Estriol
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Estriol
- III. How Estriol Works
- IV. Uses of Estriol
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Side Effects of Estriol
- VII. Interactions
- VIII. Warnings and Precautions
- IX. Contraindications and Careful Administration
- X. Special Populations
- XI. Overdose and Handling Precautions
- XII. Storage Information
I. Introduction
Estriol, a member of the estrogen hormone group, has a vital role to play in women's health. This article seeks to explore the aspects of Estriol, including its molecular structure and its diverse applications in both approved and nonapproved contexts by the FDA.
II. Composition of Estriol
Estriol has a structure specifically designed to carry out its physiological functions. It stands out from well-known estrogens such as estradiol and estrone due to its distinct affinities for estrogen receptors. Estriol, with the formula C18H24O3, exhibits lesser potency than estradiol and estrone but has a favorable safety profile. It is available in forms, including tablets, creams, and injectables.
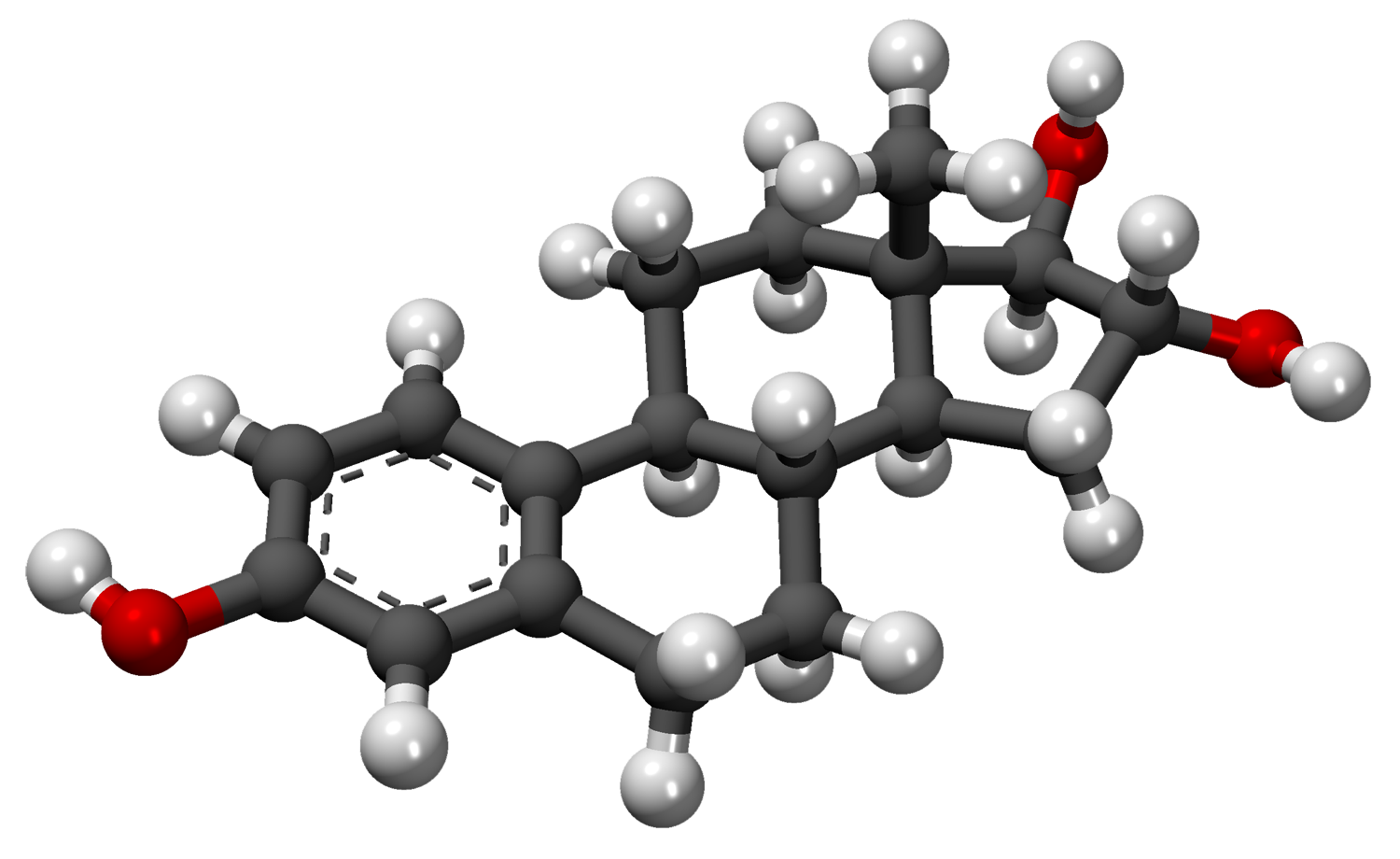
III. How Estriol Works
To fully comprehend the versatility of Estriol in applications, it is essential to understand how it works—estriol functions by attaching itself to estrogen receptors, which then influences gene expression and various cellular activities. Regarding health, Estriol plays a vital role in maintaining the endometrial lining and regulating menstruation. Estriol also impacts tissues such as the breast, bone, and cardiovascular system.
IV. Uses of Estriol
a. FDA-Approved Uses
Estriol is a type of estrogen, a female hormone that is produced by the ovaries. Estriol is not FDA-approved for any medical condition in humans, except for diagnostic testing1. However, some compounding pharmacies may mix estriol with other hormones or medications for off-label use, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopause2. HRT can help relieve symptoms caused by low estrogen levels, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Estriol may also have some benefits for bone health and prevent osteoporosis, a condition that causes weak and brittle bones34. However, HRT also has some risks and side effects, such as increased risk of blood clots, stroke, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. Therefore, HRT should be used with caution and under the guidance of a doctor.
Some possible references for this content are:
- Estriol vs. estradiol: Differences, similarities, and which is better for you
- Menopause & Hormones Common Questions | FDA
- Estriol: Benefits, Function, Hormone Levels & Testing - Cleveland Clinic
- Menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis - UpToDate
b. Off-Label Uses
Estriol is a type of estrogen, a female hormone produced by the ovaries. Estriol has not been approved by the FDA for medical use in humans except for diagnostic testing. However, some studies have suggested that estriol may have some potential benefits for various medical conditions, such as:
- Wrinkles: Estriol may help reduce the appearance of wrinkles by increasing skin hydration, elasticity, and collagen synthesis1.
- Memory and cognitive well-being: Estriol may help improve memory and cognitive function by modulating neurotransmitters, neurogenesis, and neuroprotection in the brain23.
- Multiple sclerosis: Estriol may help reduce the relapse rate and improve the symptoms of multiple sclerosis. This autoimmune disease affects the central nervous system, by regulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
However, these studies are preliminary, and more research is needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of estriol for these conditions. Estriol may also have some risks and side effects, such as an increased risk of blood clots, stroke, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. Therefore, estriol should not be used without the guidance of a doctor.
Reference:
- Estrogen in skin aging: A comparative study of pre- and postmenopausal women
- Estrogen effects on cognition and hippocampal transcription in middle-aged mice
- Estriol‐mediated neuroprotection in multiple sclerosis localized by voxel‐based morphometry
- Estriol treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS): effect on cognition
- Estriol combined with glatiramer acetate for women with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial
V. Dosage and Administration
a. Standard Dosages
Here are some general dosage guidelines for treatments; however, it's important to note that personalized regimens may differ. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) dosage typically falls between 1 to 2 mg per day. The dosage for Osteoporosis varies. Should always be supervised by a medical professional.
b. Special Considerations
People with existing health issues such as liver or kidney problems may need to take amounts of medication. To start, begin with doses and increase gradually depending on how effective the treatment is.
VI. Side Effects of Estriol
a. Common Side Effects
Like medications, Estriol can cause several side effects, but most of them are manageable. Some common side effects include feeling nauseous experiencing weight gain, and having mood swings.

b. Less Common but Serious Side Effects
It is crucial to remain vigilant regarding uncommon yet significant adverse effects. These may include blood clotting, a risk of specific types of cancers, and potential liver problems.
VII. Interactions
Estriol's effectiveness may change when taken with substances. It's essential to be cautious when combining it with anticoagulants or other hormonal medications as this could lead to effects. Additionally consuming alcohol while using Estriol can enhance its products. It's also crucial to be aware of interactions if you have pre-existing medical conditions such, as liver disease or cardiovascular issues.
VIII. Warnings and Precautions
a. Warnings
Long-term usage of Estriol should be approached with caution due to specific considerations. There is a potential for an increased risk of estrogen cancers with prolonged exposure. Therefore, it is essential to monitor for any adverse events during long-term usage.
b. Important Precautions
To protect yourself from dangers, it is important to take specific essential measures. It is advisable to check the functioning of your liver through screenings. Additionally, as part of monitoring, it is recommended to perform breast self-exams and undergo mammograms.
IX. Contraindications and Careful Administration
a. Contraindications
Certain groups of people should avoid using Estriol because it has contraindications. It is not recommended during pregnancy and lactation due to its teratogenic effects. Additionally, individuals with a history of hormone cancer should not use Estriol as it can increase the risk of disease progression.
b. Careful Administration
Different groups of individuals require management. For patients with problems, it is necessary to monitor their heart health closely. For patients with a history of liver disease, it is crucial to observe them and potentially adjust their dosage if needed. This detailed presentation offers a guide on Estriol, covering its therapeutic benefits, potential risks, and important considerations for various populations.
X. Special Populations
a. Administration to Elderly
The elderly population requires a customized method for administering Estriol. Due to differences in how the body processes the medication and an increased likelihood of having health conditions, it is crucial to adjust the dosage. It is recommended to start with initial doses and gradually increase them as needed. Monitoring for any potential adverse effects on the heart or liver is also essential.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Contrary to what most people believe, it is not recommended to use Estriol during pregnancy and breastfeeding. We need to consider the risks involved such as the potential for birth defects, in the baby and hormonal imbalances.
c. Administration to Children
The use of Estriol in patients is still a topic that lacks a clear consensus among medical professionals. The limited research makes it difficult to determine its safety and effectiveness in this population. When it comes to trials, there is a scarcity of data, which consequently restricts the approved applications for pediatric use. Currently, no indications are approved by the FDA for the benefit of Estriol in children.
XI. Overdose and Handling Precautions
a. Overdose
Experiencing an amount of Estriol can be a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. The symptoms can. It may include both neurological and gastrointestinal issues. Recognizing signs like vomiting, severe abdominal pain, and confusion is crucial. Failing to intervene can lead to long-term consequences, potentially resulting in irreversible damage to vital organs.
b. Handling Precautions
It is absolutely essential to have a protocol in place for storing and disposing of Estriol. Ensuring that it is not accidentally ingested, by children and pets is a responsibility that cannot be overlooked. Storing Safely; It is best to keep Estriol in a dark place away, from any moisture. Disposal Methods: It is highly advisable to follow the guidelines provided by agencies and drug disposal programs when disposing of Estriol.
XII. Storage Information
Maintaining the integrity of pharmaceuticals is crucial for their effectiveness. It is essential to follow guidelines when storing Estriol. The ideal storage conditions for this medication involve maintaining a temperature range of 20 25°C. As, for its shelf life, it is generally recommended to use Estriol within 24 months from the date of manufacture. If you have expired medication, it is advisable to dispose of it through authorized drug take-back programs.