Ebetaxel Injection
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Uses of Ebetaxel Injection
- 3. How Ebetaxel Injection Works
- 4. Paclitaxel dosage and Administration
- 5. Composition of Ebetaxel Injection
- 6. Storage and Handling Precautions
- 7. Paclitaxel side effects
- 8. Paclitaxel interactions
- 9. Paclitaxel warnings and Paclitaxel contraindications
- 10. Administration to Specific Populations
- 11. Overdosage and Its Management
- 12. Important Precautions
- 13. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
1. Introduction
Overview of Ebetaxel Injection
Ebetaxel Injection is commonly used in the field of oncology as a chemotherapy treatment option that works by slowing down cell division to specifically attack growing cancer cells—a choice, in cancer treatment due, to its strong effectiveness.
Classification and Therapeutic Category
Taxane drugs, like Ebetaxal, are known for their ability to stabilize microtubules and interfere with the division of cancer cells during mitosis processes in the body's fight against cancer.
Importance in Cancer Treatment
The introduction of Ebetaxel has transformed the landscape of cancer treatment by fighting against aggressive cancers such, as those affecting the breasts and ovaries as well as lung tumors; thus becoming a crucial tool in oncology practice and enhancing patient survival rates and overall well being, through tumor reduction.
FDA Approval and Global Usage
It was initially authorized by the FDA to treat breast cancer patients at a glance through its significant safety and efficacy records in various patient groups worldwide.
Paclitaxel success rates
The five year survival rates were 76% 82%, with higher rates, for those receiving weekly paclitaxel or docetaxel compared to every 3 weeks administration of these medications.
2. Uses of Ebetaxel Injection
Approved Uses
Treatment of Breast Cancer
Ebetaxel is a first-line therapy for metastatic breast cancer, often administered in combination with other agents. Its targeted action helps shrink tumors and prolong remission.
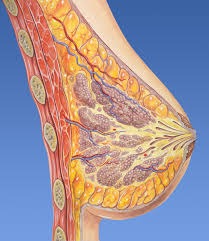
Management of Ovarian Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapy
Off-Label Uses
Treatment of Gastric Cancer
Ebetaxel shows promise in gastric cancer management, particularly in advanced or refractory cases.
Pancreatic Cancer Management
Ebetaxel has not received approval. But has been under investigation for its potential in the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma during clinical trials.

Advanced Head and Neck Cancers
In studies on head and neck cancers, approaches have been employed to enhance survival rates for patients not responding well to treatments.
3. How Ebetaxel Injection Works
Paclitaxel mechanism of action
Ebextaxel interferes with the movement of structures within cells, known as microtubule dynamics, by making them more stable and stopping the process of cell division in its tracks during mitosis.This leads to the programmed cell death of rapidly multiplying cancer cells.
Cellular Targets and Effects on Tumor Growth
The medication focuses on attacking cancer cells by disrupting the structures that control cell division and internal transport processes. This disruption stops tumor growth and aids in causing cell death.
Impact on Healthy Cells
Although Ebetaxel mainly focuses on attacking cancer cells, it might also impact dividing cells, which could result in side effects such as neutrophilia and hair loss.
4. Paclitaxel dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages Based on Indications
Dosages vary depending on the cancer type, typically ranging from 100 to 175 mg/m² administered intravenously every three weeks.
Methods of Administration (IV Infusion Techniques)
- Administered as a slow IV infusion over 3 hours.
- Pre-medication with corticosteroids and antihistamines is essential to reduce hypersensitivity reactions.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Dosage modifications are required for patients with hepatic impairment or those experiencing severe toxicities.
Duration of Treatment Cycles
Cycles are typically repeated every 21 days, with a maximum number determined by treatment response and tolerability.
5. Composition of Ebetaxel Injection
Active Ingredients and Concentrations
Depending on the formulation, Ebetaxel contains paclitaxel, with concentrations varying from 6 mg/mL to 30 mg/mL.
Excipients and Their Roles
Excipients like Cremophor EL and ethanol stabilize the active ingredient and ensure solubility.
Packaging and Available Forms
The medication comes in vials of 5 mL, 16, ML. or 50 mL, with each designed for dosage requirements.
Nab paclitaxel
Nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane) is a chemotherapy drug that treats breast, lung, and pancreatic cancer.
Paclitaxel and carboplatin
A mixture of carboplatin and paclitaxel is frequently employed in chemotherapy to address forms of cancer such as cancer and lung cancer, among others.
Paclitaxel and trastuzumab
A treatment plan for HER2 breast cancer involves a combination of two medications, which: Paclitaxel (also known as Taxol), a type of chemotherapy drug known as a taxane, and Trastuzumab (commonly referred to as Herceptin), a form of targeted therapy categorized as a monoclonal antibody.
Abraxane vs paclitaxel
Abraxane is a version of the cancer medication paclitaxel that is combined with the protein present in the body.
Docetaxel vs paclitaxel
Docetaxel is also more potent in different cell lines and investigational models.
Paclitaxel vs taxol
Paclitaxel is the non-branded name of the drug, but you may hear it called by one of its brand names such as Taxol.
6. Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
Store at 20-25°C, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Do not freeze.
Shelf Life and Stability
The medication stays effective for two years if stored according to the guidelines.
Safety Guidelines for Handling
- Use personal protective equipment during preparation.
- Avoid direct skin contact; wash immediately if accidental exposure occurs.
7. Paclitaxel side effects
Common Side Effects
Nausea and Vomiting
Frequent but manageable with antiemetic pre-medications.
Paclitaxel hair loss
Temporary but distressing for many patients.
Neutropenia and Infections
Monitor blood counts regularly to mitigate risks.
Paclitaxel rash
Paclitaxel long-term side effects
Paclitaxel neuropathy
Often associated with feelings of tingling and numbness that may vary depending on the dosage used.
Severe Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is a condition that requires cessation of the triggering agent and the administration of appropriate care without delay.
8. Paclitaxel interactions
Potential Interactions with Chemotherapeutic Agents
When used at the time, cisplatin may cause increased toxicity; hence, it is important to monitor it.
Impact of Co-administration with Common Medications
Medications such as ketoconazole can disrupt metabolism, leading to side effects occurring.
Foods and Supplements to Avoid
Avoid grapefruit and St. John's Wort due to cytochrome P450 enzyme interference.
9. Paclitaxel warnings and Paclitaxel contraindications
Contraindications
Do not use in patients with hypersensitivity to paclitaxel or Cremophor EL. Severe hepatic impairment is also a contraindication.
Critical Warnings for Use
Keep an eye on the heart health of patients with existing health issues. Be careful when dealing with individuals who have a background of nerve problems.
Paclitaxel hypersensitivity reaction management
If a patient experiences a hypersensitivity reaction to paclitaxel, the infusion should be immediately stopped and the following steps should be taken: Administer 50 mg of diphenhydramine and 100 mg of hydrocortisone intravenouslyWait about 30 minutes for the symptoms to disappear before restarting the infusion
Monitoring Guidelines for High-Risk Patients
- Frequent CBC monitoring to detect myelosuppression.
- Regular liver function tests for those with hepatic impairment.
10. Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly Patients
Age-Related Considerations in Efficacy and Safety
Elderly patients often exhibit altered pharmacokinetics due to age-associated physiological changes. Ebetaxel Injection's efficacy remains significant in this demographic, but its safety profile may necessitate heightened vigilance. Age-related comorbidities such as cardiovascular conditions or renal impairment can influence treatment outcomes.
Dosage Modifications
Dose adjustments may be required to minimize adverse effects in older adults. Standard doses should be carefully titrated, starting at the lower end of the recommended range. Frequent monitoring for toxicity, especially myelosuppression and neuropathy, is essential.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Potential Risks to Fetus and Neonates
Use of Ebetaxel Injection during pregnancy is contraindicated unless the benefits outweigh the risks. It may cause embryotoxicity or teratogenicity due to its mechanism of interfering with cell division. Neonates exposed through maternal use may exhibit developmental complications.
Guidelines for Use in Pregnancy
Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for a recommended period afterward. In cases where treatment is imperative during pregnancy, detailed risk assessments and consultations with a multidisciplinary team are advised.
Pediatric Patients
Safety and Efficacy in Children
There isn't information available about giving Ebetaxel to kids, but it seems like children might face similar side effects as adults, albeit with a greater sensitivity to potential harm.
Dosage Recommendations
Pediatric dosing should be weight- or surface area-based, starting at reduced levels and gradually adjusted based on tolerability and response. Close monitoring for bone marrow suppression and neuropathy is crucial.
11. Overdosage and Its Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Overdose of Ebetaxel Injection can result in profound myelosuppression, severe neuropathy, mucositis, and even multi-organ dysfunction. Immediate identification of overdose symptoms, such as extreme fatigue, bleeding, or neurological changes, is critical.
Emergency Treatment Protocols
- Discontinue the infusion immediately.
- Initiate supportive therapy, including granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) for myelosuppression.
- Monitor vital signs and organ functions continuously in a critical care setting.
Role of Supportive Care
Supportive care, such as hydration therapy and electrolyte management, is vital in mitigating complications. Pain management and treatment of secondary infections are integral to recovery.

12. Important Precautions
Pre-Treatment Screening and Assessments
Patients should undergo comprehensive assessments before initiating treatment. Baseline blood counts, liver function tests, and cardiac evaluations are necessary to identify potential contraindications or risks.
Paclitaxel premedication
The current recommendation for premedication before paclitaxel use consists of dexamethasone 20 mg orally (PO) administered approximately 12 and 6 hours before paclitaxel, diphenhydramine (or its equivalent) 50 mg intravenous (I.V.) 30â60 min before paclitaxel, and cimetidine (300 mg) or ranitidine (50 mg) I.V.
Management of Known Risk Factors
Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes or peripheral neuropathy should be managed proactively to minimize exacerbation during therapy. Dose reductions or alternate regimens may be considered in high-risk cases.
Paclitaxel toxicity
This medication can cause liver toxicity, which your oncology care team may monitor for using blood tests called liver function tests. Notify your healthcare provider if you notice yellowing of the skin or eyes, your urine appears dark or brown, or you have pain in your abdomen, as these can be signs of liver toxicity.
Patient Education on Drug Use
- Inform patients about potential side effects and the importance of timely reporting.
- Educate on dietary restrictions and medication interactions.
- Provide guidance on recognizing symptoms of toxicity or allergic reactions.
13. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
Safety Guidelines for Preparation
Healthcare professionals must use personal protective equipment (PPE) when preparing Ebetaxel Injection. Preparation should occur in a designated biosafety cabinet to minimize aerosol exposure and contamination.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Dispose of unused or expired vials in compliance with local hazardous waste protocols. Incineration is often recommended for cytotoxic drugs.
Protective Measures to Avoid Exposure
- Wear gloves, masks, and protective gowns during handling.
- Use closed-system drug-transfer devices (CSTDs) to prevent spills and leaks.
- Wash thoroughly with soap and water if accidental skin contact occurs.
Ebetaxel Injection FAQ
- What is paclitaxel?
- How paclitaxel works?
- Is paclitaxel chemotherapy?
- What is paclitaxel used for?
- Why is carboplatin and paclitaxel given together?
- How is paclitaxel administered?
- Why is paclitaxel given before carboplatin?
- Does paclitaxel cause hair loss?
- How does paclitaxel work?
- How is paclitaxel useful as a cancer treatment?
- Who discovered paclitaxel?
- What does paclitaxel do?
- What is the life expectancy of paclitaxel patients?
- Which checkpoint in the cell cycle is affected by paclitaxel?
- What causes paclitaxel hypersensitivity?
- When was paclitaxel discovered?
- How long does paclitaxel stay in your system?
- How does paclitaxel inhibit the growth of cancer?
- What is the most concerning side effect of paclitaxel?
- Which treatment would paclitaxel be considered?
- What is the difference between paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel?
- What kind of chemo is paclitaxel?
- Why is paclitaxel given weekly?
- What is paclitaxel?
- How paclitaxel works?
- Is paclitaxel chemotherapy?
- What is paclitaxel used for?
- Why is carboplatin and paclitaxel given together?
- How is paclitaxel administered?
- Why is paclitaxel given before carboplatin?
- Does paclitaxel cause hair loss?
- How does paclitaxel work?
- How is paclitaxel useful as a cancer treatment?
- Who discovered paclitaxel?
- What does paclitaxel do?
- What is the life expectancy of paclitaxel patients?
- Which checkpoint in the cell cycle is affected by paclitaxel?
- What causes paclitaxel hypersensitivity?
- When was paclitaxel discovered?
- How long does paclitaxel stay in your system?
- How does paclitaxel inhibit the growth of cancer?
- What is the most concerning side effect of paclitaxel?
- Which treatment would paclitaxel be considered?
- What is the difference between paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel?
- What kind of chemo is paclitaxel?
- Why is paclitaxel given weekly?
What is paclitaxel?
Paclitaxel belongs to a class of chemotherapy drugs known as taxanes that hinder the growth and division of cancer cells by obstructing cell division.
How paclitaxel works?
Taxol or Paclitaxel is a medication used in chemotherapy to inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells by disrupting the microtubules that support the cells.
Is paclitaxel chemotherapy?
Yes
What is paclitaxel used for?
It addresses forms of cancer such as cancer and breast cancer as well as lung cancer.
Why is carboplatin and paclitaxel given together?
This chemotherapy blend includes carboplatin and paclitaxel (Taxol). Combining drugs is often more effective than using them since each drug targets cancer cells differently.
How is paclitaxel administered?
You will receive this medication through an infusion administered by a healthcare provider in a hospital or clinic.
Why is paclitaxel given before carboplatin?
Administering paclitaxel prior, to carboplatin is crucial to avoid any interference with the effects of paclitaxel, on arrest and apoptotic cell death caused by carboplatin.
Does paclitaxel cause hair loss?
Paclitaxel causes hair loss
How does paclitaxel work?
Paclitaxel functions, by inhibiting the division of cancer cells preventing them from forming cells and impeding the progression of the disease.
How is paclitaxel useful as a cancer treatment?
It aims at multiplying cells such as those found in cancer and induces their demise.
Who discovered paclitaxel?
Monroe E. Wall and Mansukh C. Wani
What does paclitaxel do?
Paclitaxel functions by preventing cancer cells from dividing into two cells.
What is the life expectancy of paclitaxel patients?
17.3 months
Which checkpoint in the cell cycle is affected by paclitaxel?
Mitotic checkpoint
What causes paclitaxel hypersensitivity?
Cremophor, which is utilized as a solvent for paclitaxel, comes second in importance.
When was paclitaxel discovered?
1971
How long does paclitaxel stay in your system?
Between 3–53 hours
How does paclitaxel inhibit the growth of cancer?
Paclitaxel is a type of chemotherapy medication called Taxol. It works by stopping cancer cells from multiplying and forming cells.
What is the most concerning side effect of paclitaxel?
A healthcare professional should check constant nausea and vomiting that persist without relief. Look out for symptoms of anemia, like fatigue or pale skin. Be alert for bruising or bleeding tendencies, as well as instances of fainting and confusion. Seek advice if you experience pain or notice redness/swelling in the arms or legs. Additionally be cautious if you encounter warmth and swelling with calf pain. If you find yourself coughing up blood, it's important to seek attention.
Which treatment would paclitaxel be considered?
Paclitaxel injection is prescribed for treating stages of cancer as well as breast cancer and nonsmall cell lung cancer or Kaposi sarcoma.
What is the difference between paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel?
Nab paclitaxel consists of paclitaxel bound to albumin nanoparticles. Does not contain any solvents.
What kind of chemo is paclitaxel?
Taxanes
Why is paclitaxel given weekly?
Frequent administration of amounts could potentially be more effective than the dosing schedule every three weeks since it allows for prolonged exposure of actively dividing cancer cells to its harmful properties.
What is paclitaxel?
Paclitaxel is a taxane class of chemotherapy drugs that inhibits cell division and hinders the growth and division of cancer cells.
How paclitaxel works?
Paclitaxel, also known as Taxol, is a chemotherapy medication that works by disrupting the microtubules that support cancer cells' growth and division processes.
Is paclitaxel chemotherapy?
Yes
What is paclitaxel used for?
It addresses forms of cancer, such as cancer and breast cancer, as well as lung cancer.
Why is carboplatin and paclitaxel given together?
This specific chemotherapy mix involves the medications carboplatin and paclitaxel, also known as Taxol. These medications are used together for enhanced effectiveness compared to using a drug since each drug targets cancer cells in different ways.
How is paclitaxel administered?
You will receive this medication through an infusion administered by a healthcare provider at a hospital or clinic.
Why is paclitaxel given before carboplatin?
Carboplatin might greatly affect how paclitaxel works in stopping cell division and causing cell death unless paclitaxel is given before carboplatin.
Does paclitaxel cause hair loss?
Yes
How does paclitaxel work?
Paclitaxel functions, by inhibiting the division of cancer cells preventing them from forming two cells thereby impeding the progression of the growth.
How is paclitaxel useful as a cancer treatment?
It aims to multiply cells such as those found in cancer. Induces their demise.
Who discovered paclitaxel?
Monroe E. Wall and Mansukh C. Wani
What does paclitaxel do?
Paclitaxel functions by preventing cancer cells from dividing to form two cells.
What is the life expectancy of paclitaxel patients?
17.3 months
Which checkpoint in the cell cycle is affected by paclitaxel?
mitotic checkpoint
What causes paclitaxel hypersensitivity?
The use of Cremophor as a solvent for paclitaxel is considered secondary.
When was paclitaxel discovered?
1971
How long does paclitaxel stay in your system?
between 3–53 hours
How does paclitaxel inhibit the growth of cancer?
Taxol or Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy treatment that works by stopping cancer cells from dividing and forming new cells.
What is the most concerning side effect of paclitaxel?
Continuous. Vomiting that persists without relief; indications of anemia, like fatigue and pale complexion; frequent bruising and bleeding with ease; sudden fainting spells; mental confusion; discomfort or inflammation or weakness in the arms or legs; warmth and swelling in the calves accompanied by pain; expelling coughed up substances.
Which treatment would paclitaxel be considered?
Paclitaxel injection is prescribed for treating stages of cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and Kaposi sarcoma.
What is the difference between paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel?
Nab paclitaxel consists of paclitaxel bound to albumin in a nanoparticle form. It does not contain any solvents.
What kind of chemo is paclitaxel?
Taxanes
Why is paclitaxel given weekly?
Administering doses frequently could potentially enhance effectiveness compared to the standard regimen of doses every three weeks by ensuring continuous exposure of dividing tumor cells to its cytotoxic effects.











