Dorzolamide Ophthalmic
I. Introduction to Dorzolamide Ophthalmic
Dorzolamide Ophthalmic is a medication mainly used to treat eye conditions like glaucoma. By reducing intraocular pressure, this medicine plays a vital role in helping patients avoid progressive vision loss. Thanks to its effectiveness in preventing the effects of untreated eye disorders, the importance of Dorzolamide in managing eye conditions is significant.
II. Composition of Dorzolamide Ophthalmic
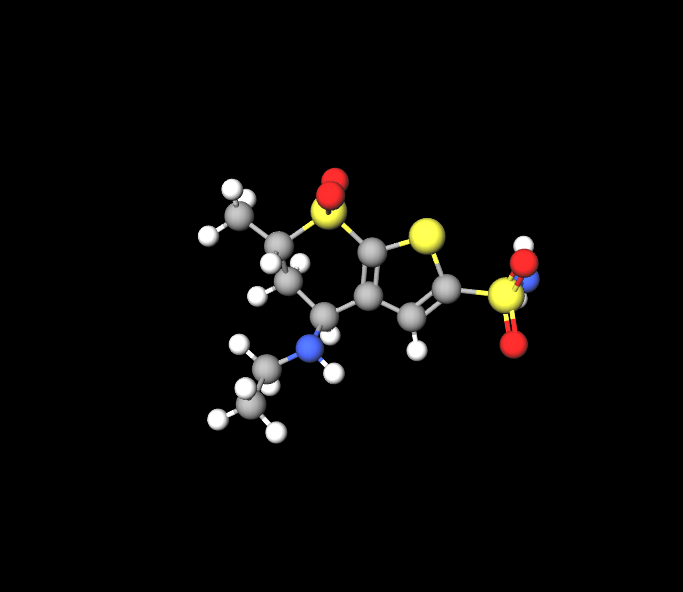
The Dorzolamide Ophthalmic formulation contains an active substance called dorzolamide hydrochloride, which plays a key role in reducing aqueous humor production. This decrease in assists in effectively managing intraocular pressure. In addition to the ingredient the solution also contains several excipients, like hydroxyethyl cellulose, mannitol and sodium citrate. These additional components help to regulate the pH and osmolarity of the solution maintaining its stability and effectiveness.
III. How Dorzolamide Works
Dorzolamide mainly decreases pressure inside the eye by inhibiting the anhydrase enzyme in the ciliary processes. This leads to a reduction in the production of humor, ultimately lowering eye pressure. Additionally, it helps improve drainage from the eye, which assists in further reducing pressure and protecting the optic nerves' health, which is crucial for sustaining visual capabilities.
IV. Uses of Dorzolamide Ophthalmic
Dorzolamide Ophthalmic is a medication commonly used for the treatment of glaucoma, particularly open-angle glaucoma, and in cases where other medications have not adequately controlled intraocular pressure. It is notably effective in addressing elevated intraocular pressures, which is a prevalent issue among individuals with ocular hypertension1.
V. Off-label Uses of Dorzolamide
While researchers have explored potential uses beyond glaucoma treatment, such as treating cystoid macular edema and secondary glaucoma, further research is necessary to establish robust clinical support for these applications1.
Dorzolamide for dogs
While its primary use is in humans, veterinarians prescribe it for pets, including cats, dogs, and horses, to manage glaucoma. However, this use is considered off-label or extra-label1234.

VI. Dosage and Administration
The right amount of Dorzolamide Ophthalmic to use depends on how serious and what kind of eye condition you have. Normally, you should put one drop in the affected eye(s) three times a day.
- How to Use: You use this medicine as an eye drop, so it's important to be clean and accurate to prevent any contamination.
- Tips for Using: It's recommended that patients not let the dropper touch the eye directly and wait around five minutes before using any eye medication.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and Timolol maleate
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol eye drops are prescribed to reduce elevated eye pressure in individuals diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension when a beta blocker medication alone is ineffective in managing the eye pressure.
Drinzolamide vs Dorzolamide
In summary, when it comes to lowering pressure, using brinzolamide 1% twice a day showed similar results to dorzolamide 2% twice a day alongside timolol 0.5% twice a day. However, brinzolamide caused less discomfort in the eyes compared to dorzolamide.
VII. Side Effects of Dorzolamide
Common side effects of Dorzolamide may include a sensation of stinging or burning when applied, some discomfort in the eyes, and slightly blurred vision. These effects are usually mild and short-lived. Addressing these side effects often involves educating the patient on the way to administer the medication and providing reassurance that these symptoms tend to improve as the body gets used to the medicine.
Long-term side effects of Dorzolamide
Occasional blurred vision, sensations of burning, stinging, itching, or redness in the eyes, teary eyes, dryness of the eyes, heightened sensitivity to light, a bitter taste in the mouth, or a headache.
VIII. Important Precautions When Using Dorzolamide
Before starting treatment with Dorzolamide Eye Drops, it's vital to assess the patient's eye health and any other health conditions that could affect the treatment results.
Selecting the patients and evaluating individual risks are crucial steps. Monitoring is important; eye exams, checking eye pressure, and visual field tests are necessary to adjust treatment and ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Due to the serious side effects of Dorzolamide Hydrochloride and Timolol Maleate Eye Drops without preservatives on nursing babies, a decision must be made whether to stop breastfeeding or discontinue the medication, considering how important it is for the mother.
IX. Contraindications for Dorzolamide Use
Patients who are known to be sensitive to dorzolamide hydrochloride or other sulfonamides should avoid using it. Additionally, individuals with renal impairment or chronic renal conditions should refrain from using it to reduce the chances of experiencing systemic side effects.
X. Careful Administration Considerations
Extra caution is needed when giving Dorzolamide to groups. These groups consist of individuals with weakened health or a background of kidney issues. It's important to make dosage changes according to each person's reaction and any other health conditions they may have. Regularly checking for how it works and any adverse effects is advised.
XI. Interactions with Other Medications
When taking Dorzolamide, it's important to be aware of how it can interact with medications, which might change their effects or make side effects worse.
- One should especially avoid combining it with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and high-dose salicylates to prevent additional systemic effects such as metabolic acidosis.
- To stay safe, it's recommended to discuss all the medications you're taking with your healthcare provider and keep an eye out for any symptoms.
Dorzolamide Alternative
- Timolol eye drops,
- Xalatan,
- Brimonidine eye drops,
- Travatan Z,
- Dorzolamide and
- timolol eye drops,
- Combigan.
XII. Administration to Special Populations
When giving Dorzolamide to groups like elderly pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children, it's important to consider individual factors.
- For elderly patients, it's crucial to manage the dosage carefully to prevent any unwanted effects from systemic absorption.
- Limited data is available for pregnant women and nursing mothers using Dorzolamide; therefore, its use should be based on weighing the potential benefits against potential risks to the baby.
- As for children, there is still uncertainty about the safety and effectiveness of Dorzolamide in patients. Hence, using it cautiously when dosing is necessary.
XIII. Handling and Storage of Dorzolamide
To keep Dorzolamide Ophthalmic effective it's important to store it Keep it at room temperature away, from light and moisture to prevent the active ingredients from breaking down.
When handling or disposing of the product make sure the container remains intact and dispose of any expired items responsibly to prevent environmental harm.
XIV. Dealing with Overdosage
An excessive intake of Dorzolamide may result in disruptions in levels and acid-base equilibrium. Symptoms of an overdose may manifest as imbalances in electrolytes, feelings of dizziness, or respiratory complications. The recommended course of action involves medical attention with a focus on providing symptomatic relief and support, which may entail monitoring and potentially adjusting electrolyte and pH levels.