Etoposide Injection
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Composition of Etoposide Injection
- 3. Uses of Etoposide
- 4. Off-Label Uses of Etoposide
- 5. Mechanism of Action: How Etoposide Works
- 6. Dosage and Administration
- 7. Administration Guidelines
- 8. Side Effects of Etoposide
- 9. Special Precautions and Warnings
- 10. Etoposide and Specific Populations
- 11. Handling and Storage of Etoposide
- 12. Managing Overdose
1. Introduction
Overview of Etoposide as a Chemotherapy Agent
Etoposide, a cancer treatment drug, is mainly used to treat different types of cancers, such as testicular cancer and small-cell lung cancer. Its effectiveness lies in its capability to block DNA synthesis, which stops the growth of cancer cells.
Historical Development and Approval Status
Etoposide was created in the 1960s and received FDA approval in the 1980s. Since its introduction, it has been used in cancer treatment protocols, greatly improving patients' survival rates.
2. Composition of Etoposide Injection
Active Ingredients
Etoposide injections primarily consist of etoposide itself, which is commonly administered as a salt to improve solubility and stability.
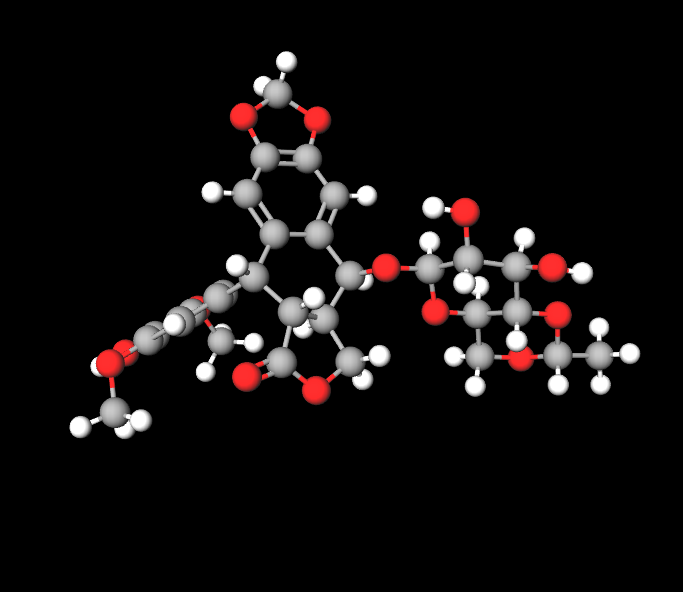
Excipients and Their Roles
Polysorbate 80 improves the solubility of etoposide in water-based solutions, while benzyl alcohol is a preservative to uphold the solution's sterility.
3. Uses of Etoposide
Primary Indications: Types of Cancer Treated
Detailed Analysis of Efficacy in Various Cancers
Research shows that etoposide can greatly improve treatment results for types of blood cancers and solid tumors, especially when combined with other chemotherapy drugs.
4. Off-Label Uses of Etoposide
Exploration of Non-approved Uses
Clinical Studies Supporting Off-Label Applications
Recent studies suggest that the way etoposide works could potentially be helpful in treatment approaches, for different types of aggressive cancers.
5. Mechanism of Action: How Etoposide Works
Cellular Interaction and DNA Impact
Etoposide works by creating a three-part complex with DNA and the enzyme topoisomerase II, resulting in DNA damage and ultimately causing the death of cancer cells.
Comparison with Other Chemotherapeutic Agents
Etoposide works differently from alkylating agents by targeting the DNA breakage reunion cycle specifically hindering the religation process. This unique mechanism provides benefits for cancer treatments.
6. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions
The amount of etoposide needed can differ greatly depending on the cancer type typically ranging from 50 to 100 mg/m² per day, for days.
Adjustments for Specific Patient Groups
Patients with kidney issues or those with high energy levels may require changes to their treatment plan.
7. Administration Guidelines
Intravenous Administration Techniques
Pre- and Post-Administration Care
Keeping an eye out for any reactions during the infusion and making sure the patient stays hydrated can help reduce some of the dangers linked to giving etoposide.
8. Side Effects of Etoposide
Common Side Effects: A Detailed List
- Alopecia
- Mucositis
- Myelosuppression
Serious Adverse Reactions: Risks and Symptoms
Although uncommon, serious issues, like cancers and significant suppression of bone marrow, can arise, requiring careful observation.
9. Special Precautions and Warnings
Contraindications for Use
Patients with liver or kidney problems should avoid using Etoposide as it can lead to higher chances of harmful side effects.
Interactions with Other Medications
When using etoposide in combination with medications that impact bone marrow function or liver enzymes, caution should be exercised.
10. Etoposide and Specific Populations
Administration to the Elderly
Elderly individuals might need changes in their medication doses and regular checkups to handle the higher chances of experiencing harmful side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Etoposide should not be used in women because studies on animals have shown it can harm the embryo and cause birth defects.
Administration to Children
Research on the safety and effectiveness of using this treatment in children is limited. A few studies indicate that it could be considered with careful monitoring by medical professionals.
11. Handling and Storage of Etoposide
Storage Conditions
To ensure that etoposide remains effective and stable, it should be kept in a refrigerator at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C. It's important to shield it from light to prevent the medication from breaking down quickly.

Guidelines for Safe Handling
- Healthcare workers need to wear gear like gloves and masks to protect themselves from skin and breathing exposure.
- Be careful not to create aerosols when handling etoposide, which is a substance that can be risky if inhaled.
- Follow guidelines, for disposing of unused etoposide and contaminated materials to prevent harm to the environment.
12. Managing Overdose
Symptoms of Overdose
Taking much etoposide can lead to significant bone marrow suppression, resulting in low white blood cell count, decreased platelet count, and anemia. Other signs to watch out for are issues, like intense nausea and vomiting that should be promptly addressed by a healthcare professional.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
In case of taking much etoposide, it is important to act promptly. Providing care, especially for issues like bone marrow suppression and gastrointestinal problems, is vital. While there isn't a remedy for etoposide overdose, treatments like hematopoietic growth factors can be given to help the bone marrow recover. It's crucial to observe patients in a healthcare facility where they can receive effective supportive treatment, for any complications that may arise.









