Edurant, Rilpivirine
- Introduction to Edurant (Rilpivirine)
- Uses of Edurant
- How Edurant (Rilpivirine) Works
- Dosage and Administration of Edurant
- Composition of Edurant
- Storage Instructions for Edurant
- Side Effects of Edurant
- Warnings and Precautions
- Drug Interactions
- Contraindications for Edurant
- Careful Administration
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Overdosage of Edurant
- Handling Precautions
Introduction to Edurant (Rilpivirine)
Overview of Edurant
Edurant is another name for Rilpivirine. It is an antiretroviral drug used to manage HIV infections caused by the virus HIV 1 effectively in modern medical treatments. Its primary purpose is to slow down the progression of the virus. It plays a crucial part in the treatment of individuals who have not received treatment before, as it helps in controlling the viral load effectively.
Classification as a Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor (NNRTI)
Edurant is part of the group of medications known as Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs). These drugs work by focusing on the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which plays a role in the replication of HIV virus cells thereby stopping the virus progression in its stages effectively.
Approved Indications and Primary Uses
- Edurant is approved for treating HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents.
- It is typically prescribed in combination with other antiretroviral agents.
These indications underscore its pivotal role in comprehensive antiretroviral therapy regimens.
Overview of its Importance in HIV Management
The medicine's exceptional effectiveness and received tolerability are factors in managing HIV effectively, especially for maintaining viral suppression, in patients chosen carefully for treatment.
Uses of Edurant
FDA-Approved Uses of Rilpivirine
Edurant is commonly used to treat HIV type 1 infection in individuals who are new to treatment for the condition. It works best when the patient's initial viral load is equal to or than 1000 copies per milliliter.
Treatment of HIV-1 Infection in Treatment Patients
For individuals who have recently been diagnosed with HIV infection Edurant offers a choice especially when they stick to the prescribed dosage regimen consistently.
Off-Label Uses of Rilpivirine
- Management in virologically suppressed patients switching antiretroviral regimens.
- Exploration of its role in pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), though this remains investigational.
How Edurant (Rilpivirine) Works
Mechanism of Action as a Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor
When Rilpivirine connects specifically to the reverse transcriptase enzyme, it causes it to change shape in a way that slows down its function. This stops the process of turning RNA into DNA which's crucial for HIV to reproduce.
How it Inhibits HIV Replication
Edurant works by hindering the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which in turn hampers the production of DNA and limits the virus's capability to invade host cells and replicate.

Synergistic Effects When Used in Combination Therapy
When combined with medications that fight HIV infection, Rilpivirine collaborates effectively to combat the virus at points in its life cycle, resulting in improved treatment effectiveness.
Dosage and Administration of Edurant
Recommended Standard Dosages for Adults
The usual recommended dose for Edurant in adults is 25 mg to be taken by mouth a day along with a meal.
Dosage Adjustments for Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment is required, but caution is advised.
- Hepatic Impairment: Mild to moderate hepatic impairment does not necessitate dose changes, but severe impairment lacks sufficient data for safety assurances.
Administration Guidelines
- Edurant must be taken with a meal to ensure proper absorption.
- Consistency in timing enhances therapeutic outcomes.
Missed Dose Instructions
If you forget to take a dose for over 12 hours, just skip it. Continue with your dosing routine without taking two doses at once.
Composition of Edurant
Active Ingredient: Rilpivirine Hydrochloride
Each tablet includes 25 milligrams of Rilpvirine hydrochloride as the ingredient.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Functions
The composition comprises lactose monohydrate, along with povidone and additional components that assist in maintaining the stability of tablets and enhancing absorption properties.
Available Forms and Strengths
Edurant comes in the form of tablets for daily dosages.
Odefsey vs edurant
Generally speaking, Odefsey is considered to be safer for the bones and kidneys compared to HIV treatments. Edurant is deemed safe for individuals with mild to liver and kidney conditions. The two drugs may result in side effects such as depression and liver complications.
Genvoya vs edurant
Both Genvoya and Edurant are prescribed for treating HIV infection; Genvoya comprises four drugs in a combination form. Edurant is a drug used for the same purpose.
Sustiva vs edurant
Edurant has effects on LDL cholesterol levels and overall cholesterol levels as well as triglycerides when compared with Sustiva; however, Edurant may pose risks for liver complications, particularly in individuals with a background of hepatitis B or C infection.
Truvada vs edurant
Truvada and Edurant are prescription drugs prescribed for managing HIV infection, with Truvada also being utilized for HIV prevention before exposure (PrEP). At the same time, Edurant is indicated for individuals who have not undergone treatment for HIV infection.
Cabotegravir and rilpivirine
Cabotegravir combined with rilpivirine (LA CAB/RPV), which has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and endorsed in the treatment guidelines for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), serves as a recommended approach for individuals living with HIV (PLWH). This strategy applies to those who have achieved suppression with antiretroviral therapy and do not have a prior history.
Rilpivirine class
One type of drug known as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) includes rilpirivine.
Storage Instructions for Edurant
Optimal Storage Conditions
Please keep the item in a location with room temperature ranging between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Remember to shield the item from temperatures and humidity while also keeping it away, from sunlight.

Shelf Life and Expiration Considerations
Inspect the expiration dates to guarantee that the medicine remains effective.
Handling Tips for Maintaining Efficacy
- Keep the tablets in their original container.
- Avoid exposing the medication to damp environments.
Side Effects of Edurant
Common Side Effects
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Insomnia and vivid dreams

Serious Side Effects
- Depression, mood swings, and suicidal ideation
- Hepatotoxicity, indicated by jaundice and elevated liver enzymes
- Severe dermatologic reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome
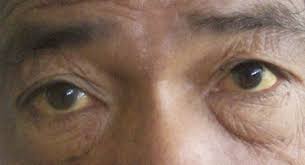
Rare but Critical Adverse Reactions
Though rare occurrences happen with hypersensitivity reactions and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), prompt medical attention may be necessary.
Warnings and Precautions
Risk of Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome (IRS), an issue linked to starting treatment like Edurant, could affect individuals with severe HIV or a low CD4 count by sparking an inflammatory reaction to latent infections as their immune system strengthens anew.

Importance of Liver Function Monitoring
It's crucial to keep an eye on liver health in individuals taking Edurant – those with existing liver issues or co-infections like hepatitis B or C. If liver enzymes are high or if there are any signs of liver problems, like jaundice showing up it's important to seek medical help right away to prevent the situation from getting worse and leading to serious liver complications.
Awareness of QT Interval Prolongation
Edurant has been associated with QT interval prolongation, particularly at supra-therapeutic doses. This effect increases the risk of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. Patients with a history of cardiac conditions or those taking other QT-prolonging medications should be managed cautiously.
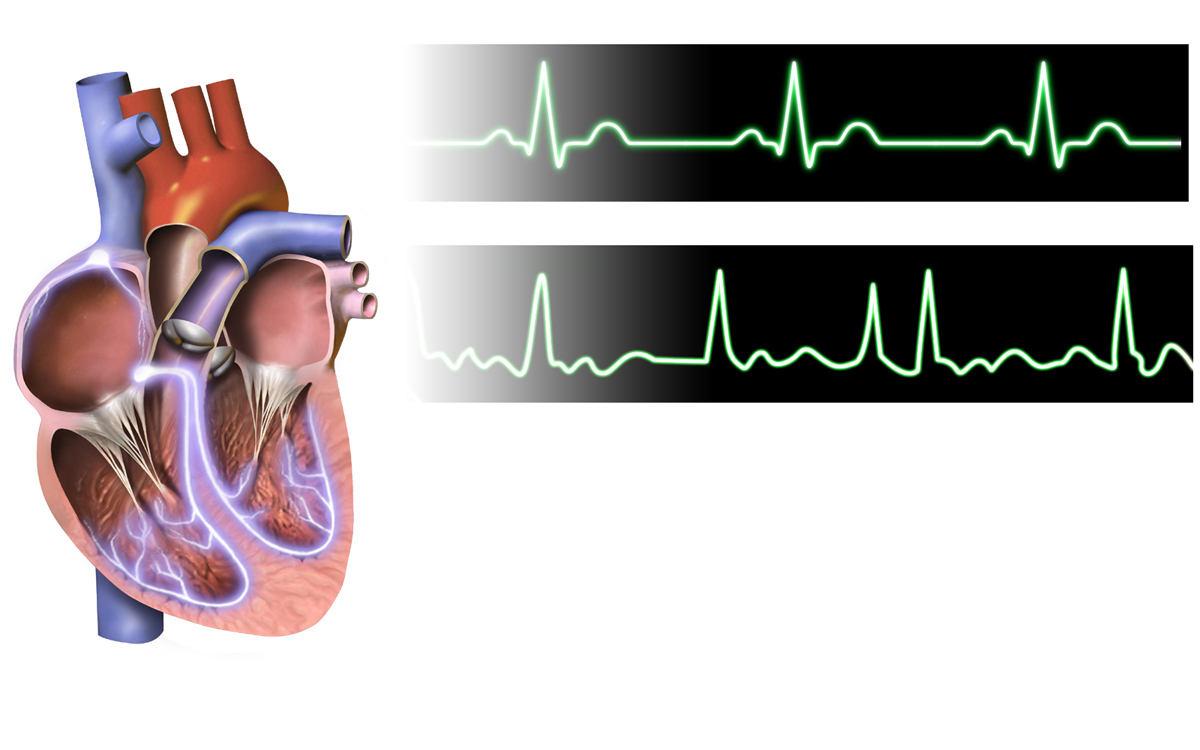
Precautions Related to Hypersensitivity Reactions
Occurring hypersensitivity reactions can present as skin rashes or fever and may even show systemic symptoms in some cases. Duly advising patients to inform healthcare providers of any signs of hypersensitivity can lead to the discontinuation of the medication.
Drug Interactions
Common Drug Interactions
Edurant shows interactions, with medications which require thorough examination of a patients medication schedule to prevent potential reduction, in effectiveness or heightened risk of side effects.
Proton Pump Inhibitors and Antacids
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and Antacids can greatly impact the absorption of Rilpivirine by changing the acidity levels in the stomach. Using them at the time is not recommended; it's better to explore treatment options instead.
Rifampin, Carbamazepine, and Other Enzyme Inducers
Avoid co-administering CYP3a inducers like rifampin and phenytoin with Rilpivirine to ensure their effectiveness as they speed up metabolism and reduce therapeutic levels.
It's important to be cautious when mixing Edurant with antiretrovirals that may have metabolic pathways to avoid potential complications or interactions between medications. It's always an idea to seek advice, from an HIV specialist when putting together a treatment plan that involves combining medications.
Impact of Herbal Supplements Like St. Johnâs Wort
St Johns Wort can cause a decrease in the plasma levels of Rilpivirine by affecting CYP enzyme activity which's essential for its metabolism Patients should be cautious, about using supplements that may impact the effectiveness of their treatment
Contraindications for Edurant
Absolute Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to Rilpivirine or any of its components.
- Co-administration with drugs such as rifampin, carbamazepine, and PPIs due to significant drug interactions.
Relative Contraindications and Considerations
Patients who have existing liver issues or a history of QT prolongation should be closely monitored before starting any treatment that involves taking medications that may interact with each other to ensure the outcome for their health.
Careful Administration
Use in Patients with a History of Depression or Psychiatric Disorders
Individuals who have previously dealt with depression or mental health issues might notice a worsening of their symptoms when using Edurant medication, so it's advised to undergo health evaluations to catch any negative psychological impacts promptly.
Careful Administration in Patients with Hepatitis Co-Infection
Having both hepatitis B or C at the time requires attention because of the risk of liver function decline and worsening over time, which could be critical for your health condition to be stable, in check with regular checkups and proactive treatment for any liver issues that may occur.
Monitoring for Signs of Resistance Development
Inadequate compliance with treatment raises the likelihood of developing resistance to Rilpivirine medication, which underscores the importance of resistance testing and thorough patient education about adherence for management.
Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly Patients
Changes in the body due to aging, like decreased kidney or liver function, can impact how Edurant works in the body of individuals. A careful observation is recommended to modify medication doses for patients.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Risks and Benefits During Pregnancy: Edurant may be used during pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Close monitoring for virologic suppression is essential.
- Rilpivirine Levels in Breast Milk and Impact on Infants: Although the transfer of Rilpivirine into breast milk is minimal, breastfeeding is generally discouraged in HIV-positive mothers to prevent transmission.

Children
Edurant is authorized for children aged 12 and above who weigh 35 kg. Dosage adjustments for weight and age in children must be meticulously adjusted according to their body weight and developmental stage.
Overdosage of Edurant
Symptoms of Rilpivirine Overdose
Symptoms of an overdose might manifest as a headache or dizziness. It could also include nausea or QT prolongation in some cases. In instances of overdose, it may lead to cardiac arrhythmias that require urgent medical intervention.
Recommended Management of Overdose
- Provide symptomatic treatment.
- Monitor vital signs and ECG to assess cardiac function.
- Activated charcoal may be administered if the overdose is detected promptly.
Role of Supportive Care and Symptomatic Treatment
Providing support and care plays a role in managing overdoses, as maintaining constant vigilance and taking timely action are essential for achieving the best results for patients.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling and Disposal of Medication
Make sure to keep the Edurant tablets in a place where children cannot access them and dispose of them properly to avoid ingestion or harm to the environment.
Recommendations for Caregivers Administering Edurant
Make sure the patient consumes the medication during a meal for absorption results. Make sure to stick to a routine to improve consistency in following through with tasks or plans.
Avoiding Contamination or Exposure to Heat and Moisture
Remember to keep Edurant in its packaging, along with the desiccant, to avoid any damage due to moisture or high temperatures, as handling it properly will maintain the effectiveness of the medication and its therapeutic benefits.
Edurant, Rilpivirine FAQ
- What is the use of EDURANT tablet?
- Is there a generic for EDURANT?
- What is the dosing for EDURANT?
- When was EDURANT approved by the FDA?
- What are the ingredients in EDURANT?
- Why is rilpivirine contraindicated with omeprazole?
- How does EDURANT work?
- What is the indication for EDURANT?
- What are the side effects of rilpivirine?
- Is rilpivirine FDA approved?
- Does rilpivirine cause depression?
- How does rilpivirine work?
- Does rilpivirine cause weight gain?
- Why is omeprazole contraindicated with rilpivirine?
- How do you take rilpivirine?
- What class of drug is rilpivirine?
- What drugs interact with rilpivirine?
What is the use of EDURANT tablet?
This medication prescribed for HIV helps in treating HIV infection in individuals by incorporating the HIV drug rilpivirine—a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor also known as NNRTI.
Is there a generic for EDURANT?
No
What is the dosing for EDURANT?
The advised amount of edurant, for grown-up patients, is a 25 mg tablet to be ingested once a day, alongside a meal.
When was EDURANT approved by the FDA?
May 20, 2011
What are the ingredients in EDURANT?
Each tablet contains 27 and a half milligrams of rilpivirine hydrochloride.
Why is rilpivirine contraindicated with omeprazole?
Taking Rilvipirine with Omeprazole is not recommended because it can lead to a decrease in Rilvifirine levels in the blood, reducing its effectiveness as a treatment option.
How does EDURANT work?
Edurant functions by decreasing the level of HIV in your system and enhancing your system. Lowering the chances of contracting diseases associated with HIV infection.
What is the indication for EDURANT?
An NNRTI drug is prescribed along with medications to treat HIV type 1 infection in patients aged 12 and above who are starting therapy and weigh at least 35 kg.
What are the side effects of rilpivirine?
Depression, headache, trouble sleeping (insomnia), and rash
Is rilpivirine FDA approved?
Yes
Does rilpivirine cause depression?
Yes
How does rilpivirine work?
It functions by reducing the level of HIV in the bloodstream. Although rilpivirine does not provide a cure for HIV, it may lower the risk of developing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) as HIV-related conditions, like severe infections or cancer.
Does rilpivirine cause weight gain?
Yes
Why is omeprazole contraindicated with rilpivirine?
It's not recommended to take Rilpvirine with Omeprazole because it can lead to a drop in the levels of Rilpvirine in the blood, potentially reducing its effectiveness as a treatment.
How do you take rilpivirine?
Take with food
What class of drug is rilpivirine?
Medications like rilipivirine belong to a group known as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs).
What drugs interact with rilpivirine?
Certain medications that might have an impact when used alongside this drug are Orlistat and other types of HIV NNRTIs, like efavirenz and nevirapine. Additionally and worth noting is a combined HIV treatment called elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/or tenofovir. It is also important to consider proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), examples of which include esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, and rabeprazole.