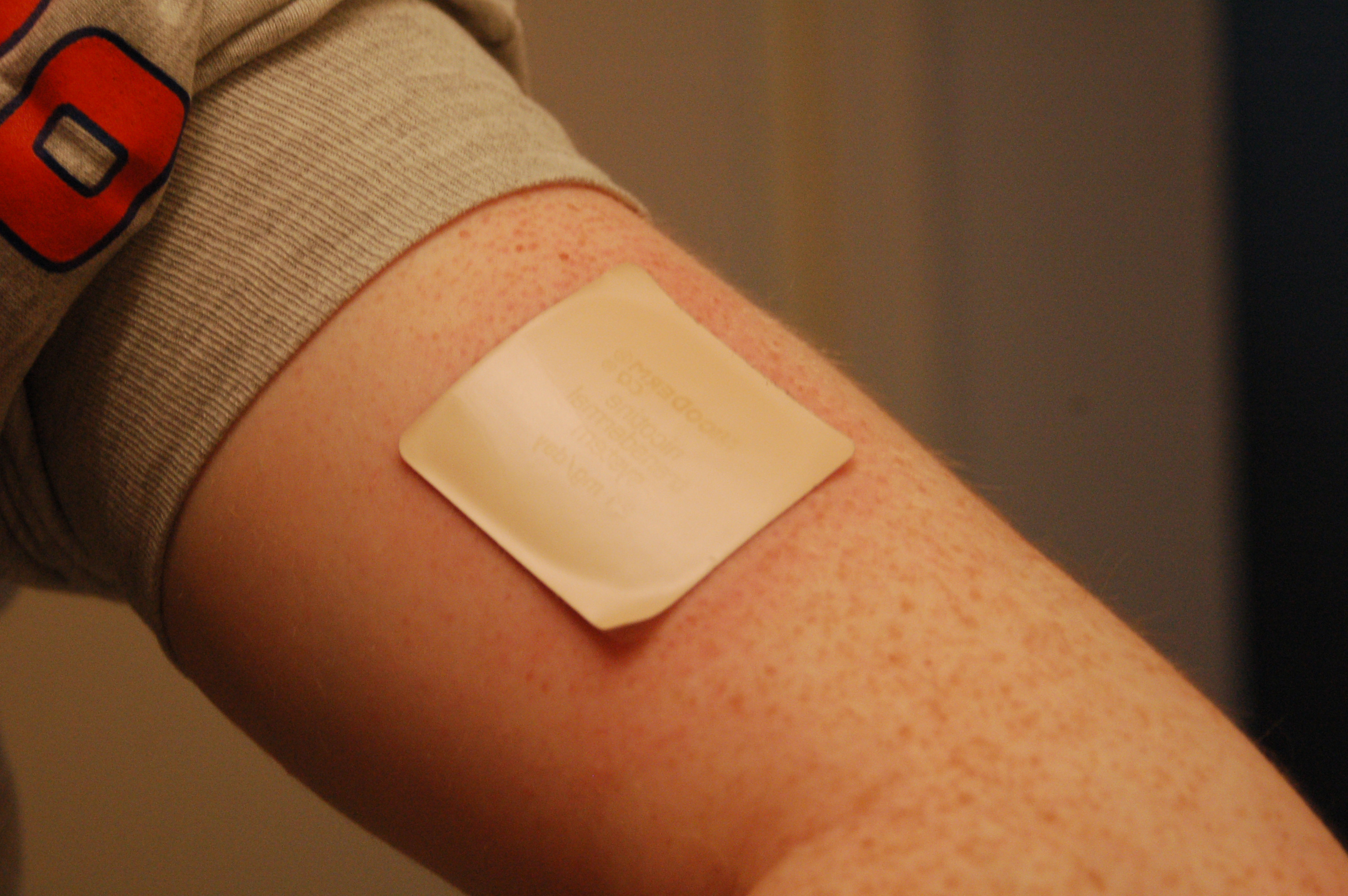
Exelon Transdermal Patches
- Introduction
- Composition and Formulation
- Mechanism of Action: How Exelon Transdermal Patches Work
- Uses and Off-Label Applications
- Dosage and Administration
- Safety Profile and Side Effects
- Warnings, Contraindications, and Important Precautions
- Administration in Special Populations
- Rivastigmine interactions
- Overdose Management and Emergency Protocols
- Storage and Stability Considerations
Introduction
Overview of Exelon Transdermal Patches
Background and Development
Exelon transdermal patches epitomize a transformative advance in the management of cognitive disorders. Developed after extensive clinical research and innovative formulation techniques, these patches were engineered to overcome the limitations of traditional delivery systems.
Role in Managing Cognitive Disorders
Designed primarily for patients experiencing cognitive decline, the patches deliver rivastigmine steadily over time. Their mechanism minimizes the fluctuations typically observed with oral medications. In practice:
- They maintain consistent plasma concentrations.
- They reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
- They enhance patient adherence through ease of use.
These attributes significantly bolster their clinical efficacy.
Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredient Profile
At the core of Exelon patches is rivastigmine, a potent cholinesterase inhibitor with a distinctive pharmacodynamic profile. Its precision in modulating cholinergic pathways is unparalleled. Highlights include:
- High specificity for acetylcholinesterase inhibition.
- Optimized receptor affinity and sustained action.
- A prolonged therapeutic window that maximizes efficacy.
Its sophisticated action renders it superior in managing cognitive deficits.
Inactive Components and Patch Technology
The efficacy of the Exelon patch is not solely reliant on its active ingredient. Inactive components, including sophisticated matrix designs and advanced adhesive systems, play a pivotal role. They ensure:
- Reliable skin adhesion.
- Uniform drug diffusion across the application site.
- Overall stability of the formulation.
Such engineering nuances contribute immensely to the patch's performance.
Rivastigmine vs donepezil
Rivastigmine and donepezil had similar effects on measures of cognition and behavior, but rivastigmine showed a statistically significant advantage on measures of activities of daily living and global functioning
Mechanism of Action: How Exelon Transdermal Patches Work
Pharmacokinetics and Transdermal Absorption
The pharmacokinetic profile of Exelon patches is marked by its methodical absorption and sustained release. The transdermal route enables:
- Effective penetration through the stratum corneum.
- Minimized fluctuations in plasma drug concentrations.
The design ensures that the therapeutic agent is delivered in a controlled manner.

Sustained Drug Release Benefits
Sustained drug release is critical to maintaining optimal cognitive function. This delivery method:
- Reduces peak-to-trough variability.
- Provides continuous symptom management.
- Enhances overall patient outcomes.
The steady release mechanism ensures a reliable and prolonged therapeutic effect.
Neuropharmacological Impact
Exelon patches exert a profound neuropharmacological influence by enhancing cholinergic transmission. This leads to:
- Augmented synaptic efficacy.
- Improved neural connectivity.
- Potential neuroprotective benefits.
Ultimately, these actions contribute to a notable improvement in cognitive performance.
Rivastigmine effectiveness
Rivastigmine is well-tolerated and effective. It improves cognition, participation in activities of daily living, and global evaluation ratings in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease.
Uses and Off-Label Applications
Approved Therapeutic Uses
The primary indication for Exelon patches is the management of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. They are also approved for:
- Treatment of dementia associated with Parkinson's disease.
- Alleviation of cognitive deficits in targeted patient groups.
These indications are supported by extensive clinical data.
Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
Beyond approved uses, clinical investigations have explored off-label applications. Emerging data suggest potential benefits in:
- Cognitive impairment related to other neurodegenerative conditions.
- Adjunctive therapy in select psychiatric disorders.
- Innovative investigational applications under rigorous clinical studies.
These applications indicate an expanding horizon for transdermal therapeutics.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines
Adherence to dosage guidelines is paramount. Initiation involves a careful titration schedule to accommodate individual patient responses. Typically:
- Initial Dose: Treatment typically begins with a 4.6 mg/24 hours patch.
- Dose Titration: After a minimum of four weeks, if the patient tolerates the initial dose, the dosage may be increased to 9.5 mg/24 hours. If the 9.5 mg/24 hours dose is well-tolerated after another minimum of four weeks, the dosage may be further increased to the maximum recommended dose of 13.3 mg/24 hours.
- Maintenance Dose:
The effective dosage range for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia is generally 9.5 mg/24 hours or 13.3 mg/24 hours.
For severe Alzheimer's disease, the effective dose is 13.3 mg/24 hours.
Step-by-Step Application Instructions
The application process is straightforward yet demands precision. Recommended steps include:
- Cleansing the skin thoroughly before application.
- Applying the patch to a clean, dry area.
- Rotating patch sites to prevent localized irritation.
Short sentences, clear instructions, and precise techniques ensure optimal drug absorption.
Careful Administration Practices
Proper administration is critical for maximizing therapeutic benefits. It involves:
- Ensuring adequate patch adhesion.
- Monitoring patient compliance meticulously.
Regular clinical review is essential to sustain effective treatment outcomes.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Overview of Potential Adverse Reactions
Gastrointestinal Issues
Neurological Effects

Less Common or Serious Side Effects
Cardiovascular Effects:
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
- Fainting
Psychiatric Effects:
Other Potential Issues: Allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling) Difficulty urinating Seizures
Management of Side Effects
The management of side effects is guided by prompt intervention. Strategies include:
- Employing topical agents to alleviate skin irritation.
- Seeking timely consultation for severe or persistent reactions.
Such proactive measures are vital to sustaining patient well-being.
Warnings, Contraindications, and Important Precautions
Critical Warnings and Safety Alerts
Clinicians must be cognizant of key warnings associated with Exelon patches. These include:
- Black box warnings signifying high-risk scenarios.
- Vigilance for signs of allergic reactions and patch-induced dermatitis.
Immediate recognition of adverse signs is imperative.

Rivastigmine contraindications
Certain patient populations must avoid Exelon patches. Contraindications comprise:
- Individuals with a known hypersensitivity to rivastigmine.
- Patients suffering from severe hepatic impairment.
Such exclusions are crucial to ensuring safety and optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Rivastigmine withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms may occur if Rivastigmine is abruptly discontinued as it is a cholinesterase inhibitor (ChEI) commonly prescribed for treating dementia. These symptoms may manifest as challenges in focusing or concentrating, sleep disturbances, fluctuating moods, hallucinations, delusions, changes in awareness levels, agitation, and cognitive decline.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Adjustments for Age-Related Skin Changes
In the geriatric cohort, the integumentary system exhibits unique alterations that necessitate bespoke patch application techniques. The epidermis may be attenuated, and dermal elasticity diminished; hence, clinicians are advised to:
- Employ gentler adhesives.
- Optimize the patch placement on regions with robust vascularization.
This adaptive strategy ensures superior transdermal absorption and mitigates localized irritation.
Monitoring for Cognitive and Systemic Effects
Vigilance is paramount when administering Exelon patches to elderly patients. Periodic evaluations should be instituted to monitor:
- Cognitive performance metrics.
- Systemic responses that may be atypical due to polypharmacy.
The integration of both qualitative observations and quantitative assessments ensures comprehensive oversight of therapeutic outcomes.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Risk-Benefit Assessment and Current Guidelines
For pregnant women and lactating mothers, an exacting risk-benefit analysis is indispensable. Current guidelines emphasize:

Rivastigmine interactions
Known Drug-Drug Interactions
Anticholinergic Medications:
Rivastigmine increases acetylcholine levels, while anticholinergic drugs block them. This creates an opposing effect that potentially reduces the effectiveness of both medications. Examples of anticholinergic medications include some antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, and certain bladder control medications.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Other Cholinergic Agonists
Combining rivastigmine with other cholinesterase inhibitors (like donepezil or galantamine) or other cholinergic agonists can increase the risk of cholinergic side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bradycardia (slow heart rate)
Beta-Blockers
Rivastigmine can increase the risk of bradycardia, and beta-blockers (like propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol) can also slow heart rate. Using them together requires careful monitoring.
Succinylcholine and Other Neuromuscular Blockers
Rivastigmine can potentiate (strengthen) the effects of succinylcholine and other neuromuscular blockers used during anesthesia or surgery. This could lead to prolonged muscle relaxation.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Rivastigmine can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, especially in patients with a history of peptic ulcers. The risk may be higher when combined with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen.
Handling and Disposal Protocols
Safe Removal and Disposal of Used Patches
The proper disposal of used patches is a nontrivial concern. Recommended protocols include:
- Secure encapsulation in designated biohazard containers.
- Adherence to local regulatory guidelines.
These practices prevent inadvertent exposure and environmental contamination.
Overdose Management and Emergency Protocols
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Indicators
Overdose scenarios demand an immediate and discerning clinical response. The clinical tableau may include:
- Severe cholinergic crisis.
- Pronounced gastrointestinal distress.
Diagnostic indicators, such as aberrant vital signs, necessitate prompt recognition and intervention.
Immediate Steps for Suspected Overdose
Upon suspicion of an overdose, the following steps are imperative:
- Discontinuation of the transdermal patch.
- Initiation of supportive measures.
Rapid assessment and management are the bedrock of efficacious overdose intervention.
Emergency Treatment Guidelines
Recommended Interventions and Supportive Care
Emergency protocols call for a stratified approach to patient stabilization. The recommended interventions include:
- Intravenous administration of anticholinergic agents.
- Rigorous cardiovascular and respiratory support.
These measures are critical in ameliorating the systemic sequelae of an overdose.
Storage and Stability Considerations
Proper Storage Conditions
Temperature and Humidity Guidelines
Optimal storage conditions are paramount for preserving the pharmacological integrity of Exelon patches. Manufacturers stipulate:
- Maintenance within a narrow temperature bandwidth.
- Controlled humidity levels to prevent degradation.
Adherence to these parameters is essential for sustained product efficacy.
Protection from Light and Contaminants
In addition to climatic controls, the patches must be safeguarded from extrinsic contaminants and photodegradation. Recommended practices include:
- Shielding from direct sunlight.
- Storage in opaque, airtight packaging.
Such measures ensure that the formulation remains uncompromised over time.
Exelon Transdermal Patches FAQ
- What is the Exelon patch used for?
- What is a transdermal patch used for?
- When do you apply for the Exelon patch?
- Where do you put an Exelon patch?
- How long can you wear a transdermal patch?
- Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
- How long is Rivastigmine effective?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- What is Rivastigmine used for?
- What are the side effects of Rivastigmine?
- How does Rivastigmine work?
- What is Rivastigmine patch used for?
- Is Rivastigmine a controlled substance?
- Does Rivastigmine work?
- Does Rivastigmine make dementia worse?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- What are Rivastigmine patches used for?
- What is the Exelon patch used for?
- What is a transdermal patch used for?
- When do you apply for the Exelon patch?
- Where do you put an Exelon patch?
- Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
- How long is Rivastigmine effective?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- What is Rivastigmine used for?
- Does Rivastigmine work?
- Does Rivastigmine make dementia worse?
- What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
- What are Rivastigmine patches used for?
What is the Exelon patch used for?
Exelon Patch has rivastigmine as its ingredient. A medication categorized as a cholinesterase inhibitor that helps manage Alzheimer's disease by addressing memory loss and cognitive changes linked to brain alterations in individuals experiencing this condition.
What is a transdermal patch used for?
Transdermal treatments offer a method for treating ailments like blood pressure nausea, during travel, discomfort, and severe headaches.
When do you apply for the Exelon patch?
Start by using a 4. milligram patch applied to your skin once every day as a patch for a day's duration. After a month's time has passed, the amount may be raised to 9.5 milligrams. The most that can be taken of this medication is a 13.3 milligram patch every twenty-four hours.
Where do you put an Exelon patch?
The back, back, upper arms, or chest have minimal to no hair present.
How long can you wear a transdermal patch?
72 hours
Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
Medications often prescribed for managing symptoms associated with dementia may include Rivastigmine—a common choice for individuals with Alzheimer's or Parkinsons' disease diagnoses due to its ability to boost brain chemicals that enhance function.
How long is Rivastigmine effective?
It's important to keep in mind that the effectiveness of Rivastigmine can vary depending on each individual's body chemistry. In some cases, doctors recommend it as a long-term treatment to help manage symptoms of dementia. However, patients should be aware that noticeable improvements may take some time to become apparent. It could be weeks or even months before significant changes are seen.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Evaluating the situation of patients is important in practice where doctors suggest using Rivastigmine to treat dementia related to Alzheimer's or Parkinsons disease conditions in individuals. This medication works by boosting the activity of choline acetyltransferase in patients which results in increased levels of acetylcholine being released into the brain and subsequently helps alleviate symptoms.
Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
When it comes to looking after people dealing with signs of dementia, it's important to provide tailored care and focus on their needs, specifically in cases where Rivastigmine can be helpful in addressing these symptoms. Its main goal is to assist individuals dealing with Alzheimer's or Parkinson 's-related dementia by triggering specific chemical changes in the brain that enhance memory retention and improve their ability to carry out daily tasks efficiently.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Doctors often prescribe Rivastigmine to help manage the symptoms of dementia related to Alzheimer's disease or Parkinsons' disease, which may lead to memory recall, heightened concentration, and increased alertness, as well as improved everyday task performance by supporting the brain's natural substances that enable these functions.
What is Rivastigmine used for?
Rivastigmine is recognized as a choice among the medications prescribed for Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and Parkinsons due to its ability to enhance the levels of key neural chemicals involved in memory and cognitive function retention.
What are the side effects of Rivastigmine?
unpredictable gastric manifestations that lead to a low desire for food resulting in weight loss
How does Rivastigmine work?
Rivastigmine has been proven in studies to work by inhibiting enzymes, like acetylcholinesterase. This action prevents the breakdown of the brain neurotransmitter "acetylcholine," which is linked to memory and cognitive function of allowing it to happen. It increases precursor chemicals instead to help alleviate symptoms associated with dementia.
What is Rivastigmine patch used for?
The Rivastigmine patch provides an option for individuals dealing with mild dementia linked to Alzheimer's or Parkinsons' disease. The patch works by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain, resulting in improvements in memory retention and cognitive function for patients.
Is Rivastigmine a controlled substance?
It's a misconception that Rivastigmine is a controlled substance; in reality, it falls under the prescription medications category instead. It is mainly prescribed to manage symptoms of dementia often seen in people with Alzheimers and Parkinsons disease.
Does Rivastigmine work?
Rivastigmine shows potential as a remedy for individuals dealing with dementia related to Alzheimers and Parkinsons diseases by boosting acetylcholine levels for cognitive function and enhancing daily activities.
Does Rivastigmine make dementia worse?
Debunking any misconceptions that Rivastigmine worsens dementia symptoms is crucial since this medication was created to address challenges associated with Alzheimer's and Parkinsons' diseases specifically. Rivastigmine boosts acetylcholine levels for memory formation and overall cognitive function, thereby improving brain activity for individuals dealing with these conditions.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Medical professionals frequently suggest Rivastigmine to help lessen the impact of mild dementia associated with Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease due to its ability to improve memory and increase alertness, aiding in daily tasks.
What are Rivastigmine patches used for?
Individuals with mild dementia linked to Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease can benefit from using Rivastigmine patches as a treatment option that provides a continuous delivery of Rivastigmine into the body system. This method aims to reduce side effects commonly associated with taking medication.
What is the Exelon patch used for?
The active ingredient in the patch, called Exelon Patch, includes rivastigmine, which falls under a group of substances known as cholinesterase inhibitors and aids in managing Alzheimer's disease—a disorder marked by brain changes leading to issues with memory retention and cognitive function as behavioral changes.
What is a transdermal patch used for?
Transdermal treatments offer a method for treating issues like blood pressure, nausea, motion sickness, pain relief, and headaches.
When do you apply for the Exelon patch?
You start with a 4.6-milligram patch that you apply to your skin as a patch every 24 hours and can increase to 9.5 milligrams after one month of use if needed, with the dosage being 13.3-milligram patch every day.
Where do you put an Exelon patch?
Areas such as the back or arms and chest are typically characterized by having minimal to no hair growth.
Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
People with symptoms linked to dementia often receive treatment that involves the use of Rivastigmine medication commonly prescribed for individuals diagnosed with Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease to help boost brain chemicals that enhance function.
How long is Rivastigmine effective?
It's important to keep in mind that the effectiveness of Rivastigmine can vary depending on each individual's body composition and response to the medication. Doctors usually recommend it as a long-term treatment to help ease symptoms related to dementia. However, patients should be aware that noticeable changes may only become noticeable after weeks or longer periods possibly stretching out over many months.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Evaluating the situation of the patient is crucial, in practice when it comes to addressing dementia linked to either Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease. Healthcare professionals often suggest Rivastigmine as a remedy for this condition. The medication works by boosting the activity of choline acetyltransferase in patients, resulting in levels of acetylcholine being released into the brain. This ultimately helps reduce the severity of distressing symptoms.
Does Rivastigmine help dementia?
Rivastigmine can be helpful in addressing dementia symptoms. It is designed for patients who are dealing with Alzheimer's or Parkinson's related dementia. It works by making distinct changes in the brain chemistry to enhance memory retention and improve performance in activities.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Doctors often prescribe Rivastigmine to help manage dementia symptoms linked to Alzheimers disease or Parkinsons disease, which may lead to memory retention, heightened focus, and improved alertness, enabling individuals to carry out tasks more effectively by supporting the brain's natural substances responsible for these functions.
What is Rivastigmine used for?
Rivastigmine is recognized as a choice among the medications for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and dementia accompanied by Parkinsonism, as it works by increasing the levels of neural chemicals important for memory retention and cognitive function.
Does Rivastigmine work?
Rivastigmine shows potential as a treatment for individuals suffering from dementia related to Alzheimer's and Parkinsons' disease by boosting acetylcholine levels for cognitive function and enhancing everyday activities.
Does Rivastigmine make dementia worse?
It's important to dispel any ideas that Rivastigmine worsens symptoms associated with dementia because this medication was created to help with the challenges related to Alzheimers and Parkinsons' diseases specifically. The medication boosts levels of acetylcholine, which plays a role in memory formation and overall cognitive function. This enhances brain function for individuals dealing with these conditions.
What is Rivastigmine used to treat?
Medical professionals frequently suggest Rivastigmine to alleviate the decline associated with mild to dementia resulting from conditions like Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease. This medication is known for its ability to improve memory and increase alertness levels which can greatly improve activities and functioning.
What are Rivastigmine patches used for?
People with mild to dementia linked to Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease find Rivastigmine patches to be a treatment option that offers steady and reliable delivery of the medication into the bloodstream compared to traditional oral intake methods.