Deticene Injection
- Introduction to Deticene Injection
- Composition of Deticene Injection
- Uses of Deticene Injection
- Dacarbazine mechanism of action
- Dosage and Administration of Deticene Injection
- Dacarbazine side effects
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications of Deticene Injection
- Special Considerations for Administration
- Drug Interactions with Deticene Injection
- Overdosage and Management
- Storage and Handling of Deticene Injection
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Deticene Injection
Overview of Deticene Injection
Deticene Injection is a specialized pharmaceutical product primarily used to treat certain types of cancer. Its mechanism targets malignant cells, disrupting their ability to grow and increase. Deticene is renowned for its efficacy in specific clinical scenarios, making it a cornerstone in advanced oncology therapies.
History and Development of Deticene
Developing over years within cancer research initiatives Deticene symbolizes a culmination of drug creation efforts. The creation of this medication was guided by the necessity, for treatments that could reduce systemic toxicity while increasing effectiveness in combating cancerous cells.
Therapeutic Classification of Deticene
Deticene is considered as one of the drugs that fall under the category of medications. This classification emphasizes its role in stopping the division of cancer cells—a characteristic that makes it valuable for treating cancer patients.
Composition of Deticene Injection
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
Deticene Injection contains dacarbazine as its component—a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor that disrupts DNA methylation for the survival of cancer cells.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
The formulation consists of stabilizers and buffering agents along, with solubilizers to improve drug stability and compatibility, for patients while ensuring the effectiveness of the compound remains intact.
Available Strengths and Formulations
- Deticene is typically available in single-dose vials.
- Strengths include 50 mg and 100 mg per vial.
- Designed for reconstitution prior to intravenous administration.
Uses of Deticene Injection
Approved Therapeutic Uses
The FDA has authorized the use of Deticene to treat myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and other types of blood cancers that demand precise treatment approaches, an area where Deticene proves to be particularly effective.
Treatment of Specific Cancers
Deticene plays a pivotal role in managing acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), particularly in patients unable to tolerate intensive chemotherapy regimens.
Role in Hematologic Malignancies
Its efficacy in modulating abnormal hematopoiesis has positioned Deticene as an indispensable agent in treating bone marrow disorders characterized by dysplasia and ineffective blood cell production.
Off-Label Uses
Emerging Applications in Non-Cancer Conditions
Recent research has explored Deticene's utility in conditions like sickle cell anemia and autoimmune disorders due to its immunomodulatory properties.
Experimental Applications in Clinical Trials
Ongoing studies investigate Deticene's potential in epigenetic therapy for solid tumors, underscoring its versatility in oncology.
Dacarbazine mechanism of action
Mechanism of Action at the Cellular Level
Deticene inhibits DNA methyltransferase enzymes, resulting in DNA hypomethylation. This action reactivates tumor suppressor genes, curbing cancer cell growth.

Dacarbazine chemotherapy
While primarily targeting rapidly dividing cells, Deticene's effects on healthy cells are minimized through precise dosing regimens reducing systemic adverse effects.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
Deticene demonstrates rapid systemic absorption upon intravenous administration with a short half-life necessitating controlled infusion protocols.
Dosage and Administration of Deticene Injection
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Approved Uses
Typical regimens involve daily administration for five consecutive days followed by a rest period as part of a 28-day cycle.
Dosage Modifications for Specific Populations
- Elderly Patients: Age-related physiological changes require careful dose adjustments to balance efficacy and tolerability.
- Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Reduced clearance rates necessitate lower doses to avoid drug accumulation and toxicity.
Administration Protocols and Techniques
Hospitals usually give Deticene through an IV drip for about 1 to 2 hours in a environment.
Missed Dose Management
In case a dose is forgotten tey consulting a healthcare provider is important to avoid any interruptions, in the treatment plan.
Dacarbazine side effects
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Symptoms such as nausea and stomach pain can be treated with measures and changes in the diet.
Hematologic Abnormalities
Serious Side Effects and Long-Term Implications
Uncommon serious responses may involve neutropenia and opportunistic infections, highlighting the importance of timely intervention in such situations.
Reporting Adverse Reactions
Healthcare professionals are advised to record and disclose any reactions to pharmacovigilance systems for safety monitoring purposes.
Warnings and Precautions
Key Warnings for Safe Use
Patients who have previously experienced hypersensitivity reactions to decitabine are advised to steer clear of Deticene due to the risks of developing malignancies, with prolonged use needing careful consideration.

Precautionary Measures During Treatment
In advance, it's crucial to check blood counts and organ function to prevent any possible complications.
Risks Associated with Prolonged Use
Prolonged contact could lead to a buildup of effects in the body over time, such as decreased bone marrow function that may require medical monitoring.
Contraindications of Deticene Injection
Absolute Contraindications
- Severe hypersensitivity to any component of Deticene.
- Pregnancy due to teratogenic risks.
Relative Contraindications Requiring Risk Assessment
Patients with severe hepatic or renal impairment, uncontrolled infections, or significant comorbidities should undergo thorough evaluation before initiating therapy.
Special Considerations for Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
Deticene Injection requires meticulous consideration when administered to elderly patients. Advanced age often correlates with diminished physiological reserves and comorbidities, necessitating tailored dosage regimens. While the therapeutic benefits remain significant, risks such as heightened myelosuppression or organ toxicity demand vigilance.
Age-Specific Risks and Benefits
- Risks: Increased susceptibility to side effects, including hematologic toxicity and infection.
- Benefits: Improved quality of life in managing hematologic malignancies with careful monitoring.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The use of Deticene Injection during pregnancy is contraindicated due to its teratogenic potential. Exposure can lead to severe fetal harm, including congenital anomalies or miscarriage. For nursing mothers, the excretion of Deticene in breast milk remains unverified, but precautions should be taken to avoid potential neonatal exposure.

Risks to the Fetus and Breastfeeding Safety
- Fetal Risks: Teratogenicity and embryotoxicity.
- Breastfeeding Risks: Potential unknown transfer through lactation necessitates cessation of breastfeeding during treatment.
Administration to Children
In pediatric patients, Deticene usage is rare and limited to specific clinical scenarios, often under investigational protocols. Proper dosing is calculated based on body surface area (BSA), ensuring optimal therapeutic levels while minimizing risks.
Pediatric Dosage Guidelines and Safety Considerations
- Dosage: Determined on a case-by-case basis, with frequent monitoring of hematologic parameters.
- Safety Considerations: Potential for developmental interference, necessitating stringent follow-up protocols.
Drug Interactions with Deticene Injection
Common Drug Interactions and Their Impact
Concurrent use of Deticene with other myelosuppressive agents can amplify adverse hematologic effects. Drugs affecting hepatic enzyme systems may alter Deticene metabolism, leading to suboptimal or toxic plasma levels.
Interaction with Over-the-Counter Medications
OTC medications, particularly NSAIDs and antacids, may interact with Deticene, potentially increasing gastrointestinal irritation or interfering with its absorption.
Food and Supplement Interactions
No significant food interactions have been documented; however, caution is advised when consuming supplements that affect liver function or hematologic parameters, such as vitamin K antagonists or iron supplements.
Overdosage and Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Overdosage with Deticene may manifest as severe myelosuppression, profound fatigue, febrile episodes, or gastrointestinal distress. Early recognition of symptoms is critical to mitigating complications.
Immediate Actions and Supportive Care Measures
- Discontinue Deticene immediately.
- Provide supportive care, including hydration, electrolyte management, and blood transfusions as needed.
Antidotes and Specific Interventions
No specific antidote for Deticene exists. Treatment focuses on symptomatic management and prevention of complications, such as infections or hemorrhage.
Storage and Handling of Deticene Injection
Recommended Storage Conditions
Deticene Injection should be stored at controlled room temperature (20-25°C), protected from light and moisture. Reconstituted solutions must be used promptly or stored according to the manufacturer's guidelines.
Shelf Life and Expiration Considerations
- Unopened vials remain stable until the expiration date.
- Reconstituted solutions must be used within a specified time frame to ensure potency.
Proper Handling and Disposal Procedures
Handling requires compliance with cytotoxic drug protocols. Unused or expired Deticene must be disposed of according to hazardous waste regulations to prevent environmental contamination.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Protective Measures During Preparation and Administration
Healthcare professionals must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, gowns, and eye protection, to minimize exposure during preparation and administration.
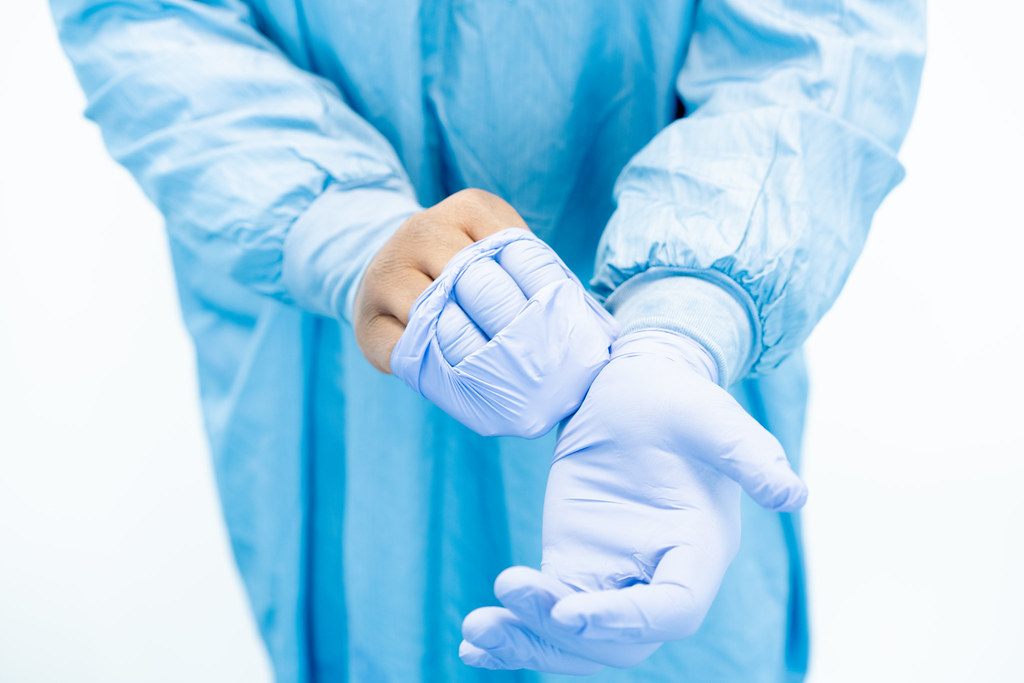

Preventing Exposure and Contamination Risks
- Work in designated areas equipped with biosafety cabinets.
- Employ closed-system drug transfer devices (CSTDs) to reduce aerosolization risks.
- Immediately clean any spills using approved cytotoxic spill kits.









