Ezedoc, Ezetimibe
- Introduction to Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
- Ezetimibe Mechanism of Action
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition and Formulations
- Active Ingredient: Ezetimibe
- Available Strengths and Dosage Forms
- Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
- Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin
- Ezetimibe and Statin Combination
- Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin
- Bempedoic Acid and Ezetimibe
- Tylenol with Codeine and Ezetimibe
- Fenofibrate vs. Ezetimibe
- Ezetimibe vs. Crestor (Rosuvastatin)
- Ezetimibe vs. Lipitor (Atorvastatin)
- Ezetimibe vs. Statins
- Uses of Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
- Off-Label Uses of Ezetimibe
- Ezetimibe Side Effects
- Potential Serious Side Effects
- Ezetimibe Interactions
- Interaction with Statins and Increased Risk of Myopathy
- Effects When Combined with Fibrates (Especially Gemfibrozil)
- Interaction with Bile Acid Sequestrants (e.g., Cholestyramine)
- Potential Effects with Cyclosporine and Anticoagulants
- Ezetimibe Food Interactions
- Ezetimibe and Grapefruit
- Ezetimibe Interactions with Vitamins
- Ezetimibe Contraindications
- Important Precautions Before Using Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
- Ezetimibe Warnings
- Special Considerations for Specific Populations
- Use in Elderly Patients
- Adjustments Based on Age-Related Hepatic or Renal Impairment
- Risk-Benefit Analysis in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
- Use in Pregnant and Nursing Women
- Pregnancy Category and Fetal Risk Assessment
- Use in Breastfeeding: Excretion into Human Milk and Ezetimibe Nursing Considerations
- Ezetimibe Nursing Implications
- Alternative Lipid-Lowering Options During Pregnancy
- Use in Pediatric Patients
- Approved Age Range for Pediatric Use
- Clinical Data on Safety and Efficacy in Children
- Special Dosing Considerations for Pediatric Hypercholesterolemia
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Handling and Storage of Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
Introduction to Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
Overview of Ezedoc and Its Active Ingredient, Ezetimibe
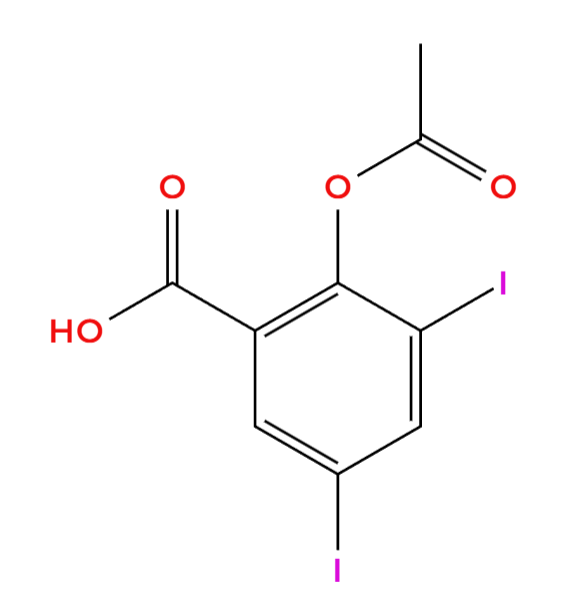
Ezedoc, contains ezetimibe, which is a potent cholesterol-lowering agent primarily used for the management of hypercholesterolemia. As a selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor, ezetimibe reduces the intestinal uptake of dietary and biliary cholesterol without affecting triglyceride absorption. It's distinct mechanism of action differentiates it from other lipid-modulating agents, making it a valuable adjunct in dyslipidemia treatment strategies.
Therapeutic Classification and Mechanism of Action
The type of medication is a cholesterol absorption inhibitor. Main Purpose; Lower the level of cholesterol (LDL-C) in Hyperlipidemic patients. Ezetimibe works by targeting the Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) transporter found in the lining of the intestines to block the absorption of cholesterol into chylomicrons molecules, in the body system. This process helps to reduce cholesterol levels in the liver and improves the removal of LDL through receptors.
Comparison with Other Lipid-Lowering Agents
Unlike statins that work by blocking HMG CoA reductase to reduce cholesterol production within the livers cells; ezetimibe operates at the level resulting in additional lipid lowering benefits when paired with statins. In monotherapy treatment situations Ezetimibe offers a decrease in LDL C levels, but physicians commonly recommend combination therapy for the best outcomes to enhance the lipid profile effectively.
Ezetimibe Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Cholesterol Absorption in the Intestine
Blocking NPC1L1 transporters within the intestine through the use of ezetimibe effectively reduces the intake of cholesterol into the bloodstream. This process triggers an increase of LDL receptors that improve the removal of cholesterol from plasma and consequently lowers circulating LDL C levels.
Comparison with Statins: Complementary Effects on Lipid Metabolism
Statins lower the production of cholesterol, by blocking HMG Co A reductase activity. By taking ezetimibe medication as prescribed by your doctor helps in blocking the absorption of cholesterol from your diet and gallbladder into the liver. Both mechanisms working together result in a decrease, in LDL C levels. Enhance the overall outcomes of lipid panels.
Effects on LDL, HDL, and Triglycerides
- When taken alone as a treatment option, for lowering LDL C levels in the body's cholesterol profile without any medications involved in the process as part of the therapy plan or when used in combination with statins to improve its efficacy further leads to a reduction of, around 18 to 25%.
- HDL-C has a minimal effect overall. However, there may be some room, for a slight uptick in levels.
- Triglycerides experience a decrease, as a result of less cholesterol being absorbed into chylomicrons, in the intestine.
Impact on Overall Cardiovascular Health
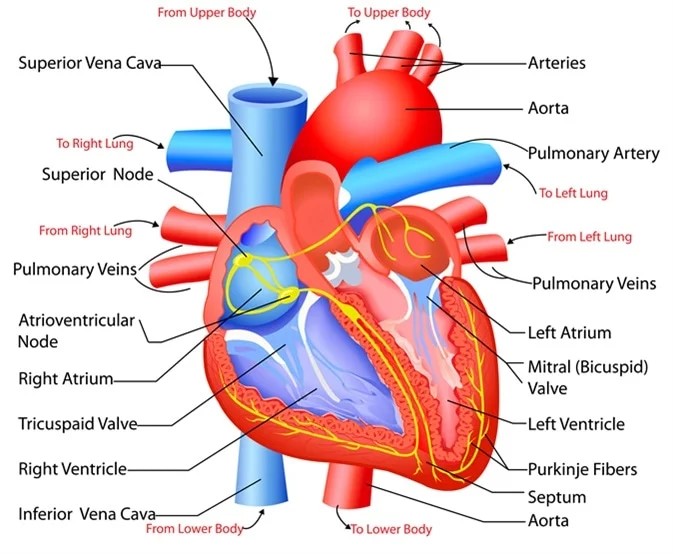
Clinical trials, like the IMPROVE-IT study have proven that combining ezetimibe with statins can effectively lower risks for individuals at risk of heart related issues. By adding ezetimibe to statin treatment, the occurrence of events such, as heart attacks and strokes is reduced, according to research.
Dosage and Administration
Ezetimibe Dose
The typical suggested amount of ezetemibe is 10 milligrams taken daily, which offers the cholesterol-lowering effects while ensuring a safe and well-tolerated treatment regimen.
Standard Dosing Regimen for Adults
- Prescription recommendation, for solo use is 10 milligrams to be taken daily.
- Using a mix of treatments involving 10 mg of ezetimibe alongside the prescribed dose of statin medication.
- In addition, there are ways of lowering lipids such as fibrates or bile acid sequestrants, under the advice of a doctor.
Dosage Adjustments in Hepatic Impairment
Patients who have liver problems classified as Child Pugh score B or higher are advised to steer clear of using ezetimibe as it could lead to changes, in how the body processes the drug and a higher chance of experiencing harmful side effects.
Administration with or Without Food
You can take Ezetimibe with or, without food since its absorption is not greatly affected by meals. The pill should be swallowed whole with a glass of water at the time every day.
Recommendations for Combination Therapy with Statins or Fibrates
- When statins are used in combination, with Ezetemibe there is a reduction in LDL C levels beneficial for patients, with high cardiovascular risk.
- When taking fibrates along, with fenofibrate usually doesn't cause any issues; however, it's advised to avoid using gemfibrozil at the time because it could lead to liver problems.
Missed Dose Instructions
If the patient forgets to take a dose of their medication and remembers on. It's close, to the time for the next dose already scheduled in their routine regimen they should skip it and not take double doses to make up for the missed one.
Ezetimibe Max Dose
The highest safe daily amount of ezetemibe is 10mg as per recommendations, going beyond this limit won't offer advantages and could raise the chances of experiencing unwanted side effects.
Composition and Formulations
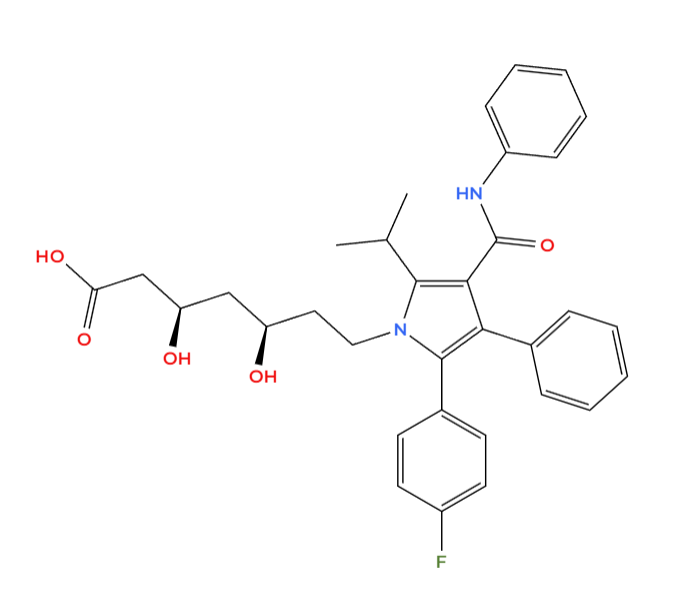
Active Ingredient: Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe acts as an inhibitor of cholesterol absorption by targeting the Niemann- Pick c1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) transporter found within the small intestine. Through this mechanism of action, ezetimibe effectively hinders the absorption of biliary cholesterol from the intestine resulting in a reduction of circulating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. In contrast to statins, which act by inhibiting the production of cholesterol within the liver, ezetimibe exerts its effects at the level, providing a unique yet complementary approach, to managing lipid levels.
Available Strengths and Dosage Forms
10 milligram tablets are typically used as the recommended dosage, for either treatment or when combined with other medications.
Fixed dose combination tablets are also created with statins to improve the effectiveness of lowering lipids.
- A combination of Ezetimibe and Simvastatin
- A combination of Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin
- The combination of Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin
- Medication containing Ezetimibe and Bempedoic Acid.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
The inactive ingredients present, within ezetimibe tablets play a role by maintaining the stability of the drug while also enhancing its bioavailability and taste appeal. The typical additives found include;
- Microcrystalline cellulose serves as a filler. Contributes, to the tablets solidity and structure.
- The addition of monohydrate helps to improve the solubility of the ingredient.
- Povidone serves as a binder that enhances the cohesion of tablets.
- Magnesium stearate functions, as a lubricant to prevent sticking during the manufacturing process.
- Sodium lauryth sulfate is a substance that helps drugs disperse in the body when taken.
Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin
When ezetimibe and rosuvastatin are used together they create a partnership that reduces levels effectively Rosuvastatin is a statin that hampers the production of cholesterol, by the liver Concurrently ezetimibe diminishes the absorption of cholesterol from the intestines This combined strategy notably decreases LDL C levels beneficial for patients facing difficulties, with statins or needing intensive lipid control measures
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin
Ezetemibe and simvastatin combined formulations work together by utilizing the benefits of each medication. Simivastatin reduces cholesterol production within the liver, while ezetemibe helps decrease cholesterol absorption from the intestine. This approach has been proven through studies to lower LDL C levels more effectively, than using each medication alone.
Ezetimibe and Statin Combination
When you use ezetemibe along with a statin it offers a rounded strategy for treating dyslipidemia, which is especially advantageous, for;
- Individuals with a heightened risk of heart-related issues necessitating management of cholesterol levels.
- People who do not achieve lowering of LDL-C levels with statins alone.
- Patients may have to reduce their intake of statins because of side effects, like muscle pain or liver problems.
Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin is a prescribed statin that is frequently given alongside ezetemibe to optimize the lowering of cholesterol levels. This pairing significantly decreases LDL-C and cholesterol levels while keeping a safety record. It is commonly recommended for individuals, with hypercholesterolemia or those who have suffered from incidents before.
Bempedoic Acid and Ezetimibe
For patients who cannot tolerate statins well and are looking for a way to lower their cholesterol levels without experiencing muscle related side effects the use of bempedoic acid alongside ezetimibe offers an alternative approach, to managing lipid levels effectively by inhibiting ATP citrate lyase enzyme and reducing hepatic cholesterol synthesis through a different pathway compared to traditional statins.
Tylenol with Codeine and Ezetimibe
There are no documented drug interactions, between ezetimibe and Tylenol, with codeine or acetaminophen/codeine combination medication as it is commonly known as well; however, individuals taking ezetimibe should exercise caution when using opioid based medications because of liver metabolism issues to take into account particularly if they have existing liver conditions.
Fenofibrate vs. Ezetimibe
In managing lipids, Fenofibrate and ezetimibe play roles.
- Ezetimibe focuses on lowering LDL cholesterol by blocking the absorption of cholesterol with impact, on triglycerides and HDL cholesterol levels.
- Sometimes doctors prescribe both ezetimibe and fenofibrate to treat levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides at the time.
Ezetimibe vs. Crestor (Rosuvastatin)
Rosuvastatin, known as Crestor is a statin that effectively lowers LDL cholesterol levels and offers anti-inflammatory advantages when compared to ezetemibe.
- When taken on its own, rosuvastatin is better, at reducing LDL cholesterol levels.
- Patients, with statin-related muscle issues tend to tolerate ezetimibe.
- When ezetimibe is combined with rosuvastatin it results a reduction of LDL C compared to using each agent.
Ezetimibe vs. Lipitor (Atorvastatin)
Atorvastatin, known as Lipitor continues to be prescribed for cholesterol levels while there are distinct variances, between ezetimibe and atorvastatin.
- Atorvastatin effectively lowers LDL-C levels by blocking the production of cholesterol, in the body.
- When taken on its own, Ezetimibe has an impact. When paired with atoravastatin, it boosts the reduction of LDL C levels.
- Patients who cannot tolerate doses of statins can achieve management of their lipid levels by supplementing with ezetimibe while taking lower doses of statins.
Ezetimibe vs. Statins
Both ezetimibe and statins work to lower LDL cholesterol levels. Do so through methods.
- Statins work by blocking an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, in the liver to lower the production of cholesterol.
- Statins usually lead to a decrease in LDL C levels. It can sometimes result in side effects like muscle pain and liver issues as well as a higher chance of developing diabetes.
- On the contrary Ezetemibe is generally well received. It can be considered as an option or supplement for individuals in need of cholesterol-lowering treatment.
Uses of Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
Ezetimibe Used for Primary Indications for Hypercholesterolemia Treatment
Patients with high cholesterol levels benefit from ezetemibes use to lower LDL C levels when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to achieve control over cholesterol levels; this medication selectively inhibits the absorption of dietary and biliary cholesterol specifically, within the small intestine.
- Statin treatment alone falls short in achieving the desired LDL C goals.
- Patients may encounter side effects from statins, like muscle pain or liver issues.
- An alternative, to statins is needed because some people cannot take statins due to contraindications.
Use in Combination Therapy with Statins
Ezetemibe shows its effectiveness, as a treatment. Truly shines when paired with statins for better clinical outcomes. The way statins work involves reducing cholesterol production by the liver through HMG CoA reductase inhibition, while ezetemibe acts at the level to block cholesterol absorption. These two actions working together lead to improved reduction of LDL C levels and better lipid lowering results than when either medication is used. Combining these therapies is especially advantageous, for;
- Patients who have a risk of heart problems and need to reduce their LDL cholesterol levels.
- People who fail to reach cholesterol levels using statins alone.
- Individuals who require amounts of statins because of side effects or existing liver conditions.
Use in Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial Hypercholesterolemia FH is a condition that causes high levels of LDL-C from a young age and can lead to heart problems if not treated properly. Ezetimibe plays a role, in treating both homozygous FH patients.
- Patients with hypercholesterolemia experience positive outcomes when using a combination of ezetimibe and statins to lower their LDL-C levels significantly.
- Individuals, with hypercholesterolemia often experience significant increases in cholesterol levels and might need to take ezetimibe along with statins PCSK ne inhibitors or lipid apheresis, for treatment.
- Adding ezetimibe, to the treatment plans for hypercholesterolemia enhances lipid management and reduces the risks of cardiovascular complications over time.
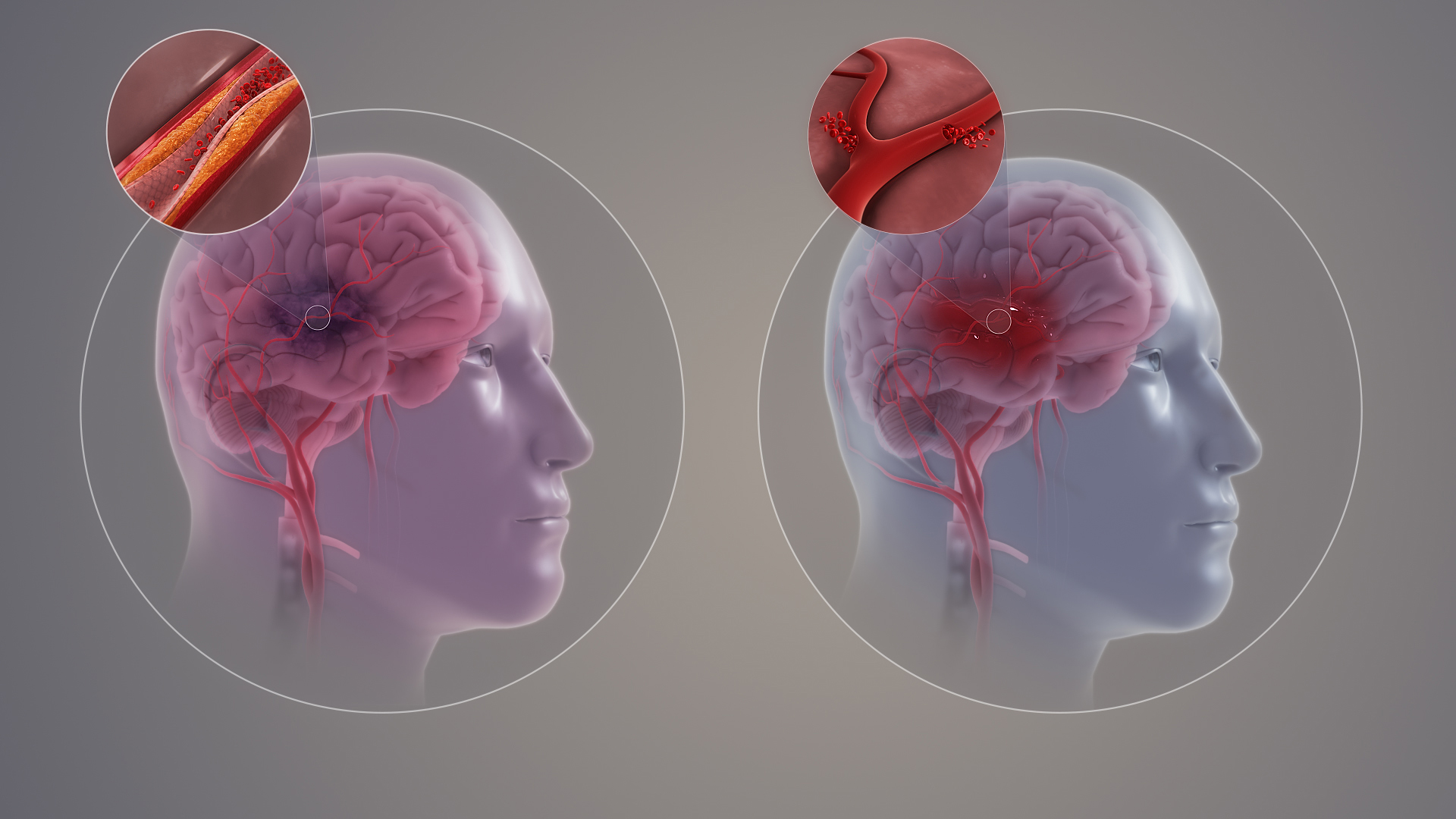
Use in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
Ezetimibe offers more, than controlling cholesterol levels; it has proven advantages when it comes to lowering the risk of cardiovascular incidents as well. Research studies like the IMPROVE IT trial indicate that combining ezetimibe, with treatment results not only decreases major cardiovascular events but also helps prevent heart attacks and strokes. The ways ezetimibe aids cardiovascular risk reduction involve mechanisms that play a role.
- Reducing levels of LDL C is a factor that can be modified to lower the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Addressing the issue of inflammation, within the body. Improving how blood vessel linings function when cholesterol levels are high.
- Improving the levels of fats in the blood without causing changes, in how the body processes glucose is possible with some statins at doses, unlike certain high-dose statins that may impact both aspects differently.
Ezetemibe is frequently recommended for people, with a risk of heart problems, like artery disease or diabetes, because of the advantages it offers.
Ezetimibe Cholesterol
Ezetimibe therapy relies heavily on managing cholesterol levels by blocking cholesterol absorption within the enterocytes brush border to reduce LDL C without interfering with lipid processes. It's influence, on HDL C and triglycerides is limited compared to its ability to lower LDL levels, effectively making it a key element of lipid control strategies. The effects of ezetimibe, on lowering cholesterol levels are noteworthy;
- Lowers LDL cholesterol by around 18 to 25 percent when used as a treatment.
- Boosts the decrease in LDL-C by a 15 to 20 percent when paired with statins.
- It slightly lowers cholesterol levels without affecting triglycerides.
Ezetimibe is an option, for patients who need to manage their cholesterol levels as it helps lower LDL C effectively while minimizing the risk of negative side effects.
Ezetimibe Weight Loss
Although ezetimibe isn't meant for weight loss purposes specifically identified as a weight loss aid, on its label, different populations might experience some changes related to body weight while using it nonetheless. Entailed as a modulator of lipids it doesn't meddle with the breakdown of fats or the absorption of calories. However, certain metabolic impacts could play a role shifts, on the scale. Some possible pathways connecting ezetimibe to alterations in body weight are;
- Enhancing profiles could result in improved metabolic efficiency.
- Improvements, in inflammation levels could help enhance how sensitive insulin is and how efficiently the body utilizes energy.
- Patients who have existing metabolic conditions might see their weight remain stable because of balance, in their bodies.
However, ezetmiibe should not be viewed as a replacement, for making lifestyle changes like improving your diet and increasing physical activity levels.. Any impact it has in terms of weight is secondary, to its function of controlling cholesterol levels.

Off-Label Uses of Ezetimibe
Potential Use in Treating Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of metabolic issues that are linked together and can raise the chances of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes. It is identified by belly fat, dyslipidemia( levels of lipids), insulin resistance and high blood pressure. Ezetimibe is commonly prescribed for managing lipid levels. It's also being looked at for helping with some of these metabolic problems. There are ways, by which ezetimibe could be helpful, in managing metabolic syndrome;
- Ezetimibe plays a role by lowering LDL C levels to tackle the dyslipidemia aspect of metabolic syndrome.
- Some research suggests that ezetimibe might offer benefits, for insulin sensitivity related to glucose metabolism; however; its impact, on regulating glucose levels is still being studied.
- Ezetimibe could help decrease inflammation and oxidative stress levels that play a role, in the development of metabolic syndrome by improving function.
Although not usually the initial choice, for treatment purposes ezetimibe could be considered as an option, for people dealing with metabolic syndrome who also have high cholesterol levels.
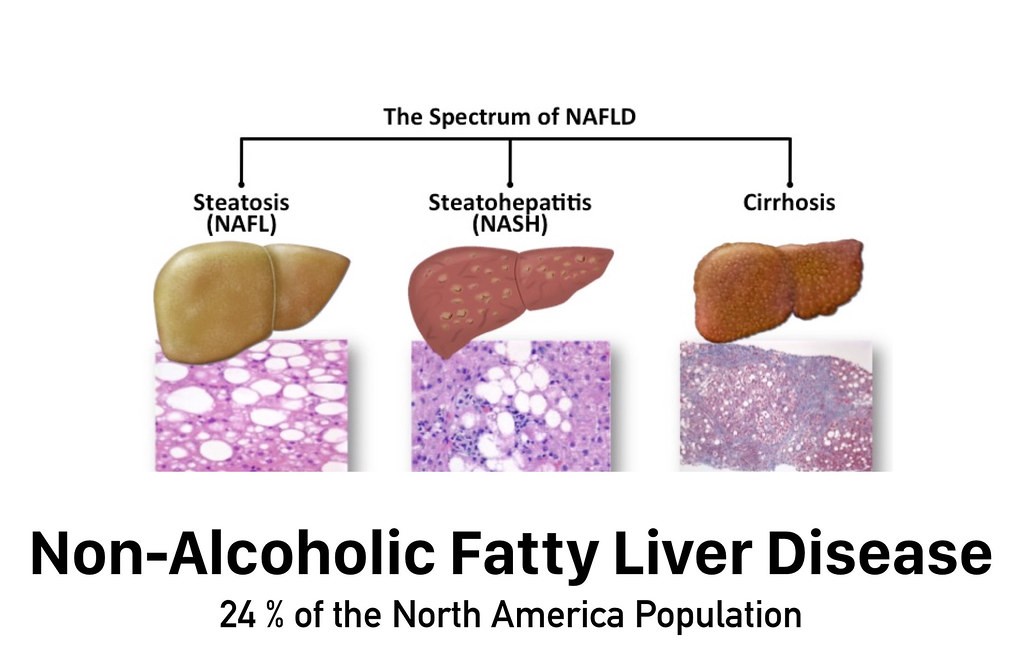
Use in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non alcoholic fatty liver disease is becoming an issue in public health as obesity and metabolic problems continue to rise rapidly. NAFLD is identified by a buildup of fat in the liver. It can advance to more severe conditions like non alcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) fibrosis or cirrhosis. Researchers have looked into using Ezetimibe as a treatment for NAFLD because of its impact on how lipids are absorbed and how cholesterol levels, in the liver are regulated;
- Reduced intake of liver fats may occur as ezetimibe hinders the absorption of cholesterol, from the intestines that could lead to cholesterol buildup within the liver.
- Clinical research indicates that there is evidence to support the idea that the use of ezetimibe may lead to decreased levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase. Indicators of liver inflammation.
- Animal studies suggest that ezetimibe might have properties that could slow down the development of liver scarring known as fibrosis.
Although these initial discoveries are encouraging; additional studies are required to determine the impact of ezetemibe, on NAFLF treatment and distinguish it from the effects of statins.
Investigational Use in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Patients
People who have long-term kidney problems frequently show lipid levels known as dyslipidemia, which includes triglycerides and low levels of HDL cholesterol, along with a dominance of small and dense LDL particles in their bloodstreams. Using methods to lower lipids like statins may not be very effective for individuals with kidney disease because their bodies process drugs differently and they face a risk of side effects. A medication called Ezetimibe has been considered as an alternative or addition to managing lipid issues in patients with kidney disease.
- Studies have shown that combining ezetimibe with simvastatin can effectively lower risks for patients with kidney disease, as seen through the findings of trials like the SHARP study, the Heart and Renal Protection trial.
- Due, to its circulation of renal excretion like certain statins do, ezetimibe has minimal renal clearance, which makes it a safer choice for people, with kidney issues.
- Recent studies indicate that ezetemibe could potentially help reduce low-level inflammation often seen with CKDs and linked to heart issues.
Considering the heart health challenges faced by individuals with chronic kidney disease(CHF), ezetimibe could serve as an addition, to the treatment plans aimed at reducing cholesterol levels among this group of patients.
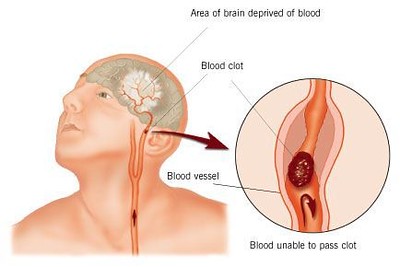
Possible Benefits in Stroke Prevention
The build-up of plaque, inside blood vessels leading to disease is a factor contributing to strokes; lowering LDL C levels is crucial for preventing strokes. Statins are commonly used for this purpose. There is growing evidence that ezetemibe can offer benefits by further reducing stroke risks. Especially among individuals, at high risk. Some potential advantages of using ezetemibe for preventing strokes include;
- Greater reduction of LDL cholesterol levels can be achieved when ezetimibe is used alongside statins, leading to the management of lipids and potentially reducing the likelihood of stroke occurrences.
- Enhanced endothelial function is supported by the potential of ezetimibe to prevent the buildup of cholesterol within the walls of arteries and support the health of blood vessels that supply the brain with oxygen and nutrients.
- Stroke pathophysiology includes inflammation and oxidative stress that could potentially be reduced with the help of ezetimibe due, to its inflammatory properties.
Ezetimibe is not commonly included as part of the procedures for preventing strokes; however it could be an addition, for patients needing more intensive management of their lipid levels.
Ezetimibe Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Side Effects (Diarrhea, Abdominal Pain)
Changing how the body absorbs cholesterol in the intestines could lead to effects, on digestion, for some people when taking Ezetimibe medication at the start of treatment.
- Diarrhea may occur in some individuals due, to levels of bile acid excretion and alterations, in the gut microbiota leading to stools or diarrhea.
- Reports have mentioned experiencing cramps or discomfort, in the lower abdomen that could be related to changes, in how lipids are digested.
- Some people might feel a bit queasy at first when taking the medication. Usually it goes away once the body gets used to it.
Usually these stomach-related issues are not severe. Tend to resolve by themselves without the need, for treatment.
Musculoskeletal Complaints (Myalgia, Arthralgia)
Some patients taking ezetemibe may experience muscle and joint pain. The occurrence is less common than with statins.
- Muscle pain known as myalgia can cause an achy feeling, in areas like the legs or lower back, even without any apparent inflammation or muscle damage occurring underneath.
- Joint pain (arthralgia); Certain people experience stiffness or mild discomfort in their joints—, in areas that bear weight.
These signs typically are not severe. May require assistance if they continue or worsen. Especially, for individuals taking statins in combination therapy.
Headache and Dizziness
Users of ezetimibe have reported experiencing system symptoms like headaches and dizziness. The reasons, behind these effects are not fully known. Could be linked to alterations, in lipid processing or overall blood circulation.
- Most headaches are usually mild. Tend to go within a few days of starting treatment.
- Rare instances of feeling lightheaded may occur in individuals who are susceptible to changes in blood pressure levels.
Staying hydrated and getting rest can usually help ease these symptoms; however if they persist you may need to adjust your dosage or consider trying a treatment option.

Ezetimibe Side Effects Weight Gain
Weight increase is not a mentioned outcome of using ezetemibe medication. some people might observe modifications, to their body structure due, to it; however.
- Changes, in how the body processes fats and oils.
- Changes, in the way fat is absorbed can result in alterations, in how energy is stored within the body.
- Factors such, as diet and lifestyle choices can play a role in affecting changes, in body weight over time.
Ezetimibe typically does not cause changes, to weight, for the majority of patients.
Ezetimibe Side Effects Hair Loss
There isn't proof connecting ezetemibe, with hair loss. However, some people mentioned experiencing thinning hair. That might be the cause.
- Changes in lipid processing that impact the operation of hair follicles.
- Changes, in absorption affecting the production of keratin.
- There may be a tendency or to use of medications, at the same time.
If you notice hair loss while using the medication, it commonly resolves once you stop taking it.
Ezetimibe Side Effects Muscle Pain
Muscle discomfort is an issue, with ezetemibe treatment; however it occurs often compared to statins usage and does not typically affect muscle function significantly.
- It is more common, among patients or those taking medications.
- Pre-existing musculoskeletal conditions may make the situation worse.
- It usually gets better when the medication is stopped or the dosage is changed.
Severe or ongoing muscle discomfort should be evaluated by a doctor to rule out issues such, as myopathy.
Ezetimibe Side Effects Blood Pressure
Although ezetimibe does not specifically impact blood pressure levels directly. Certain people might encounter the following effects;
- Rarely does hypotension (low blood pressure) occur. It may be associated with changes, in the body's lipid levels.
- In some rare instances hypertension ( blood pressure) has been. Could be attributed to unique metabolic differences, among individuals.
Patients who already have heart-related conditions need to keep an eye on any changes, in their blood pressure when starting treatment.
Ezetimibe Side Effects in Elderly
As people grow older they might experience side effects easily because of changes, in their bodies related to aging.
- There is a chance of experiencing muscle soreness and discomfort, in the joints.
- Increased awareness of stomach issues.
- There might be some memory issues reported by individuals. There is still uncertainty surrounding the evidence.
It's important to keep an eye, on patients who are prescribed ezetemibe medication and are also taking multiple medications at the same time.
Potential Serious Side Effects
Liver Enzyme Elevations and Hepatic Dysfunction
Patients who take ezetimibe along with statins may experience increased levels of liver enzymes, like ALT and AST; although uncommonly seen but significant liver issues might require stopping the medication.
- It is advised for individuals at risk to undergo liver function tests.
- Symptoms of liver trouble may manifest as yellowing of the skin (jaundice), darkening of urine coloration and enduring tiredness.
People who already have liver issues should be careful when taking ezetimibe medication.
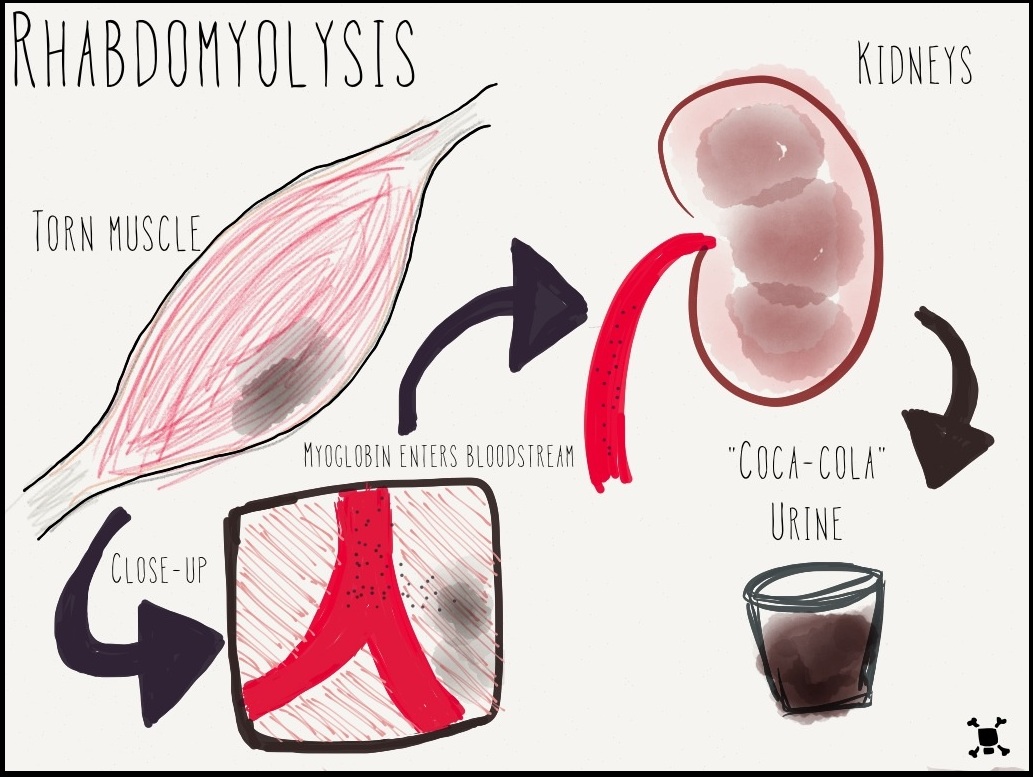
Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis (Especially in Combination with Statins)
While the chances of developing myopathy are reduced with ezetemibe when compared to statins; there have been instances of muscle deterioration known as rhabdomyolysis reported among individuals using both medications simultaneously.
- Signs of the illness comprise muscle discomfort, fatigue, and urine that appears darker, in color.
- Seek help if you suspect someone has rhabdomyolysis.
Approach the combination of high-dose statins with caution.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Rarely seen in practice. Possible are hypersensitivity responses that might present as;
- Skin irritation, like a rash or itchiness or hives may occur.
- Severe cases can lead to swelling on the face, known as angioedema.
- Trouble breathing could be a sign of anaphylaxis.
Patients who are having reactions should stop using the product. Consult a doctor immediately.
Risk of Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a yet serious side effect of ezetemibe that causes inflammation of the pancreas and can be identified by warning signs such, as.
- Experiencing pain, in the abdomen that extends to the back area.
- Frequent feelings of queasiness and continuous episodes of throwing up.
- Serum amylase and lipase levels are higher, than normal, in the blood sample analysis.
If you suspect pancreatitis it's important to seek an evaluation.
Ezetimibe Side Effects Cancer
The possible connection, between ezetimibe and cancer is still being studied continuously by researchers. A few observational studies have shown worries, about an occurrence of cancers; however a clear cause and effect relationship has not been confirmed as of yet.
- Long term studies, in the field have yet to establish a direct link, to cancer directly.
- Further research is required to assess the dangers that may arise.
Currently there is no proof indicating a chance of developing cancer from taking ezetimibe medication.

Ezetimibe Interactions
Interaction with Statins and Increased Risk of Myopathy
Doctors commonly recommend pairing ezetemibe with statins to improve cholesterol lowering effects, although this mix can lead to an uptick, in the likelihood of experiencing myopathy—a condition marked by muscle discomfort and weakness—particularly when higher statin doses are used.
- Combining ezetimibe with statins, like simvastatin and atorvastatin, could worsen muscle-related side effects.
- In some instances of myopathy can advance to rhabdomyolysis. A serious condition where muscle fibers break down and pose a potential life-threatening risk.
- It's advisable to check the levels of creatine kinase (CK), in patients, at high risk.
If individuals encounter muscle discomforts without a cause, they should promptly consult with a healthcare provider, for assessment purposes. Particularly if they are undergoing treatment involving two medications simultaneously.
Effects When Combined with Fibrates (Especially Gemfibrozil)
To control levels of triglycerides known as hypertriglyceridemia, fibrates like fenofibrate and gemfibrozil are employed. There is a risk of reactions when ezetimibe is used alongside them.
- Gemfibrozil can increase the levels of ezetimibes presence within the bloodstream which may lead to a likelihood of experiencing side effects.
- Taking fenofibrate along, with medications might be safer compared to using gemfibrozil, but it's essential to keep a close watch and monitor the effects diligently.
- Cholesterol processing, in the body can be improved by this mix despite the risk of liver damage requiring consideration.
Patients who are prescribed both ezetimibe and fibrates should have their liver function and muscle toxicity checked regularly.
Interaction with Bile Acid Sequestrants (e.g., Cholestyramine)
Cholesterol lowering medications such, as cholestyramine and colestipol work, by binding to cholesterol found within the intestines to lessen its absorption rate there; however when taken together with ezetimibe they may actually reduce its effectiveness significantly.
- When bile acid sequestrants interact, with ezetimibe they can lower its absorption into the body by binding to it within the tract.
- To reduce the impact of this interaction, with ezetimibe and a sequestrant medication should be separated by 2 hours before or 4 hours after taking it.
Timing the administration correctly maximizes the effectiveness of reducing lipids in the body.
Potential Effects with Cyclosporine and Anticoagulants
Cyclosporine is a drug used to suppress the system after organ transplants. It can raise the levels of ezetimibe plasma, which may lead to more side effects occurring.
- Regular checks of cholesterol levels and kidney function are recommended for patients taking medication.
In the way ezetimibe could affect blood thinners such, as warfarin by impacting the metabolism of vitamin K.
- Regularly checking the normalized ratio (INR) I believe it is important to monitor to avoid much thinning of the blood, which can lead to an increased risk of bleeding.
Ezetimibe Food Interactions
Unlike statins, ezetimibe does not have major dietary restrictions. However, certain foods may impact its absorption and efficacy.
- High-fat meals may slightly alter the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe but do not necessitate dietary changes.
- Patients should maintain a consistent diet to ensure stable cholesterol management.
Ezetimibe and Grapefruit
Many lipid-lowering medications may interact with grapefruit and grapefruit juice; this is especially true, for statins. Does not significantly affect ezetmibe intake.
- When ezetemibe is consumed with grapefruit there haven't been any changes observed regarding its pharmacokinetics.
- Ezetimibe works differently from statins as it undergoes glucuronidation of relying on CYP/ metabolism like statins do; this helps it avoid interactions, with grapefruit.
Patients who are using a combination of ezetimibe and statins should be careful because grapefruit can affect how statins are metabolized.
Ezetimibe Interactions with Vitamins
The interaction of Ezetimibe, with vitamins is generally minimal in nature. It can influence the levels of soluble vitamins indirectly through its impact, on cholesterol absorption.
- Long-term users may experience a decrease, in their levels of Vitamin A,D,E, and K.
- Usually regular food intake can make up for this impact; however, taking supplements might be an option if theres a lack of nutrients, in the body.
Ezetimibe Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to Ezetimibe or Excipients
Individuals who have a confirmed sensitivity to ezetimibe or any of its ingredients are advised to steer clear of the medication as it may trigger allergic responses such as;.
- Skin rash may cause itching and swelling on the skin.
- Experiencing dizziness. Struggling to breathe (anaphylaxis).
If you experience hypersensitivity it's important to stop and seek help.

Contraindications in Active Liver Disease
Individuals, with liver disease or unexplained elevations in enzymes should avoid using ezetimibe due, to its enteroheptic circulation process.
- Patients who have existing liver issues need to be watched for any signs of their liver function getting worse.
- Using statins in combination therapy, for patients with liver issues raises the chances of liver damage occurring.
Use in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Patients, with kidney issues should use ezetmibe cautiously as their liver primarily processes it. Altered drug excretion and metabolism may affect them differently.
- It's best to steer clear of dose statin ezetimibe combinations when dealing with advanced renal disease.
- It is recommended to check kidney function in populations, at risk.
Ezetimibe and Alcohol
Although ezetimibe does not have an interaction, with alcohol consumption itself; excessive intake of alcohol can worsen its impact, on the liver.
- Drinking alcohol can raise the chances of liver enzyme spikes and liver damage.
- It's advisable, for individuals, with a background of liver issues to restrict their alcohol consumption when undergoing treatment.

Ezetimibe Food Contraindications
There are no food restrictions, for ezetimibe, but certain dietary selections could affect how well it lowers lipids.
- Diets high, in cholesterol and saturated fats can offset the cholesterol lowering effects of the medication.
- Ensuring you have a rounded diet that includes plenty of fiber and plant sterols can help improve your lipid profile.
Important Precautions Before Using Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
Monitoring Lipid Levels and Liver Function Tests
Ensuring that patients lipid profiles are routinely checked is crucial to evaluate how well ezetemibe is working to control cholesterol levels. A thorough lipid panel test should be done before starting the treatment, and regular follow-up tests should be conducted to track progress, towards treatment targets.
- During the testing phase of the study we will be looking at the cholesterol levels as well, as the specific LDL C (low density lipoprotein cholesterol) HDL C (high density lipoprotein cholesterol) and triglyceride levels.
- Please conduct follow-up evaluations to check lipid levels every 6 to 12 weeks when making changes, to the medication dosage.
- Moreover it is advisable to conduct liver function tests when ezetimbie is taken alongside statins. High levels of liver enzymes could suggest liver issues requiring observation or discontinuation of the medication.
Risk Assessment for Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis
While the chances of developing myopathy from taking ezetemibe are minimal; the risk increases when paired with statins or fibrates. Myopathy might present as muscle soreness and weakness; Tenderness and may even escalate to rhabdomyolysis – a condition characterized by muscle breakdown and possible harm, to the kidneys.
- Factors that increase the risk include being older, in age and having issues with the kidneys or thyroid function along, with taking doses of statins for treatment purposes.
- Signs to keep an eye out for include muscle pain without a cause, urine that appears dark in color, and extreme tiredness.
Patients should notify healthcare providers promptly if they experience any muscle-related symptoms. If myopathy is suspected in patients cases of treatment use should be. Creatine kinase (CK ) levels ought to be tested.
Considerations for Patients with Gallbladder Disease
Taking Ezetimibe may lower the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. Could impact the composition of bile in the body. This could potentially raise the chances of developing gallstones in people who are more prone to it— those, with existing gallbladder issues or a past of choleliasis.
- Patients who have trouble, with their bile acid secretion might encounter symptoms that indicate a risk of cholestasis.
- Individuals who have had issues should be careful, about the formation of gallstones.
Regularly monitoring patients health status and providing them with information, about symptoms related to gallbladder issues are essential, for these groups of individuals.
Importance of Lifestyle Modifications Alongside Medication
Simply using medication is not enough to manage lipids. incorporating Ezetrol into an approach that involves adjusting your diet and exercise routine, as well as maintaining a healthy weight is key.
- When thinking about your diet choices it's important to focus on foods that're good for your heart, like those in fiber and lean proteins, with unsaturated fats to help lower cholesterol levels effectively.
- Engaging in exercise can enhance lipid metabolism and promote better cardiovascular health.
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol in moderation are both important for lowering the risk of issues.
Embracing these lifestyle changes enhances the effectiveness of treatments. Leads to results, in the long run.
Ezetimibe Warnings
Patients who have existing liver conditions or significant kidney problems or those who are sensitive to ezetimibe should be cautious when taking this medication. It's important to evaluate the use of this medication alongside cholesterol-lowering drugs like fibrates as there is a higher chance of liver damage and muscle problems.
Special Considerations for Specific Populations
Use in Elderly Patients
Adjustments Based on Age-Related Hepatic or Renal Impairment
As people get older their liver and kidney function may decrease, which can impact how the body processes ezetemibe medication. Even though there are no changes needed to the dosage, for patients it's a good idea to keep an eye out for any changes by checking their liver enzymes and kidney function regularly.
- Ezetrol's effectiveness can be affected by kidney function despite being broken down by the liver.
- Changes, in the way the liver processes substances may require adults to be monitored closely due to age related alterations, in enzyme activity affecting hepatic metabolism.
Risk-Benefit Analysis in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
Older people commonly have existing heart-related issues that require the management of their cholesterol levels. However it's important to consider the advantages of using ezetimibe while also taking into account possible negative impacts, especially, for frail individuals or those who are, on multiple medications.
- Taking statins together as a treatment method provides protection, for the heart. May also raise the chances of experiencing side effects related to muscles.
- It's important to keep track of things for this group, such, as lipid tests and checking for symptoms regularly to make sure the treatment is working well.
Use in Pregnant and Nursing Women
Pregnancy Category and Fetal Risk Assessment
Regarding Ezetemibes classification, during pregnancy; It falls under category C which means that while animal studies have indicated risks, to the fetus data is scarce; therefore it should only be used if the benefits outweigh the risks.
- Limited research indicates that there could be effects, on the development of a fetus specifically related to changes, in how lipids are processed during pregnancy.
- It's generally advised not to use it during pregnancy unless there are no other options.
Use in Breastfeeding: Excretion into Human Milk and Ezetimibe Nursing Considerations
The presence of ezetemibes excretion into milk remains uncertain, to date; hence nursing mothers are recommended to either stop taking the medication or consider switching to a treatment for lowering lipid levels due to potential risks, for their breastfeeding infants.
- Safety issues arise due, to a lack of information regarding infant exposure levels.
- Consider using bile acid sequestrants, for managing lipid levels in women who are breastfeeding.
Ezetimibe Nursing Implications
Healthcare professionals need to inform pregnant or breastfeeding women about the dangers of using ezetemibe medication. It is advisable to check the levels of the mother and monitor the health of the baby if other treatment options are being considered.
Alternative Lipid-Lowering Options During Pregnancy
Pregnant women who need to control their cholesterol levels are advised to opt for drug treatments first and consider medication only if absolutely needed; safer options, in such cases include;
- When it comes to bile acid sequestrants they don't pass through the placenta, making them a safer choice.
- Omega‐three fatty acids could potentially assist in managing levels without posing risks to the fetus.
Use in Pediatric Patients
Approved Age Range for Pediatric Use
Children who are 10 years and older can be prescribed Ezetmibe to treat hypercholesterolemia. It is advised against using it for younger children as there is limited safety information available, for that age group.
Clinical Data on Safety and Efficacy in Children
Studies have shown that ezetimibe is successful, at lowering LDL C levels among children with cholesterol during clinical trials; however there is still a lack of extensive information on its long-term effects, on growth and development.
LDL-C reduction shows effectiveness rates as seen in adults.
Side effects are usually well received and come with impacts, on individuals.
Special Dosing Considerations for Pediatric Hypercholesterolemia
Ezetemibe is commonly prescribed alongside statins to help children with hypercholesterolemia reach their desired lipid levels effectively.
- Suggested intake amount is 10 milligrams, per day. A dosage, to what adults take.
- In addition, to changes it is important to have an organized eating plan along, with medication therapy.
Regular monitoring of cholesterol and fat content, in the blood, as well as checking growth and liver health is crucial for ensuring the safe and effective long-term use of medications, in children.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Ezetimibe Overdose
While instances of overdosing on ezetemibe are uncommon owing to its range; consuming it excessively can result In heightened medication effects and disruptions, throughout the body system. Based on the quantity taken and individual factors, like existing health issues and concurrent use of medications; symptoms may differ.
- Digestive issues such, as feeling queasy or having an upset stomach, like vomiting or diarrhea can happen when there is cholesterol building up in the digestive system.
- Experiencing dizziness and headaches, along, with difficulties have been noted when individuals consume too much ezetimibe.
- Individuals, with existing liver issues might display increased levels of liver enzymes, which could indicate disturbances.
- Muscle-related impacts should be noted as there may be muscle pain or weakness arising when using statins or other drugs that lower lipid levels.
While severe toxicity is rare and not usually life-threatening, seeking attention is crucial if an overdose is suspected.
Ezetimibe Withdrawal Symptoms
Discontinuing the use of Ezetimibe does not result in dependence or withdrawal symptoms; nonetheless, stopping suddenly could cause a rise, in cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart problems, for patients.
- Following the cessation of the medication it is possible for both LDL C and total cholesterol levels to revert back, to their baseline levels in a matter of weeks.
- High-risk individuals, with heart conditions might see their cholesterol levels worsen if they switch from using ezetemibe to a treatment plan losing the benefits, for their cardiovascular health.
Patients who stop taking ezetimibe should talk to their doctor to make sure their cholesterol levels are managed correctly with changes, to their diet or lifestyle or, by trying medications.

Recommended Medical Interventions and Supportive Care
In situations where an overdose is suspected in a patients care plan, the main focus should be, on providing care addressing symptoms as they arise and closely monitoring metabolic indicators.
- Monitoring signs such, as blood pressure and heart rate is crucial for ensuring stability in a patient's condition. keeping an eye on respiratory function is also important, during this process.
- Hydration, through fluids may be required to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting or diarrhea.
- Ensure that any disruptions, in levels caused by issues are addressed and rectified promptly.
- Patients, with a history of heart issues might need to undergo observation to check for any irregularities, in their heart function.
Given that ezetimibe shows a strong preference, for circulation patterns, within the body, systemically minimizing its absorption is a goal of medical treatment efforts.
Activated Charcoal and Symptomatic Management
In instances of an overdose ingestion incident occurring within one to two hours of intake by the individual in question activated charcoal might be given as a form of treatment.
- Activated charcoal works by attaching to ezetimibe within the system to reduce its absorption into the body.
- Administration Note: For patients it may be advisable to administer a dose of activated charcoal, usually ranging from 50 to 100 grams, for adults.
Additional treatments, for symptoms like nausea medication or pain relievers, for muscle aches can be utilized when necessary's necessary to use them accordingly. Severe situations that necessitate hospitalization may require more thorough observation and care to warrant more intensive monitoring when needed.
Handling and Storage of Ezedoc (Ezetimibe)
Proper Storage Conditions to Maintain Potency
To maintain the effectiveness and stability of ezetimibe, over time, on the shelf requires keeping it stored properly throughout its lifespan.
- Keep it in a place, with a temperature of around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Its okay for it to occasionally vary between 15°C and 30°C (59°F, to 86°F).
- Ensure to shield tablets from moisture to avoid degradation caused by humidity levels.
- Remember to keep the exposure in check by storing the item in a sealed container and away, from direct sunlight to preserve its chemical composition intact.
Storing medication incorrectly could weaken its strength. Limit its ability to treat effectively.
Safe Handling and Disposal Guidelines
To avoid any contamination or accidental ingestion, by individuals it's important to handle ezetemibe.
- Please keep this product out of the reach of children and pets to avoid overdose incidents.
- Remember to handle tablets with your hands as moisture from your hands might harm the integrity of the tablet.
Make sure to dispose of any medication that is not being used or has expired in accordance, with the regulations, for disposing of waste in your area.
Instructions for Pharmacists and Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers must follow the recommended guidelines when prescribing and storing ezetimibe medication.
- Pharmacists should make sure to provide patients with guidance on how to take their medication, including dosage instructions and storage tips as well, as potential interactions to watch out for.
- Healthcare professionals should make it a routine to check profiles and liver function tests regularly in order to enhance the effectiveness of treatment plans.
- Make sure to keep quantities of supplies, in hospitals and clinics in areas, with controlled temperature to prevent tampering or damage.
Effective management of medications is essential, to safeguarding patient well-being and upholding the quality of ezetimibe.
Ezedoc, Ezetimibe FAQ
- What is Ezetimibe used for?
- What does Ezetimibe do?
- Is Ezetimibe a statin?
- What is Ezetimibe?
- How long do Ezetimibe side effects last?
- What are the side effects of Ezetimibe 10 mg?
- What is the main side effect of Ezetimibe?
- What is the most common side effect of Ezetimibe?
- Is Ezetimibe safer than statins?
- Does Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
- What to avoid when taking Ezetimibe?
- Can Ezetimibe cause hair loss?
- Can I take Ezetimibe every other day?
- Is Ezetimibe a controlled substance?
- Do Ezetimibe side effects go away?
- What are the side effects of Ezetimibe?
- Should Ezetimibe be taken at night?
- What does Ezetimibe look like?
- How long does Ezetimibe stay in your system?
- What foods should be avoided when taking Ezetimibe?
- Best time to take Ezetimibe?
- How much does Ezetimibe lower LDL?
- Ezetimibe/Simvastatin price?
- How does Ezetimibe work?
- Can Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
- Is Ezetimibe linked to dementia?
- What are the bad side effects of Ezetimibe?
- Does Ezetimibe lower blood pressure?
- Does Ezetimibe cause joint pain?
- Is Ezetimibe safe?
- Does Ezetimibe cause weight loss?
- Are Ezetimibe statins?
- Are Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin the same?
- Are Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin the same?
- Are Ezetimibe and Simvastatin the same?
- Are Ezetimibe tablets statins?
- Can Ezetimibe cause erectile dysfunction?
- Can Ezetimibe cause hair loss?
- Can Ezetimibe cause muscle pain?
- Can Ezetimibe cause liver damage?
- Can Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
- How Ezetimibe works?
- How Ezetimibe/Simvastatin works?
- Ezetimibe how to pronounce?
- Ezetimibe how does it work?
- Ezetimibe how to take?
- What Ezetimibe used for?
- What Ezetimibe does to your body?
- What does Ezetimibe do?
- Ezetimibe what time to take?
- EZETIMIBE when should it be taken?
- When was Ezetimibe approved by FDA?
- Where is Ezetimibe manufactured?
- Where does Ezetimibe work?
- Where is Ezetimibe metabolized?
- Where does Ezetimibe act?
What is Ezetimibe used for?
Ezetimibe is mainly prescribed for reducing cholesterol levels in individuals, with cholesterol (hyperlipidaemia) those with elevated low density lipoprotein (LDT). Doctors often recommend it along with changes. May also use it alone or in conjunction, with statins to improve cholesterol management.
What does Ezetimibe do?
Ezetimibe functions, by blocking the intake of cholesterol, in the intestine to lower cholesterol levels in the bloodstream effectively It aids in lowering LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels which may help in minimizing the chances of diseases
Is Ezetimibe a statin?
Ezetimibe isn't a statin; it falls under a category of drugs that lower cholesterol called cholesterol absorption inhibitors that work in a way compared to statins which block cholesterol production in the liver.
What is Ezetimibe?
Ezetimibe is a drug that helps reduce cholesterol levels by preventing its absorption, in the intestines. It is commonly given to people, with cholesterol levels who may not be able to take statins or need treatment to lower their cholesterol levels effectively.
How long do Ezetimibe side effects last?
The length of side effects differs depending on the person and the particular response they experience varies from individual to individual Some general side effects might fade away within a days to a couple of weeks. If you are experiencing more lasting effects it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
What are the side effects of Ezetimibe 10 mg?
Common adverse reactions of taking Ezetimibe 10, mg consist of headaches, diarrhea, muscle soreness, fatigue and stomach discomfort. Common but severe side effects might involve increased liver enzymes, allergic responses and muscle disease especially when used alongside statins.
What is the main side effect of Ezetimibe?
What is the most common side effect of Ezetimibe?
The primary side effect of Ezetimibe often includes headaches first and foremost with muscle pains and digestive problems, like diarrhea or abdominal discomfort following.
Is Ezetimibe safer than statins?
Ezetimibe is often seen as having side effects compared to statins because it doesn't impact liver enzymes or muscle tissue much directly. However it's worth noting that its ability to lower cholesterol is not as strong, as that of statins.
Does Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
WhileEzetimibe isn't linked to weight gain far as we know so far; it's possible that some individuals might feel bloating or gastrointestinal discomfort that could be confused with changes, in weight.
What to avoid when taking Ezetimibe?
It's advisable, for individuals using Ezetimibe to steer of overindulging in alcohol as it could affect liver function adversely. Furthermore; it's important that they adhere to guidelines and seek advice from their physician before combining EZETIMIBE with fibrates or cyclosporine since these drugs might have interactions.
Can Ezetimibe cause hair loss?
Hair loss isn't frequently mentioned as a side effect ofEzetimibe ; though in instances people might notice differences, in their hair growth patterns changing over time If someone experiences hair loss while taking this medication it would be best to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and advice, on further steps to take care of your health and well being.
Can I take Ezetimibe every other day?
Ezetimibe is typically recommended for use. Its important to take it every day as prescribed to ensure it effectively lowers cholesterol levels.If you are considering changing the dosage frequency it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
Is Ezetimibe a controlled substance?
Ezetimibe is not categorized as a controlled substance; it requires a prescription. Is not deemed to pose a risk of addiction.
Do Ezetimibe side effects go away?
The potential side effects ofEzetimibe , like headaches or digestive issues might lessen as your body gets used to the medication over time.If the side effects continue or get worse it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
What are the side effects of Ezetimibe?
Frequent adverse reactions of Ezetimibe consist of headaches and muscle discomfort, along with tiredness and joint pain being symptoms well has diarrhea to watch out for; whereas infrequent but severe complications could involve issues with liver function and rhabdomyolysis especially when used alongside statins next, to hypersensitivity reactions.
Should Ezetimibe be taken at night?
You can take Ezetimibe at any time during the day, with or without food long as you take it consistently at the time every day.There's no benefit, to taking it at night.
What does Ezetimibe look like?
Ezetimibe is usually found in the form of a pill that is oval or oblong, in shape and may have numbers or letters stamped on it to indicate the manufacturer.
How long does Ezetimibe stay in your system?
Ezetimibe stays in the body for quite a few days after the dose due, to its half life of around 22 hours; nonetheless its ability to lower cholesterol remains effective as long as it is used regularly.
What foods should be avoided when taking Ezetimibe?
It's advisable to steer of foods, in cholesterol and fat as they might hinder the medication’s effectiveness; also be mindful of grapefruit and alcohol intake as they could impact liver function when taken with Ezetimibe even though there are no strict dietary rules to follow for patients.
Best time to take Ezetimibe?
You can consume Ezetimibe at any time of the day, with or without food for results, in lowering cholesterol levels.
How much does Ezetimibe lower LDL?
Usually Ezetimibe can lower LDL cholesterol levels by, around 15 25%. When paired with a medication it could potentially boost the reduction, by an extra 15 20%.
Ezetimibe/Simvastatin price?
The cost ofEzetimibe /Simmvastatincan fluctuate based upon the brand name chosen. The dosage required in locations or pharmacies. Generic options are usually more budget friendly compared to their brand name counterparts which tend to be pricier. It's advisable to inquire at pharmacies or explore vendors for the most, up, to date pricing information.
How does Ezetimibe work?
By blocking the uptake of cholesterol in the intestine ezetimibe decreases the cholesterol entering the bloodstream resultng, in reduced LDL cholesterol levels and aiding in the prevention of diseases.
Can Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
Ezetimibe is not typically associated with causing an increase, in weight gain among individuals using it.Typically there are no concerns about weight changes attributed to its usage; nevertheless some individuals might notice symptoms of bloating or fluid retention that could be misinterpreted as changes, in body weight.
Is Ezetimibe linked to dementia?
There isn't proof that directly connects Ezetimibe with dementia risks yet some research has looked into the possible impact, on cognitive function of cholesterol lowering drugs without reaching definitive conclusions.
What are the bad side effects of Ezetimibe?
Does Ezetimibe lower blood pressure?
Ezetimibe mainly focuses on managing cholesterol levels and does not directly impact blood pressure levels specifically; nevertheless enhancing cholesterol levels can play a role, in promoting well being which could indirectly aid in regulating blood pressure.
Does Ezetimibe cause joint pain?
Joint discomfort (arthralgia) while not side effect of Ezetimibe according to reports is advised to seek advice if the pain persists or becomes severe.
Is Ezetimibe safe?
Ezetimibe is typically deemed safe when taken as directed by healthcare providers.The medication is known to have side effects, than statins; however it is recommended to monitor liver function and watch out for muscle related symptoms.
Does Ezetimibe cause weight loss?
Ezetimibe is not typically associated with causing weight loss according to knowledge. Its main purpose is to lower cholesterol levels; any alterations, in weight are often considered secondary, than a result of the drugs effects.
Are Ezetimibe statins?
Ezetimibe isn't actually a statin—it falls into a category of medications known as cholesterol absorption inhibitors that function in a manner from statins by blocking the absorption of cholesterol of limiting its production in the liver.
Are Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin the same?
Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin are not the same. Ezetimibeworks by decreasing the absorption of cholesterol in your body while Atorvastatin a type of statin that decreases cholesterol by stopping its production in the liver.
Are Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin the same?
Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin have mechanisms of action. Ezetimibe blocks cholesterol absorption while Rosuvastatin inhibits cholesterol synthesis, in the liver.
Are Ezetimibe and Simvastatin the same?
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin are not the same. Simvastatin is a type of statin that lowers cholesterol production in the liver where as Ezetimibe functions, by blocking cholesterol absorption in the intestine.
Are Ezetimibe tablets statins?
Ezetimibe tablets are different, from statins as they act as cholesterol absorption inhibitors than directly lowering LDL cholesterol levels, like statins do by inhibiting the absorption of biliary cholesterol in the intestines.
Can Ezetimibe cause erectile dysfunction?
Impotence is not often cited as a consequence of Ezetimibe usage; albeit in instances certain cholesterol lowering drugs may be linked to sexual issues.
Can Ezetimibe cause hair loss?
Hair loss isn't frequently mentioned as a side effect of EZETIMIBE medication. If you notice thinning or loss of hair while taking Ezetimibe it's important to explore causes and seek advice, from a healthcare professional.
Can Ezetimibe cause muscle pain?
Muscle discomfort (myalgia) can occur as a side effect of Ezetimibe when taken with statins; it's important to notify a healthcare professional if experiencing muscle pain.
Can Ezetimibe cause liver damage?
Some individuals may experience an increase, in liver enzymes due to Ezetimibe use when combined with statins. Thus emphasizing the importance of liver function checks for those, with existing liver issues.
Can Ezetimibe cause weight gain?
Ezetimibe does not usually lead to weight gain; any fluctuations, in weight when using the drug are commonly linked to factors, like diet habits or lifestyle choices than the medication itself.
How Ezetimibe works?
Ezetimibe functions, by blocking the activity of the NPCl Like 2 protein found in the intestine which hinders the intake of cholesterol from food and bile content into the body system thereby causing a drop in cholesterol concentration, within the blood vessels that predominantly results in decreased LDL cholesterol levels.
How Ezetimibe/Simvastatin works?
Ezetimibe/simvastatin, by merging two methods for reducing cholesterol levels; Ezetimibe decreases cholesterol absorption in the intestine. Simsvatatin is a type of statin that blocks HMG CoA reductase. An enzyme for cholesterol production in the liver.They work together to achieve a decrease, in LDL cholesterol levels.
Ezetimibe how to pronounce?
Ezetimibe can be pronounced as "eh ZET mibe ". Ee ZET mibe,”, with variations depending on the region.
Ezetimibe how does it work?
Ezetimibe functions, by inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine which results in a decrease, in the cholesterol entering the bloodstream leading to reduced levels of LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol thereby aiding in the prevention of diseases.
Ezetimibe how to take?
You usually take Ezetimibe once a day; you can take it with or, without food. Swallow it whole with water at the time every day, for best outcomes.
What Ezetimibe used for?
Ezetimibe is prescribed to reduce levels of cholesterol, in the body by targeting LDL cholesterol for individuals with hyperlipidemia conditions.It can be taken either on its own or along, with statins to minimize the chances of developing diseases.
What Ezetimibe does to your body?
Ezetimibe works by decreasing the amount of cholesterol absorbed in the intestines which results in cholesterol levels in the bloodstream.This helps lower LDL cholesterol and overall cholesterol levels which reduces the chances of developing atherosclerosis and heart disease.
What does Ezetimibe do?
By blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines Ezetimibehelps decrease LDL cholesterol levels. Reduces the likelihood of developing disease.
Ezetimibe what time to take?
You can take Ezetimibe at any time of the day, with or, without food; it's best to take it at the time each day for consistency.
EZETIMIBE when should it be taken?
You can consume Ezetimibe at any point during the day; however it's important to take it at the time every day without the need, for food, for absorption purposes.
When was Ezetimibe approved by FDA?
Ezetimibe received approval, from the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA ) on October 25th 2002 to aid in managing levels of cholesterol, in the body.
Where is Ezetimibe manufactured?
Ezetimibe is produced by pharmaceutical companies globally such as those, in the United States, Europe and India based on the brand or generic variant.
Where does Ezetimibe work?
Ezetimibe operates within the intestine by inhibiting the uptake of cholesterol to hinder its entry into the bloodstream.
Where is Ezetimibe metabolized?
Where does Ezetimibe act?
Ezetimibe works by blocking the uptake of cholesterol from food and bile in the lining of the intestine.