood pressure; however, Valsartan showed an advantage by significantly lowering the chances of adverse effects, like a cough.
Are valsartan and diovan the same?
Valsartan, commonly referred to as Diovan, falls under the category of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). It is prescribed for the management of blood pressure in both adults and children.
Are valsartan and amlodipine the same thing?
Amlodipine is classified as a calcium channel blocker (CCB). It impacts the flow of calcium into the heart and blood vessel cells to ease the vessels and enhance blood and oxygen supply to the heart while decreasing its strain.Valsartan serves as an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB).
Are valsartan and losartan the same?
Valsartan remains active in the body for 24 hours regardless of the dose used, while losartan's activity duration is shorter when taken in doses.
Will valsartan make you sleepy?
Taking an amount of valsartan may result in blood pressure symptoms such as dizziness and fatigue with a rapid heartbeat (palpitations). The threshold for an overdose differs from individual to individual.
Will valsartan make you gain weight?
Usually, Valsartan does not lead to weight gain; however, a few individuals might experience some weight gain while taking it due to issues like swelling or fluid retention.
Will valsartan make you tired?
Some of the side effects of valsartan are dizziness, tiredness, and headaches.
Will valsartan cause ed?
Valsartan is not expected to lead to dysfunction (ED).
Why take valsartan and metoprolol together?
Sometimes, people may combine valsartan and metoprolol to address health issues such as heart failure (CHD) and acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Why take valsartan at night?
Taking valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide or olmesartan at night proved to be more effective in lowering blood pressure (SBPs) and improving sleep duration.
Will hydrochlorothiazide cause hair loss?
Potential mild adverse reactions associated with the use of hydrochlorothiazide may involve experiencing hair thinning.
Why hydrochlorothiazide for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
Hydrochlorothiazide is often prescribed for managing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ND) as it helps lower the production of urine.
Why hydrochlorothiazide and spironolactone given together?
The duo of spironolactone and hydrochlorothiazide is prescribed for managing hypertension.
Who uses hydrochlorothiazide?
Hydrochlorothiazide is prescribed to manage hypertension in both adults and children.
Hydrochlorothiazide which type of diuretic?
Hydrochlorothiazide functions as a thiazide diuretic commonly referred to as a water pill.
Hydrochlorothiazide when to take?
Morning with food
What hydrochlorothiazide good for?
It is prescribed for managing blood pressure. It can also help alleviate swelling associated with heart conditions or diseases of the kidneys and liver by aiding the kidneys in eliminating excess fluid and salt from the bloodstream through urine excretion.
What hydrochlorothiazide used for?
Hydrochlorothiazide is commonly prescribed either on its own or in combination with medications, for the management of blood pressure, also known as hypertension.
Hydrochlorothiazide how long to work?
Hydrochlorothiazide typically takes effect in your system within two to four hours after ingestion.
How hydrochlorothiazide cause hyperglycemia?
Taking Hydrochlorothiazide (commonly known as HCTZ), a type of thiazide diuretic, may lead to increased blood sugar levels by affecting how the body processes glucose and secretes insulin.
Can hydrochlorothiazide cause weight gain?
Yes
Can hydrochlorothiazide cause dehydration?
Hydrochlorothiazide may lead to a lowering of blood pressure and dehydration due to water loss from the body.
Can hydrochlorothiazide cause low potassium?
Hydrochlorothiazide has the potential to reduce your levels, and combining it with corticosteroids may lead to electrolyte loss, particularly potassium.
Can hydrochlorothiazide cause gout?
Some individuals may experience acid or gout levels as a result of the way HCTC interacts with the renal elimination of uric acid through the organic anion transporter. 2.
Are hydrochlorothiazide and hydralazine the same?
Hydralazine functions, as a vasodilator, by relaxing blood vessels to expand them (known as dilation). Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) on the other hand acts as a thiazide diuretic (commonly referred to as a water pill) operating within the kidneys to eliminate water from the body thereby reducing blood pressure and reducing swelling.