Depo-provera Injection
- Introduction
- Uses of Depo-Provera Injection
- How Depo-Provera Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition of Depo-Provera
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Side Effects of Depo-Provera
- Common Side Effects
- Interaction with Other Medications
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Precautions for Specific Populations
- Important Precautions
- Overdosage and Management
- Clinical Guidelines for Careful Administration
- Handling and Safety Measures
Introduction
Overview of Depo-Provera
Depot Provera is a known birth control method that includes medroxyprogesterone acetate—a synthetic form of progestin—as its active ingredient. This option serves as an alternative to having to remember to take a pill for contraception by offering effective birth control that lasts for three months with just a single shot. It plays a role in enabling individuals to take charge of their well-being efficiently.
Historical Development and Approval Timeline
Depot Prover was initially authorized by the FDA in 1992 for birth control purposes. Its roots can be traced back to the 1960s when it was created for hormonal balance regulation reasons. The usage of Depot Prover has evolved over time to encompass more than just contraception treatment options due to advancements in research and its continual importance in womens health care.
Key Benefits and Role in Medical Treatments
- Convenient, long-lasting contraception
- Reduction in menstrual-related symptoms such as dysmenorrhea
- Potential therapeutic benefits for specific medical conditions
Uses of Depo-Provera Injection
FDA-Approved Uses
- Contraception: A reliable, reversible method of preventing pregnancy.
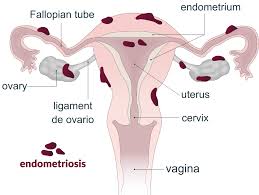
- Endometriosis Management: Alleviates pain and suppresses the growth of endometrial tissue.
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Controls excessive or irregular bleeding.
- Endometrial Hyperplasia Prevention: Used in postmenopausal women undergoing estrogen therapy.
Off-Label Uses
- Management of hormone-sensitive malignancies, such as breast cancer
- Suppression of menstruation for specific medical or personal circumstances
- Treatment of androgenic disorders, including hirsutism and polycystic ovary syndrome
How Depo-Provera Works
Mechanism of Action in Contraception
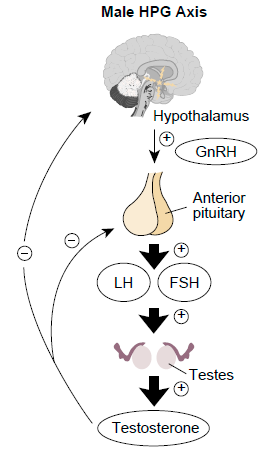
Depro Provera works by stopping ovulation from happening so that no egg is released for fertilization. This is done by reducing the secretion of gonadotropins.
Effect on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian Axis
The medicine interrupts the communication of hormones between the hypothalamus and ovaries to stop the process necessary for ovulation and menstrual cycles.
Influence on Uterine Lining and Cervical Mucus
Changes are triggered in the lining of the uterus, which reduces its readiness for implantation while also thickening mucus to create a barrier against sperm entry.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Contraception
The typical dosage for birth control involves receiving a 150 mg injection in the muscle every 12 weeks, and it's important to stick to the schedule for it to work effectively.
Dosage Guidelines for Other Approved and Off-Label Uses
Dosages can differ depending on the condition being addressed, with healthcare professionals adjusting regimens accordingly.
Injection Schedule and Administration Techniques
- Administered in the gluteal or deltoid muscle
- Professional supervision is recommended for accurate administration
Importance of Adhering to the Injection Timeline
It's crucial to stick to a schedule of injections every 12 weeks to maintain contraceptive coverage and therapeutic advantages.
Composition of Depo-Provera
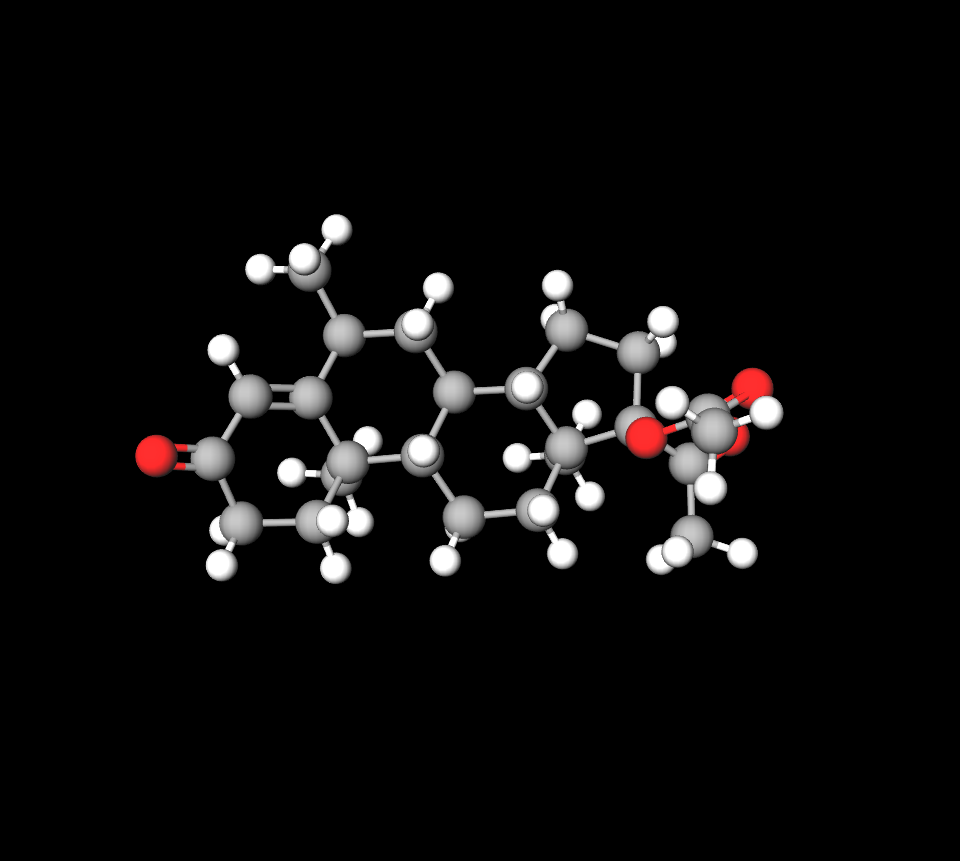
Active Ingredient: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
This man-made progestin imitates the effects of progesterone to support its contraceptive and healing functions.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Roles
The mixture contains substances that keep the solution stable and improve its absorption in the body, ensuring its effectiveness.
Formulation Details
Depot Proverais is offered in a crafted liquid form for injection into muscles.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
Remember to keep the vial in a place at room temperature (15 to 30 degrees Celsius) away from freezing temperatures and direct sunlight.
Shelf Life and Expiration Considerations
Check the expiration date before using and properly dispose of any expired items.
Safe Handling and Disposal
- Remember to dispose of needles in a sharps container.
- Please refrain from touching the product with your skin or eyes.
Side Effects of Depo-Provera
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Categorization
- Mild: Nausea, minor headaches, or spotting
- Moderate: Prolonged amenorrhea, mood swings
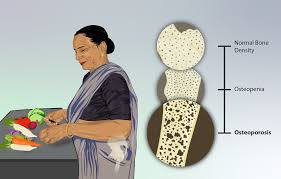
- Severe: Significant weight changes, bone density reduction
Common Side Effects
- Irregular menstrual cycles or complete cessation
- Weight fluctuations
- Frequent headaches or fatigue
- Emotional disturbances, such as irritability or depression
Interaction with Other Medications
Drugs That May Reduce Efficacy
Medications such as rifampin and certain anticonvulsants can diminish the contraceptive effectiveness of Depo-Provera.
Potential Interactions with Anticoagulants and Corticosteroids
Using these drugs together could change how well they work or how safe they are for you; it's important to keep an eye on them.
Risk of Adverse Effects When Combined with Herbal Supplements
St. Johns Wort might affect how it works in your body.
Warnings and Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
- Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy
- Active thromboembolic disorders
- Diagnosis of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast cancer

Relative Contraindications and Conditions Requiring Caution
- History of cardiovascular disease
- Severe liver dysfunction
- Uncontrolled hypertension
Precautions for Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients: Risks and Considerations
The use of Depo-Provera in elderly individuals warrants careful evaluation. While hormonal contraceptives are rarely indicated in this population, certain off-label uses may apply. Aging-related factors, such as diminished renal and hepatic function, necessitate dosage adjustments and vigilant monitoring to mitigate adverse effects. The increased risk of thromboembolic events in older patients further underscores the importance of individualized treatment plans.
Use in Pregnant Women: Potential Fetal Risks and Teratogenic Effects
Depo-Provera is contraindicated during pregnancy due to potential teratogenic effects. Exposure to medroxyprogesterone acetate during gestation has been associated with fetal anomalies, although rare. Healthcare providers should confirm the absence of pregnancy before initiating treatment and advise patients to report any suspected pregnancies promptly.
Administration to Nursing Mothers: Impact on Lactation and Infant Health
Depo-Provera is generally considered compatible with breastfeeding. Its progestin component has minimal impact on milk production and composition. However, small amounts of the drug may be excreted into breast milk. Healthcare providers should evaluate the benefits versus potential risks, particularly in mothers of preterm or low-birth-weight infants.
Safety Profile in Pediatric Populations
Depot Provera is sometimes given to teenagers for birth control and to manage menstrual flow issues, and it works well. However, there are worries about how it affects bone strength if used for a long time in young people. Monitor regularly. Make sure to take calcium and vitamin D supplements to reduce this risk.
Important Precautions
Long-Term Use and Risk of Bone Density Loss
Prolonged use of Depo Provera can lead to a reduction in bone mineral density among individuals younger than 25 years old, with this impact partially reversible upon discontinuing the medication regimen. Healthcare professionals are advised to restrict the duration of treatment whenever feasible and suggest lifestyle adjustments, like engaging in weight-bearing activities and consuming calcium-rich foods, to mitigate bone weakening.
Monitoring for Signs of Thromboembolism
Patients using Depo-Provera should be advised to report symptoms suggestive of thromboembolic events, such as sudden leg swelling, dyspnea, or severe headaches. Regular clinical evaluations can aid in early detection and prevention of complications.
Importance of Patient Education on Potential Side Effects
Informing patients about serious side effects can improve compliance and prompt reporting of reactions. It is important to talk about changes in weight or mood and irregularities in cycles during counseling sessions to help patients understand what to expect from their treatment outcomes effectively.
Overdosage and Management
Symptoms of Overdose
An excessive amount of Depro Prover is uncommon. It might show up as feelings of sickness or lightheadedness, and hormonal imbalances, like an extended absence of periods, appear in rare cases. Severe instances could result in bodily effects that demand urgent medical intervention.
Emergency Response and Treatment Options
When someone overdoses on a substance by mistake or accidentally takes medication, the main approach to treatment focuses on managing symptoms by providing supportive care. This includes ensuring the person stays hydrated and monitoring their signs closely. If you suspect someone has overdosed unintentionally, it is vital to reach out to poison control or seek attention.
Long-Term Health Implications of Overdose
While acute toxicity is uncommon, prolonged excessive dosing could exacerbate risks such as osteoporosis or thromboembolic events. Patients should undergo follow-ups to address any lingering health concerns.
Clinical Guidelines for Careful Administration
Screening for Medical History and Contraindications
Before starting Depro Proverra treatment, it's important to undergo screening that covers cardiovascular health assessment as well as checking for any history of cancer or current liver and kidney conditions to reduce potential risks related to the therapy.
Periodic Follow-Ups and Monitoring During Use
Healthcare providers often conduct check-ins to track side effects and ensure patients are sticking to their injection schedules while also addressing any worries they might have. The need for bone density scans and metabolic assessments may arise for individuals who use the medication over a period of time.
Transitioning Off Depo-Provera and Alternative Options
Stopping the use of Depro Prover requires consideration to avoid pregnancies and address any withdrawal symptoms effectively. It's important to discuss birth control options, like birth control pills or intrauterine devices, with patients based on their health needs.
Handling and Safety Measures
Protocols for Healthcare Providers Handling the Injection
Following hygiene procedures when preparing and giving injections lowers the chances of infections. Sticking to safety guidelines set by the institution helps keep both patients and healthcare workers safe.
Preventing Accidental Needle Injuries
Utilizing safety-enhanced syringes to reduce the risk of exposure. Prompt disposal of used needles in specified sharps disposal units. Training sessions for staff regarding the handling of needles and protocols for responding to injuries.
Patient Instructions for Proper Post-Injection Care
Patients should be instructed to monitor the area where the injection was given for redness or swelling and refrain from engaging in activities that involve that area for a day to avoid any issues arising.
Depo-provera Injection FAQ
- Will depo provera stop my period?
- Will depo provera affect a pregnancy?
- Why is depo provera dangerous?
- Why depo provera causes bleeding?
- Why depo provera is bad?
- Who should not take depo provera?
- Who uses depo provera?
- Where to inject depo provera?
- Where is depo provera administered?
- When is depo provera effective?
- When does depo provera start working?
- When depo provera starts working?
- When depo provera wears off?
- What is depo provera effectiveness?
- What does depo provera contain?
- What depo provera effect side?
- How often depo provera given?
- How depo provera is administered?
- How depo provera prevent pregnancy?
- How depo provera works?
- Can depo provera cause pcos?
- Can depo provera cause hair loss?
- Can depo provera cause blood clots?
- Can depo provera cause endometriosis?
- Can depo provera cause cancer?
- Can depo provera cause infertility?
- Are depo provera?
Will depo provera stop my period?
After receiving two to three injections of the medication, numerous women may cease having periods as the lining does not develop at all.
Will depo provera affect a pregnancy?
No negative impact on the growth of the baby has been observed when Depro Prover is administered to a woman or in the scenario where a woman conceives despite receiving the injection.
Why is depo provera dangerous?
The FDA recently cautioned women about the risk of bone density loss associated with the use of Depro Proveran, highlighting it with a boxed warning.
Why depo provera causes bleeding?
Depot Prover aims to prevent pregnancy by administering a hormone shot. However, it may lead to bleeding due to its progestin content, which may disrupt the body's hormone balance.
Why depo provera is bad?
Depot Provers drawbacks may involve gaining weight and experiencing bleeding, along with bone density reduction.
Who should not take depo provera?
Depot Prover is not recommended for women dealing with the following conditions: Bleeding disorders or using blood thinning medications, unexplained abnormal bleeding, or a history of types of cancer.
Who uses depo provera?
Depot Prover is an injection for birth control that's generally safe for use by women without major health issues.
Where to inject depo provera?
The vaccine can be administered into the deltoid muscle, in the arm, or the gluteal muscle, in the buttocks.
Where is depo provera administered?
The injection is administered into a muscle, the arm, or the buttocks.
When is depo provera effective?
Depot Provera is effective when you receive the injection within the first five days of your menstrual cycle, showing immediate efficacy.
When does depo provera start working?
Right away if you receive it during the five days of your cycle.
When depo provera starts working?
To get the injection to work away after receiving it within the five days of your period; however, if you get it at any other time, it will take about a week to start working.
When depo provera wears off?
15 weeks
What is depo provera effectiveness?
96%
What does depo provera contain?
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
What depo provera effect side?
Nausea, bloating, headache, changes in appetite, weight gain, tiredness, swelling, acne, hot flashes, breast tenderness, or irritation/pain at the injection site
How often depo provera given?
11-13 weeks
How depo provera is administered?
Administered either into a muscle or beneath the skin every 11 to 13 weeks.
How depo provera prevent pregnancy?
Depot Prover prevents pregnancy by halting the ovary's egg release and creating obstacles for sperm to reach an egg.
How depo provera works?
When a woman uses Depro Proverne (birth control injection), her body detects the hormone's presence and stops producing hormones. The ovaries do not release an egg due to this process, which helps prevent pregnancy.
Can depo provera cause pcos?
Depot Provera (the contraceptive injection shot), contrary to belief, does not lead to the development of ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Can depo provera cause hair loss?
Only about 5 out of every 100 women using the depо shot may notice hair thinning or a lack of hair growth.
Can depo provera cause blood clots?
Depo Provera can indeed lead to the formation of blood clots; however, the likelihood of this occurring is relatively low.
Can depo provera cause endometriosis?
Depo Provera is also expected to lower the chances of developing cancer and endometrial (uterine} cancer well as potentially reducing the likelihood of endometriosis and pelvic infections.
Can depo provera cause cancer?
Depo-Provera would raise the likelihood of breast or cervical cancer occurrence.
Can depo provera cause infertility?
Depo Provera does not lead to long-term fertility issues.
Are depo provera?
Depo Provera is an injection for birth control that relies on the hormone medroxyprogesterone acetate, a type of progesterone that the body naturally produces during a woman's menstrual cycle.